Space
Jupiter planet , its features, moons and wonders
Published
1 year agoon
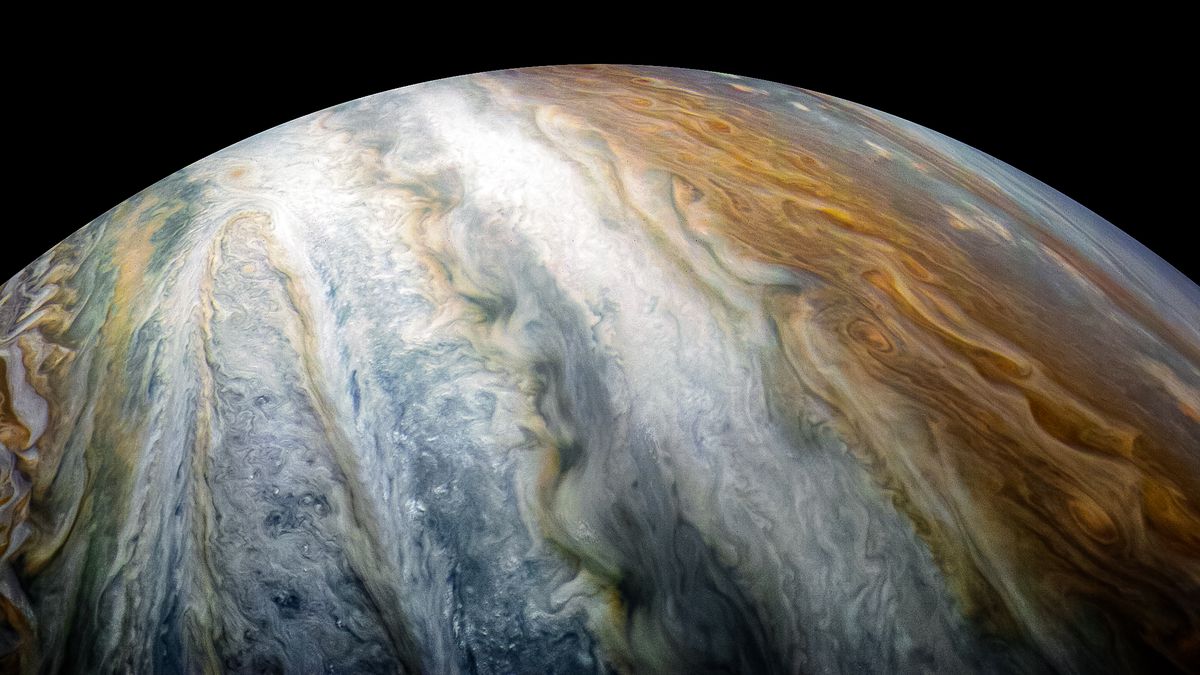


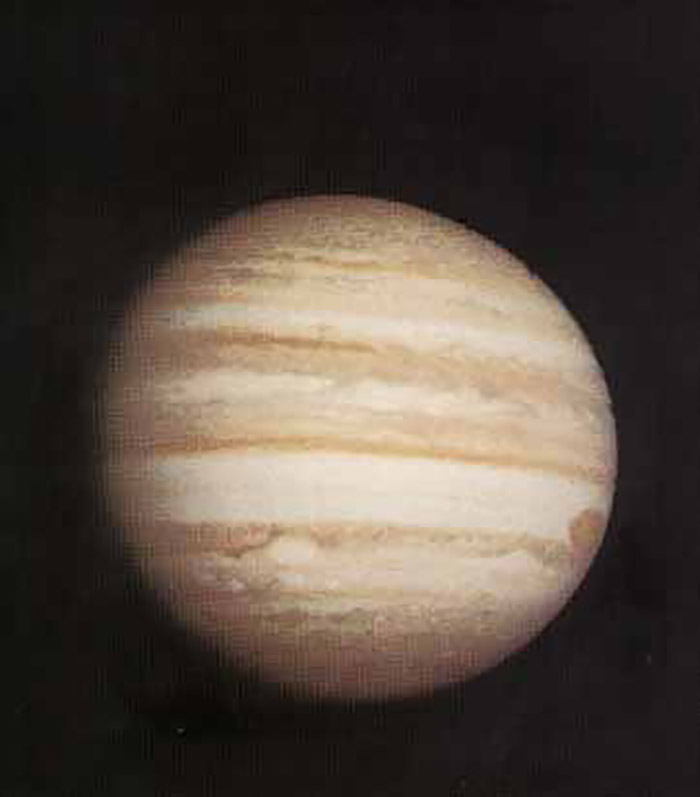
The Jupiter is the largest planet in the solar system, which is highly regarded because of its attractive features such as the Great Red Spot and the mysterious icy moons like Europa and Ganymede.
The Jupiter’s planet, known as Burjis, Hormuz or Jupiter, is the fifth and largest planet in the solar system. The Jupiter has a major role in the transformation of the solar system history, and the earth owes to the Jupiter to some extent.
The planet, along with Saturn, are gas giant. The Jupiter is a combination of hydrogen and helium and because of its high speed of rotation, its shape is not completely spherical. The Jupiter’s external atmosphere is divided into several strips of different latitudes, creating storms, storms, and vortex currents. One of the points of sharing these strips is the famous red spots; A huge storm that was first observed in the seventeenth century with a telescope.
The Jupiter’s planet has a pale ring and a strong magnetosphere. The planet, also called the King of the planets, has four approved moons. The Jupiter ranks second in the solar system in terms of the number of moons and after Saturn (with 2 lunars). The most famous moons on the planet is a four-storey collection known as the Galileo moons that were discovered in the year 6 by Italian scientist Galileo Galileo. ganymede is the largest Jupiter’s moon and the largest moon in the solar system.
Jupiter planet
Robotic spacecraft have done a lot of research on the Jupiter. The most famous Jupiter missions include Woeeiger and Pioneer and then Galileo’s circuit. In late February, the New Huraznesian probe visited the Jupiter and used the planet’s attraction to speed up and be on the Pluto route. The last mission to the Jupiter was carried out by the Juno probe, which was to orbit the planet on July 1.
The titles you will read in this article:
- What is the Symbol of the Planet?
- How was Jupiter Planet formed?
- How many times is Jupiter Earth?
- Physical properties and internal composition of the Jupiter’s planet
- How many moons does the planet have?
- Jupiter loops
- Wonders of Jupiter Planet
- Seeing the Jupiter Planet from Earth
- Jupiter probes
- Future missions to the Jupiter
Ten Interesting Facts About Jupiter Planet
- The Jupiter is the largest planet in the solar system, named after the God of heaven and thunder. The planet is mainly made up of gas (hydrogen and helium) and its inner core is almost the same as Earth.
- The Jupiter’s planet has at least 2 lunars, with four large reds: Io, europa, Ganimid and Calisto (these moons are also known as Galileo’s moons). Although the planet of Jupiter cannot host life, some of its moons have the potential for life because of the oceans below the level of life.
- The rotation of the Jupiter around it is faster than any other planet, and this leads to veins: Dark areas (belts) indicate the rise of clouds and gases; Bright areas (areas) represent a belt session.
- The speed of the Jupiter’s rotation in the equator is fast and in the poles is slow; Thus, the gas layers in the impulse collision areas cause white spots, spiral storms and vortexes. One of the most famous Jupiter storms is the large red spot three times the size of the earth. This is not a constant storm.
- The Jupiter’s planet has four rings. The Vaviger probe discovered these rings in year 2. These rings are very pale and, unlike the transparent rings of Saturn, made up of ice and rock, were made of dust particles.
During his mission, the Juno probe has come to the attractive facts about the planet’s Jupiter:
- The Jupiter’s atmosphere is amazing. According to Juno’s findings, this gas giant is much more turbulent than imagination. The cloud and wind climate is not only seen in the upper layer of the planet. Rather, but these winds also exist in the depths of the Jupiter for thousands of kilometres. Also, surprisingly, Jupiter strips disappear near its poles.
- According to hypotheses, the famous Jupiter’s gas clouds (a combination of water and ammonia) are equally combined. However, there is less ammonia at the surface and most of the ammonia is focused on the nucleus.
- At the north and south poles of the Jupiter, there are circular chains of massive tornadoes. These rotating storms are extremely dense on the continents of the earth. Their length is 2 kilometres and their width is hundreds of kilometres.
- The Jupiter’s solid core at its centre is not completely intensive. Rather, a swollen butter is half the Jupiter’s diameter. No one knows what the reason is, but according to hypotheses, a heavy crime has been treated by the Jupiter, which has made the core with other surrounding gases.
- The Jupiter has the strongest magnetic field in the solar system, but Juno shows that the field is even stronger and closer to the planet’s surface. Also, the north and south poles of the Jupiter are not similar.
What is the Symbol of the Planet?
Jupiter or Jupiter has been known since ancient times. The planet is also known in various cultures by numerous names such as Jupiter (Roman culture), Burjis, Urmd and Zavash. The Jupiter is visible in the night sky with an unarmed eye and sometimes during the day (when the sun is low). The Romans named the planet, inspired by one of the Roman myth gods, Jupiter (also known as the God of love).
The Babylonians knew the Jupiter in the name of their God, Mardok. They used the Jupiter’s 5 -year period alongside the circle to define zodiac constellations. The Romans considered the Jupiter the star. On the other hand, in Greece, the Jupiter was known as Zeus (the counterpart of the Roman God Jupiter). The ancient Greeks knew this planet as a shiny or ignorant star. The origin of the Jupiter’s astronomical symbol (image below) is unclear; But many consider it to be a thunderstorm, and according to new reports, it means eagle based on the Egyptian hieroglyphic line.
How was Jupiter Planet formed?
Jupiter is the oldest planet in the solar system. The planet, which is 1.5 times heavier than the rest of the solar system planets, has played an important role in the formation and evolution of its neighbours. Approximately 1.5 billion years ago, the solar system of gas and dust or solar nebulae was. Gravity collapsed this substance and began to rotate; The sun was created at its centre. With the formation of the sun, the rest of the materials were dense. The small particles with the gravitational force were close to each other and turned into larger particles.
Solar winds removed lighter elements, such as hydrogen and helium, and made stone and heavy materials near the sun making smaller stone worlds like Earth. Since the solar winds had less effect on lighter elements, they joined each other for the formation of gas giants.
According to the core accretion model, the planet’s stone cores initially formed, then formed lighter elements, mantles and shells of planets. In the stone worlds, the lighter elements of the atmosphere formed. The study of external planets (outside the solar system) confirms the theory of nucleus accumulation as the prevailing process. Stars that have more metal in their core (a term used by astronomers for elements other than hydrogen and helium) have larger planets in their system than stars made of metal only.
Disk instability model
The process of core accumulation for gas giants like the Jupiter requires a lot of time. The cloud of matter around the sun only lasts a short time; Either it turns into the planet or completely disappears. Giant planets were formed very quickly and only a few million years. As a result, based on a specific time range, the gas ring around the sun has only lasted 2 to 5 million years.
According to a relatively new theory called disk instability, gas masses and dust were joined early in the Solar System. Over time, these masses became larger planets. The speed of formation of these planets is, based on this theory, faster than the theory of nucleus accumulation, and sometimes even reaches several thousand years. Continuous Jupiter clashes (just like other planets) raised the temperature of the planet. Dense materials to the centre formed the nucleus. Some scientists believe that the core of the planet can be a hot sphere of liquids; However, according to other research, the Jupiter’s core is a solid stone 2 to 5 times the size of the Earth.
Team accumulation
The biggest challenge of nuclear accumulation theory is its time. According to another study, small bodies of pebbles for forming large planets at a speed of 5x faster than previous models joined each other. In year 2, two researchers, Michel Lampbracrt and Anders Johannes, from the University of Land Sweden, presented the theory of small particles. According to them, the remaining pebbles of the formation processes (previously considered trivial) can have the key to the problem of forming planets.
Jupiter relocation
In year 4, scientists unveiled the Grand Tack. According to this theory, the Jupiter had a two-step immigration after forming a two-step migration. Jupiter has formed exactly about 1.5 astronomical units of the sun and is located in the current position of 1.5 astronomical units after a two-step transfer.
During these transfers, the Jupiter is thought to have destroyed many objects, including some planets of the solar system. Without a Jupiter probably there was no earth; This planet has made the way to Earth easier to destroy smaller worlds.
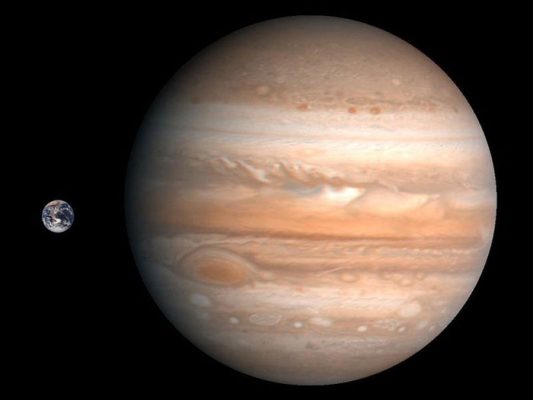
How many times is Jupiter bigger than Earth?
If we combine the mass of the entire planets of the solar system, the Jupiter’s mass will be more than twice. This gas giant can accommodate four planets on Earth. As a result, if you assume Jupiter is the size of a basketball ball, the Earth will be the same as a grape seed. The planet is also 5 times heavier than Earth. In the Jupiter’s diameter, there are four planets Earth.
Physical properties and internal composition of the Jupiter’s planet


Much of the Jupiter is made up of fluid and gas materials. The diameter of the giant reaches 1.2 kilometres. Its average density is 5 grams per cubic centimetre and is ranked second among gas giants. Much of the Jupiter is made up of gas and liquid materials and denser materials are in the lower layer. 2 to 5 percent of the upper atmosphere of the planet is hydrogen and 2 to 5 percent the helium. Overall, 5 % of the planet’s mass is hydrogen, 2 % of it is helium and the remaining one percent are other elements.
Jupiter’s atmosphere includes methane, water, steam, ammonia and silicone compounds. Carbon, ethane, hydrogen sulfide, neon, oxygen, phosphine and sulfur are also traced. The outermost layer of barley consists of frozen ammonia crystals. Material density is higher in the inner layers.
Using ultraviolet and infrared measurements, benzene and hydrocarbons have also been discovered on the planet. Based on spectroscopy results, the Jupiter’s composition is almost similar to Saturn’s composition; But the other two gas giants, Uranus and Neptune, have less hydrogen and helium than the Jupiter, and are therefore called ice giants.
Jupiter’s planet can accommodate 1300 Earth

According to gravity measurements at 2, the planet’s nucleus mass was estimated at 2 to 5 times more than Earth’s mass. The Jupiter’s core accounts for 2 to 5 percent of its overall mass. Jupiter radius is approximately one-tenth of the sun’s radius and one thousand mass; So the density of both is the same. Jupiter mass is usually used as a unit to describe the mass of other objects, especially external planets or brown dwarfs.
If the Jupiter was heavier, he would have been a hydrogen fusion and would become a star; However, the radius of the smallest red dwarf is only 5 % more Jupiter. However, the Jupiter spreads more heat than the heat received from the sun.
The amount of heat generated by the Jupiter is equal to the total solar radiation received by the planet. This process makes the Jupiter smaller every year. While it was much hotter at the beginning of the formation, its diameter was twice that of its current diameter. According to existing hypotheses, the core of the rocky Jupiter is; But its exact composition is still unknown. The nucleus may be surrounded by concentrated metal hydrogen, which makes up a 2 % radius of the planet. Raindrops, such as helium and neon, precipitate at the bottom of this layer, and the abundance of these elements in the upper atmosphere is minimized.
Climber
Like the sun’s atmosphere, much of the Jupiter’s atmosphere is made up of hydrogen and helium. Dark and light-coloured strips on Jupiter’s atmosphere are created by strong east-west winds that move more than 5 km / h. Clouds in bright areas are a combination of frozen ammonia crystals; While clouds in darker areas are formed more than other chemicals. At the deepest surface of the planet are blue clouds. Jupiter cloud tapes change over time and fall into the client’s atmosphere of diamonds.
It can hardly be said to be exactly what the Jupiter’s atmosphere is formed, as 2 % of the planet is hydrogen and 2 percent is helium. On the ground all of these gases are considered; But the strong Jupiter attraction makes the atmosphere of the planet become a multi-layer, each of which has attractive and unique features. Unlike the Earth, there is no clear boundary between the client’s atmosphere and the planet itself. With more penetration to the client’s depths, the density and temperature of hydrogen and helium change, and scientists describe the different layers of the Jupiter’s atmosphere based on these changes. Jupiter’s atmospheric layers include the troposphere, stratosphere, thermosphere and exhaustion.
Since the Jupiter lacks an integrated surface, scientists estimate the lower part of the atmosphere to be 5 kg; The planet’s atmosphere is exactly above this point. The client’s atmosphere, like the ground, decreases with height until it reaches its minimum value. The minimum amount of atmosphere can be found at the boundary between the troposphere and the stratosphere, the tropopause (approximately 2 kilometres above the Jupiter’s surface).
The stratosphere stretches to a height of 2 kilometres and reduces the pressure in the direction, with a decrease in temperature pressure. At this point, the boundary between the stratosphere and the thermosphere is defined. The thermosphere temperature at a height of 2 kilometres reaches 2 degrees Celsius. All the clouds and storms visible are placed at the bottom of the Jupiter’s troposphere and consist of ammonia, hydrogen sulfide and water.
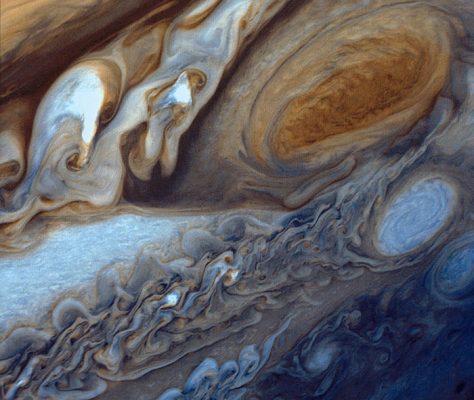
Jupiter’s large red spots
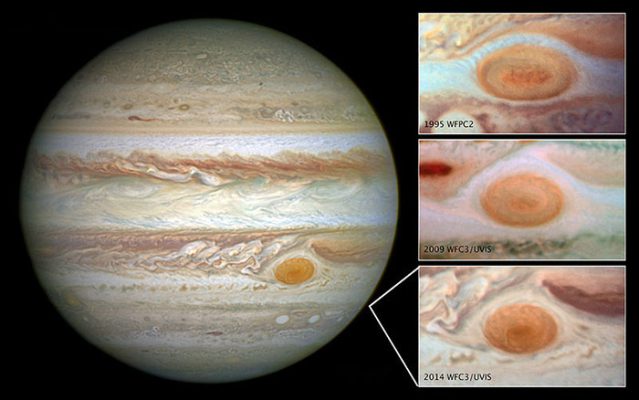

The most prominent feature of the Jupiter is its large red spot. This stain is a steady tornado storm larger than the Earth, located at an angle of the equator, based on one hypothesis of 1 and based on another hypothesis of 2. This stain is large enough to be easily visible with an amateur telescope with a 5cm aperture. To rotate this storm, unlike clockwise and its 4 -day circulation interval. The maximum height of this storm is 2 kilometres above the cloud.
According to mathematical models, this storm is stable and may be one of the sustainable features of the planet. However, the size of this stain has always declined. At the end of the century, the width of the stain was estimated at 2.5 kilometres, four times the diameter of the Earth. After the Voyager spacecraft arrived on the planet in year 2, the storm had doubled to the planet’s width.
Studies of the Jupiter’s red stain show that the size of the stain is still decreasing. On April 1, the width of the stain was estimated at 1.5 kilometres, which is 1.5 times the diameter of the Earth. The longest storm on the earth lasts 2 days, But the Jupiter has more sustainable storms because of the thousands of kilometres of the atmosphere at a much higher speed than the Earth’s rotation.
Jupiter Magnetic Square
The Jupiter’s magnetic field is fourteen times stronger than the Earth’s magnetic field. The field is thought to be created by vortex currents in the planet’s hydrogen core. Some features of the Jupiter’s magnetic field are unique and there are no such as the Earth’s magnetic field.
The Jupiter’s Jupiter’s lunar volcanoes release large quantities of sulfur dioxide, resulting in a gas halo around the orbit. This gas is ionized in the Jupiter’s magnetosphere and released sulfur and oxygen ions.
These ions, along with the Jupiter Hydrogen ion, form a plasma plate in the tropical body of the planet, the plasma on this planet rotates along with this planet, resulting in bipolar magnetic disk deformation to a magnetic disk. The electrons on the plasma plate create a powerful radio effect that produces explosions in the range of 1.2 to 5 MHz.
The Jupiter’s magnetosphere is the cause of the intense spread of radio material from the polar parts of the planet. Ivy’s volcanic activity of the planet leads to the spread of gas in the Jupiter’s magnetosphere and creates a halo of particles around it. As Io moves in this aura, the waves of alpha are created. Alfon wave is a type of hydrodynamic magnetic wave in which the ions fluctuate in response to an effective voltage on the magnetic field lines. These waves carry ionic materials in the polar areas of the Jupiter.
Rotation and Jupiter circuit
The average distance between the Jupiter and the sun is 2 million kilometres (approximately 1.5 times more than the distance between the Earth and the sun), and every 2.5 years rotate around the sun. The elliptical circuit of the Jupiter has a 1.5 -degree deviation compared to the ground. Exit from the centre of the planet’s orbit is 1.5 %, so its distance from the sun between the nearest call (peak) varies by 5 million kilometres.
Read more: How could Big Bang arise from nothing
The pivotal oscillation of this planet is relatively low: 1.5 degrees. As a result, there are not many seasonal changes compared to Earth and Mars. The Jupiter rotates around the planets of the solar system at the highest speed and completes the rotation around its axis in less than ten hours due to the high speed of a tropical protrusion, which is easily visible through an amateur telescope based on the Earth. . The Jupiter’s equator is 5 kilometres more than the diameter of its poles. Because the Jupiter is not a rigid body, its upper atmosphere has a different rotation. The rotation of the Jupiter’s polar atmosphere is approximately 5 minutes longer than its tropical atmosphere.
How many moons does Jupiter planet have?
The Jupiter has 2 approved moons. The Jupiter ranks second in the solar system in terms of the number of moons (with 2 lunars); But according to the latest research, Canadian astronomers found evidence of the existence of four small moons in the Jupiter’s orbit, and according to speculation, the number of moons on the planet could reach 5; But they have not yet reached the approval and observation stage.
Overall, of the 5 -approved Jupiter moon, the four largest Galileo moon is more popular. The moons were discovered independently by Galileo Galileo and Simon Marinus in the year 9. Early in the early days, more of the Jupiter’s moons were discovered and the names of the lovers or girls of Jupiter, the Roman God or Zeus (its Greek counterpart). Galileo moons are the largest and heaviest objects in the Jupiter’s circuit.
Eight Jupiters are from regular moons with almost circular circuits. Galileo’s moons are almost spherical due to a planetary mass. If these moons were in the orbit of the sun, they would be in the category of dwarf planets. The other four are smaller and are less than the Jupiter’s planet; These moons are resources for the formation of Jupiter circles. Other Jupiter moons are irregular and their circuit is far from the Jupiter. These moons are likely to be trapped in the attraction of the solar circuits. Twenty-two irregular Jupiters have not yet been officially named.
Regular Jupiter moons are thought to be formed from the planet’s rotary disk; A ring of gas and stone-like that is similar to the initial planetary disc. On the other hand, irregular moons are composed of asteroids that are trapped in the attraction of the Jupiter. According to many scientists, these asteroids are crushed and then formed by other small bodies, forming irregular Jupiter moons.
Lunar Group
In general, Jupiter moons are divided into two categories regular and irregular. The irregular moons themselves are divided into two groups internal moons (Amalia) and Galileo moons.
- Internal Lunches (Amalia): Matthews, Adrastia, Amalia and Group are the Jupiter’s internal moons; Because they are close to the planet. Two of the most internal moons in less than a day complete the orbit of the planet. The other two are the fifth and seventh largest moons in the Lunar System, respectively. According to the observations, the minimum member of this group, Amalia, was not formed on the current circuit but was previously farther away from the Jupiter.
- Galileo’s main group of moons: Io, europa, ganymede and Calisto are the largest moons of the solar system in terms of mass and size. The diameter of the moon is even more mass than Mercury, but its mass is less mass. These moons are the fourth (Io), the sixth (europa), the first (ganymede) and the third (Calisto) of the natural moons of the solar system accounting for approximately 1.5 % of the total mass orbit of the Jupiter. The Jupiter’s planet is 5 times heavier than its moons.
Jupiter’s irregular moons
Jupiter’s irregular moons are small objects with different circuits and farther away from the Jupiter. These moons have similarities such as deviation, exit from the centre, semi-primary axis and chemical composition. According to scientists, these are a group of colliding moons created by the clash of larger parent objects with the asteroids affected by the gravitational field.
Galileo
Galileo is one of the most well-known Jupiter moons that have been studied during various excavations and more information is available. Here are some features and excavations related to these moons.
Io


Io is the fifth largest Jupiter moon and has the most volcanic activity in the solar system. It has sulfur ducts that are published up to 2 kilometres. The surface of the iO is full of lava seas and flood plains with liquid rocks. Astronomers discovered a map of four volcanoes on the moon, some of which publishes up to 2 kilometres in the lava space. Io is a Jupiter host of 1.5 billion years old. The average orbital distance of the Io to the Jupiter is 4,000 kilometres. It takes 4.3 days to complete the Jupiter orbit. Io has a tidal lock and always one side to the Jupiter. The diameter of the Io is approximately 2 kilometres, which is slightly higher than the moon.
Io is the only moon in the solar system with active volcanoes
IO has a relatively oval shape. Among Galileo’s moons, Io is ranked higher in terms of mass and volume than Ganymed and Calisto and higher than in europa. The mean temperature of the IO -negative level is 2 degrees Celsius. For this reason, sulfur dioxide snow bodies are abundant on their surface. It is also called ice and fire.
Io was discovered by Galileo Galileo on January 1, 2008. He discovered the moon a day before, But he failed to recognize Io and europa. Galileo’s discovery was the first lunar discovery at the time. Galileo’s discoveries proved that the planets rotate around the sun, not the earth. Galileo initially named the moon Jupiter; But in the mid-nineteenth century, its name changed to Io. In Greek mythology, Io Keen Hera (wife of Zeus) and the daughter of Inchchus, King Argus. Zeus (Greek counterpart of the Roman god Jupiter) fell in love with Io, But he turned him into a cow to safeguard his wife Hera.
Io Features: The interior of the Io includes a sulfide iron kernel and an outer layer of silicate brown. This combination gives the moon a tattoo with orange, black, yellow, red and white. According to data obtained from computer models, Io was formed in an area around the Jupiter whose abundance of ice was initially high. The heat of the IO with the water on its surface within a short distance after the formation can be a sign of ancient life; Even in an environment where Jupiter radiation destroys surface water.
The most prominent features of this moon are its volcanoes. Io after the earth is the only mass of the solar system with an active volcano. Galileo left notes of volcanic activity, and the NASA Voyager spacecraft confirmed the IO volcanoes in the year. Due to volcanic activity, much of the Io is sulfur dioxide. According to the observations of the Gemini North telescope in Hawaii and the TEXES spectrometer in year 2, the olive atmosphere is likely to collapse. Io’s sulfur dioxide gas coating is frozen every day in shade mode. When Io returns to sunlight, frozen sulfur dioxide becomes gas once again.
Callisto
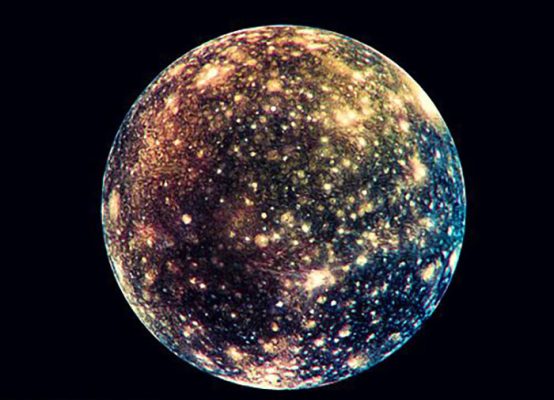


Callisto is one of the big moons in the Jupiter’s circuit. This moon has an ancient surface full of collisions that indicate that there are no geological processes; But the moon has an underground ocean, and because of its old surface, the existence of life in this ocean is still certain.
Like the other four moons, Callisto was discovered in the year 9. The name of this moon was initially Jupiter IV, But in the nineteenth century, it was called Callisto . Callisto was investigated by numerous probes, including the long-term mission of the Galileo spacecraft in the 1980s and decades. The Juno spacecraft has also recorded remote images of Callisto . Callisto is a Jupiter with its host -packed 5.5 billion years. This moon is the heaviest mass of the collision cavity in the entire solar system, But its level has remained intact for about 5 billion years ago.
Among Galileo’s moons, Callisto is the foremost moon. The moon is about one million eight hundred and eighty thousand kilometres from the Jupiter. It takes almost seven days to complete the Jupiter’s Callisto . Callisto has fewer tidal effects than other Galileo moons; Because across the belt is the main radiation of the Jupiter. Callisto has a tidal lock to the Jupiter and is always on one side of the Jupiter.
Callisto , with a diameter of 2 kilometres, is almost the same as the planet Mercury. This moon is the third largest moon in the solar system after Ganim and Titan (Saturn’s moon). The month is fifth after Io. The temperature of the Callisto level reaches -1.5 degrees Celsius. The Galileo spacecraft sent detailed information about Calisto in Year 2. In this mission, much of the moon was mapped, and its thin carbon dioxide atmosphere and evidence of the underground ocean were discovered. According to the images obtained from the Hubble Space Telescope in Year 2, Callisto’s effect on the clerical climate explosions was revealed. Their Jupiter has the aurora, But some of the Jupiter’s aurora phenomena stem from its interaction with its four large moons.
Future missions, including Juice, dedicated to the study of Jupiters’ ice moons, will reveal more facts about Calisto and the possibility of life. Articles have also been published on the modelling of the Jupiter’s and Callisto magnetic field interaction (this review provides evidence of the Callisto subsurface ocean) and the finding of atomic oxygen in the atmosphere. Other articles focus on dimensions such as the water below the surface, the number of collision openings and atmospheric characteristics.
Ganymede
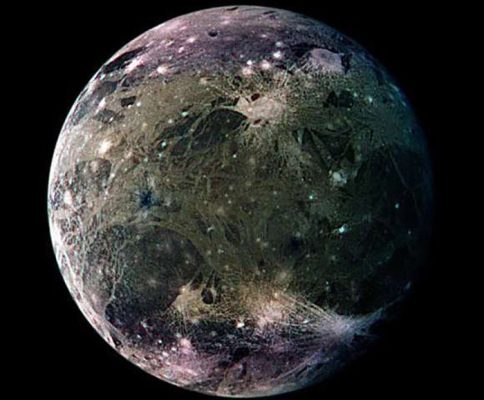


Ganymede is the largest Jupiter’s moon and the largest moon in the solar system. This moon is even larger than Mercury and Pluto, and slightly smaller than Mars; As a result, if it were in the orbit of the sun, it would easily have been in the category of planets. ganymede is likely to have a saltwater ocean beneath its icy surface; As a result, it becomes one of the strong candidates for life discoveries. ganymede is one of the goals of the Juice mission that will be launched in the 1980s.
Callisto, Ganymede and europa have a saline underground ocean
Ganymede, like Callisto and Io, is a Jupiter’s age at the age of 1.5 billion years. The moon is more than one million and seventy thousand kilometres from the Jupiter and completes the planet’s orbit within seven days. The average radius of ganymede is 1.5 km. ganymede is larger than Mercury but its mass is half the mass of Mercury and therefore has little density. The average temperature of the day at the Ganymede level reaches a negative of 2 to 2 degrees Celsius. Astronomers with the Hubble Telescope, in the year 6, obtained evidence from the Oxygen Ganymede Joe. However, this atmosphere is too thin to support the vital we know, and it is unlikely that living things will be able to settle on ganymede.
Ganymede only has a magnetosphere in the entire solar system. The magnet, commonly found on planets such as Jupiter and Earth, is a sequel in which pregnant particles are trapped and deviated. ganymede magnetism is embedded in the Jupiter’s magnetism. Galileo changed its name to Jupiter III after discovering ganymede. With the increase in the number of objects discovered in the mid -19th century, the name of the moon was renamed Genmod according to Greek myths.
Ganymede Features: Ganymede has an iron core, a stone mantle and a high thick shell, most of which are ice. There are also traces of stone formation on the ganymede surface. On February 4, NASA unveiled a precise map of ganymede in the form of video images and animation created using NASA’s Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft as well as the Galileo Circuit.
The Ganymede surface consists of two types of main surfaces: approximately 2 % of the dark ganmod surface with multiple collision openings and 2 % is light-coloured with grooves that give Ganymede a special look. The grooves are caused by tectonic activities or the spread of water below the surface.
According to scientists, Ganymede has an underground saline ocean. Scientists, using the Hubble Space Telescope, examined the Aurora and the changes between the Jupiter’s magnetic fields and ganymede. According to the evidence of these aurorae, Ganymede probably has a saline underground ocean that is even saltier than the oceans of the earth.
Some scientists have pointed to the possibility of life in ganymede. Due to the internal structure of ganymede, the pressure of the ocean floor is so high that any water that reaches it becomes ice. For this reason, hot water flows can hardly bring nutrients to the oceans.
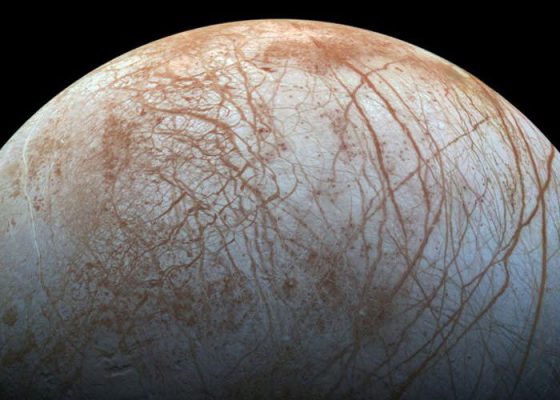
Europa
Europa is Galileo’s smallest moon. The surface of this frozen moon and covered with a layer of ice; But to scientists, there is an ocean beneath this ice surface. The ice surface has made europa one of the most reflective moons of the solar system.
Researchers, using the Hubble Space Telescope, identified signs of waterfalls from the South europaan region in year 6. After numerous efforts, the research team saw the waterfalls in years 1 and 2. europaan moon was formed about 1.5 billion years ago with its host planet, the Jupiter. On average, europa’s distance from the Jupiter is 1,800 kilometres. It takes three and a half days for europa to complete the Jupiter orbit. europa has a tidal lock to the Jupiter; So there is always one side to the Jupiter.
Europa is 5 kilometres in diameter than the moon and larger than Pluto. The europaan surface temperature at the equator is never above 2 degrees Celsius and at the poles of this moon is no more than 2 degrees Celsius. Galileo discovered europa on January 2. Of course, it had observed it a day ago on January 6; But he could not distinguish this moon from Iowa. In Greek myths, Greece is stolen by Zeus (Jupiter’s counterpart, the Roman God) and becomes a white cow to seduce europa. He brings the cow with flowers and sends it to the city of Crete. Zeus returns to their normal way in Crete and seduces europa. europa was a queen of Crete and gave birth to several children for Zeus.
One of the prominent features of europa is the high reflection capability due to the icy shell. According to scientists, europa’s level is 2 to 5 million years old. Galileo’s spacecraft images and data show that europa has a combination of silicate stone, iron core and stone mantle just like Earth. Unlike the interior of the Earth, the europaan stone space is surrounded by a layer of water or ice that reaches 1 to 2 kilometres. According to europaan magnetic field fluctuations, there is probably an ocean below the surface of the moon that can host life. The possibility of europaan extraterrestrial life has made it an attractive destination for space exploration.
The europaan level is full of fractures and gaps. According to many scientists, these gaps are the result of the tidal forces of the ocean below the europaan level. When europa approaches the Jupiter, the sea level under the ice reaches above normal. In these conditions, the continuous tidal of the sea causes gaps in the surface of the moon. In year 2, scientists realized that europa could host tectonic pages. In the solar system, only the earth has a variable shell that is useful for the evolution of life on earth.
Life in europa: The presence of water under the frozen shell has made europa the moon one of the potential candidates for hosting life in the solar system. The Deep Ice of the moon probably has channels to the mantle like the ground. These channels provide the warm environment needed to evolve life. According to a study in Year 2, europa’s oxygen was estimated at ten times its hydrogen, which is similar to Earth’s. Thus, the ocean below the europaan level becomes a better environment for life.


Jupiter loops
Jupiter’s rings are made of dust and stone and are divided into three sections of aura, the main ring and the thin ring. Jupiter’s rings were discovered by the Vaviger probe. The combination of Jupiter rings is different from Saturn’s rings made of ice. Jupiter’s rings are very dim and delicate.
- Internal: The internal part of the Jupiter’s rings made of dust surrounds the space on the planet. This is the brightest and thickest part of the Jupiter’s rings.
- The main ring section: The main part of the ring is the thinnest part and consists of dust and stone. The dust particles in this section date back to 5 years or even 5 years. This means that it is caused by the collision with larger rocks of the new dust.
- Gossamer: Gosmer is the outside of the Jupiter’s rings. This section is, like the previous two parts, a combination of dust particles; But the word gossamer means a narrow material that is suitable for this part because of its very small dust particles.
Jupiter’s rings are not shining like Saturn’s because they are composed of particles and dust, and only the strongest telescopes can observe them. Jupiter’s moons are the cause of the rings of this planet. The most internal moons, such as the Metis, Adrastea, and Amalthea, were hit by many meteors, and their dust and rock particles reached the Jupiter’s orbit, thus forming the rings of the planet.
Wonders of Jupiter Planet
Jupiter planet has many wonders because of its strong attraction and magnetic field as well as its strange moons. Here are some examples of these wonders:
The influence of the Jupiter on the solar system: The Jupiter is also famous for the vacuum cleaner of the solar system for its severe attraction and internal position of the solar system. The planet experiences the most collision with comets among the planets of the solar system and is thought to act as a shield for the internal planets of the solar system.
If the sequel to Shoemaker–Levy 2 was hit by the earth, there would be no trace of life on earth
But according to recent computer simulations, the Jupiter has not had a significant role in reducing the bombing of the internal planets of the solar system, although the debate is still going on. At least it can be said that it has rescued internal planets from a disaster called Shoemaker–Levy. Schmidker Levi 3 has experienced one of the most exciting ends. Shoemaker–Levy’s treatment of the Jupiter caused injuries to the surface of the planet that are even visible from Earth. This is the first accident in the two internal crimes of the solar system, and the traces of this comet on the Jupiter’s atmosphere are far beyond expectation.
Shoemaker–Levy comet encountered the Jupiter in year 6, and this encounter had a great deal of fear in public opinion because if a similar comet had hit Earth, life would be destroyed on the planet.
Two Armageddon films were inspired by the confrontation and were made on the subject of land-threatening objects. Congress, after the release of these films, called for NASA to search for objects close to Earth. Schumacher Levi was first discovered in March by three comets from Eugene and Caroline Shoemaker and David Levy. The group had previously collaborated and discovered other comets. For this reason, the name Schumicar Levi was chosen for this comet.
The comet was rotating around the Jupiter decades ago but was not in the trap of a strong attraction. The orbital calculations showed more that this comet had treated the Jupiter in July. At that time, the Galileo spacecraft was still on the path of the planet and could not record a close view of the collision.
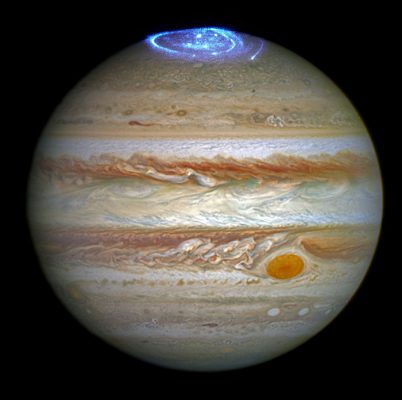
Strange Aurora: This year, the Juno probe discovered a new aurora that fluctuates on the Jupiter’s poles. Juno’s UVSA (UVS) tool recorded this bright phenomenon. This aurora extends in the form of high-speed rings between 1.2 and 2.5 km / s. According to scientists, these aurorae have been created due to pregnant particles from the edge of the massive Jupiter’s magnetosphere. Jupiter Aurora, like the earth, depends on the pregnant magnet particles. However, the Jupiter’s magneto science is 5 times stronger than the Earth’s magnetism.


New Facts of Hot Jupiter Dots: A generation after the discovery of the hot and dense atmosphere in the Jupiter, Juno’s mission came to newer answers to these points. Juno discovered hot spots that were much wider and deeper than past models and observations. The results were announced on December 5 at the annual conference of the US Geophysics Union.
More water discovery in Jupiter’s atmosphere: According to Juno probe data in year 2, approximately 2.5 % of the Jupiter’s equator molecules are water molecules. However, this does not appear to be three times higher than that of the solar water molecules based on the calculations of the components of the water, hydrogen and oxygen in the Jupiter. Juno’s measurements discovered more water than previous missions. This discovery can help scientists in search of the real Jupiter origin.
The similarity of Jupiter Wajar Clouds to Earth Clouds: Jupiter and Earth may seem like two completely different planets, but the atmosphere of the two planets is more like each other. The Juno probe captured images of small-scale wave patterns in the Jupiter’s atmosphere during the year. These images, captured by the Junocam tool, reveal the similarity of these cloud shapes to the earth. These waves in the Earth’s atmosphere are called meniscus or medium scale. Now the same waves have been discovered in the Jupiter’s atmosphere called atmospheric wave strands.


Seeing the Jupiter Planet from Earth
Jupiter is the fourth bright object in the night sky (after the sun, moon and venom). The close to Jupiter’s position varies from the sun and the earth. The mean range of the planet’s vision is 1.5 % and its standard deviation is 1.2.
Since the Jupiter’s orbit is out of the ground, the phase angle of the planet from Earth is never more than 1.5 degrees. For this reason, the planet is always seen from telescopes based on Earth. With a small telescope, even Galileo’s moon and cloud belts around the Jupiter can be observed.
Preturecopian Research
Jupiter observation dates back to Babylonian astronomers in the seventh or eighth centuries BC. Chinese astronomers also observed the Jupiter’s orbit and built the ground-branch cycle based on their approximate years.
Telescopic research based on Earth
In January, Galileo Galileo examined the planet’s Jupiter with its small telescope. His observations changed the current understanding of the universe. Galileo saw three small stars near the Jupiter. The next afternoon he was able to see the stars again, but this time they were on the other side of the planet. During a few weeks, these stars were moving around the Jupiter. Galileo gave the names of the stars of Medici to their supporters, but today they are known as Galileo’s moons.
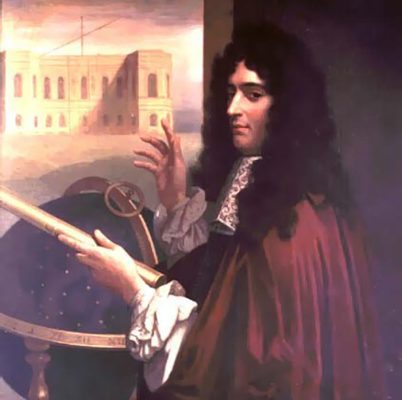


This was the first telescopic observation of the solar system (other than the moon). The day after Galileo Simon Marinus independently discovered the moons around the Jupiter but did not publish the results of his discoveries until year 6. This discovery was a turning point in the Copernican Central Sun theory of the movement of planets. Galileo was questioned for supporting this theory for insulting the sacred.
In the 1980s, Juvan Cassini used a new telescope to discover colourful tapes and Jupiter stains and was able to estimate the rotation period of the planet. Cassini discovered the difference between the rotation of the Jupiter’s atmosphere with the planet itself. The large red spot in the southern hemisphere of the Jupiter was probably monitored by Robert Hook and at Cassini at 2, though there is still debate. Astronomy named Henry Schwab released the first design of the Great Red Spot details at 2.
Borley and Cassini both made detailed tables of Jupiters’ lunar movements and predicted the movements of these moons. At 2, Bernard discovered the fifth Jupiter at the California Observatory. The discovery of this relatively small object made him famous. This is called the Mohammed. It was the last planet’s moon that was discovered directly with an eye observatory.
At 1, Robert Wildt discovered the immense methane tapes. Three rotating rings (large-scale wind rotation around a high-pressure central point unlike clockwise) called white rings were also discovered. Finally, two rings were merged in 2, and the third ring known as BA was absorbed in 2
Radiottic research
Based on radio signals, Bernard Burke and Kent Franklin were able to discover explosions of 1.2 MHz. The explosions were consistent with the rotation of the planet, and they used this information to correct the rotation ratio. Jupiter radio explosions have two major forms: Long explosions (L explosions) last for a few seconds and short explosions (S) last less than one hundred seconds.
Jupiter probes
Eight spacecraft and probes have so far examined the planet: Pioneer 10 and 11, Voyager 1 and 2, Galileo, Cassini, Yolis, New Horizons and Juno.
Pioneer 10 and 11 (Pioneer)
Pioneer 1 and 2 were the first spacecraft to review the Jupiter. The two probes recorded the first scientific observations from the planets Jupiter and Saturn and paved the way for Voyager’s missions. The external tools of these ships examined the climate of the Jupiter and Saturn, the magnetic fields, the moons and the rings, as well as the intermediate dust and magnetic areas, solar winds and cosmic rays. The two probes left the Solar System on their way.


Voyager 1 and 2 (Voyager)
NASA sent two Voyager spacecraft to the Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune in late summer. The nearest Voyager 2 contact with the Jupiter is registered on March 5. The closest gap between Voyager 2 to the planet was recorded on July 5.


Jupiter photography began in January. Wower 2 completed his mission for the Jupiter in early April, after registering 4.3 images and many other scientific measurements. The Voyager mission was from late April to early August. The two spacecraft recorded more than 1.5 % of the Jupiter and five moon images. Voyager 1 and 2 provided a lot of information on moons, magnetic fields and more to researchers. The biggest achievement of the two spacecraft was the discovery of volcanoes active on the moon.
Galileo spacecraft (Galileo Spacecraft)
The Galileo spacecraft was launched on October 5 with the Atlantis Space Shuttle missile and reached the Jupiter on 2. The probe has been in the Jupiter’s circuit for almost eight years and examined its moon. Based on the information obtained from the camera and the other four tools of the probe, the possibility of the ocean under the europaan moon was investigated. According to the discoveries, the volcanoes of the moon are very active. Another discovery of Galileo was ganymede’s separate magnetic field. Galileo was carrying a small probe that was sent deep into the Jupiter’s atmosphere and was destroyed about an hour later due to too much pressure.
Cassini spacecraft (Cassini)
Cassini was a cooperation between NASA and the europaan Space Agency (ESA) and the Italian Space Agency, and its main purpose was to investigate Saturn, the system and moons of the planet. The probe was at the closest distance to the Jupiter on December 5 and recorded numerous scientific measurements. Cassini recorded 6,000 images of the planet, rings and moon during six months of flight around the Jupiter. Cassini’s biggest achievement for the Jupiter was the most accurate colour portrait of the planet (until then).
Other Cassini observations include the dark cloud of the spinning at the top of the Jupiter’s atmosphere, almost the size of a large red spot, near the North Pole. Based on the evidence that Cassini obtained from the Jupiter’s rings, the loop is composed of an irregular structure that is probably due to the collapse of the stone from the Metis and Adrastea moons.
Ulysses’ spacecraft (Ulysses)
Ulysses was the result of NASA’s cooperation and the europaan Space Agency launched in October, with the main purpose of examining the space zone above the sun’s poles. Since Ulysses needed a lot of energy to put it in the sun’s orbit and the earth could not provide it, it was necessary to supply this space from another planet. The Jupiter was the nearest planet that could provide the prerequisites for the trip.
Ulysses reached the Jupiter six months after his departure from Earth, and on February 4, he was closest to the planet. Although the secondary goal of Ulysses was to investigate the Jupiter, in this short trip he was able to find very useful information about the very strong magnetic field of the planet.
New Horizons spacecraft
New Hurazenz was a mid-range probe built at the Johns Hopkins University Physical Laboratory (APL) and the Southwest Research Institute (SWRI) and was launched into space in year 6 to investigate Pluto. New Hurazenz used Jupiter attraction (2 times the gravity of the Earth) to be on the Pluto route.
New Hurahiznes used the Lorri tool to capture its images of the Jupiter on September 9, from 2 million kilometres. More careful Jupiter reviews continued in January with the capture of the infrared image of Calisto’s moon and a few blacksopoid images of the Jupiter itself.
One of the main goals of this probe was to examine the weather conditions and analyze the structure of Jupiter clouds. The probe for the first time was able to capture the Jupiter’s small red spots from the distance. He also succeeded in capturing images of the planet’s circular system from different angles. New Hurahizenz moved to the Jupiter’s magnetosphere with valuable information about it.
Juno spacecraft (Juno)
NASA’s Space Explorer Juno was launched on August 1 and entered the Jupiter’s orbit on July 5 to begin careful scientific investigations. The spacecraft has been rotated 2 times around the Jupiter so far and has been over the clouds of clouds for approximately one year.
The purpose of the Juno mission is to measure the composition, the gravity field, the magnetic field and the polar magnetosphere of the planet. It also looks at clues to the formation of the planet, the stone kernel, the amount of water in the atmosphere, the distribution of its crime, and its deep winds, reaching a speed of 3 km / h.
Unlike other exploratory sent to the solar system planets, Juno is reinforced with solar arrays similar to that of the ground satellites, while their isotopic thermoelectric generators are usually used inside the Solar System.
During the Juno mission, infrared tools and microwaves measured heat radiation from the Jupiter’s atmosphere. These are supplements for previous studies of the planet’s composition of abundance and distribution of water and oxygen. Data provide new views on Jupiter origin.
Juno has also found unprecedented findings about Jupiters’ atmospheric winds. According to these findings, the planet’s atmospheric winds last longer than the atmospheric processes on Earth. Juno’s measurements from Jupiter Square Square prove the asymmetry of the north and south of the planet, which is similar to the asymmetry observed in the belts and tapes of the planet. The deeper the winds, the more mass increases.
According to another Juno finding, the climate of the planet is a rigid body. This is a wonderful result, and Juno’s future measurements help to understand this transition from the air to the rigid body. Before Juno’s discovery, there was no information about the atmosphere close to the client poles. According to the information obtained from this probe, the Jupiter poles are more violent than the white and orange belts located in the lower latitudes of the planet.
The north pole of the planet is surrounded by a central tornado, surrounded by eight tornadoes with variable diameters from 1 to 2.5 km. Jupiter Antarctica also has a central tornado with five more tornadoes with variable diameters from 1 to 2 kilometres. The Juno spacecraft is currently reviewing the planet’s orbit, sending amazing images, atmospheric data and other observations about the planet.
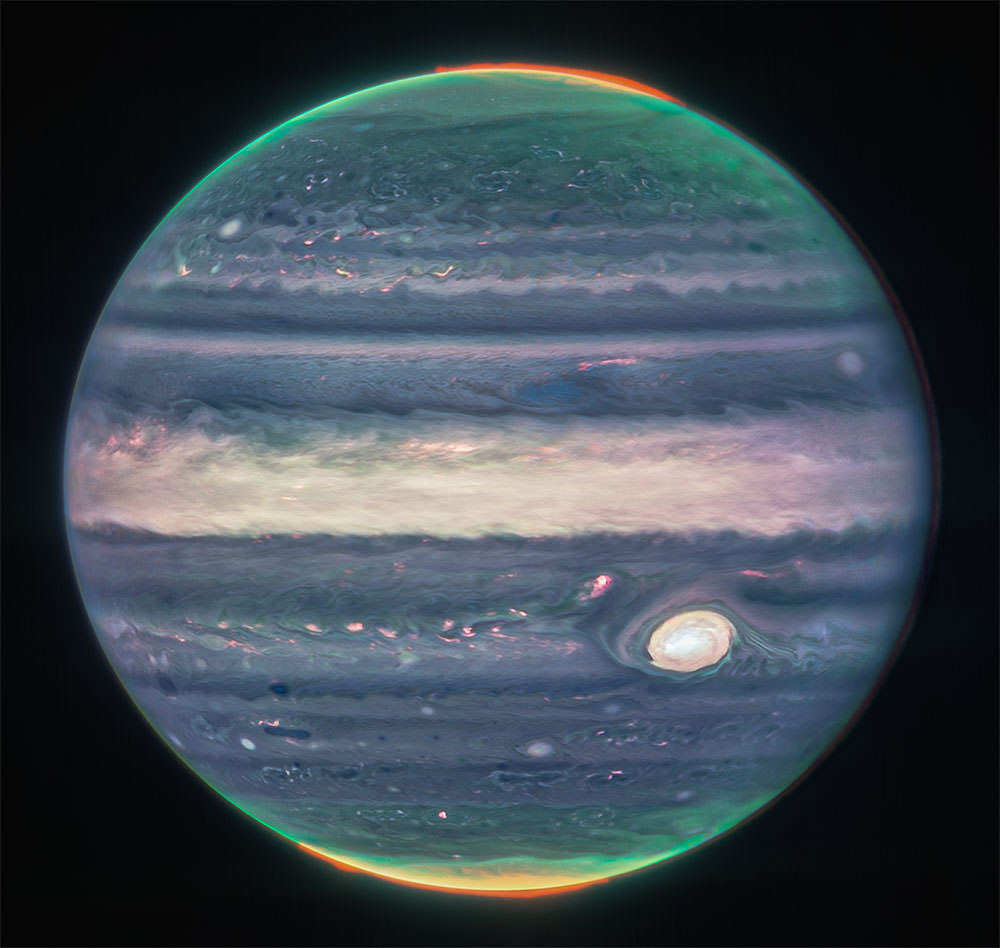
James Web Telescope images from Jupiter
The James Webb Space Telescope, which has been working since last year, has had significant observations in recent months. One of these remarkable observations is accurate images of the Jupiter’s planet and its polar Aurora. Both images of the telescope are a combination of several images made with a camera near the NIRCAM camera with different filters.


In the wider image, you can see the narrow rings of the Jupiter as well as the two moons. Almatia’s moon is a bright spot on the left and Adracetia’s moon is on the edge of the rings between Alamalea and the Jupiter. The second image is recorded from a close-up of the Jupiter’s planet. This image uses three filters to record details of the planet’s stormy atmosphere, especially the polar Aurora. You might think about why the colours of these images are not like what we see in other Jupiter images.
Read more: Meerkat telescope a new tool to observe extraterrasial signals
In these images, the James Web Telescope records light in the infrared spectrum, not the visible light spectrum; So the colours of the two images are not the same as the unarmed eye colours. The infrared data were written on the visible light spectrum, so these images are “false colour”, not “real colour”.


Future missions to the Jupiter
Juice (Jupiter Ice Coordinator): Juice is a europaan Space Agency’s mission, which has been selected as part of the Cosmic Vision Scientific Program. The probe is expected to be launched in year 6 and reaches the Jupiter after visits to the interior of the solar system in the 1980s. The probe is dedicated to studying Galileo’s ice moons: ganymede, Calisto and europa. All three moons have subsurface oceans, which increases their potential for life.
europa Clipper: The NASA europaan probe is dedicated to europa’s review of the Jupiter’s ice moon and will examine the living conditions under the ice shell. The probe will be in the Jupiter’s orbit for accurate europa. The europaan probe will be launched in the early 1980s and will reach the Jupiter’s planet after a 6.5 -year trip.
Chinese and Russian missions: China will launch its first Jupiter probe in year 6. The probe will reach the Jupiter planet in year 6. Russia is also looking to send a survey to the Jupiter that will be launched in year 6. It takes 6 months and first visits the moon and Venus. He then examines the Jupiter and its moons.


You may like


What happens when two galaxies collide?
Gravity can make extraordinary things happen. This invisible force has a significant effect on cosmic matter. Gravity is the factor that transforms gas and dust into bright stars, transforms irregular rocks into spherical planets and finally collides galaxies with each other. Sometimes two galaxies, and sometimes more, move towards each other. This movement continues until the galaxies collide with each other. In this situation, the internal materials of the galaxies may collide with each other and combine, and as a result, the slow chaos turns them into a huge galactic ball.
Astronomers have observed such events known as mergers in the past. At the beginning of the encounter, it looks like the galaxies have gathered for a space conference. At the peak of this process, gravity distorts the shape of the galaxies, and at the end, an irregular sphere remains. Then the only sign of the merger is the faint flickering of stellar material around the galaxy.
The image below, taken by the Jumnai Telescope in Hawaii, shows the beginning of a merger in remarkable detail. The two galaxies NGC 4567 above and NGC 4568 below orbit each other, their stars pushing each other and new stars shining until everything merges in about 500 million years and the final shape is a heart in the sky.
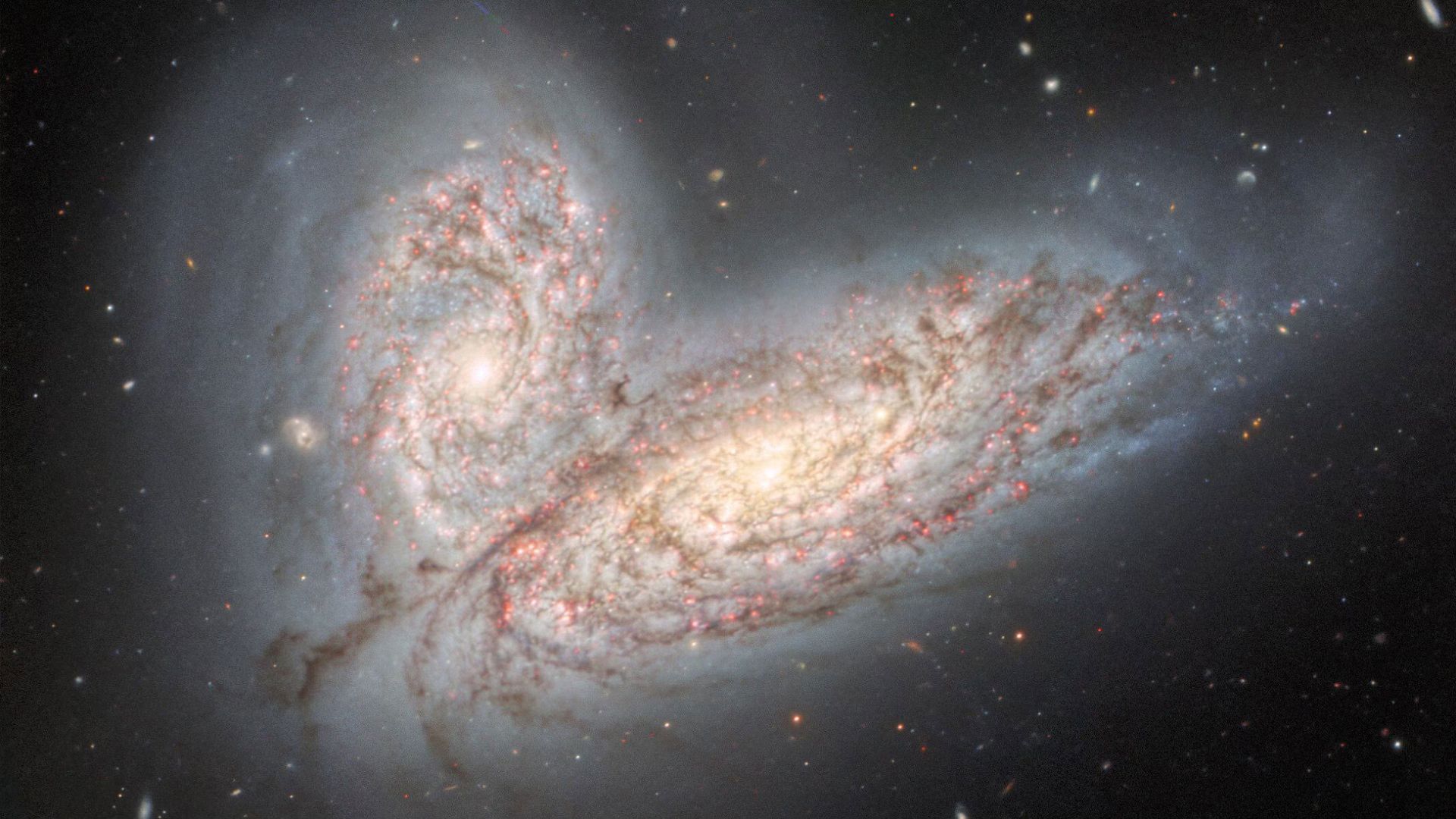

Galactic mergers are among the most fanciful events in the universe. Supernovae and black holes definitely have their charms, But galactic mergers have a lot to say. These events also provide good grounds for daydreaming about extraterrestrial life. For example, consider NGC 4568 and NGC 4567, which are full of stars and most of the stars have planets based on the observations obtained; So maybe NGC galaxies are home to other beings; But what does it feel like to be in the middle of a galactic merger? According to Vicente Rodríguez Gómez, an astronomer at the National University of Mexico:
The night view in the merged galaxies will be very promising. The sky is filled with new stars, and the curved streams of stars, gas, and dust drawn across the sky can be clearly seen. The view of this sky will be especially spectacular if you live on the outer edges of the galaxy. In this situation, the night sky is not as crowded as the center of the galaxy.
Now suppose another galaxy merges with your galaxy in the outer domains. In this condition, this galaxy appears bigger and brighter than any other star in the darkness of the night. Even more exciting, you can view this sight almost without worry because the Sun is highly unlikely to collide with another star despite the collision of galaxies. Moya McTyre, astrophysicist and author of ” The Milky Way: A History of Our Galaxy ” says:
Have you ever seen a band of military musicians? Or a performance in which two groups walk through each other? Stars similarly move through galactic mergers, passing by each other like unison musicians. Although there are many stars, space is still infinite and most stars are not in danger of colliding with anything else.
Of course, if your planet is in a remote place, you may face a problem. The pressure from the collision can throw stars from the edges of a galaxy deep into intergalactic space. On the other hand, even though the stars regularly pass by each other, the space between them can be a little irregular. According to Jehan Kartaltep, an astrophysicist at the Rochester Institute of Technology and one of the researchers of the formation of galaxies:
Galaxies have huge clouds of gas and dust, and if they collide, these huge clouds of gas and dust collide with each other.
As a result, the collision process of gas and dust can create hazy masses of gas and dust in the night sky, which eventually collapse due to their own weight and form new stars. Astronomers on Earth can observe these starburst regions in galaxy merger images.
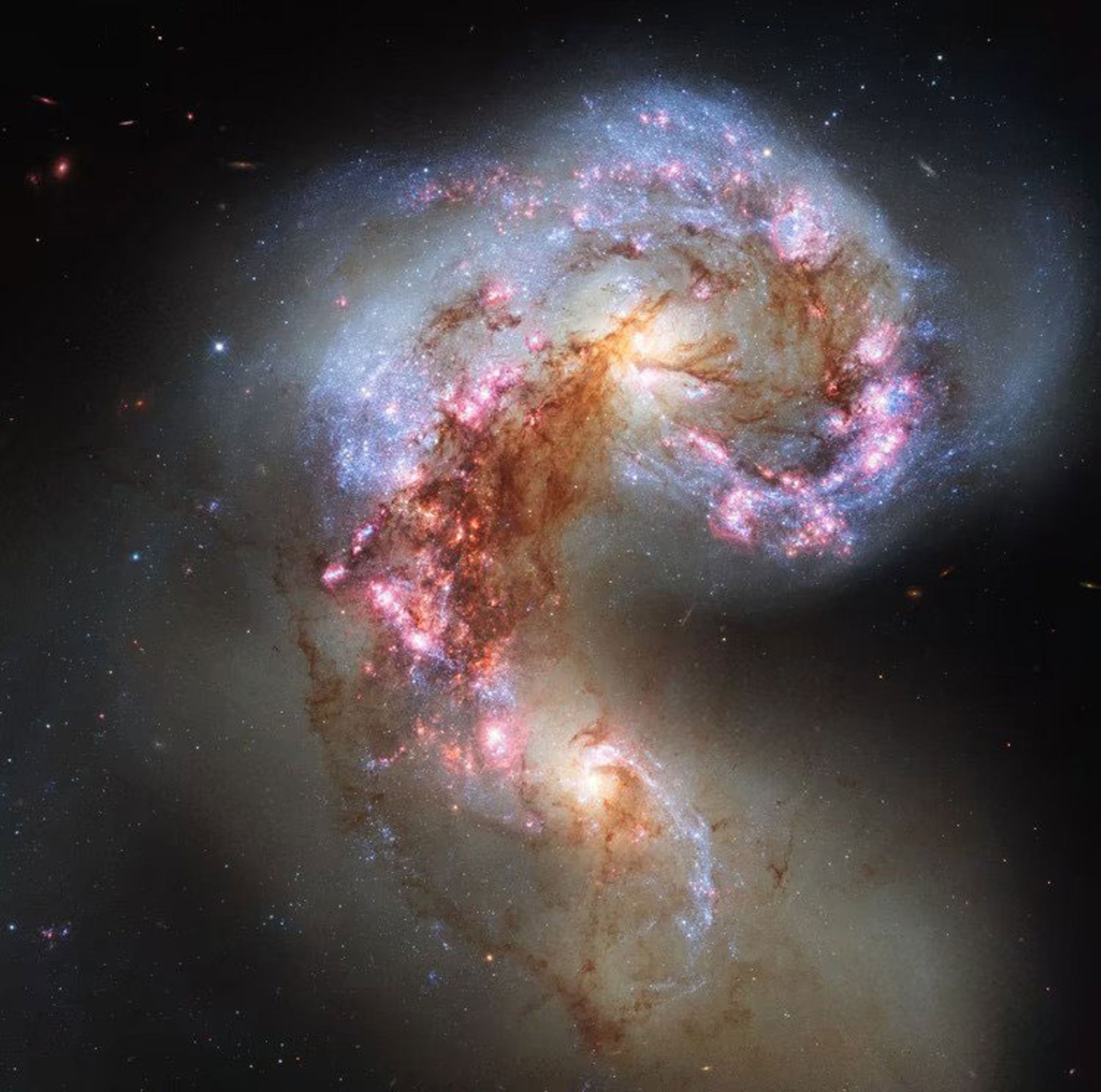
For example, consider the image below of the Hubble Space Telescope. This image shows the antennae galaxies, whose collision began approximately 600 million years ago, and as their spiral structures disappeared, new star clusters were formed, which can be seen as blue spots in the photo.

As the material of the merging galaxies migrates, the galaxies’ massive black holes also move and merge into the center of the new galaxy. In their path, these invisible heavy objects pull visible material such as meteors and stars towards them and possibly swallow some of them. Chiara Mingarelli, an astrophysicist at the University of Connecticut and the Flatiron Center for Computational Astrophysics who studies the fate of supermassive black holes in mergers, says:
When the merger of two galaxies begins, the supermassive black holes at their center are transferred to the center of the new galaxy and eventually merge with each other. In the example of three galaxies colliding, the most likely scenario is that two black holes will meet and form a binary system, and when the third black hole arrives, the less massive black hole may be ejected from the galaxy and eventually become a massive black hole wandering in the universe. .
All the above processes, such as the birth of new stars and the wandering of black holes, occur over millions or even billions of years. As a result, the hypothetical inhabitants of NGC galaxies do not see any changes during their lifetime but only know that they live inside a merger. Hypothetical astronomers of this universe could make classifications through archived observations of previous generations, collecting data for future scientists. Just as astronomers on Earth have calculated the Milky Way’s small mergers and the absorption of other small galaxies, hypothetical astronomers in the NGC could gain data about their galaxy’s past.
The Milky Way is on a collision course with another spiral galaxy called Andromeda. Today, Andromeda is seen as a dot in the night sky, but in five billion years, it will collide with our galaxy. The spiral arms of the Milky Way disappear, as does its supermassive black hole. Andromeda’s central black hole with a mass of 100 million solar masses will swallow our black hole with a mass of 4 million solar masses.
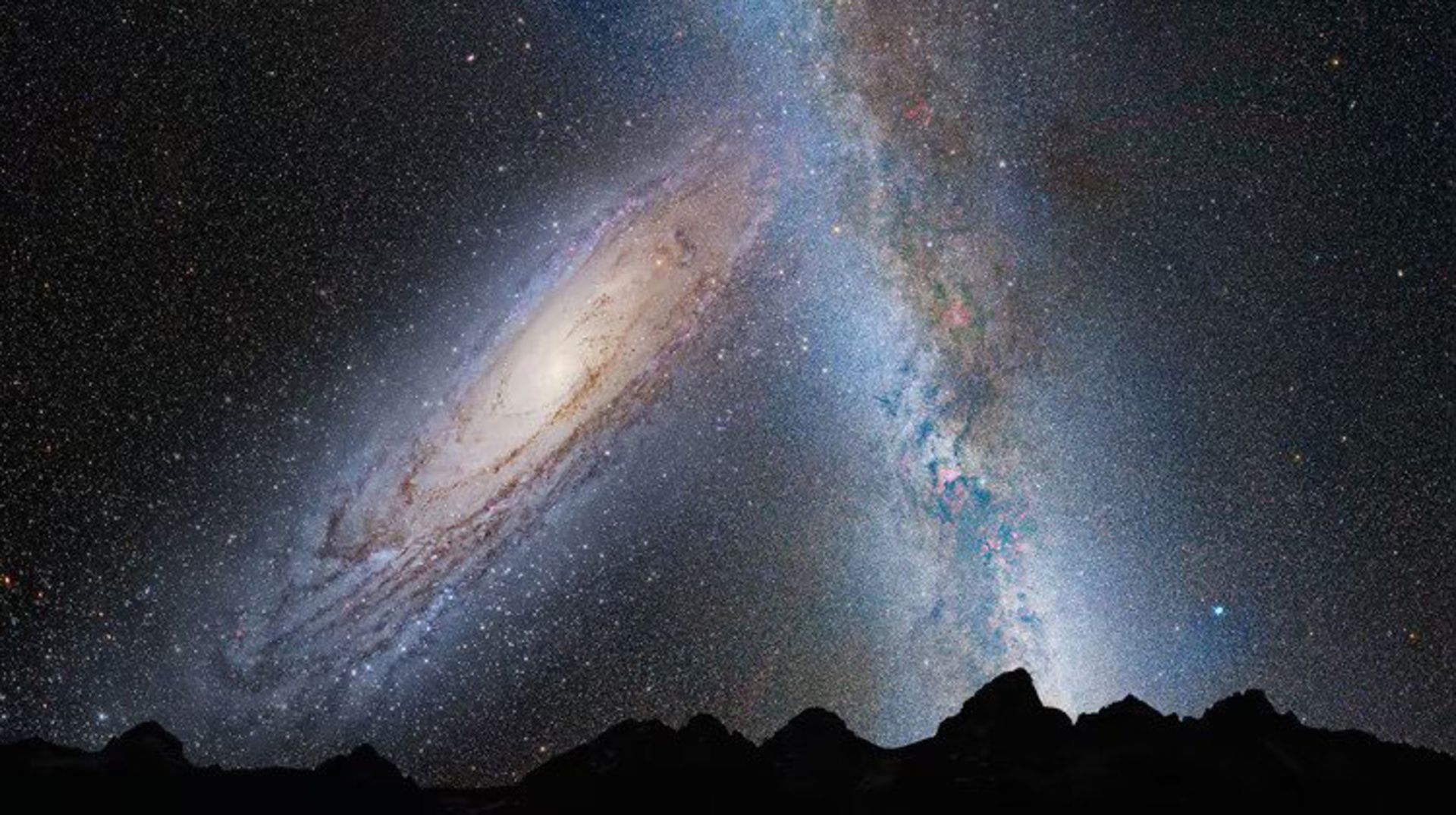

Artistic rendering of the collision between the Milky Way and Andromeda
Although galactic mergers do not lead to noticeable changes in a human lifetime, they are a great opportunity for the astronomers who live inside them. Being alone in an isolated galaxy might be a disadvantage. For example, Earth’s position in the Milky Way prevents astronomers from getting the best vantage points to study the Milky Way. There is also a lot of gas and dust on the way. McTyre says:
We should investigate other spiral galaxies to learn about the behavior and evolution of the galaxy we live in; But if there is another spiral galaxy near us and its angle is such that a large part of it can be seen, it can be studied much easier than our own galaxy.
On the other hand, being an astronomer in the middle of a galactic merger is a bit boring; Because in such conditions, the night sky is very crowded and it is not possible to examine distant objects. According to Rodríguez Gomez: “In such an environment, it is difficult to find a path without light pollution.”


The Milky Way; Facts & features
The Milky Way is a barred spiral galaxy approximately 13.6 billion years old with large rotating arms stretching across the cosmos. The diameter of the disk of our home galaxy is approximately 100,000 light-years and its thickness is 1,000 light-years.
Just like the Earth revolves around the Sun, the Solar System revolves around the center of the Milky Way. Despite moving through space at a speed of approximately 828,000 kilometers per hour, our solar system completes a complete revolution around the center of the galaxy after 250 million years. The last time our planet was in this position, dinosaurs appeared and mammals had not yet evolved.
If the center of the Milky Way is a city, we live on its outskirts. Based on this analogy, our solar system is approximately 25,000 to 30,000 lightyears away from the center of the city. Life in the suburbs is pleasant; We live in one of the smaller neighbors of the Orion-Cygnus arm, which is between the larger Perseus and Carina-Sagittarius arms. If we move towards the center of the city, we can find the arms of the Scutum-Centaurus and the arm of Norma.
Table of Contents
-
What is the reason for naming the Milky Way?
-
Characteristics of the Milky Way
-
The position of the sun in the Milky Way
-
Milky Way black hole
-
Type of Milky Way Galaxy
-
The Future of the Milky Way
-
Evolution of the Milky Way
-
Photography of the Milky Way
-
Milky way research
-
Interesting facts about the Milky Way
-
Conclusion
On a clear night without light pollution, you can see the bright lights of the Milky Way city in the night sky. This milky white spectrum of stars, gas, and dust is a window into the universe around us.
At the heart of the Milky Way is a supermassive black hole called Arc E*. With a mass of over 4 million suns, this black hole sweeps up everything in its vicinity and feeds greedily on the vast source of stellar material around it. In 2022, an image of this black hole was published for the first time.
 The motion of stars in the Milky Way galaxy in the next 400,000 years is based on data from the European Gaia probe.
The motion of stars in the Milky Way galaxy in the next 400,000 years is based on data from the European Gaia probe.
What is the reason for naming the Milky Way?
According to the American Museum of Natural History (AMNH), the name of the Milky Way is derived from its milky white appearance as it stretches across the night sky. In Greek mythology, this milky band appeared because the goddess Hera spread milk across the night sky.
Around the world, the Milky Way is known by different names. For example, in China it is called “Silver River” and in the Kalahari Desert of South Africa it is called “Night Spine”.
Characteristics of the Milky Way
The Milky Way has always been difficult to study. Astronomers sometimes compare trying to study the Milky Way to trying to describe the dimensions and structure of a forest while standing among the trees in the forest. From our position on earth, we definitely cannot have complete nobility of the Milky Way; But two space telescopes launched since the 1990s marked the golden age of Milky Way research with their data. Major steps were taken in particular with the launch of the Gaia spacecraft from the European Space Agency in 2013.
Telescopes allowed astronomers to discern the early form and structure of some of the nearest galaxies, But reconstructing the shape and structure of our home galaxy has been a difficult and slow task. This process involves making catalogs of stars, tracking their position in the night sky, and estimating their distance from Earth.
 The bright band of the Milky Way has fascinated humans for centuries.
The bright band of the Milky Way has fascinated humans for centuries.
Dutch astronomer Jan Evert, who is sometimes referred to as the Master of the Galactic System, was the first person to notice that the Milky Way was not stationary, but rotating, and estimated the speed of various stars around the center of the Milky Way. The name of the Oort cloud, a region containing trillions of comets far from the Sun, is derived from this astronomer.
Gradually, a complex vision of a seemingly ordinary spiral galaxy emerged. At the center of the Milky Way, there is a supermassive black hole, the Arc E*, with a mass of more than four million suns. This black hole was discovered in 1974 and can be observed with radio telescopes near the constellation Sagittarius.
Everything in the Milky Way revolves in a passage that ends in nothing. Around this point of nothing (black hole), there is a dense region of gas, dust, and stars known as the galactic bulge. About the Milky Way, this bump is shaped like a peanut and its diameter reaches 10,000 light years. This bulge hosts 10 billion stars out of 200 billion stars in the entire galaxy. Most of the stars in this sector are old red giants that were formed in the early stages of the galaxy’s evolution.
On the other side of the bulge, there is a galactic disc whose diameter reaches 100,000 light-years and its thickness reaches 1,000 light-years and hosts most of the stars of the galaxy, including the Sun. The stars in the disk are scattered among clouds of gas and stellar dust. When you look at the sky at night, you can see the view of the edge of this disk towards the center of the galaxy, which is very impressive.
 The structure of the Milky Way galaxy from the top angle of the galactic disk.
The structure of the Milky Way galaxy from the top angle of the galactic disk.
The stars in the disc rotate around the galactic center, forming swirling streams that appear to extend like arms from the galactic bulge. The research on the formation mechanisms of rotating arms still has a long way to go, but the latest studies show that these arms were formed in a short period of 100 million years (of the 13 billion years of the galaxy).
Inside the arms, stars, gas, and dust are compacted in the regions of the galactic disk, and this increase in density leads to the formation of more stars. As a result, the stars inside the galactic disk are younger than the stars in the bulge.
Spiral arms resemble highways of gas and stars that move slowly through the arms. As material passes through the spiral’s dense arms, it compresses and forms more stars. The Milky Way currently has four spiral arms. The two main arms are Bersavush and Kaman-Shahtakhteh, and the local arms and the bow are two smaller arms. Scientists are investigating the exact position and shape of these arms with data from the Gaia spacecraft.
The Milky Way disc is not flat, but curved. This disc moves like a sliding roller while rotating. This slip, especially the massive wobble around the galactic center, is slightly slower than the stars in the disc, taking 600 to 700 million years to complete a full rotation. According to astronomers, this fluctuation could be the result of the collision of the Milky Way with another galaxy in the past.
Globular clusters are located around the galactic disk and bulge, which form a collection of ancient stars, as well as 50 dwarf galaxies that orbit or have collided with the Milky Way. All of these are surrounded by a spherical halo of gas and dust that is twice the size of the disk. According to astronomers, the entire Milky Way galaxy is located in a larger halo of dark matter. Since dark matter does not emit any light, its existence can only be detected by its gravitational effects on the motion of the galaxy’s stars. According to calculations, dark matter makes up 90% of the mass of the Milky Way.
The mass of the Milky Way galaxy with dark matter is equal to 1.5 trillion solar masses. The visible matter inside the galaxy is distributed among 200 billion stars, their planets, and clouds of gas and dust in interstellar space. Astronomers are still not sure how many planets there are in the Milky Way, but considering the discovery of several thousand exoplanets in recent years, we can estimate that there are more than 100 billion planets in the Milky Way. The number of star systems is still a mystery.
The position of the sun in the Milky Way
The Sun is 26,000 light-years away from the Arc E* black hole at the center of the Milky Way. With a speed of 828 thousand kilometers per hour, our star completes its orbit around the galaxy after approximately 230 million years.
The Sun is located near the edge of the local arm of the Milky Way, which is one of the two small arms of the galaxy. In 2019, using data from the Gaia mission, astronomers discovered that the Sun is moving on a wave of interstellar gas 9,000 light-years long, 400 light-years wide, and oscillating 500 light-years high above and below the galactic disk. The planets of the solar system do not rotate in the plane of the galaxy but have an inclination of 63 degrees. It’s like we’re moving sideways in the galaxy.
 The Sun is one of the approximately 200 billion stars that make up the Milky Way galaxy.
The Sun is one of the approximately 200 billion stars that make up the Milky Way galaxy.
Milky Way black hole
The black hole at the center of the Milky Way is called Arc E*. This black hole is often silent and this characteristic makes it difficult to observe. According to the 2008 findings of Reinhard Genzel and Andrea Gass, Arc E* has a mass of approximately 4.3 million Suns. The approximate diameter of this black hole reaches 23.5 million kilometers.
The huge gas disk around the E* arc has extended to a distance of 5-30 light years from the supermassive black hole. This disk is very massive and thin, and its gaseous part provides the necessary materials for the activity of the E-bow. This region also emits X-rays due to the gas feeding of the black hole, as its temperature rises up to 10 million degrees Celsius due to friction within the disk.
Scientists are looking for more information about the supermassive black hole of the Milky Way to understand how it formed and the conditions of its growth. There are two scenarios for the formation of this black hole: in the first scenario, smaller black holes grew and grew bigger by feeding on the gas and dust around them. In the second scenario, several smaller black holes have merged together to form a giant black hole.
 Arc E*, as seen by NASA’s Chandra X-ray Space Observatory
Arc E*, as seen by NASA’s Chandra X-ray Space Observatory
In general, scientists are improving models for stellar black holes and intermediate black holes. These objects are formed when giant stars with several times the mass of the Sun collapse after their nuclear fusion stops. Since these stars cannot stop their gravitational collapse, they become a gravitationally powerful mass that can bend time and space around them, so that even light cannot escape.
We gradually learn about the E* arc through images like the first image of a black hole. This image shows the faint halo of hot material surrounding the black hole and its shadow. This image was captured thanks to a huge collection of observatories around the world that formed the Earth-sized telescope called Event Horizon (EHT).
 Image of the supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way known as Arc E*. This image was released on May 1, 2022 by the Event Horizon Telescope.
Image of the supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way known as Arc E*. This image was released on May 1, 2022 by the Event Horizon Telescope.
Type of Milky Way Galaxy
Scientists are continuously collecting data from the Milky Way. However, in the early 20th century, astronomers believed that all the stars in the sky belonged to our galaxy. In the “Great Debate” of 1920, astronomers such as Herbert Curtis and Harlow Shipley discussed the scale of the universe and the prospect of “island worlds” (galaxies).
On one side of the debate, Shipley believed that the Milky Way is much larger than previously estimated and that we are not at the center of it. He also claimed that “spiral nebulae” like Andromeda were part of the Milky Way. On the other side of the argument, Curtis disagreed with Shipley’s claim about the much larger size of the Milky Way, but believed that large island worlds (galaxies) like Andromeda lay outside the Milky Way.
Astronomers initially believed that all the stars in the sky were in the Milky Way
The debate ended when Edwin Hubble’s measurements of Cephasian variable stars proved that Andromeda was far outside the Milky Way. According to today’s estimates, the Andromeda Galaxy, which is our nearest galactic neighbor, is 2.5 million light-years from the Milky Way.
In the following years, astronomers tried to determine the type of our galaxy. According to the best estimates, the Milky Way is a barred spiral galaxy with a bar-like structure running through the center. Astronomers can determine the shape of the Milky Way by looking at the population of its stars as well as their movement across the sky.
 Andromeda galaxy on a collision course with the Milky Way.
Andromeda galaxy on a collision course with the Milky Way.
The Future of the Milky Way
We know that the Milky Way is located in the local group of galaxies, which includes more than 30 galaxies, including Andromeda, the Triangular Galaxy, and the Leo I galaxy. It is important to understand the nature of our neighbors because they may be closer than we think. The Milky Way moves towards Andromeda at a speed of more than 400 thousand kilometers per hour. No need to worry though, as our galaxy still has another four billion years to hit Andromeda.
For decades, NASA and other space agencies have been trying to observe distant galaxies in order to see what will happen when Andromeda and the Milky Way collide. In short, there is nothing to worry about, but the interesting thing is that these galaxies evolve after the merger.
For example, in 2022, scientists observed a three-way galactic collision with the Hubble Space Telescope and came to some interesting views about it. The largest galaxy of this group was in a coherent orbit with two other galaxies and due to very high gravity, it absorbed part of their material. This process led to the creation of streams of gas, dust, and other materials that flowed through the larger galaxy and could even be seen from Earth.
 Investigating galactic collisions will help us explore the future of the Milky Way and Andromeda.
Investigating galactic collisions will help us explore the future of the Milky Way and Andromeda.
Although the Milky Way’s arms will certainly be lost in the process, the stars will be safe because the space between them is so vast. In other words, don’t look for stellar collisions in galactic mergers, because they won’t happen in practice. However, due to the influx of large amounts of material into our galaxy, the birth of stars and the luminosity of our galaxy will increase, and this population increase will continue for years after the collision.
So our solar system might survive because of the low risk of a stellar collision, but we would find ourselves on a different path around the galactic center. One effect of the collision will be to change the constellations we see from Earth, as the stars’ orbits shift and new stars are added to the mix.
Evolution of the Milky Way
The evolution of the Milky Way began when clouds of gas and dust began to collapse due to gravity. The first stars were born from these clouds and today we see them in clusters all over the world. The oval halo was also formed at a short distance following the flat galactic disk. Our galaxy was small in the beginning and grew with the inexorable force of gravity.
90% of the Milky Way is made up of dark matter
However, there are still many mysteries about the evolution of the Milky Way. A method called galactic archeology is slowly unraveling some of the mysteries of life in the Milky Way thanks to the Gaia mission. Gaia’s mission is to measure the positions and distances of more than a billion stars, as well as their light spectra, which allows scientists to understand their composition and age.
Using star position data, astronomers can determine the speed and direction of star movement in space. Because everything in space follows paths, astronomers can reconstruct the paths of stars from billions of years ago. Combining these reconstructed trajectories into a stellar movie can reveal the evolution of galaxies over several epochs.
 Contrary to expectations, the dwarf galaxies around the Milky Way are new
Contrary to expectations, the dwarf galaxies around the Milky Way are new
Evidence suggests that the Milky Way has collided with smaller galaxies during its evolution. In 2018, a group of Dutch astronomers discovered a group of 30,000 stars that were moving in sync and in the opposite direction to the stars in the dataset. This motion pattern was consistent with what scientists had seen in computer simulations of galactic collisions. These stars were different in terms of color and brightness, and this showed that they came from another galaxy.
The remnants of another, younger collision were spotted a year later. The Milky Way has been swallowing up smaller galaxies until today. A galaxy called the Sagittarius (not to be confused with a black hole) orbits close to the Milky Way and has collided with the Milky Way’s disk several times over the past seven billion years. Using data from Gaia, scientists found that these collisions led to periods of intense star formation in the Milky Way, affecting its spiral shape. The research also suggests that our Sun was born during one of these collisions around 4.6 billion years ago.
Photography of the Milky Way
To photograph the Milky Way we need a dark night sky. As a result, we have to go to places free of light pollution, and photography equipment is needed to record the little light in the sky. Fortunately, the Milky Way is visible in both the northern and southern hemispheres and can be photographed using amateur photography equipment. For this, you need equipment such as a tripod, different types of focus, and different lenses.
 To photograph the Milky Way we need a dark night sky.
To photograph the Milky Way we need a dark night sky.
Milky way research
The Gaia spacecraft has made three updates to the stellar mass catalog since the beginning of its mission. Astronomers around the world continue to analyze the data in search of new patterns. Data from Gaia currently account for more research papers than the famous Hubble telescope. Gaia will continue its mission to survey stars until at least 2025, and its catalog could occupy astronomers for several decades.
Before Gaia, the largest data set on the positions and distances of stars in the Milky Way came from the Hipparchus mission, named after the ancient Greek astronomer. This astronomer mapped the night sky 150 years before Christ. The Hipparchus spacecraft observed almost 100,000 of the brightest stars near the Sun, while Gaia’s tally is a billion stars.
Although Gaia has observed less than 1 percent of the stars in the galaxy, astronomers can expand on their findings and simulate the behavior of the entire Milky Way galaxy.
Interesting facts about the Milky Way
- Nearly 90% of the Milky Way is made up of dark matter. Dark matter is invisible, yet its presence can be felt through its gravitational effects on galaxies.
- In the past, astronomers believed that all the stars in the universe were located in the Milky Way. Following the great debate, Edwin Hubble’s observations proved that the Milky Way is just one of billions of galaxies in the universe.
- The oldest star in the Milky Way is called HD 140283. This star, also known as Methuselah, is at least 13.6 billion years old.
- The Milky Way moves in space at a speed of approximately 600 km/s. Finally, our galaxy will collide with the Andromeda galaxy in about 4 billion years.
- If the Milky Way is reduced to less than 100 meters in diameter, the diameter of the solar system will be less than one millimeter.
- Nearly 17 billion exoplanets in the Milky Way are in the life belt of their planetary systems. Our galaxy must have between 100 and 200 billion planets, But the actual number is probably much higher than this estimate.
- Around the galactic disc are spherical halos of old stars and globular clusters. Nearly 90% of other stars are located within 100,000 light years from the center of the galaxy.
- The Milky Way and Andromeda are from the local group of galaxies. These two galaxies are the largest members of this group. 30 other galaxies are in this group.
- The supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way is called E*. The mass of this black hole reaches 4 million solar masses.
Conclusion
The Milky Way galaxy is the home of the solar system and the Earth. The Milky Way is named after the bright band that appears across the night sky. Our galaxy is home to more than 200 billion stars and is more than 100,000 light-years across.
Arc E* is the supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way with 4 million solar masses. The Milky Way has absorbed smaller galaxies in the past and has reached its current spiral bar shape. Our galaxy will merge with the Andromeda galaxy in the next 4 billion years.
Space
What are the obstacles on the way for humans to reach Mars?
Published
3 days agoon
15/05/2024

Sending the first humans to Mars has not only been a dream for countless generations, but also dates back to the early modern era. Also, one of the topics of the space age is the planning of such missions, and it is considered an integral part of the current vision for the future of space exploration, but this long-standing dream has not yet been realized.
What are the obstacles on the way for humans to reach Mars?
In the last 20 years, the public has heard claims that NASA will send the first humans to Mars by the early 2030s. First the moon, then to Mars! This is the plan NASA seemed to be sticking to for a while.
According to IA, in recent years, other players, including the China National Space Agency (CNSA) and Elon Musk’s commercial space giant, SpaceX, have joined the “race for Mars“. According to several sources, China, like NASA, plans to build infrastructure on the moon that will help the country send its first astronauts to Mars as early as 2033.
SpaceX’s plans are even more ambitious, with missions planned for the late 2020s and plans to build a self-sufficient city on Mars before the end of the decade. Unfortunately, many naysayers have said that reaching Mars by 2033 or sooner is unrealistic.
There have also been numerous delays along the way, showing how the entire Moon-to-Mars mission could fall behind its planned timeline.
2040 may be a more likely year for a manned mission to the surface of Mars, according to statements issued last summer by Deputy Administrator Jim Reuter. While delays are common in spaceflight, a seven-year delay seems significant and raises questions.
For example, why does such a mission take so long? And what would it take to send the first humans to Mars?
Answering these questions requires recalling memories.
The journey begins
Efforts to carry out missions to Mars began in 2004 with the announcement of a project called Vision for Space Exploration (VSE) by NASA. This vision came in response to the Space Shuttle Columbia disaster, the state of human spaceflight at NASA, and a desire to rekindle public interest in space exploration.

The project’s specific goals included completing the International Space Station (ISS), retiring the Space Shuttle by 2010, and creating a new fleet of heavy launch vehicles that would enable manned missions to the Moon, Mars, and beyond.
The plan included a series of robotic missions to the Moon to prepare and support future human exploration activities that began in 2008.
The plan also supports the use of lunar exploration, science, and resources to develop the technologies and systems necessary to support sustainable human space exploration to Mars and other destinations.
Meanwhile, NASA will resume sending robotic missions to Mars to search for evidence of life and prepare for the eventual arrival of manned missions. This led to the formation of NASA’s Mars Exploration Rover (MER) program, which consisted of the Spirit and Opportunity rovers and the Curiosity and Perseverance rovers.
Following this, the NASA Authorization Act of 2005 officially launched the Constellation Program.
The program called for a new group of launch vehicles, including a crew launch vehicle (CLV) and a cargo launch vehicle (CaLV), which led to the design of the Ares I and Ares V rockets.
Other vehicles included the Crew Exploration Vehicle (CEV) and the Lunar Surface Access Module (LSAM).
NASA planned to use Eriz 1 and 5 back-to-back to send astronauts to the Moon and Mars. The crew was to be launched using a two-stage Ariz-1 rocket capable of delivering 56,000 pounds (25,400 kg) to low Earth orbit (LEO). The payload was sent separately on Ariz 5, which was capable of sending 88,000 kg into low Earth orbit. This program came to fruition in 2009 when NASA completed the Launch Stop System (LAS) and the first stage of the Ariz 1 rocket. The second one was successfully tested on October 28 of the same year.
Unfortunately, the Constellation program was canceled in 2010 due to the global financial crisis known as the “Great Recession” that began in 2007-2008. Almost a year later, the Obama administration signed off on the Mission to Mars.
Details and goals of the program were published in the NASA Authorization Act of 2010 and the US National Space Policy of the same year. NASA’s priorities in this matter are summarized as follows:
Our next step is deep space, where NASA will send a robotic mission to capture and guide an asteroid into lunar orbit. Astronauts aboard the Orion spacecraft will explore the asteroid in the 2020s and return to Earth with samples. This experience in human spaceflight beyond low-Earth orbit will help NASA test new systems and capabilities, such as solar electric propulsion.
Beginning in fiscal year 2018, NASA’s powerful Space Launch System rocket will enable these missions to test new capabilities. Human missions to Mars will rely on Orion, an evolved version of the Space Launch System rocket that will be the most powerful launcher ever to fly.
In many ways, “Journey to Mars” picked up where the Constellation program left off.
While the Ariz 1 rocket and lunar lander were discarded, the Ariz 5 launcher and crewed exploration spacecraft were retained and became the basis for the Space Launch System (SLS) and the Orion spacecraft.
Timelines were also updated, with missions to Mars planned for the early 2030s.


The proposed journey will include three phases and 32 launches of the Space Launch System between 2018 and 2030. These missions send all the necessary components to space between the Earth and the Moon and then to space near Mars before landing the crew on the surface of Mars.
Phase one, called the Earth-based phase, will focus on further long-term studies on the International Space Station until 2024 and testing the Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. This included Exploration Mission 1 (EM-1) in 2018, the first flight of the Space Launch System, and the second unmanned test flight of Orion.
As with the Constellation program, NASA also planned to launch an Asteroid Redirection Mission (ARM) in 2020, in which a robotic spacecraft would rendezvous with a near-Earth asteroid and pull it into lunar orbit.
Exploration Mission 2 (EM-2) will include a manned flyby of the Moon and asteroid ARM between 2021 and 2023. At this point, NASA moves to Phase Two, shifting the focus from Earth to the space between the Earth and the Moon. The multiple launches of the space launch system will bring the important components of the mission to the lunar surface and orbit at this stage.
Since 2012, these elements have included the lunar gateway known as the Deep Space Habitat, an orbiting space station consisting of a Power and Propulsion Element (PPE), a Habitat and Logistics Base (HALO), a refueling supply system, and infrastructure. and has a communication module (ESPRIT), an international habitation module (I-Hab), and a reusable lunar lander.
Other elements include the Artemis Base Camp, which consists of a lunar base surface habitat, a habitable mobile platform, a Lunar Ground Vehicle (LTV), and a Deep Space Vehicle (DST). The spacecraft will integrate with Orion to transport a crew of up to four to Mars and other deep space destinations.
In the early 2030s, phase three (ground-independent) will begin, which will include essential elements delivered to Mars by a deep space vehicle. This second space station will be equipped with a reusable Mars lander that will allow the crew to perform scientific operations on the surface and then return to orbit.
A road map is formed
In 2017, NASA’s long-term vision to return astronauts to the Moon and Mars began. According to the National Aeronautics and Space Administration’s 2017 Transfer Authorization Act, NASA’s priorities for the Moon to Mars program were determined.
These priorities included continued development of the Space Launch System, Orion, the Lunar Gateway, and other critical mission elements. The bill also directed NASA to scrap the asteroid reorientation mission in favor of something more cost-effective. Other priorities included expanding the US commitment to the ISS and restoring domestic launch capability through the Commercial Orbital Transportation Service (COTS) and the Commercial Crew Program (CCP).
According to their timeline, the construction of the Moongate space station will be completed by 2028. The first manned missions to Mars will be launched from the Moon Gate in 2033. The crew will spend up to a year conducting science operations, then make their return trip to Earth.


The spacecraft and crew will then spend 6 to 9 months en route, returning to the lunar gateway and landing on Earth with the Orion capsule. Subsequent missions are carried out once every 26 months. These missions will lead to the establishment of a long-term habitat on Mars, allowing for return visits. It could also deliver the first Mars sample to Earth, similar to how the Apollo astronauts returned moon rocks for analysis.
Read more: Can humans endure the psychological torment of living on Mars?
However, by 2019, NASA was forced to reevaluate its priorities and long-term goals as the Trump administration inaugurated a new program.
As you can see, NASA’s long-term vision for the first manned missions to Mars has evolved since its inception 20 years ago, and even in its early stages, there were doubts that the timelines and commitments were realistic. With all these challenges, the most important pressure factors had not yet arrived. You can read these factors in the second part of this report.


What happens when two galaxies collide?


The Milky Way; Facts & features


What are the obstacles on the way for humans to reach Mars?


Unveiling of OpenAI new artificial intelligence capabilities


Samsung S95B OLED TV review


Xiaomi Pad 6S Pro review


AI PC; revolutionary technology of the future?


Motorola Edge 50 Pro review, technical specifications


Can humans endure the psychological torment of living on Mars?


Black holes may be the source of mysterious dark energy
Popular
-



 Technology10 months ago
Technology10 months agoWho has checked our Whatsapp profile viewed my Whatsapp August 2023
-



 Technology11 months ago
Technology11 months agoHow to use ChatGPT on Android and iOS
-



 Technology10 months ago
Technology10 months agoSecond WhatsApp , how to install and download dual WhatsApp August 2023
-



 Technology11 months ago
Technology11 months agoThe best Android tablets 2023, buying guide
-



 AI1 year ago
AI1 year agoUber replaces human drivers with robots
-


 Humans1 year ago
Humans1 year agoCell Rover analyzes the inside of cells without destroying them
-



 Technology11 months ago
Technology11 months agoThe best photography cameras 2023, buying guide and price
-


 Technology11 months ago
Technology11 months agoHow to prevent automatic download of applications on Samsung phones










