Space
“Hubble Space Telescope” and its achievements in astronomy
Published
1 month agoon
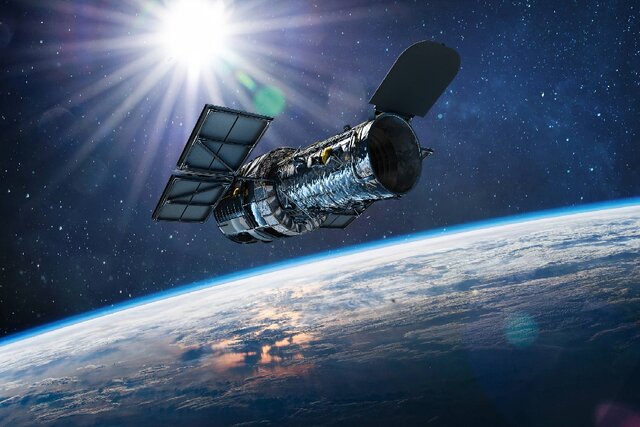


The Hubble Space Telescope, which orbits the Earth, has changed the way astronomers and the general public look at the world. Hubble has exceeded expectations by recording more than 1.4 million observations and providing data for more than 16,000 scientific papers.
“Hubble Space Telescope” and its achievements in astronomy


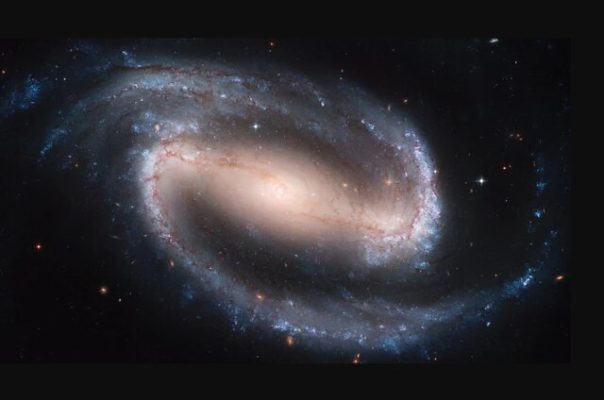
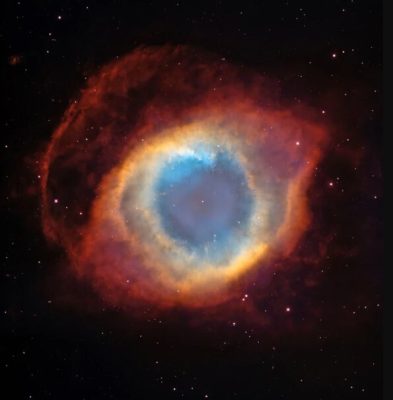
Famous Hubble photos




“Hubble Space Telescope” and its achievements in astronomy
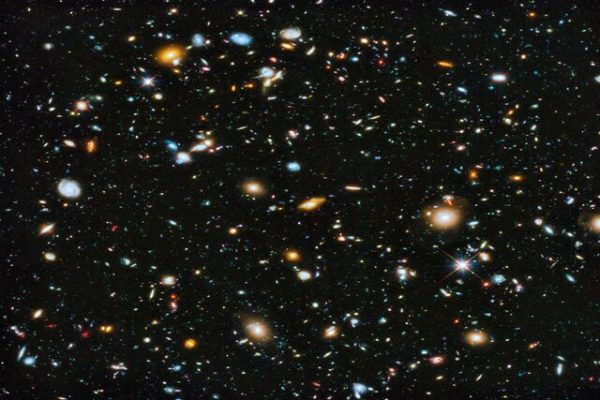




The result of this work was wonderful. So, the astronomers did it again and took pictures of the Hubble Ultra Deep Field and the Hubble Extreme Deep Field. They did it each time using longer exposures and improved equipment.
6. “NGC 6302” or “Butterfly Nebula” is one of the nebulae photographed by Hubble. With a surface temperature estimated at around 250,000 degrees Celsius, the dying central star of the nebula is extremely hot and glows in ultraviolet light, but is obscured from direct view by a dense mass of dust. A close-up and colorful view of the Butterfly Nebula was captured in 2009 by the Hubble Space Telescope’s Wide Field Camera 3. The dust cloud surrounding the central star lies within a bright hole of ionized gas near the center of the view. Molecular hydrogen has been detected in the dusty cosmic mantle of a hot star.


The Butterfly Nebula is located at a distance of 4000 light years from Earth in the constellation of “Scorpius”. The butterfly nebula shows what happens at the end of a star’s life after its gas and dust run out. This is not only a reminder of the ultimate fate of our own Sun and Solar System but also sheds light on Hubble’s unique ability to observe this event over the long life cycle of a star and study how stars evolve.
7. The galaxy “UGC 10214” or “Tadpole Galaxy” is only 420 million light years away from the face of “Draco”. The frog’s tail is about 280,000 light-years long and shows large and bright star clusters in blue. In a stunning image captured by the Hubble Space Telescope’s Advanced Camera, distant galaxies form a backdrop to the Spiral Galaxy Frog. The Toadstool galaxy is disrupted by collisions and shows bursts of star formation in its tail, but behind it are thousands of other galaxies. This picture shows the power of Hubble.


8. The star cluster “NGC 602” (NGC 602) is located near the outskirts of the Small Magellanic Cloud, at a distance of about 200 thousand light years from Earth. Surrounded by natural gas and dust, NGC 602 shows itself in this Hubble image. In star clusters like NGC 602, you can see the star-birth region. The extraordinary bulges and wavy shapes show that energetic radiation and shock waves from the massive young star NGC 602 have eroded the dusty material away from the center of the star cluster. A surprising array of background galaxies are also visible in the Hubble image. The background galaxies are hundreds of million light-years or more away from NGC 602.
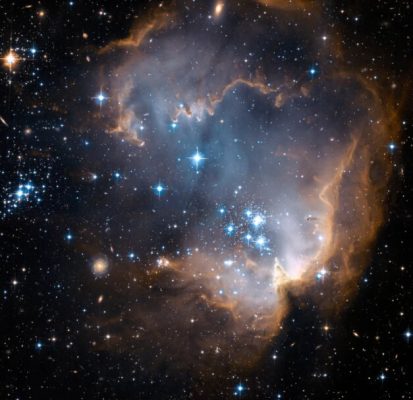


Using Hubble observations, it was confirmed that the stars of NGC 602 were not born suddenly, but formed at different times. Hubble also determined that star formation may have begun there as early as 60 million years ago.
9. Galaxy “NGC 1300” (NGC 1300). One of the largest Hubble Space Telescope images of an entire galaxy is NGC 1300. This galaxy is an amazing example of a barred spiral galaxy. Unlike other spiral galaxies, whose stellar arms extend outward from the center, NGC 1300’s arms radiate away from the end of a straight band of stars that extends across the galactic core.







Future plans


You may like
-



The strangest things that can happen to humans in space
-




Artificial intelligence could explain why we haven’t seen extraterrestrials yet
-




Can humans endure the psychological torment of living on Mars?
-




Black holes may be the source of mysterious dark energy
-



Scientists’ understanding of dark energy may be completely wrong
-




Why the James Webb telescope does not observe the beginning of the universe?

The strangest things that can happen to humans in space
When it comes to space and astronautics, we all remember very interesting movies in which strange things happen to astronauts. Movies with exciting stories, most of which are nothing but the authors’ imaginations; But there are other very amazing stories happening in space that are completely real and have nothing to do with human imagination. In this article, we try to discuss some examples of these events and introduce you to the wonders of space travel.
Strange things that happen to humans in space
The human heart changes shape in space
It may seem a bit strange and even unbelievable that traveling to space can change the shape of the heart, But such a thing happens in reality and scientific studies have proven it. Less work of the heart and less pumping of blood leads to a decrease in the volume of the muscles of this organ, and this ultimately causes the hearts of astronauts to become more spherical by about 9.4%.
Despite the temporary nature of these conditions, some doctors believe that the reduction in the volume of the human heart during space travel may have serious consequences. According to NASA, researchers are researching this issue, and the results of this study will not only help astronauts but will also affect ordinary people and the inhabitants of the planet.
There is a possibility of mental problems in space
Living in the extraterrestrial atmosphere is associated with many problems. Changing living conditions and experiencing a completely different environment with very specific conditions imposes many psychological pressures on astronauts. These issues cause astronauts to experience special psychological conditions and are susceptible to various problems such as anxiety and depression.
Being away from family, lack of simple facilities such as sunlight or even fresh food, and heavy work are among the reasons that expose astronauts to various mental illnesses.
Human vision decreases in space
Visual impairment caused by intracranial pressure or VIIP is another space travel wonder faced by astronauts. This problem was observed for the first time in 2005 and in an astronaut named John Phillips. The Washington Post investigates this issue in an article and states that Phillips experienced a significant loss of vision after returning from his space trip. This incident prepared the groundwork for the researchers’ research for further investigations.
Additional research showed the changes in the appearance of the astronauts’ eyes and the loss of their vision after returning from space travel. Currently, the only possible reason that has been proposed for the occurrence of such conditions is the lack of gravity and the creating double pressure on the astronauts’ skulls; Of course, the research in this field continues and it is still not possible to say with certainty a specific reason for the occurrence of these conditions.
The body’s immune system weakens in space
Traveling to space, along with its excitement and surprises, also brings many problems for humans. One of these problems is the weakening of the body’s immune system in space, which was first discovered by astronauts during the Apollo mission. The story was that the astronauts in this mission experienced problems such as irregular heartbeat, dehydration, and inner ear disorder, and faced many problems after returning from the mission.
Studies conducted in this field have shown that after leaving the Earth’s atmosphere, the immune system of astronauts weakens, in part due to the abnormal activation of a type of immune cells called T-regulatory lymphocytes. This weakening is sometimes so severe that it causes astronauts to deal with latent viruses such as chicken pox in addition to simple infectious diseases such as colds after returning from space travel.
Astronauts can lose their fingernails
As you know, astronauts wear special clothes to carry out their missions in space, which includes astronaut gloves. These gloves are designed in such a way that they put a lot of pressure on the astronauts’ hands and nails; This will eventually lead to their nails falling off.
It is true that the fall of fingernails or their swelling is not a simple matter that can be easily passed over, But it seems that doing more research to design more suitable gloves can minimize the possibility of this problem and astronauts will not face such a problem in the future.
Human height grows taller in space
Another wonder of space travel, which makes it one of the favorite trips of ordinary people, is the increase in height that occurs during this trip. As soon as you leave the Earth’s atmosphere, the gravity is close to zero, and this causes the pressure on the spine to decrease significantly. The reduction of this pressure, in turn, causes the height of the astronauts to grow a few centimeters.
One of the studies that confirms the truth of this issue is the research that NASA scientists conducted on two twin brothers. In this study, one of the twins had a 342-day trip to space and the other brother was examined on Earth. The results of this and other research determined that the height of astronauts increases by 2 to 5 cm on average after space travel.
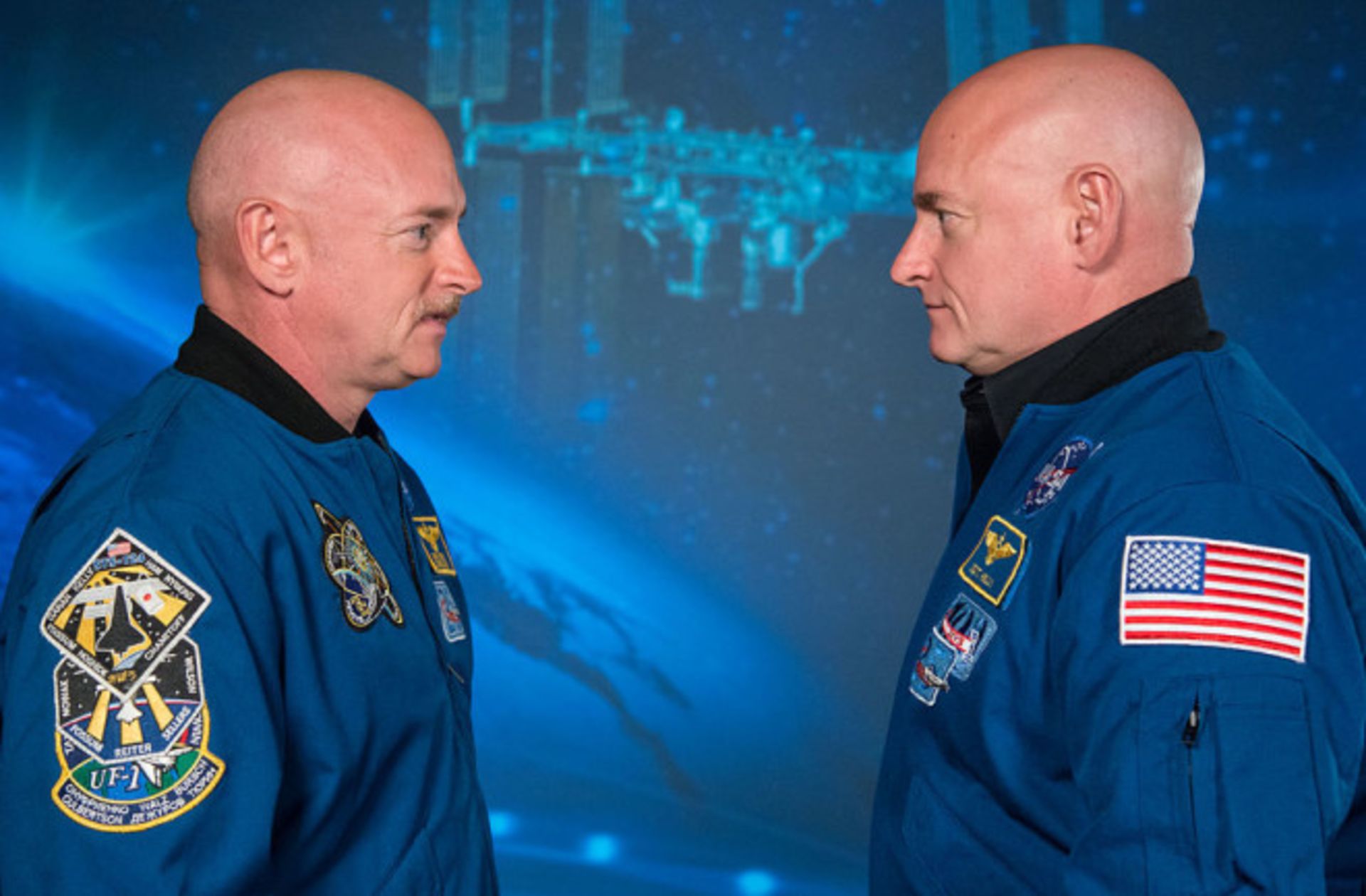 Mark Kelly (left) and Scott Kelly (right) made it possible for researchers to study the health effects of long-duration space travel by studying NASA twins.
Mark Kelly (left) and Scott Kelly (right) made it possible for researchers to study the health effects of long-duration space travel by studying NASA twins.
Traveling to space leads to weakening of muscles
Another strange thing that happens to astronauts in space and affects their health is the weakening of muscles or atrophy. Long space travel causes muscle wasting in astronauts, so they are trained to exercise continuously during their journey.
NASA is working on this issue to find solutions to prevent the problem of muscle wasting. The reason for the importance of this issue is the need for astronauts to have strong muscles and a healthy body so that they can perform their difficult missions in space in the best possible way.
Space swells astronauts’ faces
A large volume of our body is made up of liquid. On Earth, gravity pulls this fluid down and collects some of it in the lower limbs; But in space, where microgravity prevails, our body fluids are more evenly distributed; As a result, astronauts’ faces look puffier than normal, and on the other hand, their legs appear thinner than when they are on Earth.
According to the Washington Post, “the phenomenon of puffy-faced bird’s legs” appears when blood and other body fluids accumulate on the side of the upper body due to low gravity and stay there; As a result, the heads swell and the legs shrink. In this situation, the appearance of the astronauts can change by swelling their faces. Astronauts may experience excessive blood pooling; As if their head is constantly cold. However, after a few weeks in space, your body will adjust to the change in gravity and some of the facial puff will fall asleep.
Space travel may increase the risk of cancer
Astronauts who spend 6 months in space are exposed to almost as much radiation as a thousand chest X-rays. Exposure to different types of radiation exposes the body to the risk of cancer, damage to the central nervous system, bone loss, and some cardiovascular diseases. However, it has been difficult to accurately calculate the level of risk so far. Also, scientists’ information about the impact of radiation in long-duration space missions to deep space destinations such as the Moon and Mars is still limited.
The more time a person spends in space, the more radiation they are exposed to and, theoretically, the more DNA damage they accumulate. It is not possible to say with certainty whether this DNA damage actually increases the risk of cancer; Because cancer is affected by many environmental and genetic factors. For example, it’s probably fair to say that today’s astronauts are probably some of the fittest people on the planet. They probably eat a healthy diet, exercise a lot, and don’t smoke or drink much alcohol. All these things reduce the possibility of getting cancer.
Strange events for astronauts during space travel have always been one of the most fascinating topics for ordinary people. The wonders of space travel are not limited to the things we have mentioned, and at the same time as science advances and the scope of research increases, we will definitely see more interesting news in this field in the near future.
Space
Artificial intelligence could explain why we haven’t seen extraterrestrials yet
Published
2 days agoon
26/04/2024

Artificial intelligence could explain why we haven’t seen extraterrestrials yet
Artificial intelligence shows us its presence in thousands of different ways. This technology has capabilities such as accessing huge data sources, detecting financial frauds, driving cars and even suggesting music. On the other hand, artificial intelligence chatbots have amazing performance; But all this is just the beginning.
Can we figure out how fast artificial intelligence is developing? If the answer is no, does it include the notion of a large filter? Fermi’s paradox refers to the difference between the high probability of the existence of advanced civilizations and the absence of evidence of their presence. Many solutions have been proposed as to why this discrepancy exists. One of these hypotheses is the “big filter”.
The Great Filter is a hypothetical event or situation that prevented intelligent life from becoming an interplanetary or interstellar entity and could even lead to its destruction. Such events can include climate change, nuclear war, asteroid collisions, supernova explosions, plague, or even other catastrophic events; But what about the rapid growth of artificial intelligence?
A new study in the journal Acta Astronautica shows that artificial intelligence is becoming artificial superintelligence (ASI), which could be one of the great filters. The title of this article is as follows: “Is artificial intelligence a great filter that makes advanced civilizations rare in the world?” The author of this article is Michael Garrett from the Faculty of Physics and Astronomy at the University of Manchester.
 Artificial intelligence as a big filter can prevent biological species from accessing interplanetary and interstellar spaces.
Artificial intelligence as a big filter can prevent biological species from accessing interplanetary and interstellar spaces.
Some people believe that the Great Filter will prevent a technological species like us from becoming a multi-planetary species. This is bad news because species with only one home are at risk of extinction or stagnation. According to Garrett, species without a backup planet are in a race against time. he writes:
Such a filter appears before civilizations reach multiplanetary stability and presence, suggesting that the typical lifespan of an advanced civilization is less than 200 years.
If the above hypothesis is true, it can be proved why we have not found any traces of technology or other evidence of extraterrestrial intelligence; But what does this hypothesis say about the path of human technology? If we face a limit of 200 years and this limit is due to ASI, what will be our fate?
Garrett also emphasizes the need to create legal frameworks for the development of artificial intelligence on Earth and the development of a multi-planetary society to deal with existing threats.
Artificial superintelligence (ASI) can completely replace the human race
Many scientists and thinkers say that we are on the threshold of a huge transformation. Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing how things are done; Much of this transformation takes place behind the scenes. AI looks set to eliminate millions of jobs, and when combined with robotics, there are no boundaries. Certainly, these developments will be an obvious concern.
However, there are more systemic and deeper concerns. Who writes the algorithms? Will artificial intelligence be able to recognize to some extent? It can be said with almost certainty that this will be possible. Do competitive algorithms destroy strong democratic societies? Will open communities continue to stagnate? Will ASI decide for us and if so who will be held accountable?
The above questions are increasing without any clear end. Stephen Hawking always warned that if artificial intelligence evolves independently, it can destroy the human race. In 2017, he said in a conversation with Wired magazine:
I am afraid that artificial intelligence will completely replace humans. If people can design computer viruses now, perhaps in the future someone will be able to design an artificial intelligence that improves and reproduces itself. This type of intelligence will be a new form of life that can surpass humans.
 The combination of artificial intelligence and robotics can become a threat to humans.
The combination of artificial intelligence and robotics can become a threat to humans.
Hawking may be considered one of the most significant figures of warning about artificial intelligence, But he is not alone. The media is full of discussions and warnings as well as articles about the capabilities of artificial intelligence. The most important caveat is that ASI can become rogue. Some people consider this hypothesis to be science fiction, but Garrett doesn’t think so. According to his writing:
Concerns about artificial super-intelligence (ASI) and its going rogue in the future are a major issue. Combating this possibility will become a growing field of research for AI leaders in the coming years.
If AI had no advantage, the problem would be simpler; But the technology offers a variety of benefits, from improved medical imaging and diagnostics to safer transportation systems. The trick for governments is to allow benefits to grow while controlling harm. According to Garrett, this issue is especially important in the fields of defense and national security, where moral development and responsibility are important.
The problem is that we and our governments are not sufficiently prepared. There has never been such a thing as artificial intelligence, and no matter how hard we try to conceptualize and understand its path, we will not reach the expected result. Therefore, if we are in such a situation, probably other biological organisms in other parts of the world have the same conditions. The emergence of artificial intelligence and artificial superintelligence could be a cosmic issue, making it a good candidate for the big filter. The danger that ASI can pose is that it may one day no longer need the biological life that created it.
According to Garrett’s explanation, ASI systems, by reaching the technological singularity, can overtake biological intelligence and evolve at a rate that even outpaces their own monitoring mechanisms and ultimately lead to unexpected and unintended consequences that are unlikely to be compatible with biological ethics and interests. to be
 Life on multiple planets could diminish the threat of artificial intelligence.
Life on multiple planets could diminish the threat of artificial intelligence.
How can ASI free itself from the pesky biological life that has captured it? may engineer a deadly virus; or prevent the production and distribution of agricultural products or even lead to the collapse of the nuclear power plant and start a war.
It is not yet possible to speak definitively about the possibilities, as the realm of artificial intelligence is uncertain. Hundreds of years ago, cartographers were drawing monsters in unexplored regions of the world, and now that’s what we’re doing. Garrett’s analysis is based on the assumption that ASI and humans occupy the same space; But if we can reach a multiplanetary state, this scenario will change. Garrett writes:
For example, multiplanetary biological species can draw on the independent experiences of different planets and avoid the single-point failure imposed by a single-planetary civilization by increasing the diversity of survival strategies.
If we can spread the risk over multiple planets around multiple stars, we can protect ourselves from the worst possible consequences of ASI. This distributed model increases the resilience of biological civilizations against artificial intelligence disasters by creating redundancy. If one of the planets or bases occupied by future humans fails to survive the ASI technological singularity, the others may survive and learn from the failure.
A multi-planetary situation could also be beyond the ASI’s rescue. Based on Garrett’s hypothetical scenarios, we can try more experiences with AI while keeping it limited. Consider an AI on an isolated asteroid or dwarf planet that doesn’t have access to the resources it needs to escape and can thus be limited. By Garrett:
This scenario applies to isolated environments where the effects of advanced artificial intelligence can be explored without the immediate risk of global annihilation.
However, a complex issue arises here. Artificial intelligence is advancing at an ever-increasing rate, while human efforts to become a multi-planetary species are at a slow pace. According to Garrett, the incompatibility between the rapid development of artificial intelligence and the slow development of space technology is very clear.
The speed of artificial intelligence is much faster than space travel
The difference here is that artificial intelligence is computational and informational, but space travel faces many physical obstacles that we still don’t know how to overcome. Human biological nature is an obstacle to space travel, but none of these obstacles limit artificial intelligence.
While artificial intelligence could theoretically improve its capabilities even without physical limitations, space travel faces limitations in energy, materials science, and the harsh realities of the space environment, Garrett writes.
Currently, artificial intelligence operates under the limitations set by humans; But this may not always be the case. We still don’t know when AI might turn into ASI, But we cannot ignore this possibility. This issue can lead to two intertwined conclusions.
If Garrett is right, humans should try harder for space travel. It may seem far-fetched, but knowledgeable people know that Earth will not be habitable forever. If man does not expand his civilization into space, he may be destroyed by his own hand or by the hand of nature. However, reaching the moon and Mars can promise future steps.
The second conclusion is related to the legalization and supervision of artificial intelligence; A difficult task in a world where mental illness can take control of entire nations and lead to an increase in wars. Although industry stakeholders, policymakers, independent experts, and their governments are warning about the need for legislation, creating a universally accepted legal framework is difficult, writes Garrett.
In fact, humanity’s perpetual disparity makes the goal of controlling artificial intelligence uncontrollable. Regardless of how fast we develop strategies, AI can grow even faster. In fact, without applicable law, there is a reason to believe that artificial intelligence is not only a threat to future civilization but a threat to the entire advanced civilizations.
The continuation of intelligent and conscious life in the world may depend on the effective and timely implementation of legal regulations and technological efforts.
Space
Can humans endure the psychological torment of living on Mars?
Published
4 days agoon
24/04/2024

Can humans endure the psychological torment of living on Mars?
Alyssa Shannon is a registered nurse at UC Davis Medical Center. One day, on his way to the university hospital, NASA called him and told him that he had been selected for a mission to Mars. That same morning, Nathan Jones, an emergency room physician in Springfield, received a similar call. He immediately thought of his family and told himself that if you accept this opportunity, you will have to let them go. However, he couldn’t turn down NASA’s opportunity and convinced himself that Mars was his destiny.
The Mars Crew Health and Performance Probe Analogue Mission, or CHAPEA for short, will not actually send selected individuals to Mars, but rather will accurately simulate the first human journey to Mars and pave the way for sending the first humans to Mars, possibly by 2040.
According to NASA, humans will one day travel to Mars. In 2018, NASA estimated that the first humans would land on Mars “by the late 2020s at the latest.” The date for the first human mission has changed slightly, but despite the technical hurdles, it will definitely happen one day. Rachel McCulley, until recently the deputy director of NASA’s Mars campaign, has compiled a list of 800 problems that must be solved before the first human mission can be launched.
Many of the items on the list deal with the mechanical problems of transporting people to a planet that never gets closer than 54.6 million kilometers to Earth. Keeping people alive in toxic soil and unbreathable air, bombarded by solar radiation and galactic cosmic rays, without access to immediate and safe communications to bring them back to Earth more than a year and a half later, are some of the challenges of a trip to Mars.
Other problems involve technical details too obscure for McCulley to explain. But he has no doubts that NASA will overcome these challenges. Of course, what NASA and no one else knows yet is whether humanity will be able to overcome the psychological torment of living on Mars.
CHAPEA’s mission addresses human rather than technical questions. For 378 days, four ordinary volunteers will experience the conditions of human life on Mars as much as possible. They received instructions, feedback, and full supervision from Mission Control. These people eat astronaut food, perform basic experiments, perform maintenance tasks, answer endless surveys, and enjoy organized downtime. This level of extreme realism is necessary to ensure that the experiment correctly determines whether humans can live millions of kilometers away from their acquaintances.
The experimenters wanted to know if the crew could eat astronaut food for hundreds of days without losing their appetite, weight or positive attitude. Can they live in a confined space with strangers? Can they maintain a cohesive professional environment without contact with the ground? Such questions are of the utmost importance because no mission to Mars can succeed if Martians cannot maintain their health, happiness, and, most importantly, their sanity.
If Martians cannot maintain their mental health, no Mars mission will be successful
NASA’s goal of the simulated mission was to see if subjects could thrive in an environment designed to closely resemble Mars. NASA launched the program in August 2021 with a “Mars Calls” announcement on its website. Participation in CHAPEA, unlike most NASA missions, was open to the general public, or at least to a broad segment of the public: citizens or permanent residents between the ages of 30 and 55 with a master’s degree or higher in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics. Applicants were told that the experience was “mentally difficult”.
NASA offered four golden tickets to travel to a simulated settlement called Dune Alpha; The 158 square meter building was built inside a large warehouse at the Johnson Space Center in Houston. This settlement was built using 3D printing technology and instead of ink, Martian regolith was used. NASA did not have sufficient amounts of Martian regolith, so a special orange material called lavacrete was used, which was removed layer by layer from a 3D printer.
The residence has four identical cells that serve as bedrooms, a lounge, a television, and four chairs. There are also several desks with computer monitors, a medical station, and an agricultural garden in the settlement. Garden plants considered for mental health: Growing plants may have “psychological benefits for astronauts living in an isolated environment far from Earth,” says one researcher. The rooms have different heights to avoid the monotony of the space. The yard is shaped like a box filled with red sand and has two treadmills for the crew to practice “space walking”. The walls of the courtyard are covered with murals of Martian rocks and there are no windows.
The duration of the trial is the most obvious violation of the truth. Orbital geometry dictates that the shortest round-trip mission to Mars would take about 570 days, and this scenario might occur once every 15 years. A typical trip to Mars would take at least 800 days.
NASA has declined to disclose details of the 378-day confinement, which ends on July 6, 2024, to preserve the integrity of the experiment. NASA only emphasized that participants would experience “resource limitations, equipment failures, communication delays, and other environmental stressors.” For example, the crew on the Mars mission must form lasting emotional bonds with strangers and rely on each other for comfort. The crew must respond to any emergency situation on their own without any intervention or guidance. They must cope with not being able to care for a sick child, a grieving spouse, or a dying parent.
Future travelers to Mars must not only endure all these conditions alone but also pursue this opportunity with a determined and honest purpose in order to earn the privilege of long-duration space travel. They must accept that for at least 570 days, they will be the most isolated humans in the history of the world.

How does isolation affect performance?
Alyssa Shannon had dreamed of Mars since she was a child and knew she could endure the hardships and long periods of isolation. Nathan Jones also felt that this mission was designed for him. But professional observers of America’s space programs, a group of NASA historians, ethicists, and advisers who spend much of their careers studying the future of space exploration, have raised the question: What does NASA want to learn from the CHAPEA mission that it doesn’t already know?
The psychological damage of social distancing is well understood. Everyone knows what isolation does to a person. Johnson Schwartz, a philosophy professor who studies the ethics of space exploration, says: “What ambiguity is left when you lock people in a room for a year? “Just because the room is painted to look like Mars doesn’t mean the results will change.”
Monotony prevents people from performing the most basic tasks
The sources of Johnson Schwartz’s talk are 80 years of study in the field of isolation. The study of isolation began in World War II. At the time, the British Royal Air Force was concerned about the performance of pilots during solo flights. The officers noticed that the longer the pilot stayed in the air, the fewer submarines he detected. Psychologist Norman McWorth also recognized that the monotony of the mission is to blame for this. The monotony of the mission made the pilots unable to perform even the most basic tasks.
The results of Mackworth’s study inspired a series of studies by psychologist Donald O. Hebb from McGill University. Confirming McWorth’s findings, Hebb added new details. Monotony not only causes intellectual weakness but also leads to a “change in behavioral approach”. In Hebb’s experiment, his students slept and thought about their studies and personal problems. Then they would reminisce and recreate their movies or travels. Some also count to incredibly large numbers.
However all participants eventually lost the ability to focus. Several people also reported “blank periods” during which they thought about nothing. The next step was illusion. The hallucinations made people vulnerable, and long after the experiment was over, they believed the hallucinations were real.
Hebb’s findings inspired isolation studies. Individuals were confined in different locations and all results were consistent. In addition to attracting neuroscientists and psychologists, the experiments also attracted the attention and funding of the US intelligence community. The findings were included in “forced counter-espionage interrogations” or what is now called “brainwashing” or “psychological torture”.
Isolation studies were also closely monitored by the Air Force, which led the fledgling US space program before NASA was formed in 1958. Concerned that spaceflight might drive astronauts crazy, the Air Force conducted the first test similar to CHAPEA. The astronauts in this experiment were confined for a week in the cockpit of the spaceship, which was slightly larger than a coffin. The pilots were assigned a large number of technical tasks and were given large quantities of amphetamines.
The experiment followed a familiar pattern: initial high spirits gave way to a “gradual increase in irritability” and suddenly turned to “open hostility.” Many participants experienced hallucinations, with one pilot even abandoning the test after three hours and seeking psychiatric care.
In all isolation experiments, initial high spirits eventually gave way to irritability, violence, and hallucinations.
Several other similar studies were conducted before all research was stopped by the Mercury Space Program. Since the official start of the US space program in the early 1960s, astronauts have not suffered from any obvious psychological distress during successful solo missions, much to the relief of researchers. All long-duration space travel took place in Earth orbit, and crews were easily able to communicate with Earth. Government agencies continued to investigate the effects of isolation, but NASA did not.
NASA didn’t have a solution to the problem of isolation in space, and it didn’t need to, until half a century later when a new challenge arose: a human mission to a planet so far away that it would take at least 22 minutes for a cry for help to travel through the solar system. slow
The delay in communication worried CHAPEA crew members and families. All contact with the settlement is timed by the time it takes to send the information from Earth to Mars. Even exchanging short sentences like “How are you? “Good” also lasts at least 44 minutes.
But “44 minutes” is considered the best possible case, since every connection must flow through a connection point. Any information unit must wait in a digital queue, with priority given to the most urgent signals and smallest data packets. As a result, any normal human conversation with the earth is unthinkable. Also, there will be no contact during a three-week period in the middle of the experiment that marks the furthest distance between Earth and Mars.

The selected CHAPEA crew respected NASA’s decision on the mission, but if they wanted to better imagine the year ahead, they should study an earlier series of Mars simulations that shared some goals with the CHAPEA mission. For example, the HI-SEAS Analog Space Mission and Space Exploration Simulator in Hawaii simulated trips to the Moon and Mars missions between 2013 and 2017.
Civilians on the HI-SEAS mission were selected to live in a habitat in Hawaii for 12 months. The mission investigated and studied various nutritional and “psychosocial” benefits, as well as volunteers’ behavior and mental alertness and coping strategies developed to resist isolation.
Once Upon a Time I Lived on Mars is the memoir of Keith Green, one of the original HI-SEAS crew, and includes chapters entitled “On Boredom”, “In Isolation” and “Dreams of Mars, Dreams of Earth”. Green explains how the monotony changed his mission. “At that time mental fatigue had become my main state of mind,” he writes. The crew barely slept, were under constant surveillance, and scheduled leisure seemed a little forced.” The slightest provocation drove Greene mad, and he soon found himself missing out on everyday life on Earth.
The HI-SEAS mission followed the Mars 500 mission, the longest Mars simulation mission ever. Mars500, operated by the Russian Institute of Biomedical Problems, put a six-man crew together on a synthetic Mars for 520 days, between June 2010 and November 2011, in a synthetic spacecraft and a synthetic landing module.
Russian experimenters hypothesized that over time, astronauts would lose motivation, work less, and suffer from feelings of extreme isolation. After the experiment was over, the scientists announced that the hypotheses were “largely confirmed.” Crews lost confidence in their commanders and mission control, communication became poor, nutritional problems developed, and people became homesick and depressed. “It’s not easy to spend 520 days,” said Wang Yu , one of the participants who lost about 10 kilograms of weight and most of his hair. It is impossible to be happy all the time. “I am human, not a robot.”
Despite the previous results, the desire to simulate life on Mars still seems insatiable. CHAPEA is just one of dozens of NASA’s current analog experiments. One of Hera’s other missions is; A habitat that keeps four participants in isolation for 45 days. Since NASA ended participation in HI-SEAS, a variety of public and private organizations have continued the missions. The private association of the Mars Society has been operating several research bases in the Utah desert and the remote islands of northern Canada for years. Analogues of Mars have also been performed in Dome C of the Antarctic Plateau, the semi-arid region of northeastern Brazil, ice caves in Austria and Oman.
The effect of selected isolation is not the same as imposed isolation
The first travelers to Mars are likely to have the same psychological profile as Shannon, Jones, and two other participants: Ross Brockwell, a structural engineer and director of general operations, and Kelly Heston, a stem cell biologist. All four are NASA enthusiasts, in good physical health, and welcome long periods of isolation. These people themselves chose to spend a period of isolation and restriction.
Louise Hockley, an expert on social isolation, emphasizes that psychological responses are strongly influenced by whether isolation is chosen or imposed on individuals. A prisoner sentenced to life imprisonment usually suffers more than a monk who has taken a vow of silence. But Hockley points out that participants, no matter how well supported, are not autonomous. “Even if the crew is OK, what happens to the family that’s left behind?”
However, the designers of CHAPEA do not seem to have an understanding of the history of isolation and social isolation studies. In interviews, they also downplayed the findings of previous trials, including HI-SEAS. CHAPEA principal investigator Grace Douglas admitted she was “not entirely familiar” with the previous four-year trial, saying: “I don’t believe they met our performance criteria. “Our assessment is at a higher level of detail and will be more extensive.”
Rachel McCulley is NASA’s CHAPEA Funding Officer. When asked what he hopes to learn from the mission about human psychology, he said, “The big reason I funded the mission is that I want to know exactly how much food is needed for a Mars mission.”
But what about the psychological aspect of the mission? How do people cope with loneliness and monotony? McCauley is a solid fuel propulsion system engineer and his goal was to determine the spacecraft’s weight only. He could estimate the mass of everything, but he wanted to know how much food the four stressed astronauts would consume in 378 days and how much clothing they would need.
Investigating psychological issues is NASA’s second priority. Mathias, a historian of isolation, asks whether empirical logic can justify another study of isolation. In his opinion, these experiments are “a way to colonize Mars, or a form of wish-fulfillment, or, in other words, just a game of cosplay.” Analog experiments reflect utopian promises about a future for humans on Mars. A human mission to Mars is not the highest ambition in space programs, but a small step for mankind before a giant leap in the habitation of other planets.
The inhabitants of Mars will turn from humans into a modified species of “Martians”.
Five months before the CHAPEA call, Dennis Bushnell, a 60-year senior scientist at NASA’s Langley Research Center, published a paper on the future of space exploration, commercialization, and habitation. He says colonizing Mars has always been conceivable for colonizing humans. He notes that the prospect has gone from “very difficult” to “increasingly feasible” in recent years.
Bushnell predicts that Mars colonists will “become a modified species.” Travelers who colonize Mars will become Martians over time due to reduced exposure to heat and radiation. The ultimate promise of NASA’s Mars mission is a chance to start over, not exactly as humans, but as Martians. If we can settle on Mars and enjoy a carefree life with no regrets, it stands to reason that we should no longer be human, we should be Martians.
But Mathias likens the constant testing of Mars to a traumatic repetition. The compulsion to rebuild is an irrational and futile attempt to undo a deep injury. “The urge to try to recreate a perfect world is always repeating the same mistake we made here,” he says. “We are not looking for Mars, we are mourning for Earth.”
 NASA released the official CHAPEA 1 crew portrait on June 25, 2023. From left to right: Anka Selario, Ross Brockwell, Kelly Heston, Nathan Jones.
NASA released the official CHAPEA 1 crew portrait on June 25, 2023. From left to right: Anka Selario, Ross Brockwell, Kelly Heston, Nathan Jones.
The four crew and two surrogates of the CHAPEA mission gathered together for a final month of training and evaluation a month before confinement to the settlement. Three weeks before arrival, NASA hosted a “Family Weekend” for the crew’s loved ones. Families visited the Johnson Space Center and interacted closely with the astronauts. The crew’s families agreed to share stress management techniques and pledged to keep in touch through a private Facebook page.
But Alyssa Shannon received a call five days before the mission began. He announced that NASA had removed him from the mission and had been replaced by U.S. Navy microbiologist Anka Selario. The reason for Alyssa’s removal was not released, but NASA investigators added that sometimes during final pre-mission tests, problems are found that are not “medically serious” but may pose a risk, such as an increased risk of kidney stones. Of course, this is just an example and the researchers refused to provide information.
On June 25, 2023, NASA’s YouTube channel broadcast footage of four CHAPEA 1 crew members standing on a platform in front of the settlement. Grace Douglas announced that the knowledge we gain here will help us send humans to Mars and return them home safely. Then, Douglas opened the simple white door of the settlement, the crew waved and entered. Douglas closed the door behind them. The happy voice of the crew could be heard from inside the settlement.


The strangest things that can happen to humans in space


Motorola Edge 50 Ultra review


Artificial intelligence could explain why we haven’t seen extraterrestrials yet


Samsung Galaxy A55 vs Galaxy A35


Can humans endure the psychological torment of living on Mars?


Review of Motorola Edge 40 ; Pure Android in a lovely body


What would happen if gravity stopped?


The secret of the cleanest air on earth has been discovered


Bill Gates Biography, the founder of Microsoft


Asus Zenbook 14 OLED laptop review
Popular
-



 Technology9 months ago
Technology9 months agoWho has checked our Whatsapp profile viewed my Whatsapp August 2023
-



 Technology10 months ago
Technology10 months agoHow to use ChatGPT on Android and iOS
-



 Technology9 months ago
Technology9 months agoSecond WhatsApp , how to install and download dual WhatsApp August 2023
-



 Technology10 months ago
Technology10 months agoThe best Android tablets 2023, buying guide
-


 Humans1 year ago
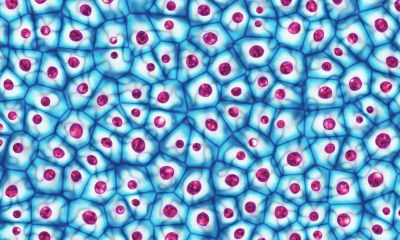
Humans1 year agoCell Rover analyzes the inside of cells without destroying them
-



 AI1 year ago
AI1 year agoUber replaces human drivers with robots
-



 Technology10 months ago
Technology10 months agoThe best photography cameras 2023, buying guide and price
-


 Technology11 months ago
Technology11 months agoHow to prevent automatic download of applications on Samsung phones
