Technology
The complete history of Android
Published
5 months agoon


Android has come a long way since it was the only product of a small startup until now it has taken over 80% of the mobile operating system market. In this article we’re going to read about the complete history of Android.
The complete history of Android


If you are also an old user of the Android ecosystem, you probably have the feeling that this popular operating system has been a constant and integral part of your experience in the world of smartphones since you can remember; Hence, it may be hard to believe that it’s only been a little over a decade and a half since the first Android-based phone was released.
Undoubtedly, the factor that caused Android’s great success was Google’s fateful decision to turn it into an open-source project. The open-source nature of Android, which puts it in direct opposition to its great and monopolistic competitor, Apple’s iOS, brought the increasing popularity of this operating system among non-Google mobile manufacturers; So that only a few years after the release of Android 1.0, smartphones based on this operating system could be found everywhere.
Android has become the most popular mobile operating system in the world, surpassing competitors such as Symbian, Blackberry, Palm, WebOS, and Windows Phone, and more than three billion devices worldwide are based on Android. In fact, Apple’s iOS is the only platform that is still a serious competitor to Android, and that doesn’t seem like it’s going to change anytime soon.
Now that 16 years have passed since the birth of Android and many smartphone users are enjoying the Material You design language and the new features of Android 14, let’s take a look at the rich history of the Android operating system and the changes it has undergone during this time.
Read More: The best new features of Android 14
Table of Contents
- The beginning of the Android way
- Android logo
- Release of Android 1.0
- Android 1.1
- Android 1.5 Cupcake
- Android 1.6 Donut
- Android 2.0 Eclair
- Android 2.1 Eclair
- Android 2.2 Ice Cream Yogurt
- Android 2.3 gingerbread
- Android 3.0 Honeycomb
- Android 4.0 Ice Cream Sandwich
- Android 4.1 to 4.3 Jelly Bean
- Android 4.4 KitKat
- Android 5.0 and 5.1 Lollipop
- Android 6.0 Marshmallow
- Android 7.0 Nougat
- Android 8.0 Oreo
- Android 9.0 Pie
- Android 10
- Android 11
- Android 12
- Android 13
- Android 14
- The future of Android
The beginning of the Android way
The story of Android begins in October 2003; That is, long before the epidemic of the term ” smartphone ” and several years before Apple introduced the first iPhone and with it the first version of iOS. The Android company was founded in Palo Alto, California, and its founders were four young men named Rich Miner, Nick Sears, Chris White, and Andy Rubin. At the time, Robin said the Android company was going to “develop smarter mobile devices that are more aware of the user’s location and interests.”


In his 2013 speech in Tokyo, Rubin revealed that the Android operating system was originally intended to be an improved version of the operating system for digital cameras; But even in those days, the digital camera market was falling. It only took a few months for the founders of the Android company to abandon their initial plans and take steps towards using this operating system in mobile phones.
In 2005, another big chapter in the history of Android took place; Google bought the Android company. Robin and the other founders remained at Google’s Android company to work on the development of the operating system. It was decided to use Linux for the development of Android OS, and this fateful decision became the basis for Android to be available to all mobile phone manufacturers as an open-source project for free. Google and the Android development team came to the conclusion that the company could make significant profits not by monopolizing the brand, but by providing services that were based on this operating system, including applications.
Robin remained at Google as the manager of the Android team until 2013; But a year later, following the publication of documents of Robin’s sexual misconduct and inappropriate behavior with employees, he was forced to leave Google to start his own growth center startup. He finally left this startup to return to the world of smartphones in 2017 with the failed Essential Phone project. Robin is no longer in the media spotlight these days, but his legacy lives on under Google’s watch.
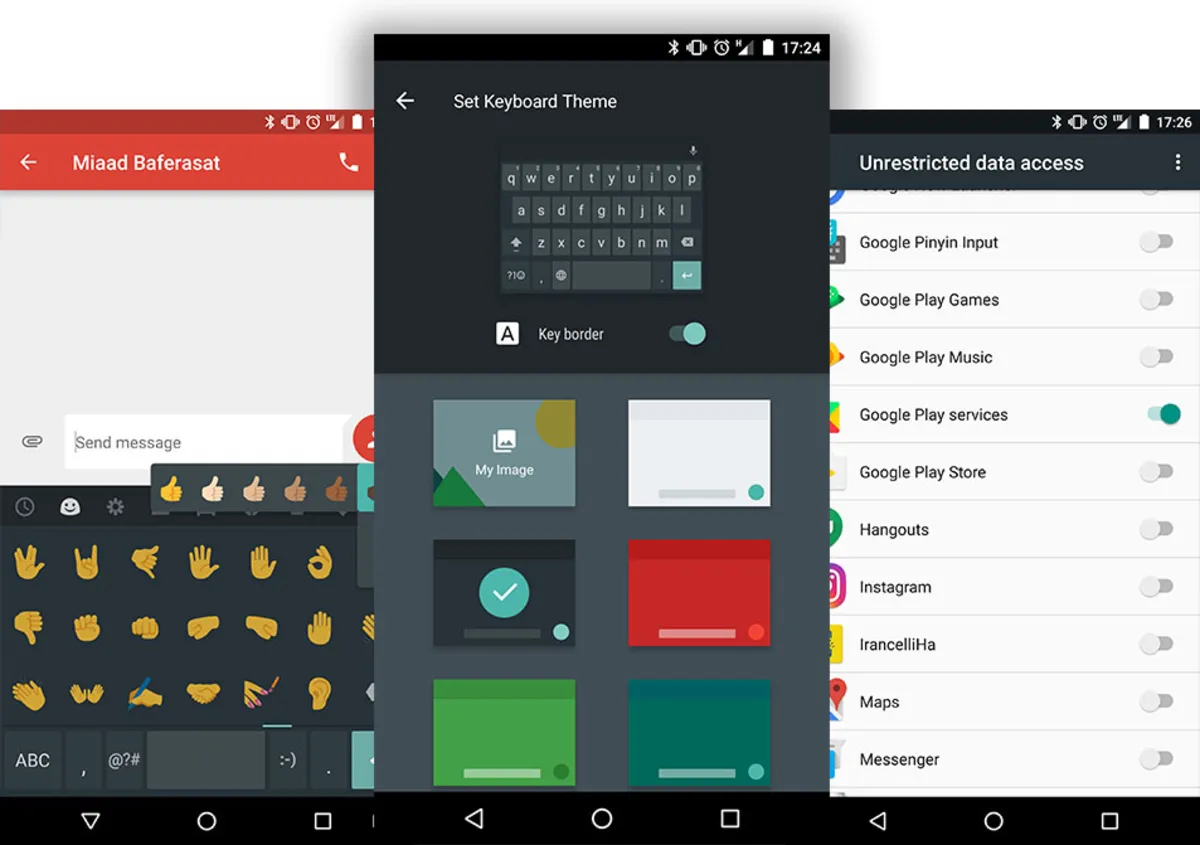
Android logo
The very familiar Android logo, which looks like a combination of a robot and a green bug, was designed by Irina Block when she was still working at Google. According to Block, Google’s design team only asked him to make the logo look like a robot (perhaps because of Robin’s fondness for his Star Wars robot toy). Block also said that part of the final Android logo design was inspired by the “male” and “female” head signs in public restrooms.
Block and Google both decided that the Android bot itself, like the operating system, would be an open-source project. Almost every other big company protects its logo with all its might against any modification of the design and use by others, but the Android robot has been used by thousands of people around the world thanks to the copyright license issued by Google. It has been manipulated.
The Android logo, also known as “Andy”, was redesigned in 2019 along with the Android brand, and although it has now lost a large part of its body, its presence is more visible in all products related to the Android brand.
Release of Android 1.0
It was in 2007 that Apple started a new era in mobile processing with the release of the first iPhone. At the time, Google was still secretly working on Android, but in November of that year, it revealed its plans to compete with Apple and other mobile platforms. In a big move, Google formed a consortium of different companies called the “Open Handset Alliance”, which included mobile phone manufacturers such as HTC and Motorola, chip manufacturers such as Qualcomm and Texas Instruments, and telecommunications companies such as T-Mobile.
After announcing the formation of the consortium, Google’s CEO at the time, Eric Schmidt, described it as “more ambitious” than any Google phone that the media had been speculating about for weeks, saying, “Our vision is that with this powerful platform, we will see the production of Let’s be thousands of different mobile phones.
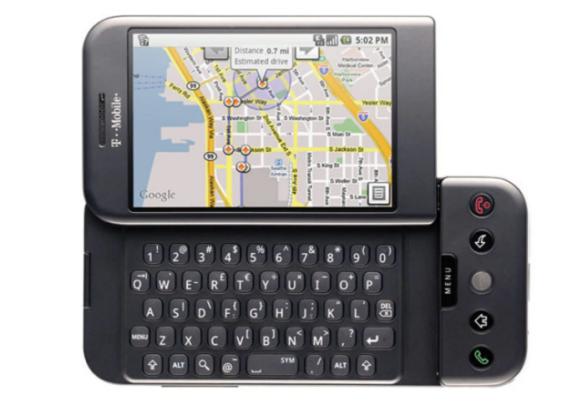
The public beta version of Android 1.0 was released to developers on November 5, 2007. In September 2008, the first Android smartphone, the T-Mobile G1, also known as the HTC Dream in some parts of the world, was introduced. This Android phone with its 3.2-inch pop-up touch screen and physical QWERTY keyboard was not so innovative in design and was even criticized by the technology media. However, Android 1.0 inside this phone also had a trace of Google’s future plans for the development of this operating system.


Android 1.0 brought together several other products and services of the company, such as Google Maps, YouTube, and the HTML browser (which was the predecessor of Chrome), which naturally used Google’s search services, and the first version of Android Market to offer “dozens of Android applications.” introduced “unique”. Other features of Android 1.0 include the notification window that is still present in newer versions of Android, widgets, and integration with the Gmail email service.

All these features seem trivial now, but with the help of these, Android’s leadership in the mobile market was sparked.
Android 1.1

The first Android update took place three months after the release of the G1 in February 2009. Version 1.1 cannot be considered an innovative product in any way, because it only included software patches to optimize the system and fix its bugs. But Android 1.1 is important because it demonstrates Google’s ability to deliver updates effortlessly. This same feature, which seems trivial these days, was considered one of the strengths of Android at the time of the release of version 1.1 because other mobile operating systems at that time did not have the ability to update in this way.
Android 1.5 Cupcake

With the release of Android 1.5 in April 2009, Google started the 10-year tradition of naming Android versions based on the names of sweets and desserts in the order of the Latin alphabet, and to begin with, the lottery was named Cupcake. Android owes this naming system to Google’s project manager, Ryan Gibson; However, until today, no one has discovered the secret of his interest in this naming model.
Android 1.5 is truly a turning point in the history of Android. In this version, in addition to introducing the special naming method of this operating system, important features were added, which of course seem trivial these days; including the ability to upload videos to YouTube, automatic screen rotation, the addition of a virtual keyboard, and support for various keyboards, which at that time, its fierce competitor, iOS, was useless.
It is interesting to know that the first Samsung Galaxy and HTC Hero phones were launched with Android 1.5
Android 1.6 Donut
A few months after Android 1.5, Google released version 1.6 under the name Donut in September 2009. Although Donut wasn’t as influential in Android history as Cupcake, it did come with a big change that happened behind the scenes. The new operating system introduced support for CDMA-based networks for the first time, making it possible for Android phones to be sold by all carriers worldwide.
Other features of Android 1.6 include the introduction of a quick search box, a quick toggle between camera options, video recording, and gallery, and the “Power Control” widget to manage Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, GPS, etc. In addition, for the first time, Donut made it possible to display the power of Android on a variety of screens with different resolutions and aspect ratios. Android Market was also launched with a new design in white and green colors, which displayed a list of the top free and paid apps. However, this version of Android had many flaws in the camera interface, which remained until Android 2.3.
Android 2.0 Eclair
In early November 2009, almost a year after the release of the G1 phone and the first version of Android, Android 2.0 was released. If we want to describe this update in one word, “big” is a good adjective, because this version of the Android operating system was a big achievement with big promises coming to big phones from big companies!
At first, Eclair was released exclusively on Verizon phones and marked one of the best collaboration experiences in this field. The factor that made Eclair successful was that in this version of Android, we saw the most changes both in terms of appearance and internal architecture. Features added to version 2.0 include support for multiple accounts, free Google Maps navigation, which is still popular and useful (before that, drivers paid a hefty fee for such an application), quick access to information Contact, improved virtual keyboard with multi-touch data recognition and browser redesign that brought it closer to today’s Google Chrome browser.
Android 2.1 Eclair
Although Google kept the Eclair name for the next Android update, it added extensive changes. Android 2.1, which was released in January 2010, was so good at the time that many new phones were equipped with it. After all, many software bugs were also fixed in this version.
With Android 2.1, Google unveiled live wallpapers for the first time, which, by displaying animated and interactive images instead of a static image in the background, were very attractive at the same time and attracted the attention of many users. In this version of Android, for the first time, we saw the ability to convert speech to text (TTS), with the help of which users could talk to their phone so that texts are entered through the user’s voice instead of typing with the keyboard. Also, from Android 2.1 onwards, the comma button in the virtual keyboard was replaced with a dedicated microphone button to make it easier for the user to access this feature. It is interesting to know that from iOS 5 onwards, this feature was also added to the keyboard of the Apple operating system.
In addition, Android 2.0 uses a new screen lock, one side of which has the option of silent mode (silent), and the other side of the screen lock, opens the main screen by touching it. Although the changes of this update were not very dramatic, it was considered a strategic change for Google and probably had a direct connection with changing the basic appearance of Android and offering customized versions for the company’s business partners in their products.
At that time, Google’s direct cooperation with HTC led to the release of the Nexus One equipped with Qualcomm’s first 1 GHz processors, which offered a pure experience of Android 2.1 and became one of the well-made Android phones. After this cooperation, Google went to Motorola to make the Motorola Droid phone with the Eclair version of Android available on the market; However, Motorola Droid’s success in this field was not as good as Nexus One.
Android 2.2 Ice Cream Yogurt
Android 2.2, known as Froyo, was released in mid-2010. It was after this that the benefits of the Nexus project showed themselves, and the Nexus One, which was equipped with Android 2.1 when it was released, was the first smartphone to be updated to this operating system.
Smartphones running Android 2.2 featured a new home screen design; The three traditional Android panels were replaced by five panels, and at the bottom of the screen there were shortcuts to the application menu and the browser.
The gallery section of Android 2.2 has also been completely redesigned and for the first time displayed the 3D features of this platform. For example, by tilting the screen or moving between different albums and photos, high-quality animations were displayed. Google also provided the traditional PIN lock screen in this version so that users who did not like the pattern lock method or were looking for a more secure method, could lock their phone by entering a code.
Android 2.3 gingerbread
About six months after the release of Froyo on the Nexus One, Google entered the next phase of the Nexus project to launch a new phone with Android 2.3 known as Gingerbread. This time, Google went to Samsung to mass-produce the Nexus S phone in the line of the successful Galaxy S phone. Although the Nexus S was technically not much better than the previous Nexus One phone, it was very different from the first member of the Nexus family in terms of appearance and gained many fans thanks to its round-edge screen and transparent and dark-colored body.
Android 2.3 was a minor update in many ways, But the multitude of these small changes caused a significant difference compared to the previous version, and in this version, we saw the most changes in appearance since the release of Android 2.1. For example, the word Malmo was removed from the analog clock widget; The home screen and user interface components have been given a green color theme, and the status bar has become more beautiful with a dark background and bright text. Gingerbread looked cleaner and more modern than previous versions, but it was actually Google’s clever trick to reduce battery consumption; Because all those bright components in the Amoled screen consumed a lot of energy.
New features added to Android 2.3 include more control over copy/paste, an advanced keyboard and improved multi-touch functionality, better tools for device management and higher battery efficiency, and video chat camera support.
Other features of gingerbread include Google’s special attention to developers and support for NFC technology, which provides the necessary infrastructure for the mobile payment system. Google also took advantage of the release of Gingerbread as an opportunity to strengthen its foothold in the mobile game market; In this version, developers were given low-level access to things like sound, device control, graphics, and data storage, which allowed them to write relatively fast-executing code; This work was the key to the developers’ success in entering the 3D game market.
Android 3.0 Honeycomb
Android 3.0 can be seen as a strange and unique phenomenon that was intended for tablets and of course mobile devices with large screens instead of smartphones. This time, Google went to Motorola to work together to launch the Xoom tablet equipped with a “honeycomb” in February 2011.
In this version of Android, the color green, which is now known as the symbol of Android, was replaced by blue; For example, the battery and antenna percentage indicator as well as the clock widget were displayed in blue color. The main screen and widget placement were also redesigned, and with the introduction of virtual buttons in the system bar, the need for physical buttons on tablets equipped with Android 3.0 for search, menus, home, and back was eliminated. With the death of physical buttons, hardware developers had more room to expand screen dimensions.
Android 3.0 was also accompanied by the introduction of a new concept called “Action Bar” which was located at the top of each application screen and can be considered a kind of status bar for applications. For the third version of Android, Google released two small updates in the form of 3.1 and 3.2, which provided important features, especially for tablets.
Beehive can be seen as the response of Google and its partners to the release of Apple’s iPad in 2010, and although this version of the operating system was readily available, some Android tablets of the time still came with previous mobile versions. In the end, Honeybee was not well received and Google decided to implement most of its features in Android 4.0.
Copy the link
Android 4.0 Ice Cream Sandwich
Android 4.0 known as “Ice Cream Sandwich” was released in October 2011 with the Galaxy Nexus phone. This was the second collaboration between Google and Samsung in the supply of Android phones, and less than a year had passed since their collaboration in the production of the Nexus S phone equipped with Android Gingerbread.
Android 4.0 can undoubtedly be considered the biggest change of Android in the field of smartphones, although its design and many new features were released in the previous version for tablets. This version had virtual buttons and its color theme changed from green to blue; Support for widgets and multitasking was improved, as well as the ability to show thumbnails of the list of open applications. Google also used a new font called Roboto to improve the user experience, and full Persian language support was added to Android from this version onwards.
Another new feature of Ice Cream Sandwich was the ability to delete notifications in the notification window, where before there was only the option to delete all of them. The artificial intelligence of the virtual keyboard has also been greatly improved and has achieved great progress in the field of text error detection and word suggestions. In fact, we can say that it was from Android 4.0 that text input, clipboard support, and the quality of the virtual keyboard became so advanced and similar to other similar applications in the market.
The key features of Android 4.0 include the Android Beam application for easy data transfer between two phones, facial recognition lock, and bandwidth usage analysis. The calendar application also took an integrated approach for the first time, which was considered a good option for people who were looking to use multiple user accounts in one application.
Android 4.1 to 4.3 Jelly Bean
The era of the “Jelly Bean” version of Android began in June 2012 with the release of Android 4.1 and continued with the rapid release of versions 4.2 and 4.3 in October of the same year and July 2013.
In version 4.1, we saw smooth movement between menus and pages, which Google referred to as “Project Butter”. The personal assistant Google Now, which was undoubtedly one of the biggest and most important ambitions of Google, was added to the search department and turned Android into a complete platform capable of processing all kinds of data, scheduling things, location, time, etc. With jelly candy, for the first time, users could use the ability to convert speech to text offline. Notifications, widgets, and text prediction in the virtual keyboard have also undergone improvements.
Android 4.2 came with the Nexus 4 phone and Nexus 10 tablet and added wireless connection to the TV via Miracast to the operating system so that users can run their favorite software and games on the larger TV screen by purchasing these boxes for $99. do In this version, new typing gestures were added, which were a precursor to the Swype keyboard. In the photography section, a panorama mode called Photo Sphere was added. Also, this version provided support for the use of one tablet by several users so that each user could have their software and personal information on a shared tablet.
Android 4.3 was made available with the second-generation Nexus 7, which was produced in collaboration with Asus. In this version, there were no major changes, only the operating system performance was improved, and some new features were added to the user interface. However, Android 4.3 brought with it the ability to support the OpenGL ES 3.0 graphics standard to run games with 3D graphics. After a short time, Apple added support for this software engine to its devices by updating the iOS operating system so that its users do not lag behind in the field of mobile games.
Android 4.4 KitKat
Android 4.4 was the first version of this operating system that used a brand instead of the generic name of a dessert or dessert. For this purpose, Google contacted Nestlé and asked for permission to use the name KitKat to name its new Android, and Nestlé accepted. Google did not repeat this model of marketing cooperation until the release of the Oreo version.
Android 4.4, which was released in October 2013, did not have many new features and most of the changes were made at the user interface level. However, the availability of one feature was enough to make the Android market hotter, and that was the optimization of this operating system to run on smartphones with less than 512 MB of RAM. This feature allowed mobile manufacturers to use the latest version of Android on much cheaper devices. Google’s Nexus 5 was also the first smartphone to be released with Android 4.4.
The most important exclusive features of Android 4.4 KitKat are the integration of Google Now with the home screen, a completely new smart dialer that adjusts according to the user’s needs, full-screen applications thanks to the notification bar and transparent control bar, integrated Hangout application for all messaging, redesigned “Clock” applications and “Downloads”, a new keyboard with emoji support and support for HDR+ photography.
Android 5.0 and 5.1 Lollipop
Android 5.0, known as Lollipop, which was introduced in the fall of 2014 with the Motorola Nexus 6 phone and the HTC Nexus 9 tablet, was a revolutionary version of Google’s mobile operating system; Because it was the first version of Android that uses the new and exclusive design language of Google called Material Design. In Material Design, the design throughout the operating system has become simpler and more minimal. To access quick settings and notifications bar, two-finger gestures were no longer needed and users could access these items with just one finger movement from the top of the screen to the bottom.
The Adaptive Brightness feature replaced Auto-Brightness so that in addition to the device changing the brightness level automatically based on the ambient light, the user can also increase and decrease the brightness level as desired with the help of the slider. There were no more widgets on the lock screen, and Google only showed the time and date in the middle of the screen.
It was in this version of Android that the Interruptions feature was added with the same function as Do Not Disturb in the iPhone, and it allowed users to block all notifications to increase concentration and avoid distractions. The Power Saver feature was also added to this version, where the user could set this feature to be activated automatically when the battery charge reaches a certain level.
Version 5.1 of Android Lollipop was released in March 2015 for Nexus phones, which was accompanied by some features and minor changes and bug fixes of the previous version. For example, Priority mode was added to Interruptions. With the screen pinning feature, you could pin a specific application so that the person who is working with it on your phone cannot leave this page and go to other parts of the phone; Unless it has your PIN code. Support for two SIM cards is also possible in this version of Android.
Android 6.0 Marshmallow
A week after the introduction of new Nexus devices in the fall of 2015, Google introduced the final version of Android 6 with the name Marshmallow. This version of the operating system did not change much in appearance compared to Android 5 Lollipop, but it benefited from minor changes in order to be smarter; including vertical scrolling in the app drawer, the ability to increase and decrease the volume of different sections individually, the ability to change the icons of the notification bar section, and the addition of the Doze function to improve battery consumption.
In addition, in this version of Android, for the first time, we saw the addition of support for the fingerprint sensor and USB Type-C, which the new Nexus 6P and 5X were equipped with.
Android 7.0 Nougat
Android 7.0, known as Nougat, is the seventh version of the Android operating system, which was released in the fall of 2016. This version of the operating system was not much different in appearance from its previous version, But significant software changes were made to it. For example, after a long time, Google added Split-Screen support to its operating system so that users can have two applications open and visible on the screen at the same time. In this version, users could directly respond to messages in the notification section without the need to run the application. Among the other improvements made in the multitasking section is a quick switch between two recently used applications. This was also done simply by double-tapping the Overview square key.
In the version of Android 7.0, the ability to personalize and support various themes for the keyboard was added. Emojis were also now offered with multiple skin tones. Behind the scenes, Google also improved the performance of the operating system, the appearance of Android games, and the security of media file management, and added file-based encryption. Google also equipped Android Nougat with two partitions for the operating system, just like the Chrome operating system, so that a completely new operating system is sent to the user’s phone and installed on the inactive partition.
Google also used the release of Android Nougat as a bold excuse to market its luxury phones. Google’s Pixel and Pixel XL phones, along with the LG V20, were among the first flagship phones to come with Nougat.
Android 8.0 Oreo

In April 2017, we saw the release of Android 8 known as Oreo, which after the introduction of the KitKat version, was Google’s second attempt to use the brand name of another company to name its operating system. At first glance, Android 8 was not much different from the Nougat version, and only a few small and big changes were made in the previous version.
In Android Oreo, Google brought the picture-in-picture feature to other applications in addition to the YouTube application. The notification management was improved in this version so that the user could set different permissions for each application. It was in this version that Google allowed applications to display their notification icon on the icon. The number of emojis was also increased in this version and users had more control over the background activity of applications. The first phone released with Android Oreo was Google’s own Pixel 2.
Android 9.0 Pie
August 2018 was the time of the release of Android 8 known as Pie, which was first introduced as Android P during the Google I/O event. This version of Android was accompanied by new and great changes and features; Among other things, the addition of motion gestures with the aim of replacing the popular Android navigation bar that we have seen before on the iPhone 10. The new motion gestures of Android 9 allowed the user to return to the home screen, switch between running apps, and go back to the previous stage by making gestures from the bottom edge of the device.
Android 9 also uses machine learning to help the user use the full potential of their phone and manage battery consumption better than before. For example, the adaptive brightness feature, which was introduced with Android 5, provided the user with the ability to manually adjust the display brightness after getting to know the user’s favorite brightness level. “Actions” were also considered another intelligence of Android 9 Pie, which is based on the expected user pattern and is actually a shortcut for access to items that are used continuously.
Another smart feature of Android 9 was the new Slice API, which allowed developers to directly access their key features from the search menu.
Android 10
2019 was a year full of big changes for the Android ecosystem. For the first time, Google abandoned its 10-year tradition of naming different versions of Android based on sweets and desserts and modernized the traditional Android logo. The reason for abandoning this naming tradition was that the names of some of these sweets were unfamiliar to many countries with different cultures. The Android brand, which was previously only introduced with the green word Android, is now black, and next to it is the green head of a lovely robot, which, according to Ud Gandon, Android’s global brand manager at that time, makes this brand “more human.”, entertaining and friendly.
Android 10 (formerly known as Android Q) was officially released on September 3, 2019, for Google’s Pixel devices and included several new features, API, and significant improvements.
The most visible operating system change was the new and redesigned Android Gestures interface, where the three buttons at the bottom of the screen for going home or going back were removed and became completely swipe-based. Of course, unlike the previous version, in all phones based on Android 10, the use of swipe instead of the button was optional, and Google has included this option in its operating system so far.
A less obvious change was to the way the operating system was updated, which eventually led to faster and more regular releases of smaller, more focused patches. This version of Android had other small but important improvements; Including the updated access permission system, which gave the user more control over how and when applications use location-related data.
In addition to these, Android 10 also included these features: a dark mode for the entire system, support for foldable phones that were on the way, smart replies in all messengers, a new focus mode that allowed the user to press a button on the screen, the number of notifications for each Limit the application and the new design of the sharing menu that we have been waiting for a long time. Android 10 also introduced the new Live Caption feature, first for Pixel phones and then for other phones, with the help of which text could be placed on recorded images, videos, podcasts, or audio files.
Android 11
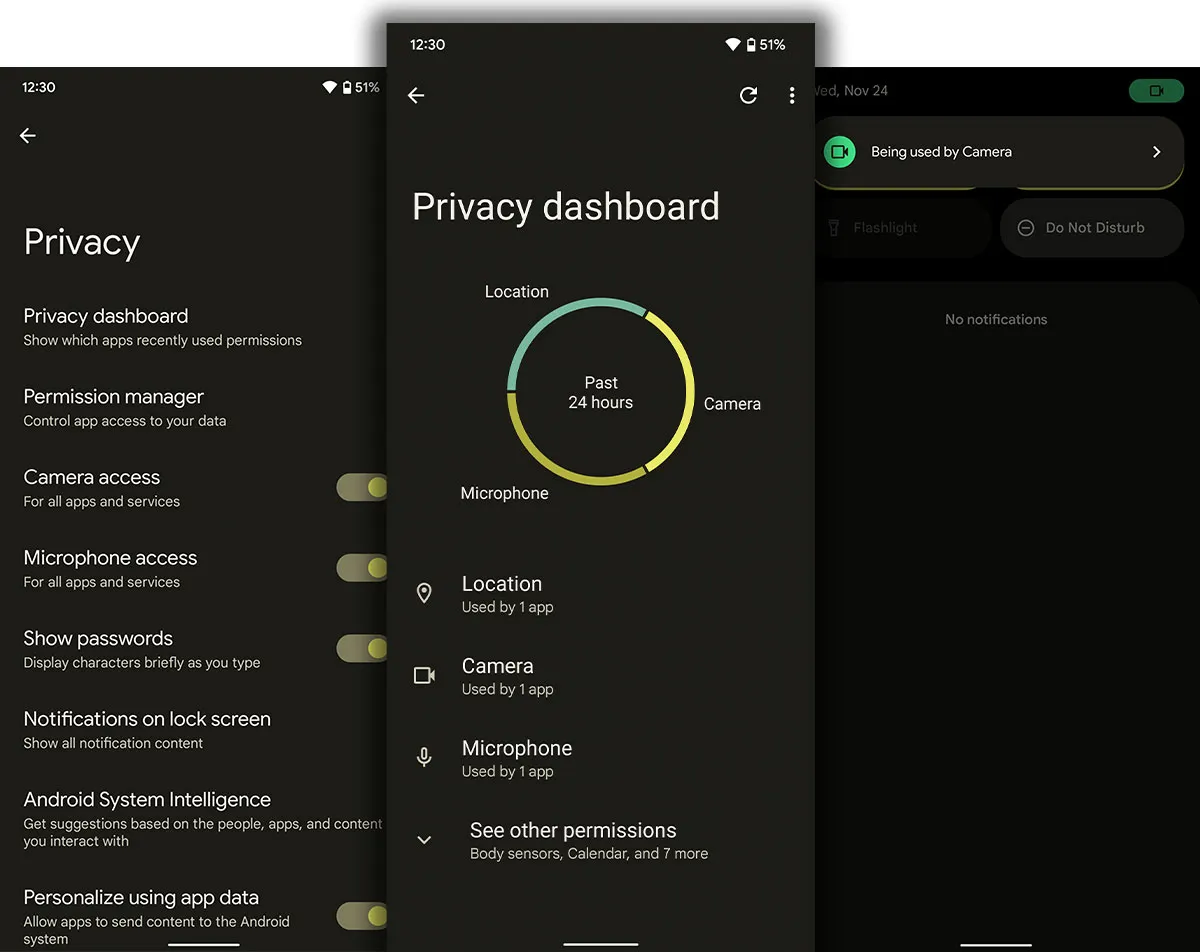
Android 11, which was released in September 2020, was considered a significant update both in terms of visible changes and changes under the skin. The most important changes of this version were related to privacy; The access permission system, which was introduced with Android 10, has now been expanded and users can determine the access level of applications based on location, camera, or microphone access. In Android 10, users could restrict access to only the duration of the app’s use, but in Android 11, the app can be given one-time access.
Android 11 also allows the system to access the location in the background so that it is more difficult to request access to applications and the possibility of accidentally activating these accesses by the user is less. Another new feature that was introduced in the same area, the access permission of applications that have not been opened for several months, was automatically taken from them, and the user needs to manually activate this permission again.
Other than that, Android 11 no longer allowed an app to see other installed apps on a user’s phone and limited the ways apps could interact with local storage to further protect data stored on the phone.
The Bubble feature of Android 11, which was rumored since 2019 and is reminiscent of the Chat Heads of Facebook messenger, allowed the conversations held in different messengers such as Telegram or Google’s own Messages to float together like a bubble on the surface of the user interface, so that You can quickly access them in any environment and after finishing the conversation, leave their bubble in a corner of the user interface.
The ability to select, copy, and share text or photos from the application with another application was also provided in this version. Other new features of Android 11 include separate notifications, integrated control of multimedia content, video recording of the phone’s software environment with the ability to record sound and show where the screen is touched, and better compatibility with the design of foldable devices.
Overall, Android 11 wasn’t an update that came with a ton of groundbreaking features, but it did improve the user experience of the Android smartphone and showed that Google is moving in the right direction.
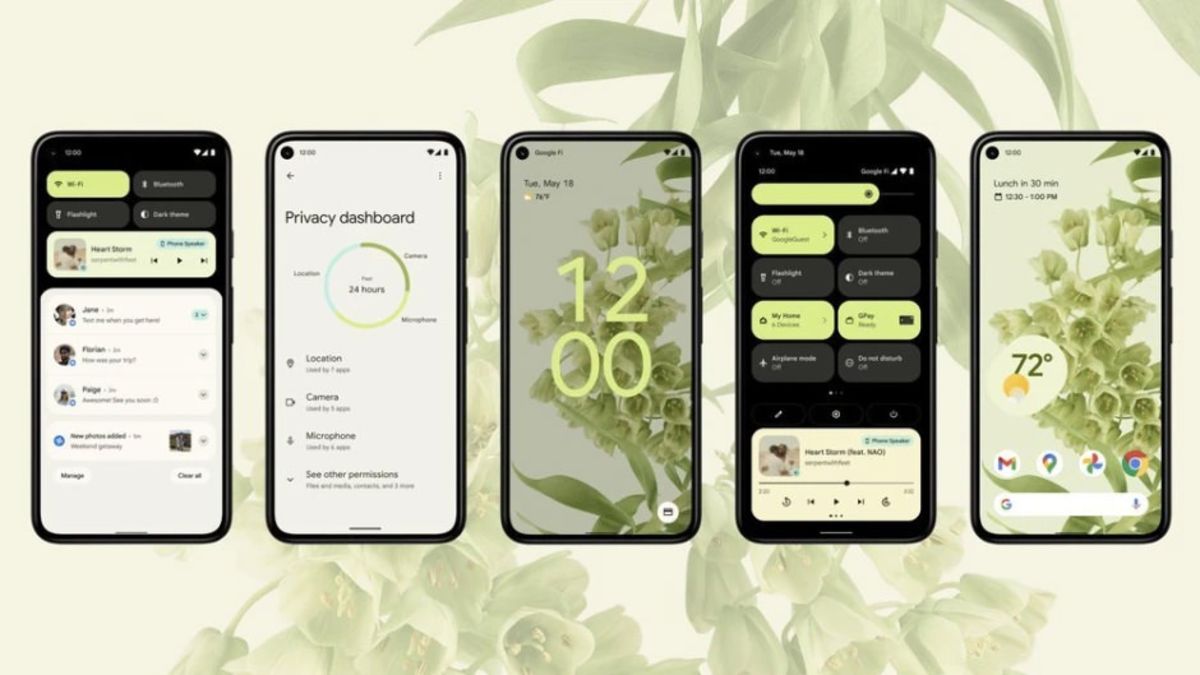
Android 12
Google officially released the final version of Android 12 in October 2021 along with the Pixel 6 series phone. Google’s latest operating system update is more of a step forward than a giant leap, But these small improvements have been able to make a significant difference in the user experience.
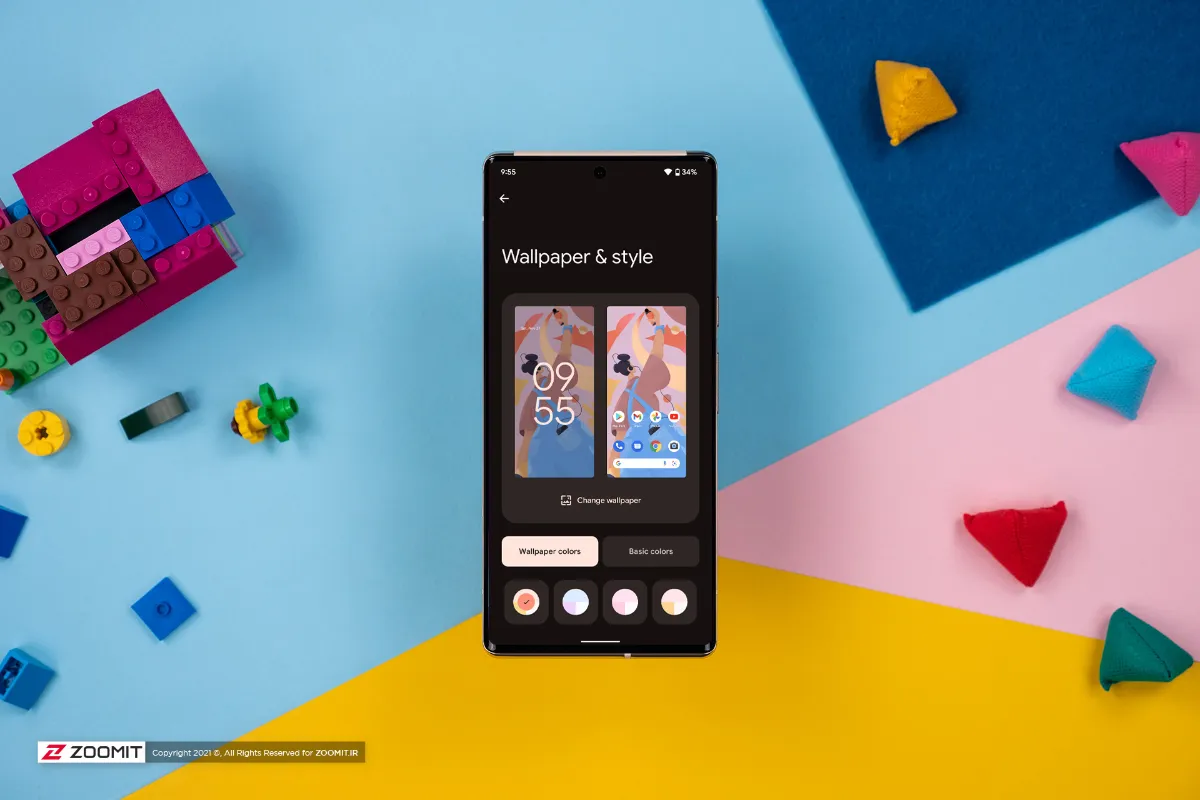
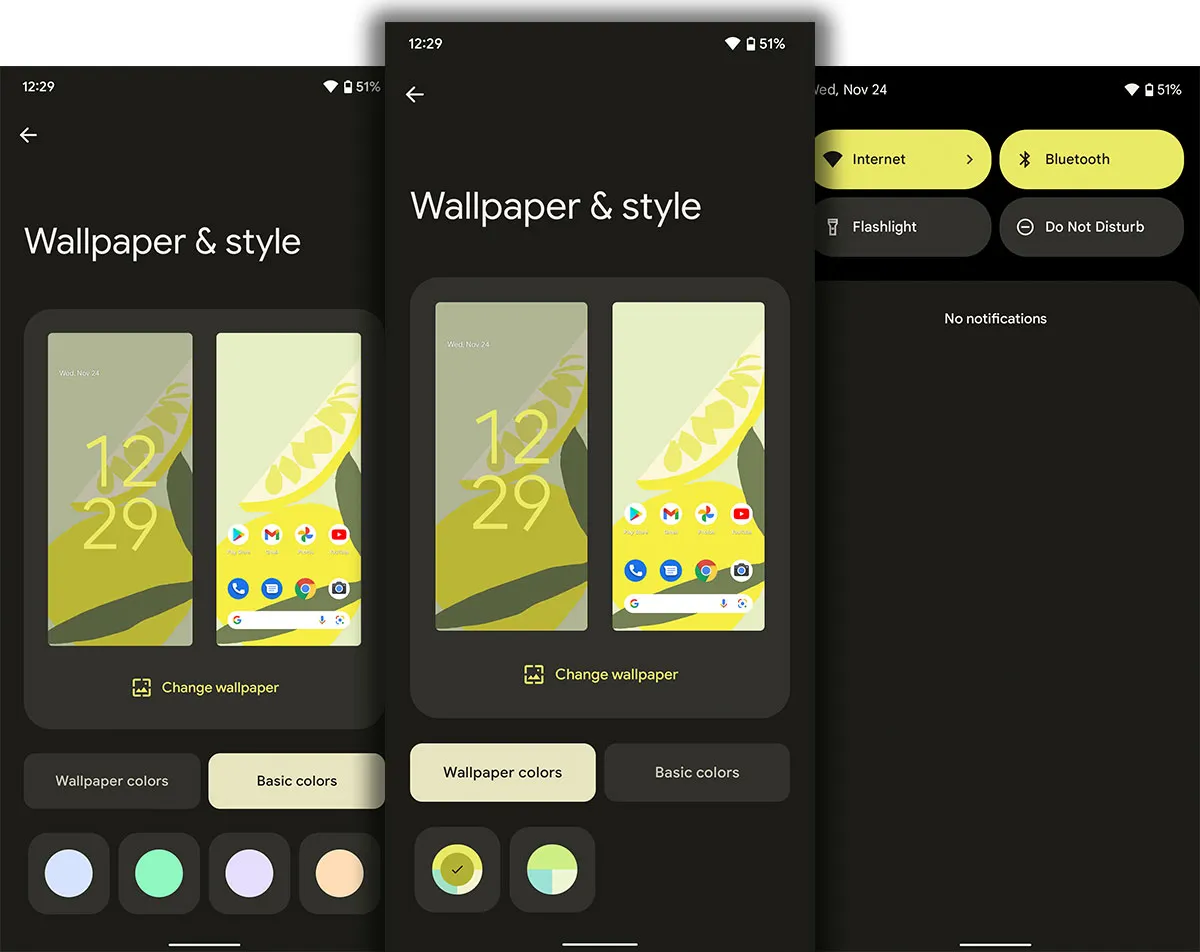
Unlike the previous versions where most of the changes were done away from the user’s eyes, we see the most important changes of Android 12 in the appearance and user interface. Almost 8 years have passed since the start of using the Material Design design language that was introduced with Android 5, with Android 12 and Material You, we finally see a big change and transformation in the popular Google operating system that prioritizes the user’s taste and more personalization options. puts it at his disposal.
The biggest change that attracts attention in Android 12 is the alignment of the phone’s color palette based on the background image chosen by the user, and this color change is applied throughout the operating system, from the lock screen to the application icon, notification screen, volume control, and even widgets. The quick settings panel has also undergone fundamental changes and the number of choices is reduced to four options at first glance, to access additional settings options, it is necessary to fully open the drop-down menu at the top of the screen. To make the quick settings menu quieter, Google has integrated the mobile internet and Wi-Fi buttons into one button called Internet, which may not be a pleasant change for some users.
Notifications are also neater in Android 12 and are displayed with rounded corners. In addition, more content is displayed in each notification. The updated applications also run faster and smoother with the touch of their notifications and make the user experience more enjoyable.
Apart from the appearance changes, Android 12 focuses more on widgets, improved performance, security, and privacy. With the addition of a privacy dashboard, this update gives the user more control over the level of access that apps have to data, and Google stores the data collected from the user that is needed for artificial intelligence tasks completely locally in a separate partition in the operating system. so that they never leave the device.
The gaming experience is also at the center of Google’s attention, and users can benefit from features such as a frame rate counter, a shortcut for streaming on YouTube, a shortcut for taking a screenshot, and recording screen content by accessing the Game Dashboard.
Other features of Android 12 include device-wide search, scrolling screenshots, improved auto-rotation, live translation, and the Magic Eraser tool, which is only available for Pixel phones and allows photography enthusiasts to remove elements from photos.
To find out whether your Android phone is on the Android 12 eligible list or not, you can visit the article on which phones will receive the Android 12 update.
Android 13
Android 13 was introduced in August 2022 and unlike Android 12, it was accompanied by limited changes. In this version of the operating system, Google has focused most of its efforts on solving the previous problems and is content with providing only a few limited features to improve the quality of life of its users.
One of the biggest changes in Android 13 is the addition of the Live Transcribe feature, which allows simultaneous conversion of voice messages, video audio, or even the conversation of the contact during a call.
The next interesting feature is the ability to copy a part of the text or save a photo in the list of programs running in the background. To use this feature, just swipe up from the middle and bottom of the screen to see the list of all the programs running in the background.
Android 13 has brought the ability to change the language of each application individually to Android devices. With this feature, for example, you can choose the Farsi language for a program, while the general environment language of the device is English.
Improved Material Your design language also allows you to change the phone’s user interface based on wallpaper colors. Full access to the features of Material You, which was previously reserved for Google applications in Android 12, is now possible for other applications as well; Thus, you can match the icon of all applications that support this design language with the color of your chosen theme.
Another important thing is the improvements to app licensing to respect privacy. This means that every app in Android 13 will ask for your permission before sending notifications, either right after installation or later in its privacy settings.
Another interesting feature of Android 13 is the ability to monitor programs that are active in the background. You can see these applications at the bottom of the screen in Quick Settings and close anyone you don’t need to reduce the phone’s battery consumption.
Android 14
Android 14 was released in early October 2023 (October 1402) in the middle of the Pixel 8 and Pixel 8 Pro introduction event, and like the previous version, it does not benefit from significant changes in appearance. This is partly because Google has moved to a development cycle that revolves more around small but continuous updates rather than big OS-level releases that only appear once a year.
Despite its unimpressive appearance, Android 14 offers a set of relatively significant features; From a new system for dragging and dropping texts in different applications and using an Android phone as a webcam to new customization options for the lock screen and simulating programs.
Android 14 has been accompanied by several improvements in security and privacy; Including a new integrated settings dashboard to manage all health data and control the access level of individual applications and devices to it.
But the most prominent feature of Android 14, especially in Pixel phones, goes back to artificial intelligence capabilities. For example, the AI Wallpaper feature allows you to create a new wallpaper for your phone using descriptive sentences and changing words. The Live Caption feature is also used to subtitle videos, live videos, and phone conversations. The Summarise feature summarizes long articles so you can read more articles in less time. The Best Take tool will also be very useful for those times when you take a group photo and someone blinks or shakes in the photo.
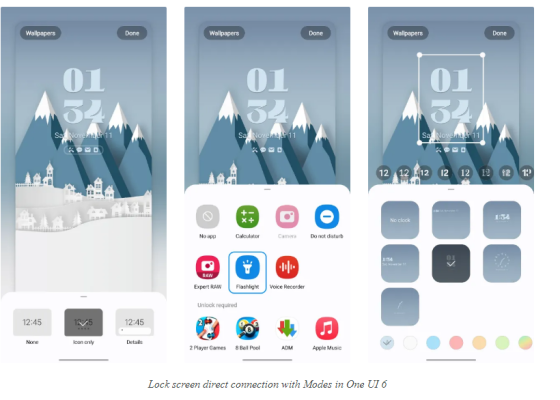

The new features of Android 14 in the One UI 6 user interface for Samsung phones include small but pleasant improvements such as changes to the Notifications panel and Quick Settings and the direct connection of the lock screen with Modes, which you can read a full review on Zoomit.
The future of Android
Android has come a long way from its very humble beginning when it was the only product of a small startup to become the leading mobile operating system in the world today with 80% of the market share.
Mountain View is still stubbornly committed to Android development, although there are some indications that the company is focusing on other long-term plans that may replace Android in the distant future. For example, in the past few years, Google has been working on an operating system called Fuchsia, which unlike many current operating systems, including Android, is not based on Linux kernels. Fusha is used in the Nest Hub smart display and may support smartphones, tablets, and even notebook and desktop computers in the future. However, it is not yet known whether Fyusha will really come to an end or, like many projects of this company, it will go away and join the Google graveyard
Leaving aside other Google programs, the Android project itself becomes better and more efficient than before with each update, and the future of this operating system is very bright and exciting for application developers, in the shadow of the more widespread artificial intelligence and machine learning; However, one cannot ignore the challenges ahead.
The release of Android updates has improved and become faster thanks to projects like Treble ( Project Treble ) and Mainline ( Project Mainline ), but due to the open source, there is still the problem of fragmentation of the operating system. Additionally, although companies like Samsung and OnePlus offer up to four years of updates for many of their phones, other phone makers end support after two or even a year; For example, Google itself provided only 3 years of software updates for Pixel before Pixel 8; According to Google, this support has now reached 7 years.
Although you can have the best Android experience these days with Pixel phones, the main concern is the innovative designs of other phone makers that are pushing the boundaries of Android’s current capabilities every day. Folding phones equipped with two screens may have been able to open their place in the smartphone market with a luxury price tag and benefit from the “special” feature, but on the other hand, they have also shown the weakness of Android’s performance on larger screens.
Anyway, Android will continue to dominate the mobile operating system market for a few more years. This operating system can be run on both low-end phones and supports luxury and expensive flagships, and this flexibility, along with annual updates, has solidified Android’s position as the leader of the industry for years to come.


You may like
Technology
Unveiling of OpenAI new artificial intelligence capabilities
Published
2 days agoon
14/05/2024

OpenAI claims that its free GPT-4o model can talk, laugh, sing, and see like a human. The company is also releasing a desktop version of ChatGPT’s large language model.
Unveiling of OpenAI new artificial intelligence capabilities


Natural human-computer interaction
What exactly does the introduction of this model mean for users?
Strong market for generative artificial intelligence




Samsung S95B OLED TV review
What can be placed in a container with a depth of 4 mm? For example, 40 sheets of paper or 5 bank cards; But to think that Samsung has successfully packed a large 4K OLED panel into a depth of less than 4mm that can produce more than 2000 nits of brightness is amazing. Join me as I review the Samsung S95B TV.
Samsung has a very active presence in the smartphone OLED display market, and by the way, it also has some of the best and most stunning small OLED panels in its repertoire; But surprisingly, it has been a little more than a year since he seriously entered the OLED TV market; Of course, Samsung launched its first OLED TV in 2013 and quickly withdrew from the large-size OLED market and left the field to its traditional and long-standing rival, LG.
In the years after withdrawing from the OLED TV market, Samsung focused on the evolution of LCD TVs with technologies such as Quantum Dot and MiniLED; But after almost 10 years, Samsung decided to once again try its luck in the world of OLEDs, and thus, in 2022, it launched the S95B TV in two 55-inch and 65-inch models.
In 2023, Samsung introduced the S95C TV as a successor to the S95B and unveiled the S95D model at CES 2024; While Samsung’s 2024 TV has just been launched in international markets a few months after its launch, it is still hard to find its 2023 model in the Iranian market. Accordingly, we have prepared the 65-inch S95B model from 2022 for review. It is more numerous than the 2023 model in the market of the country.
Slim design… super slim
What draws attention to Samsung TV at first sight is not its eye-catching image and ear-pleasing sound, but its infinite slimness. The S95B was so slim that when I unboxed and installed it, I experienced the same level of anxiety I had on exam night! Samsung OLED TV is only 3.89 mm thick; For this reason, despite all the company’s efforts in strengthening the body, it still simply shakes and sways.

Samsung calls the ultra-slim design of its TV LaserSlim; Because the laser beam is narrow and sharp; So you should be very careful when installing the TV. I wish we knew what is the logic behind the childish efforts of companies to make the world’s thinnest TV. To some extent, the narrowness of the TV helps to make it more modern and better installed on the wall; But the strength of the TV should not be sacrificed to make it thinner.

Samsung designers have not spared even the edges of the TV! The width of the edges around the panel does not exceed 8 mm. The narrowness of the edges helps the user to immerse well in the depth of black and the extraordinary contrast of the OLED TV panel and enjoy the content to the fullest.

The S95B TV has a high-quality and well-made body, the frame of the device is metal, and like most OLED TVs in the market, there is a wide plastic protrusion in the lower half of which parts such as the board, speakers, and power supply are placed. Due to this protrusion, the thickness of the body reaches 4.1 cm in the maximum state.




Unfortunately, just like LG’s OLED TVs, the base of the S95B is also located in the middle of the device; Although the base itself is metal and relatively wide; the large dimensions of the TV and its very small thickness make it not to be firmly and firmly placed on the table and not to wobble; Of course, you can install the TV on the wall with a 300×200 mm VESA mount.


All the ports of the S95B TV, including HDMI and USB, are included in the plastic protrusion on the back of the device. These ports are covered with a plastic screen to integrate and beautify the back of the device. After installing it, surprisingly, you won’t be able to access the ports! Samsung TV ports are as follows:
- Four HDMI 2.1 ports with the ability to transfer 4K120 image signal; Two ports facing down and two ports on the side of the frame
- Two USB 2.0 ports on the side of the frame
- A network port
- Internal and external receiver input
- An optical audio output
One of the HDMI ports (number 3) has eARC capability and can be used to connect the device to the soundbar. USB ports are also different in terms of current and voltage; One of the ports is limited to 0.5 amps and 5 volts and the other is limited to 1.0 amps and 5 volts; Therefore, it is considered a more reasonable option for connecting an external hard drive.
Stunning brightness and disappointing color accuracy
I mentioned earlier that we had the 65-inch S95B model available for review. With such dimensions, you can enjoy the 4K resolution of the panel the most if you sit at a distance of about 2 meters from the TV; At closer distances, pixels can be separated, and at distances greater than 2 meters, your brain’s perception of a 4K image will be no different from a 1080p image.

The Samsung S95B TV uses a 10-bit OLED panel with a resolution of 4K or 2160 x 3840 pixels and can display more than a billion colors. Supporting this number of colors is essential to provide an optimal experience of HDR content playback. In the following, I will explain more about the compatibility of Samsung TVs with HDR standards and the quality of color display.
Unlike LCD panels, where the light needed by the pixels is provided by a number of LED lights on the edge or back of the panel, in OLED panels, each pixel provides its own light; As if instead of a limited number of exposure areas, for example 500-600 in MiniLED TVs, we have more than 8 million exposure areas; Thus, to display the color black, the pixels are turned off, so that instead of a spectrum of gray color, we see a deep black and experience an extremely high contrast.
 The absence of any Blooming thanks to the precise control of light in the TV’s OLED panel
The absence of any Blooming thanks to the precise control of light in the TV’s OLED panel
The great advantage of self-lit pixels (pixels that provide their own light) in displaying deep black and preventing the Blooming phenomenon (creating a halo around bright subjects in a dark background) thanks to the very precise control of the light distribution, also has some weaknesses; The greater vulnerability to burn-in phenomenon during long-term static image display and the lower level of OLED panel brightness compared to MiniLED samples are among these weaknesses.
Like other OLED TVs, the S95B TV is not immune to the risk of burn-in. In order to reduce the possibility of this phenomenon, the Koreans have considered solutions such as moving the image slightly in different time periods. Unfortunately, we do not have the possibility to examine the TVs for a long time to evaluate their performance in preventing the risk of burn-in; But at least based on RTINGS’ long-term and unrealistic test, the S95B seems to be more vulnerable compared to its competitors; However, in real use, it is unlikely that a user would want to watch TV with such intensity.
To overcome the inherent weakness of OLED panels in achieving higher levels of brightness, Samsung engineers have combined quantum dot technology with OLED panels. Quantum dots are very small crystal particles that are layered in the heart of the display panel. With the help of the quantum dot layer, the panels achieve higher brightness and produce more vivid colors. Samsung calls its combined panel QD-OLED and claims that with the help of the Neural Quantum processor in the heart of the S95B TV, this panel can raise the brightness to a higher level than its competitors.
|
Samsung S95B 65-inch TV brightness with default settings |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Image modes/pattern white percentage |
10 percent |
50 percent |
100 percent |
|
|
SDR |
Dynamic |
1065 |
633 |
364 |
|
Standard |
740 |
487 |
281 |
|
|
Movie |
430 |
399 |
229 |
|
|
HDR |
Dynamic |
2094 |
— |
— |
|
Standard |
2179 |
— |
— |
|
|
Movie |
2179 |
— |
— |
|
|
FILMMAKER Mode |
2175 |
— |
— |
|
In my measurements, when only 10% of the screen was lit and the device was playing a normal SDR image, the brightness of the S95B panel reached 1100 nits in the highest mode, which is a very good number and better than the brightness of the C2 and C3 TVs in the same conditions, respectively. It is about 300 and 100 nits more.
Aside from the S95B’s excellent performance in SDR image brightness, the real magic happens when the device is playing HDR video. In this situation, when 10% of the screen is lit, the brightness reaches a stunning number of about 2200 nits, which is 700 nits more than the HDR brightness of the C2 and C3 TVs. Achieving such a level of brightness helps the TV to deliver a stunning HDR movie viewing experience.
|
Comparison of brightness and contrast of S95B with other TVs |
||
|---|---|---|
|
TV/parameter (the brightest profile) |
Brightness (50% pattern) |
contrast |
|
Samsung S95B |
633 |
∞ |
|
LG C3 |
603 |
∞ |
|
LG QNED80 |
580 |
116 |
|
LG NANO84 |
295 |
149 |
|
LG C2 |
525 |
∞ |
|
LG QNED96 |
470 |
— |
Note that the stunning numbers of 1100 and 2200 nits are obtained when a small part of the screen is bright, which is often the case in movies and series, and the entire image is not full of bright colors; But when the whole screen is lit; For example, consider a scene from The Lord of the Rings where we see Galadriel in the land of the elves, in such a situation, the maximum brightness of the whole screen is about 370 nits, which is still 40 nits higher than the LG TV.

Thanks to the panel’s excellent brightness and the deep blacks produced by the muted pixels, it’s no surprise that the Samsung TV’s image contrast is superb; Especially since there is an anti-reflective coating on the panel so that you can enjoy the image even in bright environments; Note that unlike what comes from the corners of the panel, you should not remove this anti-reflective layer from the panel; Otherwise, you will face problems like us!
If you think that the S95B is the best TV on the market so far, I must say that not everything about the S95B is rosy.
The S95B TV provides the user with the following four color profiles, all of which tend to be very cold by default and do not produce very accurate colors.
- Dynamic
- Movie
- Standard
- FILMMAKER Mode
Like most OLED TVs on the market, the S95B TV also covers a wide range of colors. In my tests, the Samsung TV managed to cover about 148% of the sRGB color space, nearly 100% of the DCI P3 wide space, and 75% of the Rec 2020 ultra-wide space. These numbers are great, But the disappointing thing is the very low accuracy of the device in producing the mentioned colors with factory settings.
|
Samsung S95B 65-inch TV performance in covering color spaces with default settings |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Image mode/color space |
sRGB |
DCI-P3 |
Rec. 2020 |
|||
|
cover |
mean error |
cover |
mean error |
cover |
mean error |
|
|
Dynamic |
146 |
— |
98.6 |
13.7 |
77.9 |
— |
|
Standard |
147.7 |
— |
99.7 |
12.1 |
78.7 |
— |
|
Movie |
125.4 |
— |
89.5 |
4.6 |
65.5 |
— |
|
FILMMAKER Mode |
121.9 |
— |
89.5 |
4.1 |
64.6 |
— |
Note that the FILMMAKER mode belongs to the UHD union and most big companies like Samsung, LG and Hisense use it in their TVs. On paper, with FILMMAKER mode, we should see movies as the director intended.
|
Comparison of Samsung S95B color accuracy with other TVs (default settings) |
||
|---|---|---|
|
TV/parameter (the most accurate profile) |
DCI P3 |
|
|
Covering |
Color accuracy |
|
|
Samsung S95B |
89.5 |
4.1 |
|
LG C3 |
96.8 |
3.0 |
|
LG QNED80 |
90.7 |
2.7 |
|
LG NANO84 |
82.9 |
— |
|
LG C2 |
98.7 |
2.1 |
|
LG QNED96 |
90.8 |
3.9 |
The most accurate colors of the S95B TV are depicted by the FILMMAKER Mode profile with an error of 4.1, in which the TV covers about 90% of the DCI P3 color space; As a comparison, in the review of the C3 TV, the color display error in the same FILMMAKER mode was 3.6 and in the most accurate color profile it was 3.0; Therefore, Samsung TV does not have an interesting performance in terms of factory calibration of colors.
We were so surprised by the results that we returned the TV and got another S95B to review, But the results did not change.
Fortunately, Samsung TV provides you with various settings to change parameters such as gamma, color temperature, color hue, and brightness limiter (ABL) so that you can achieve your desired style and style for displaying colors; For example, I was able to reduce the color display error in the Standard profile from a terrible number of 12.1 to a very good number of 3.0 by making the following changes.
|
Color accuracy of S95B TV after minor changes in panel settings |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Image mode/color space |
DCI-P3 |
||
|
Settings |
Average error (recommended: less than 3) |
Color temperature (neutral: 6500 K) |
|
|
Standard |
default settings |
12.1 |
14236 |
|
ABL: Off Contrast Enhancer: Low Gamma: 2.2 |
3.0 |
8180 |
|
Another weakness of Samsung S95B TV compared to LG OLEDs is that it does not support HDR videos with Dolby Vision standard; The iPhone, for example, records HDR video using the same standard. Samsung TV supports HDR10, HDR10+, and HLG standards.

Like other OLED TVs, the Samsung S95B TV has wide viewing angles, and even from the corners, it displays colors with the least drop in freshness; So if you use wide furniture at home, you can safely go to S95B.
Samsung has focused a lot on the gaming capabilities of its TV; The device uses a 120 Hz panel with support for FreeSync Premium and G-Sync technologies, and the TV itself provides the user with Game Mode, which, by activating it, significantly reduces Input Lag, makes available a variable refresh rate, and The frames of the games can also be seen.

Samsung compensates for the visual weaknesses of the S95B TV with the amazing listening experience of its powerful speakers; While a TV like the LG C3 uses 40-watt speakers, Samsung engineers have used 60-watt speakers with a 2.2.2 channel combination in the S95B’s slim body; In the sense that two speakers throw the sound down, two speakers throw the sound up, and two woofers are responsible for producing low frequencies.
The S95B TV supports Dolby Atmos surround sound and its sound output is considered excellent for a TV; The volume is high, you can hear the pounding bass, and at high volumes, the distortion is controlled at a reasonable level.
Tizen; The user interface is more limited and different from competitors
Finally, we must avoid the TV user interface; Samsung’s OLED TV, like the rest of the company’s TVs, uses the Tizen operating system. The user interface of the device is smooth and smooth, moving between different menus of the user interface is done without problems, although sometimes with a little slowness; But the device can play most of the video formats.




A number of functions are also available, which doubles the enjoyment of the TV experience, provided that the user uses a Samsung phone; For example, you can run the Samsung phone’s desktop mode or Dex on the TV and use the phone’s screen as a trackpad. The phone can even be used as a webcam to make video calls with Google Mate on the TV.
If you want to write a text, you can call Microsoft365 from the Workspace section of the user interface by connecting a Bluetooth mouse and keyboard to the Samsung TV and start writing in Microsoft Word software.

Samsung Internet Browser is available in the S95B TV user interface; But the Samsung remote control, despite its compact design and the possibility of being charged with a solar panel or USB-C port, does not have the ability to use a mouse; So you have to browse the web with the arrow keys of the remote control; In my opinion, this is one of the main weaknesses of Samsung TV compared to LG TV with its practical magic remote.



As another weakness, we should mention Samsung’s not very rich store; For example, you can’t find some useful apps like Spotify or native apps like Filmo in the Samsung TV store.
Read more: How to connect to the TV with a Samsung phone?
Without a doubt, the S95B is one of the most stunning TVs we’ve ever reviewed on Zoomit; An attractive and extremely slim device that will amaze you with its stunning brightness and contrast, impressive gaming capabilities, and very powerful speakers.
In terms of factory color calibration, the S95B appears below expectations and a bit disappointing; So, if you are not very fond of the image and do not know much about color parameters, you will have to start with inaccurate and very cold colors; But if you are aware of the color parameters, you can change them and enjoy the attractive picture of the TV to the fullest.

The S95B TV is one of Samsung’s 2022 flagships, and now its 65-inch model is sold in the price range of 105 million Tomans; In this range, go for the more updated LG C3 TV with more accurate colors, or for a little more money, choose the Sony A80L TV for 2023, which is powered by a more practical Android operating system; In addition, C2 TV is also available at a price of 10 million less than in 2022.
what is your opinion? Do you think the S95B is a reasonable choice or do you prefer other models from LG or Sony?
Pros
- Very high brightness
- 6 powerful speakers
- Very modern and attractive design
- Deep black and excellent contrast
Cons
- Low color accuracy with default settings
- Too thin and vulnerable body
Technology
MacBook Air M3 review; Lovely, powerful and economical
Published
1 week agoon
06/05/2024

MacBook Air M3 review; Lovely, powerful and economical
If you are looking for a compact, well-made and high-quality laptop that can be used in daily and light use, the MacBook Air M3 review is not for you; So close the preceding article, visit the Zomit products section and choose one of the stores to buy MacBook Air M1 ; But if you, like me, are excited to read about the developments in the world of hardware and are curious to know about the performance of the M3 chip in the Dell MacBook Air 2024 , then stay with Zoomit.
The design is a copy of the original from the last generation
Almost two years have passed since Apple said goodbye to the familiar and wedge-shaped MacBook Air design; A different design that accompanied this ultrabook from the first day of its birth in 2008; But finally in 2022, with the aim of harmonizing the design language of the Apple laptop family, it was abandoned so that the MacBook Air 2022 will have a similar appearance to the 14-inch and 16-inch MacBook Pro.
The new MacBook Air is uniform in thickness; But it was slimmer, the screen was bigger, the edges were narrower and the corners were rounded, and a relatively large notch was added to it, whose only existence was to host the device’s 1080p webcam. MacBook Air 2022 also marked the return of the MagSafe magnetic charging port to Apple’s popular Ultrabook.

Previously, in the review of the MacBook Air 2022 with the M2 chip, we have talked comprehensively and deeply about its design and its positive and negative points. I suggest that if you haven’t read the article, you must visit it; Because the MacBook Air M3 is no different from the MacBook Air M2 in terms of appearance, display, or ports.
We also see the same incredibly well-made and metal body of MacBook Air 2022 in the new generation of Apple Ultrabooks; A body that, like the rest of Apple laptops, is carved from an aluminum block instead of the usual method of using aluminum sheets, and for this reason, it has a strong and dense structure so that we do not see the body sinking when pressing the keyboard area or the screen frame swinging.
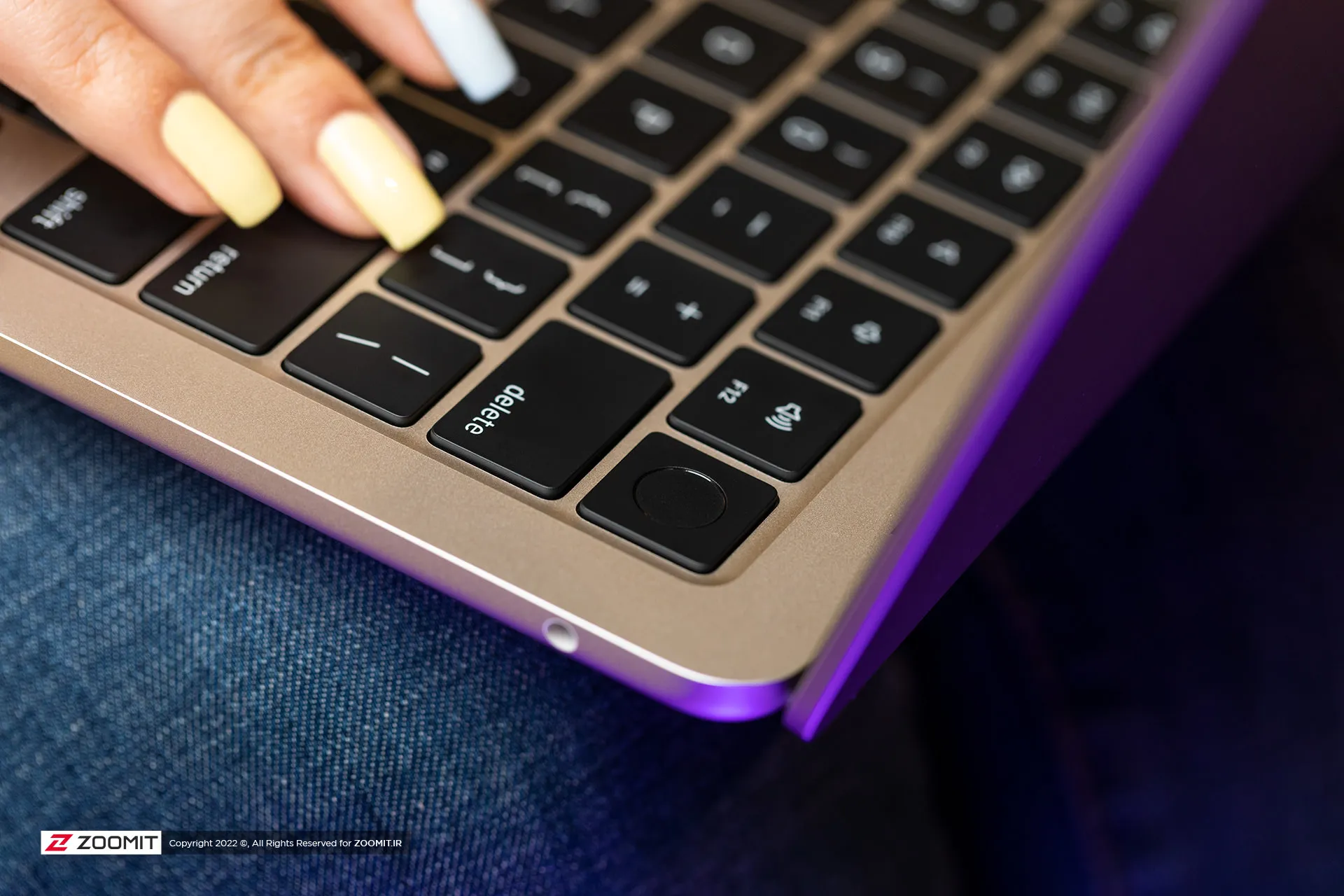



All the parts of the MacBook Air 2024 are assembled with the utmost care; So that there is no gap between them. As expected, the hinge of the laptop is also well-adjusted so that you don’t need to use two hands to open the laptop door. All in all, the combination of the quality of components and Apple’s exemplary engineering precision, brings an extremely enjoyable and unique feeling to the user while using the MacBook Air.
Just like the previous generation, the new MacBook Air is sold in four colors: gray, silver, dark blue, and cream. One of the flaws that could be found in the design of the MacBook Air 2022 was that fingerprints and grease remained on the body; The item that was more noticeable in dark blue color. Apple says this year it has used a new coating that reduces the severity of this problem. We did not have the 2022 model available for comparison at the time of writing the following review, But traces of fat and finger still remain on the body of the MacBook Air 2024.
 Grease and fingerprints on the laptop body
Grease and fingerprints on the laptop body
MacBook Air keyboard is among the best examples in the market in terms of arrangement and dimensions, feedback, and key stability; But the matte coating on the keys absorbs the fat of the fingers very quickly, and on the other hand, like other MacBooks, there is a possibility that the matte coating will disappear and the keys will become shiny. Depending on your usage, this can happen very quickly or over time; For example, for me, who is constantly writing, the keys on my MacBook Pro M1 burned out in less than a year.
Apparently, the buyers of used laptops are very sensitive about the keys being electrocuted; Therefore, if you plan to replace your Macbook with another laptop after one or two years, be sure to keep this in mind and use an external keyboard for long typing.
As always, the trackpad is one of the main strengths of any MacBook, and the MacBook Air M3 follows the same rule. The glass trackpad of the device is large in size and has little friction on its surface, it offers flawless, accurate, and smooth performance, and its Fortouch mechanism, which makes it possible to click on the entire surface of the trackpad, is so efficient that after the MacBook, it is impossible to work with the trackpad of any laptop. Another enjoyed.
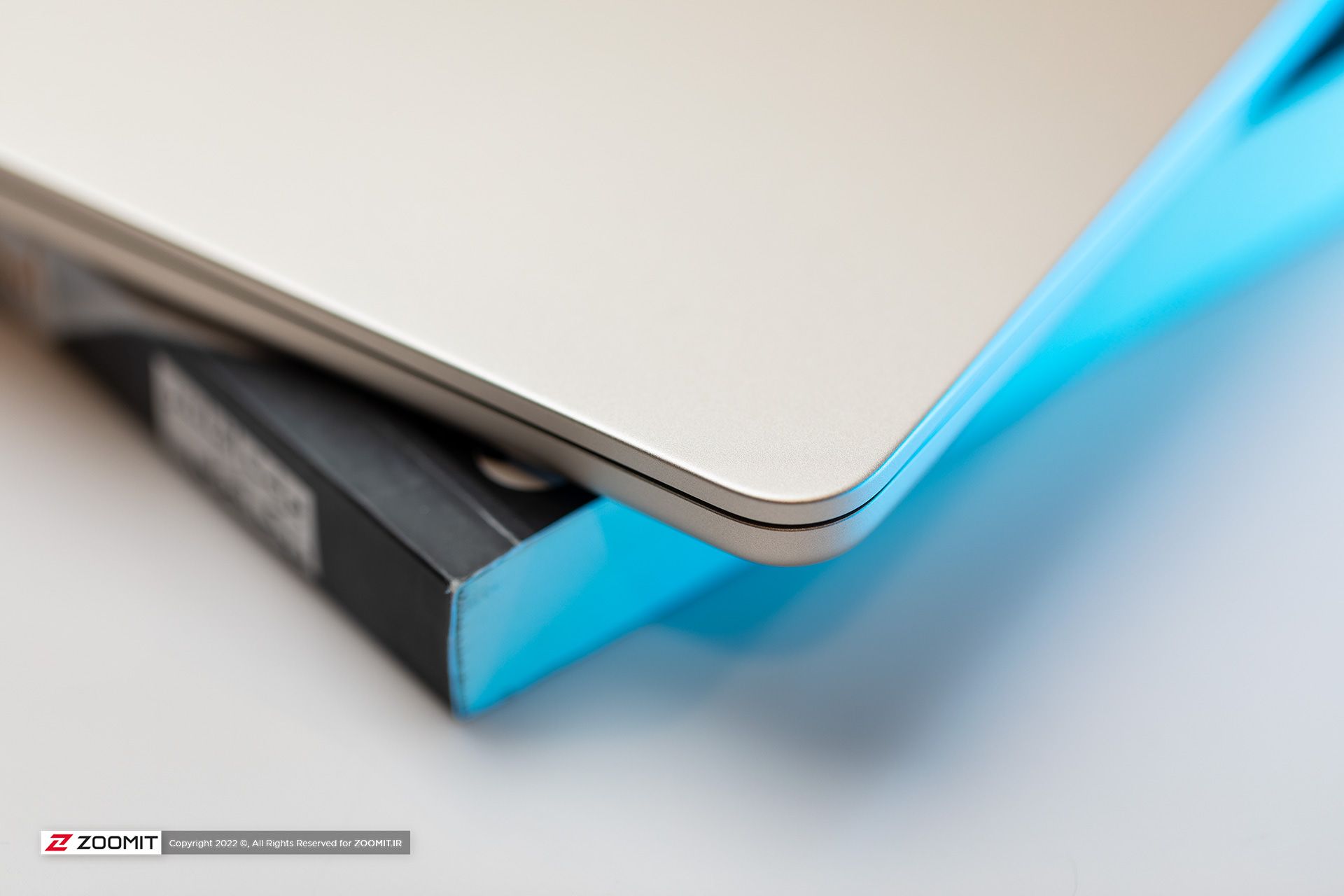
 MacBook Air 2022
MacBook Air 2022
The set of MacBook Air 2024 ports is limited and has not changed; On the right side of the device, there is a headphone jack, and the left side of the device hosts two USB4 ports and a MagSafe magnetic charging port. Along with the basic model, Apple provides a relatively small 30-watt adapter with a cloth cable of the same color as the device’s body; But you can also get the laptop with a more powerful 35 or 70-watt adapter, which charges the battery up to 50% within half an hour.
USB4 ports support Thunderbolt 3 standard with a bandwidth of 40 Gbps, But it is not possible to connect external graphics. Both ports also transmit the image signal with the DisplayPort standard. In the new MacBook, if you close the laptop door, you can connect a 6K monitor and a 5K monitor (both 60Hz) to the device at the same time; But with the laptop’s screen on, just like the MacBook Air M2, the image output is limited to a 6K monitor; It is interesting that the Intel version of MacBook Air could output images to two 4K monitors at the same time as its own screen is on!
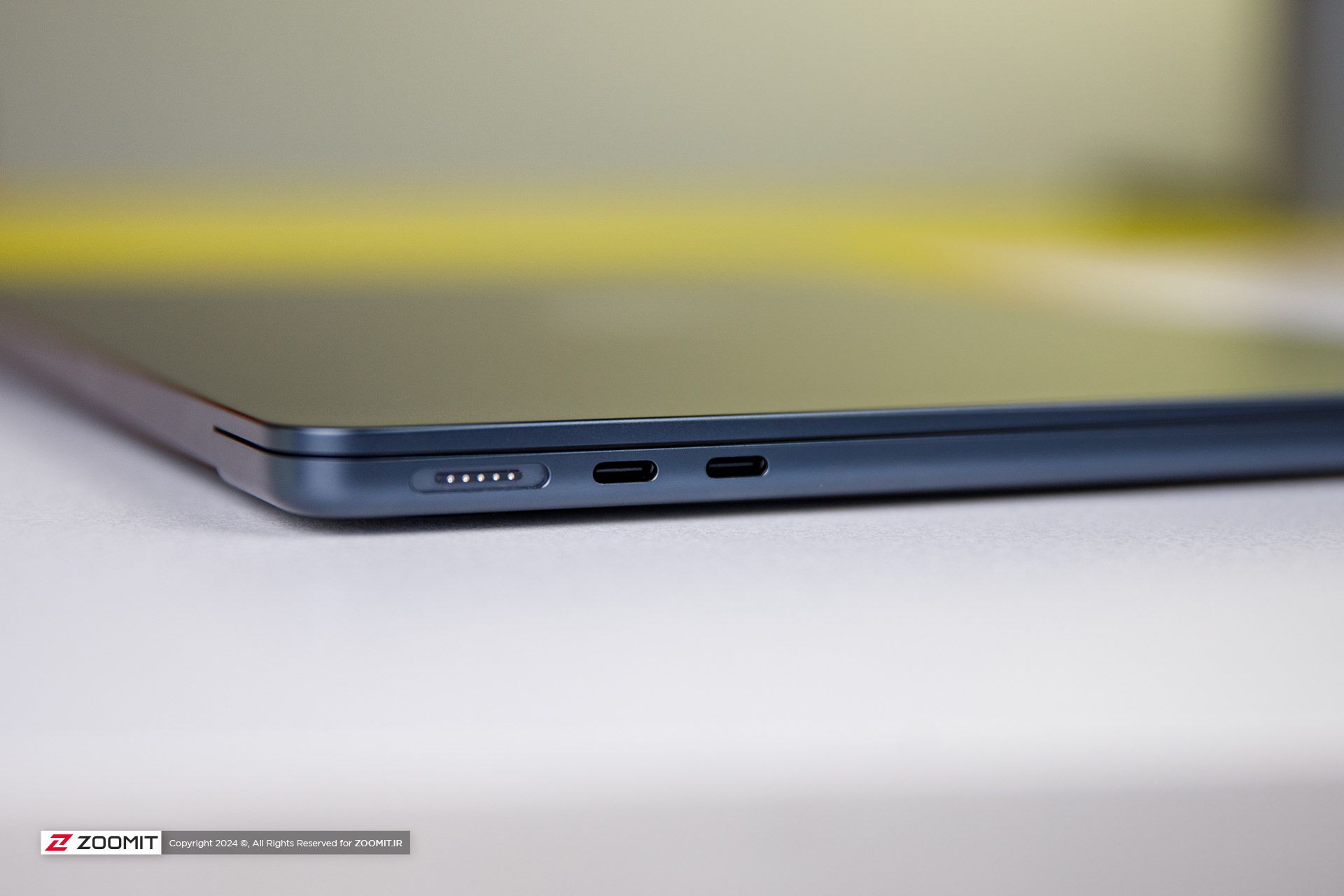
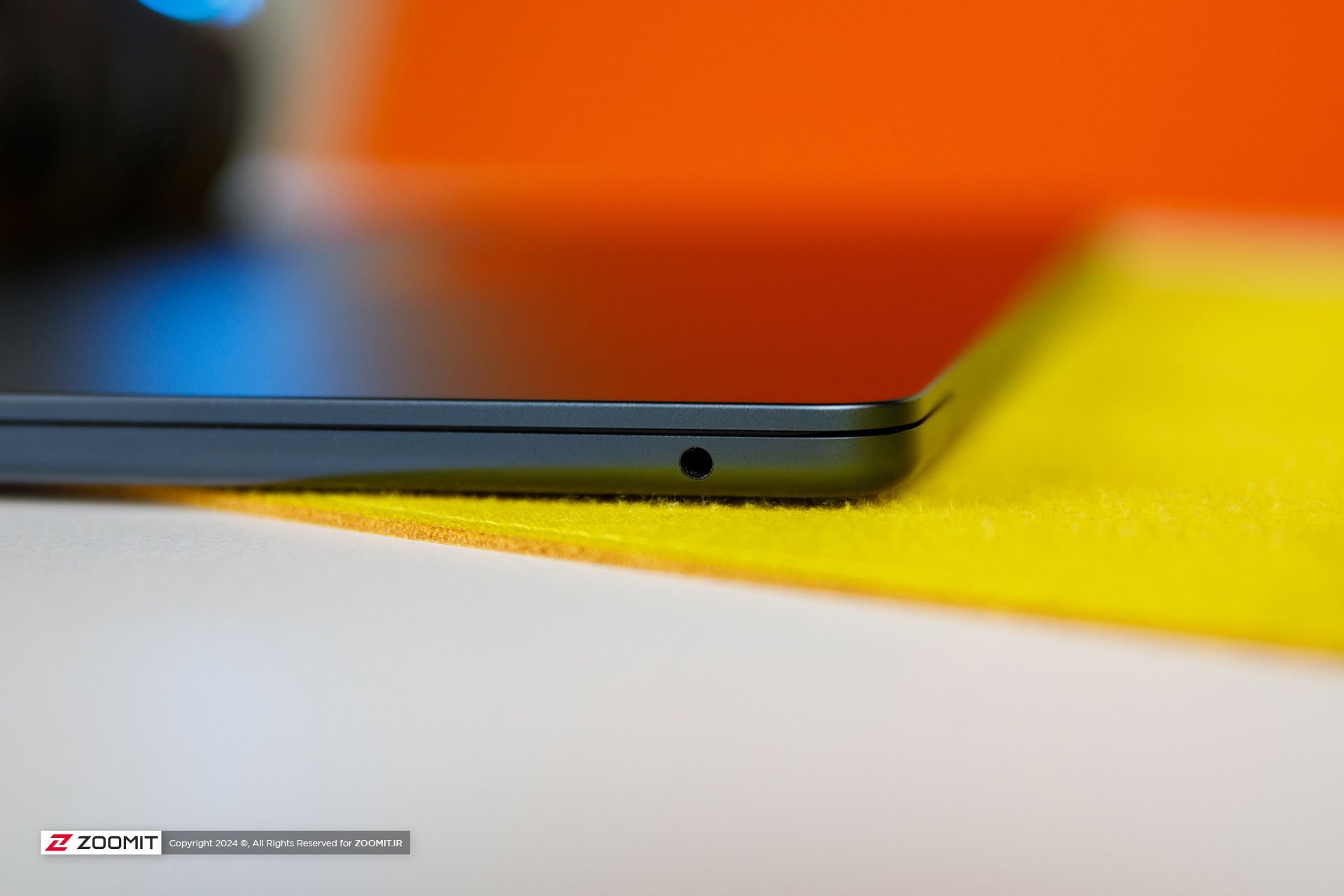


As in the previous generation, Apple uses Bluetooth version 5.3 in its Ultrabook; But the Wi-Fi module has upgraded the device from Wi-Fi 6 to Wi-Fi 6E, which incompatible networks can increase the communication bandwidth of MacBook Air 2024 with the router and the rest of the devices in the network from 1.2 to 2.4 Gbps.
Attractive display with more attractive competitors
Like most parts of the device, the screen of the new MacBook Air does not change; Of course, in this field, you can’t criticize Apple much, since 2018, when the MacBook Air screen became Retina, it has always been among the best; However, today, with OLED competitors with stunning colors and infinite contrast, Apple’s Retina display no longer has its former glory.
MacBook Air M3 can be purchased just like the previous generation in two 13.6-inch and 15.3-inch models. The pixel density of both versions is a very good number of 224 pixels. With this density, the MacBook Air screen produces a very clear image. So that it is difficult to distinguish the pixels from each other. We have the 13.6-inch MacBook Air M3 with a resolution of 2560 x 1664 pixels available for review.

Unfortunately, unlike the expensive models of MacBook Pro or even Windows Ultrabooks with the same price as Zenbook, the panel of the MacBook Air is 60 Hz and it does not have amazing technologies such as OLED and MiniLED to produce 1000 nits of brightness and extraordinary colors. MacBook Air uses an 8-bit IPS LCD panel with back exposure, which, by using FRC technology, can give the user the feeling of 10-bit panels with a billion colors.
MacBook Air covers the wide DCI P3 color space with high accuracy. The Apple Ultrabook covers 98.4% of this space with an error of 1.9 (an error of less than 3 is ideal), perhaps the only color weakness of the panel can be considered a slight tendency to be cold; However, thanks to the True Tone feature, the device evaluates the ambient light temperature with high accuracy and adjusts the color temperature accordingly to give you a satisfying visual experience.
In our measurements, with a 50% raster standard, we reached a maximum brightness of 443 nits, which in itself is a very good number, and thanks to the anti-reflective coating on the panel surface, in environments with different light conditions, it brings a satisfactory experience of working with a laptop. Without the appearance of the shadow of the environment on the panel, the user will not be bothered.
|
MacBook Air 2024 screen performance against other laptops |
||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Laptop / test |
White image |
Black image |
contrast ratio |
AdobeRGB |
sRGB |
DCI-P3 |
||||
|
Maximum brightness |
Minimum brightness |
Average brightness |
Native |
cover |
Average error |
cover |
Average error |
cover |
Average error |
|
|
MacBook Air 2024 |
443 intentions |
0.00 nits |
0.67 nits |
661 |
87.9 |
— |
100 |
2.4 |
98.4 |
1.9 |
|
Zenbook 14 |
512 intention (788 nits HDR) |
0.27 nits |
0 intentions |
∞ |
89.6 |
2.6 |
100 |
0.6 |
99.7 |
1.3 |
|
MacBook Pro 2022 |
437 intentions |
0.00 nits |
0.5 nits |
874 |
86.3 |
— |
99.8 |
2.7 |
97.5 |
— |
|
MacBook Air 2022 |
447 intentions |
0.1 nit |
0.65 nits |
693 |
87.5 |
— |
100 |
2.5 |
98.1 |
— |
|
Galaxy Book 3 Ultra |
441 intentions |
4 intentions |
0 intentions |
∞ |
97.3 |
3.7 |
99.6 |
1.9 |
99.8 |
2.3 |
|
MacBook Pro M1 Max |
455 intentions (1497 nits HDR) |
0 intentions |
0 intentions |
∞ |
85 |
— |
121.6 |
— |
97.3 |
2.5 |
In addition to the reasonable maximum brightness of 442 nits in bright images, unlike most laptops with IPS LCD screens, the black color brightness is also very low in the MacBook Air display; So that the device achieves a very high contrast. On the other hand, the minimum brightness of the display was 0 nits even with the 0.01 nits accuracy of the Zoomit luminance meter; In the sense that while using the laptop, there will be a little pressure on your eyes.
The attractive screen of the MacBook Air is completed by a set of 4 speakers; Speakers that have a very large sound volume compared to the size of a laptop, produce clear sound, and at high volumes, they are confused and distorted. MacBook Air speakers support Dolby Atmos and are easily ahead of most Windows laptops.
M3 chip and championship called TSMC
The main changes of MacBook Air 2024 have happened in its heart; Where it hosts the M3 chip as the beating heart of the device. Next, before we put the performance of the M3 under the microscope, we take a look at the details of the technical specifications of this chip.
The M3 chip is manufactured using TSMC’s 3nm-based manufacturing process known as N3B, hosts 25 billion transistors on its surface, and uses the same layout and configuration as the M2 for the CPU and GPU cores. Apple says the processor and graphics used in the M3 are about 35 and 65 percent faster than the M1, respectively.
|
Technical specifications of M3 against M2 and M1 |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
|
parameters/chip |
Apple M3 |
Apple M2 |
Apple M1 |
|
manufacturing process |
3 nanometer N3B TSMC |
TSMC’s second-generation 5nm |
5 nm N5 TSMC |
|
CPU |
4 powerful cores with a maximum frequency of 4.05 GHz 4 low-power cores with a maximum frequency of 2.75 GHz |
4 Avalanche cores with a maximum frequency of 3.5 GHz 4 Blizzard cores with a maximum frequency of 2.4 GHz |
4 Firestorm cores with a maximum frequency of 3.2 GHz 4 Icestorm cores with a maximum frequency of 2.0 GHz |
|
cache memory |
16 MB shared L2 cache and 320 KB L1 cache for each of the powerful cores 4 megabytes of shared L2 cache and 192 kilobytes of L1 cache for each low-power core 8 MB system cache for the entire chip |
16 MB shared L2 cache and 320 KB L1 cache for each of the powerful cores 4 megabytes of shared L2 cache and 192 kilobytes of L1 cache for each low-power core 8 MB system cache for the entire chip |
12MB shared L2 cache and 320KB L1 cache for each Firestorm core 4 MB shared L2 cache and 192 KB L1 cache for each Icestorm core 8 MB system cache for the entire chip |
|
memory bass |
128 bits |
128 bits |
128 bits |
|
DRAM |
8 to 24 GB LPDDR5-6400 |
8 to 24 GB LPDDR5-6400 |
8 or 16 GB LPDDR4x-4266 |
|
Memory bandwidth |
100 GB per second |
100 GB per second |
68.2 gigabytes per second |
|
GPU |
8 or 10 cores with hardware support of ray tracing |
8 or 10 cores |
7 or 8 cores |
Like the last two generations, the M3 chip uses a combination of 4 high-power cores and 4 low-power cores, respectively, with maximum frequencies of 4.05 and 2.75 GHz as CPU. Apple has made minor changes in the architecture of the cores, and the main difference of the cores is the 15% increase in frequency compared to the M2 cores.
Apple has not even changed the amount of cache memory of the M3 chip compared to the M2; Each of the high-power and low-power cores have access to 320 and 192 KB of ultra-fast L1 cache, respectively, the set of four high-power and low-power cores also have access to 16 and 4 MB of L2 cache, respectively, while the system cache is 8 MB for the set of chip processing blocks. GPU and CPU are included.

The M3 chip is used in Apple laptops in two versions with 8- and 10-core graphics processors. We had the MacBook Air with 8-core graphics available for review, which in total, just like the last generation, has 128 execution units with 1024 calculation and logic units in its heart, which operate at an almost identical frequency of 1.38 GHz.
The main difference between the M3 graphics compared to the previous generation is the addition of the Ray Tracing hardware accelerator, Mesh shading, and Dynamic Caching technology, the latter of which allows the chip to provide the memory required by the GPU in real-time and based on the type of processing. Thus, it optimizes the amount of memory consumption.
The M3 chip uses a 16-core neural processing unit (NPU) with a computing power of 18 trillion operations per second, and in addition to ProRes and ProRes Raw videos, it now has a separate engine for AV1 video codec decoding. Due to its two 64-bit channels and support for LPDDR5X-6400 RAM, this chip can achieve a bandwidth of 102 GB/s for data exchange with its integrated RAM.
|
Performance of the MacBook Air M3 in benchmarks while plugged in |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Laptop/benchmark |
Technical Specifications |
Web browsing |
Performance in graphics |
CPU performance in rendering |
CPU computing power |
GPU computing power |
|
3 Dark |
CineBench R23 |
GeekBench 6 |
GeekBench 6 |
|||
|
Speedometer 2.1 |
TimeSpy |
Single Multi |
Single Multi |
OpenCL Metal/Vulkan |
||
|
DirectX 12 |
||||||
|
MacBook Air 2024 |
Apple M3 8 core GPU |
680 |
— |
1897 9872 |
3143 2008 |
25845 41671 |
|
Zenbook 14 |
Core Ultra 7 155H Intel Arc GPU |
396 |
3453 |
1637 13367 |
2290 12256 |
34889 38268 |
|
MacBook Pro 2022 |
Apple M2 10-core GPU |
407 |
— |
1579 8730 |
2581 9641 |
28852 42673 |
|
MacBook Air 2022 |
Apple M2 8 core GPU |
405 |
— |
1577 8476 |
2578 9655 |
27846 39735 |
|
MacBook Pro 2020 |
Apple M1 8 core GPU |
209 |
— |
1512 7778 |
2335 8315 |
21646 32743 |
|
MacBook Pro 14-inch 2021 |
M1 Max 24Core GPU |
300 |
— |
1549 12508 |
2378 12239 |
65432 101045 |
MacBook M3 appears about 20-25% faster than M2 in single-core and multi-core benchmarks, and in comparison with M1, it increases its superiority to about 35-45%; Therefore, considering the 15% increase in frequency and the improvement of TSMC’s manufacturing process, it seems that Apple has not changed much in the architecture; But in any case, CPU performance on par with the M1 Pro is a surprising result for the M3.
Compared to the new Asus ultrabook with the Core Ultra 7 155H chip, MacBook Air M3 leads by 15-35% in single-core benchmarks; But in multi-core benchmarks, it loses the field to the competitor with a single-digit difference of up to 25%. We will talk more about the difference between the two chips in productivity and power consumption.

Apple laptops have a stunning performance in terms of web surfing experience and M3 has taken this performance to a whole new level; MacBook Air 2024 outperforms Asus Ultrabook 2024 with a 65% difference in the Zoomit web browsing test. The stunning superiority of the MacBook Air shows that Apple’s laptop offers faster and smoother performance on the web.
Apple’s new ultrabook appears in almost the same level of computing processing as the last generation. It seems that M3 remains behind its Intel competitor by 25% in the processes that take place on the basis of the OpenCL framework; But instead, thanks to Apple’s exclusive Metal framework, it surpasses the performance of Core Ultra 7 in processes based on Vulkan, with a difference of 10%.
Let’s skip the benchmarks and talk about how the MacBook Air 2024 performs in professional software and games. For this, we considered Photoshop and Premiere Pro software, Python code execution, and the Rise of the Tomb Raider game.
The set of games available for macOS is much more limited than for Windows; However, thanks to the tool that Apple introduced at WWDC 2023 for porting Windows games (Game Porting Toolkit), some were able to run titles such as Medium and Cyberpunk 2077 on Macs with powerful graphics processors such as the M2 Max, and it is hoped that in the future, this same tool, pave the way for more games to be released.
We were able to run the old game Rise of the Tomb Raider at 1200p resolution, High graphics settings and an average frame rate of 50.5 fps, which shows an advantage of about 25 percent of the M3 compared to the M2.
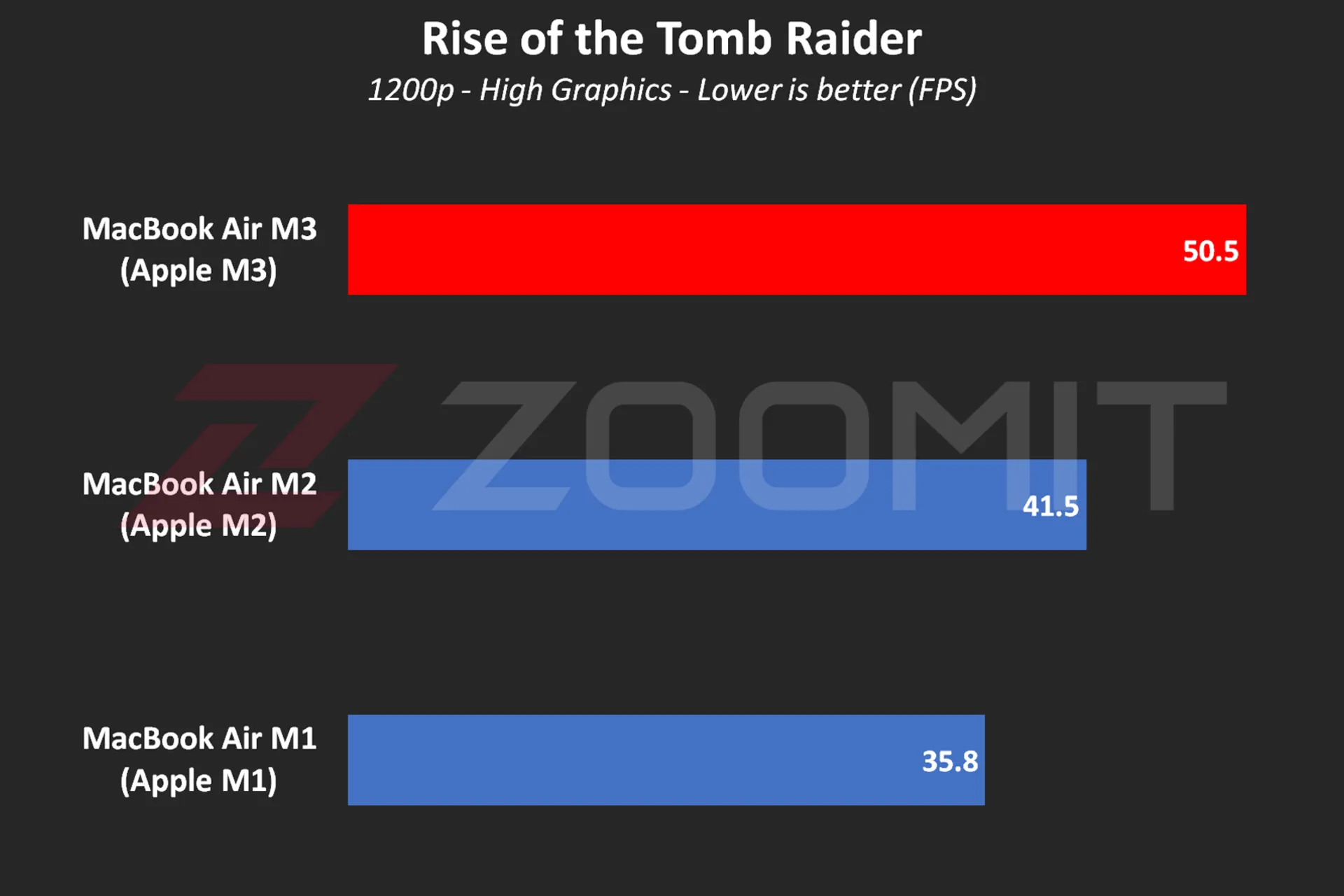 MacBook Air M3 performance while playing Rise of the Tomb Raider game
MacBook Air M3 performance while playing Rise of the Tomb Raider game
MacBook Air M3 works about 10 to 20 percent faster than its two previous generations and ZenBook 14 while using Photoshop software for tasks such as resizing large photos and implementing the blur effect or lens correction.
 MacBook Air M3 performance in Photoshop software
MacBook Air M3 performance in Photoshop software
In Premier Pro software, while performing tasks such as blur effect implementation, image sharpening, or 4K video output, the performance of the device is 20-30% better than the MacBook Air M2 and Zenbook 14.
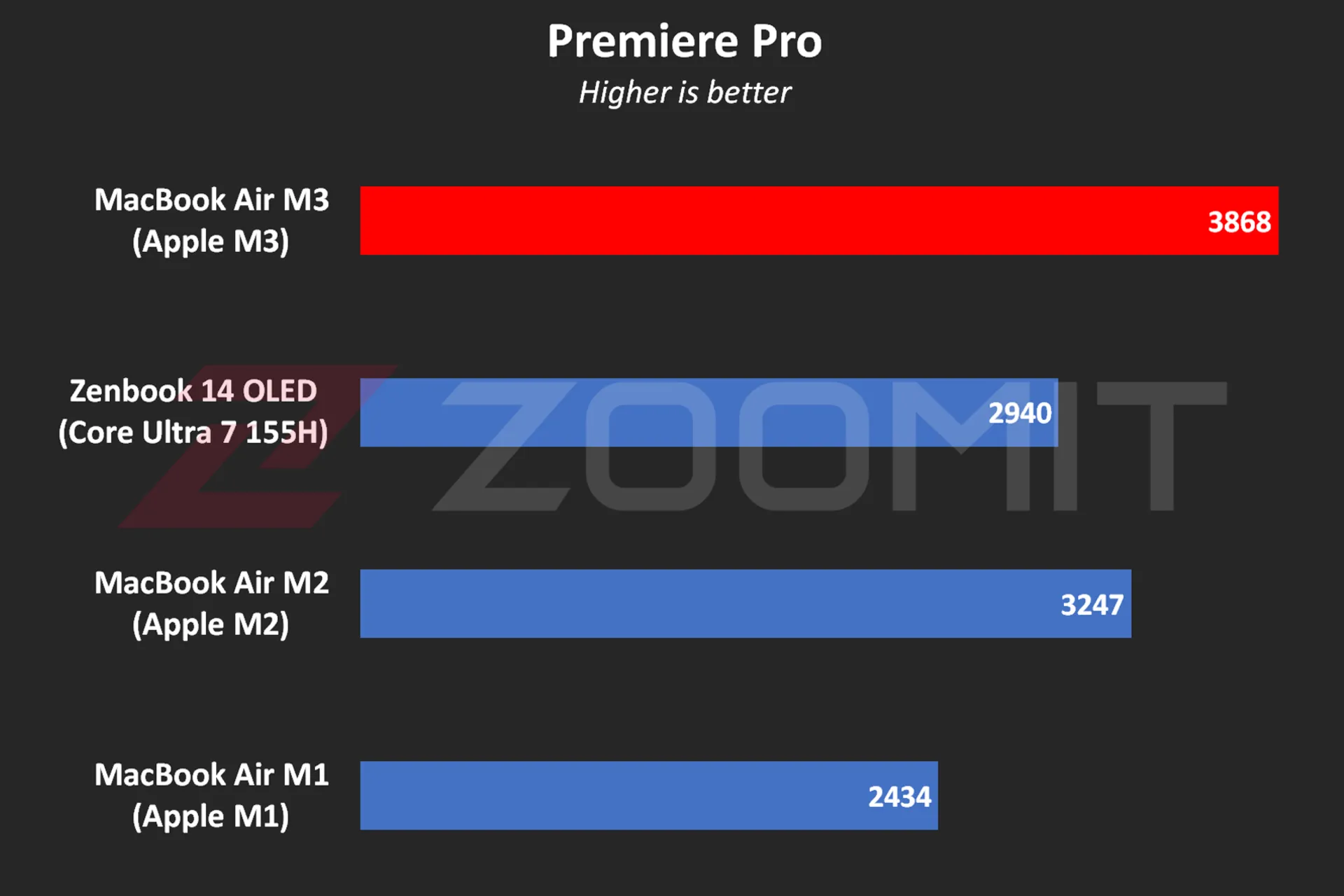 Performance of MacBook Air M3 in Premier Pro software
Performance of MacBook Air M3 in Premier Pro software
Note that in software such as Premiere Pro, where we are dealing with heavy projects, the low RAM overshadows the performance level and you may even get stuck in scenarios like editing 4K videos. Next, we will talk about the MacBook Air M3 RAM.
The MacBook Air was able to run Zoomit’s Python code in about 45 seconds, which is about 13 seconds faster than the M2 and 33 percent faster than the M1.
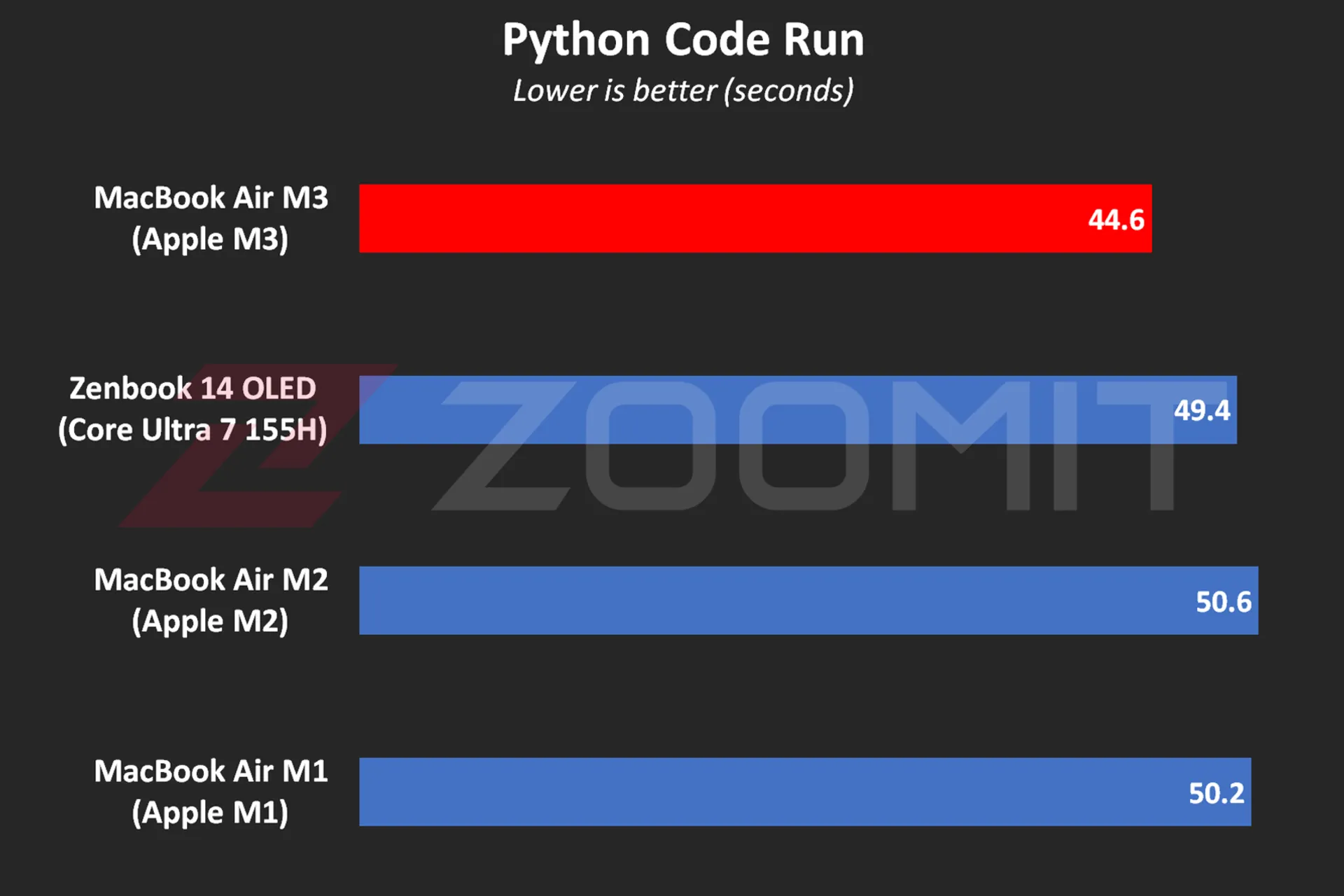 MacBook Air M3 performance while running Python code
MacBook Air M3 performance while running Python code
One of the most attractive features of MacBooks is that they work equally well, whether connected to electricity or relying on batteries; For example, when running Python code while plugged in, the MacBook Air M3 beats the ZenBook 14 by just 4 seconds; But by disconnecting the laptops from the electricity and Zenbook’s performance drop, the time difference reaches 11 seconds!
In addition to running Python code, the MacBook Air also displays similar performance in other software in both plugged-in and battery-powered states; In the table below, you can see the difference in performance of MacBook Air M3 in Plugged and UnPlugged modes in a number of users:
|
Performance of MacBook Air 2024 when connected to electricity and with battery |
||
|---|---|---|
|
Test/Performance |
Plugged result |
Result UnPlugged |
|
CineBench 2024 (MultiCore) |
574 |
573 |
|
Speedometer 2.1 |
680 |
681 |
|
Photoshop |
6488 |
6588 |
|
Premiere Pro |
3868 |
3881 |
|
Python |
44.6 seconds |
44.7 seconds |
In the MacBook Air 2022 review, we said that the lack of an active cooling system (fan) makes this ultrabook unable to provide stable performance under continuous processing loads. Now it’s time for MacBook Air 2024 with the same cooling system; But this time with a more optimized chip, it will be wider. Does the MacBook Air M3 offer stable performance?
To evaluate the cooling system, the performance stability level and measure the power consumption and other parameters of the MacBook Air M3, we first ran the CineBench R23 multi-core test on the device for 30 minutes consecutively in both power-connected and battery-based modes; Then we went to the 20-minute Wild Life Extreme test.
|
MacBook Air 2024 laptop performance under continuous processing load |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Laptop status |
CPU score at first |
CPU score after 30 minutes |
GPU score first |
GPU score after 20 minutes |
|
Connected to electricity |
9872 |
7841 |
6989 |
5207 |
|
with battery |
9833 |
8322 |
6996 |
5271 |
MacBook Air M3 shows more or less the same behavior whether in Plugged or UnPlugged mode; After 30 minutes, the CPU performance drops by about 15-20%, and in a 20-minute graphics processing load, the GPU drops by 25%.
Contrary to the numbers stated in the technical specifications of the M3 chip, the MacBook Air 2024, whether in multi-core or single-core processing, never reaches the frequency of 4.05 GHz in powerful cores; In my measurements, the frequency of the most powerful cores in the multi-core test remained at 3.7 GHz for a few seconds; But it immediately begins the gradual process of decline and reaches below 2.5 GHz from the 10th minute, which is lower than the stable 2.75 GHz frequency of low-power cores!
Read more: Asus Zenbook 14 OLED laptop review
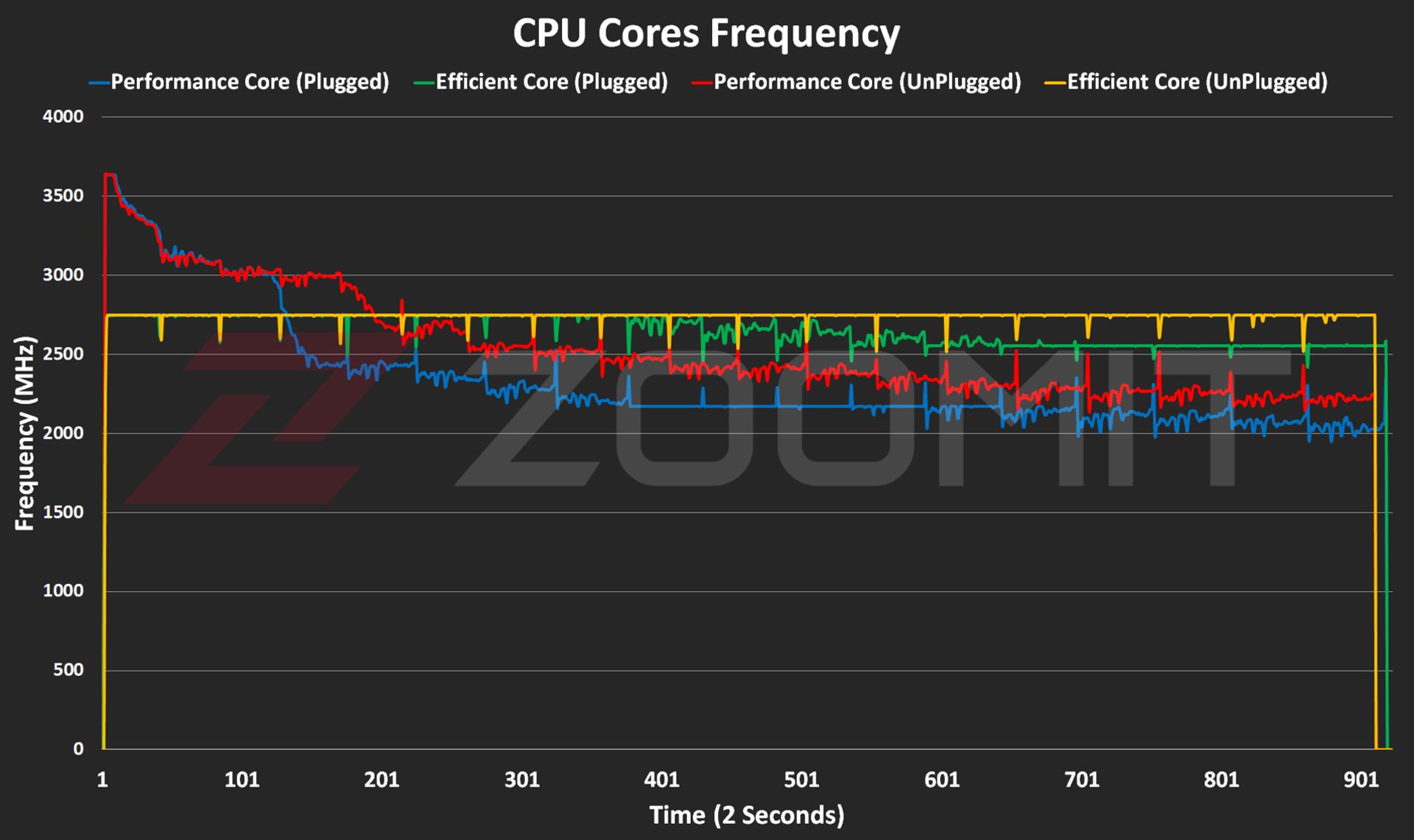 CPU frequency in MacBook Air M3
CPU frequency in MacBook Air M3
The frequency drop process starts when the temperature of the hottest point of the chip reaches 103 degrees Celsius; It seems that Apple has adopted a more conservative strategy this year; Because in MacBook Air M2, the maximum temperature of the chip reaches 109 degrees Celsius. The temperature of 103 degrees of the chip continues for 5-6 minutes and then, thanks to the frequency drop, it decreases to the range below 90 degrees Celsius.
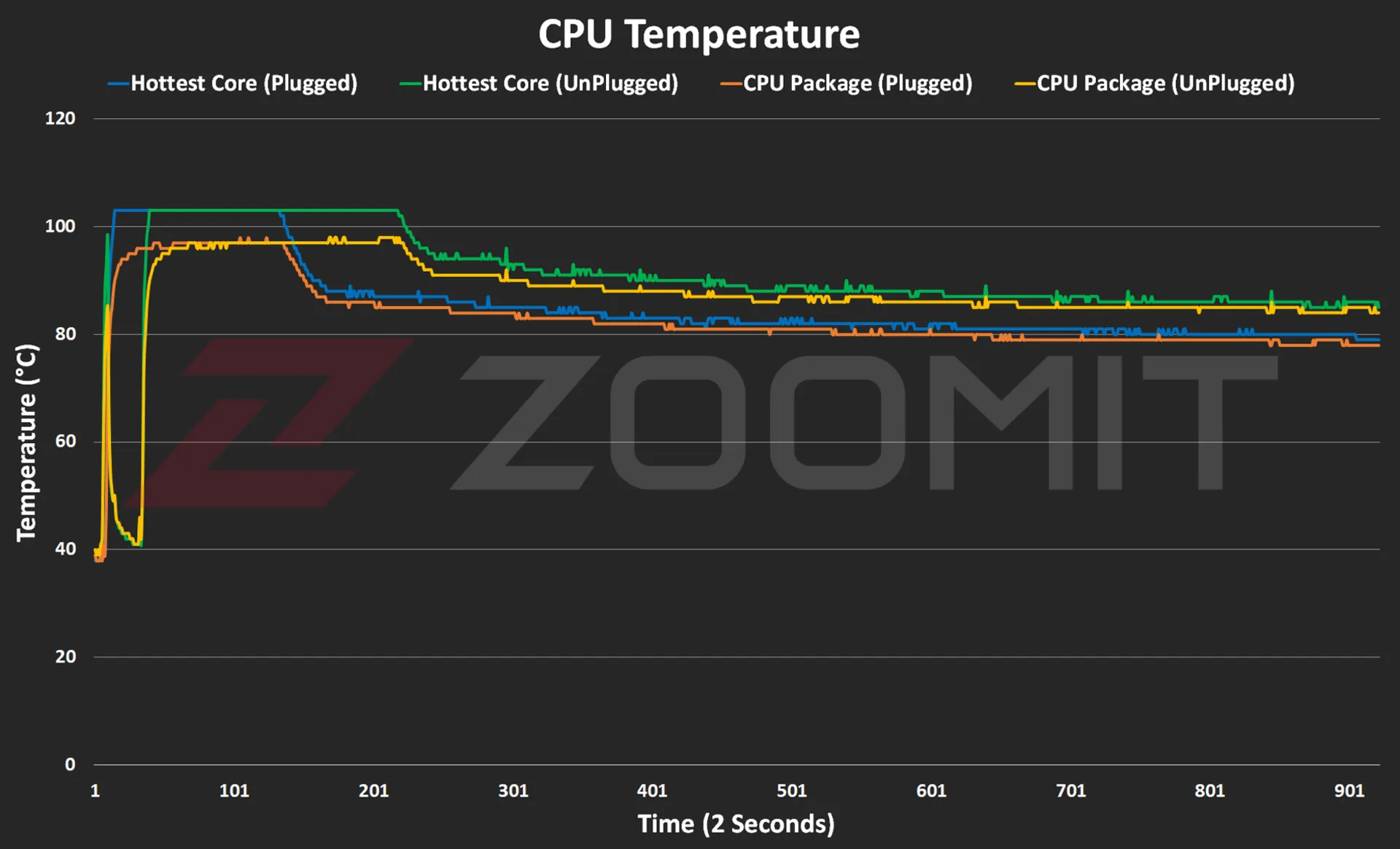 CPU temperature on MacBook Air M3
CPU temperature on MacBook Air M3
The temperature of the laptop body rises to 46-47 degrees Celsius, especially in the upper area of the keyboard; But in general, the body heat is not such that you cannot continue working with the laptop.
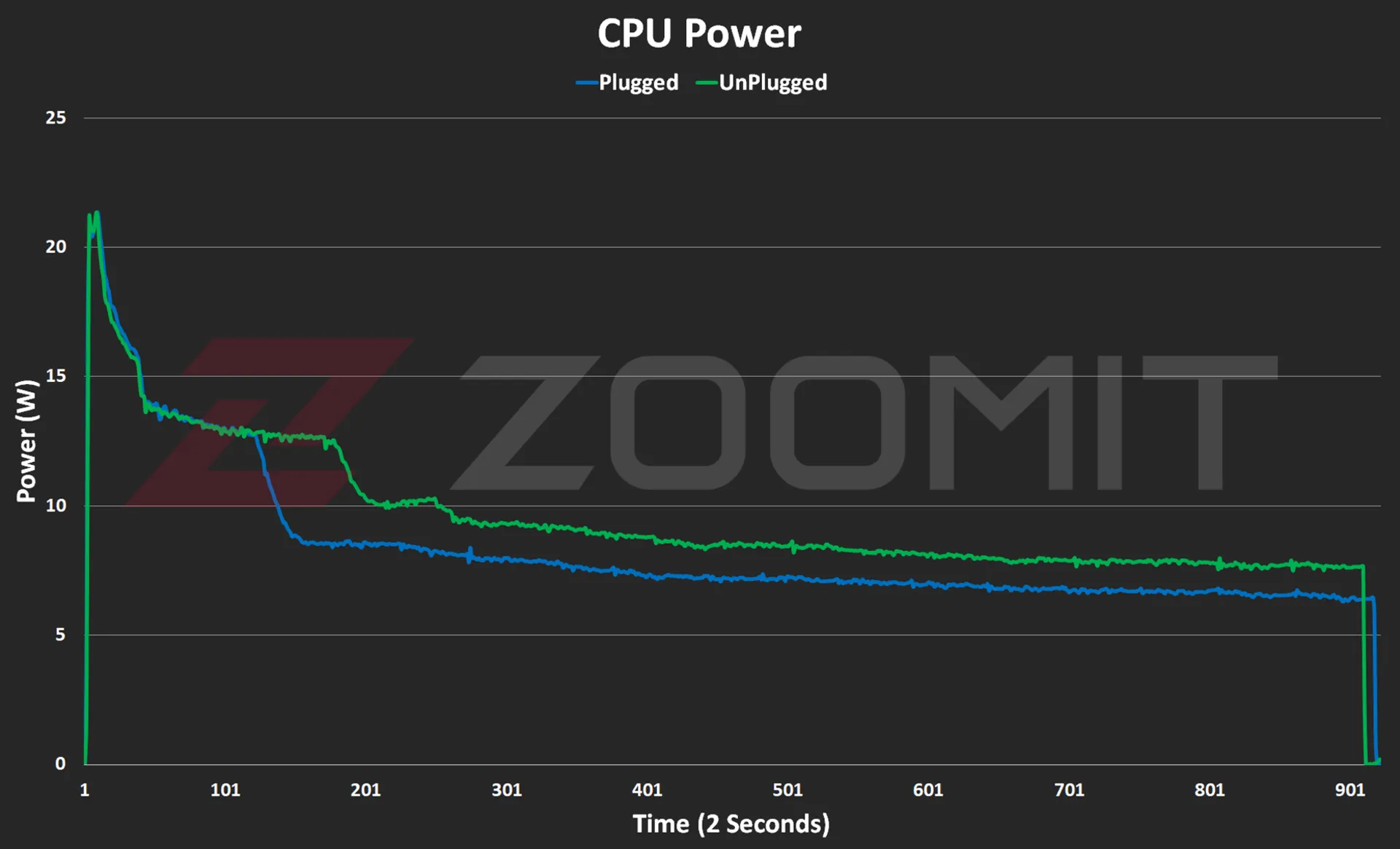 CPU consumption in MacBook Air M3
CPU consumption in MacBook Air M3
As you can see in the power consumption graph, the CPU consumes about 21 watts in the first few seconds; But as the body heats up, the power consumption gradually decreases and after a few minutes it reaches below 10 watts and reaches the range of 7-8 watts.
As you can see from the graphs below, the M3 GPU also follows a similar path to performance degradation from overheating the device.
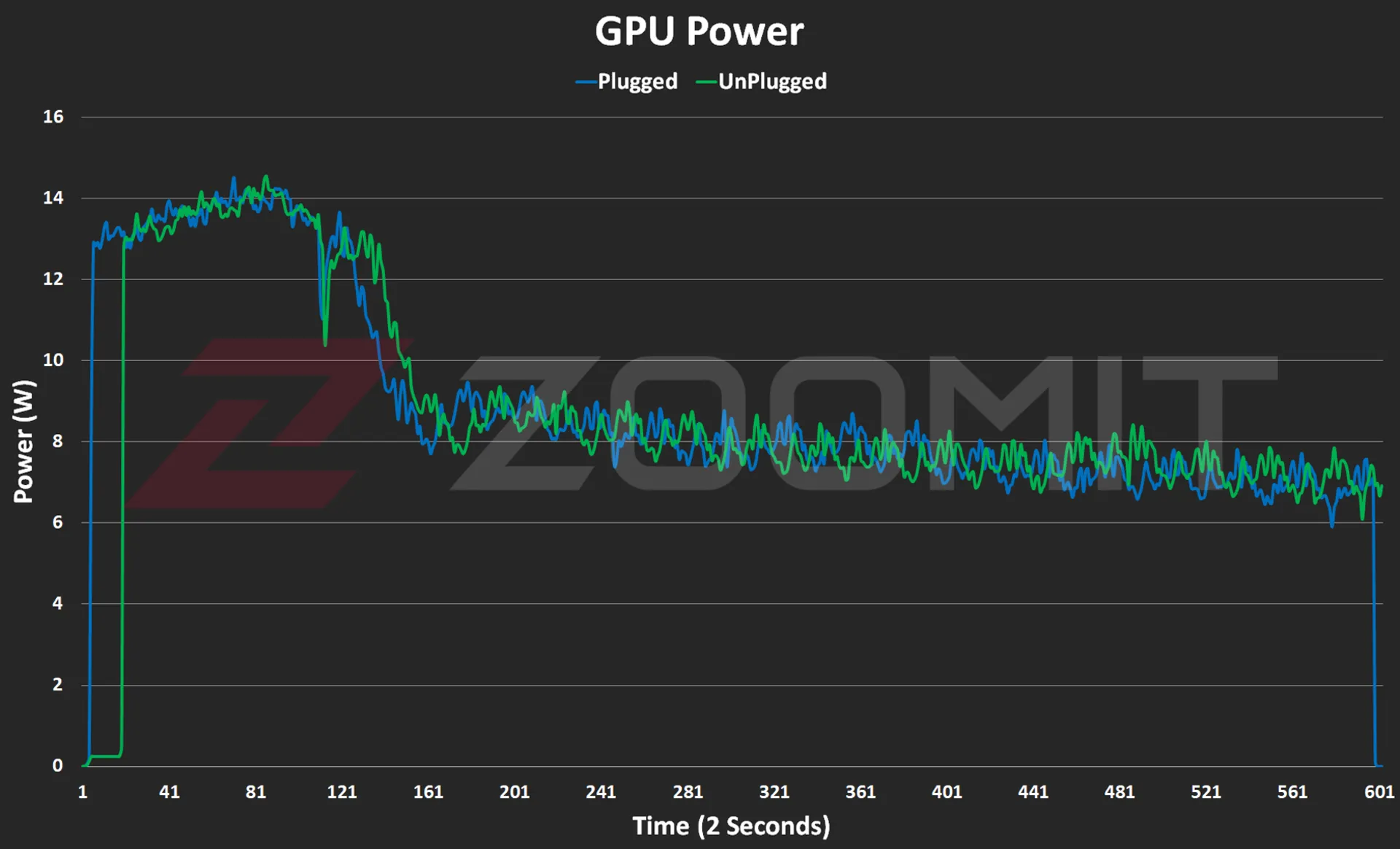 GPU consumption in MacBook Air M3
GPU consumption in MacBook Air M3
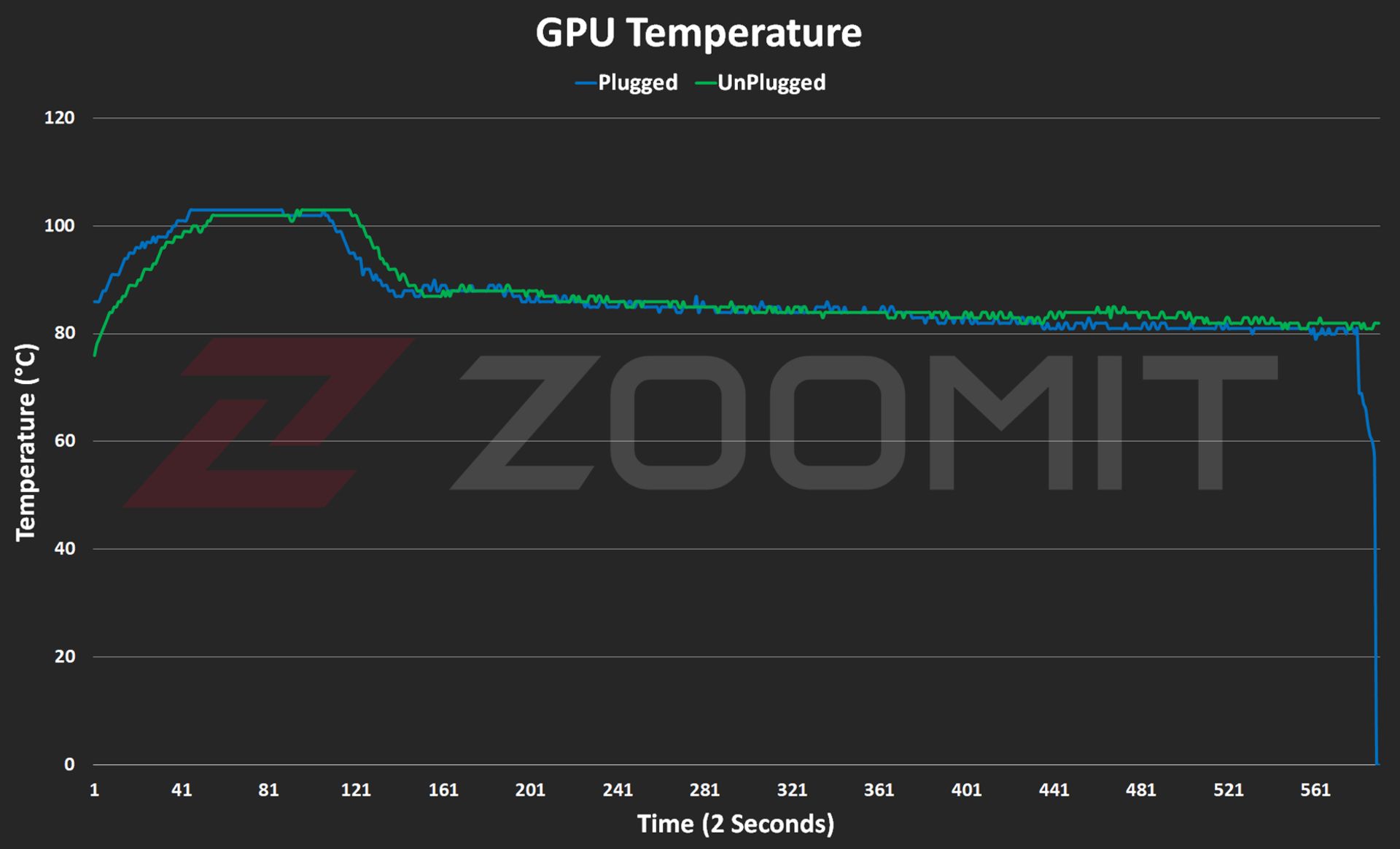
GPU temperature on MacBook Air M3
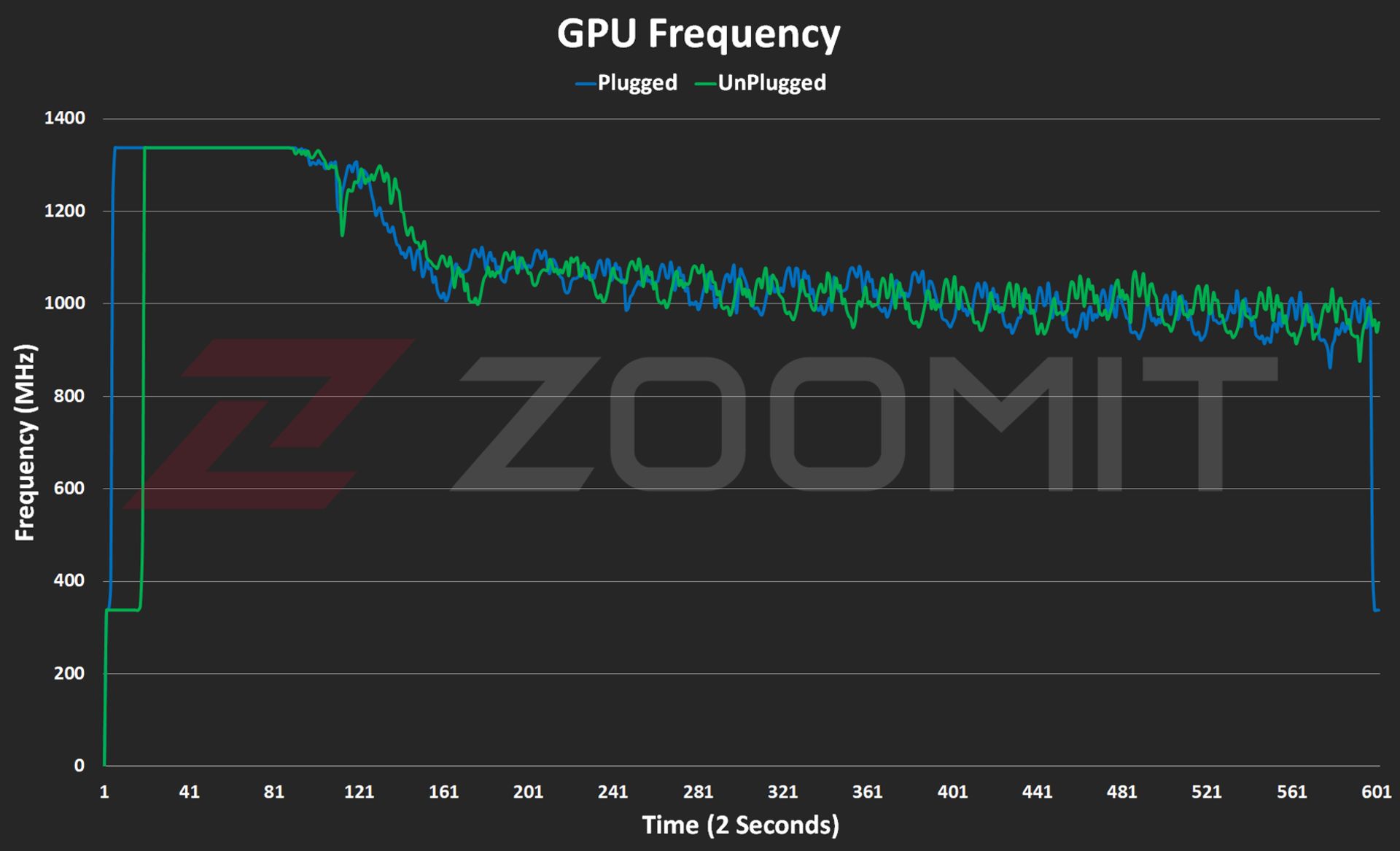
GPU frequency on MacBook Air M3
About 2-3 minutes after the start of graphic processing, in order to prevent the chip temperature from exceeding 103 degrees Celsius, the frequency of the GPU drops from about 1350 MHz and its power consumption from about 14 watts to 1000 MHz and below 8 watts. is approaching
My tests show that the MacBook Air M3 uses its powerful core stably with a frequency of about 3,750 MHz in single-core processing, this number is about 3,200 and 2,980 MHz in the MacBook Air M2 and MacBook Air M1 laptops, respectively.

In order to have a general outline and limits of architecture changes and IPC (the number of instructions executed per processing cycle), we can divide GeekBench’s single-core score by the chips’ single-core frequency; Note that this measure is not exact and only provides a general picture of the state of architectural changes. To accurately measure IPC, one should go to an expensive tool such as SPECView, which unfortunately is not available in Iran.
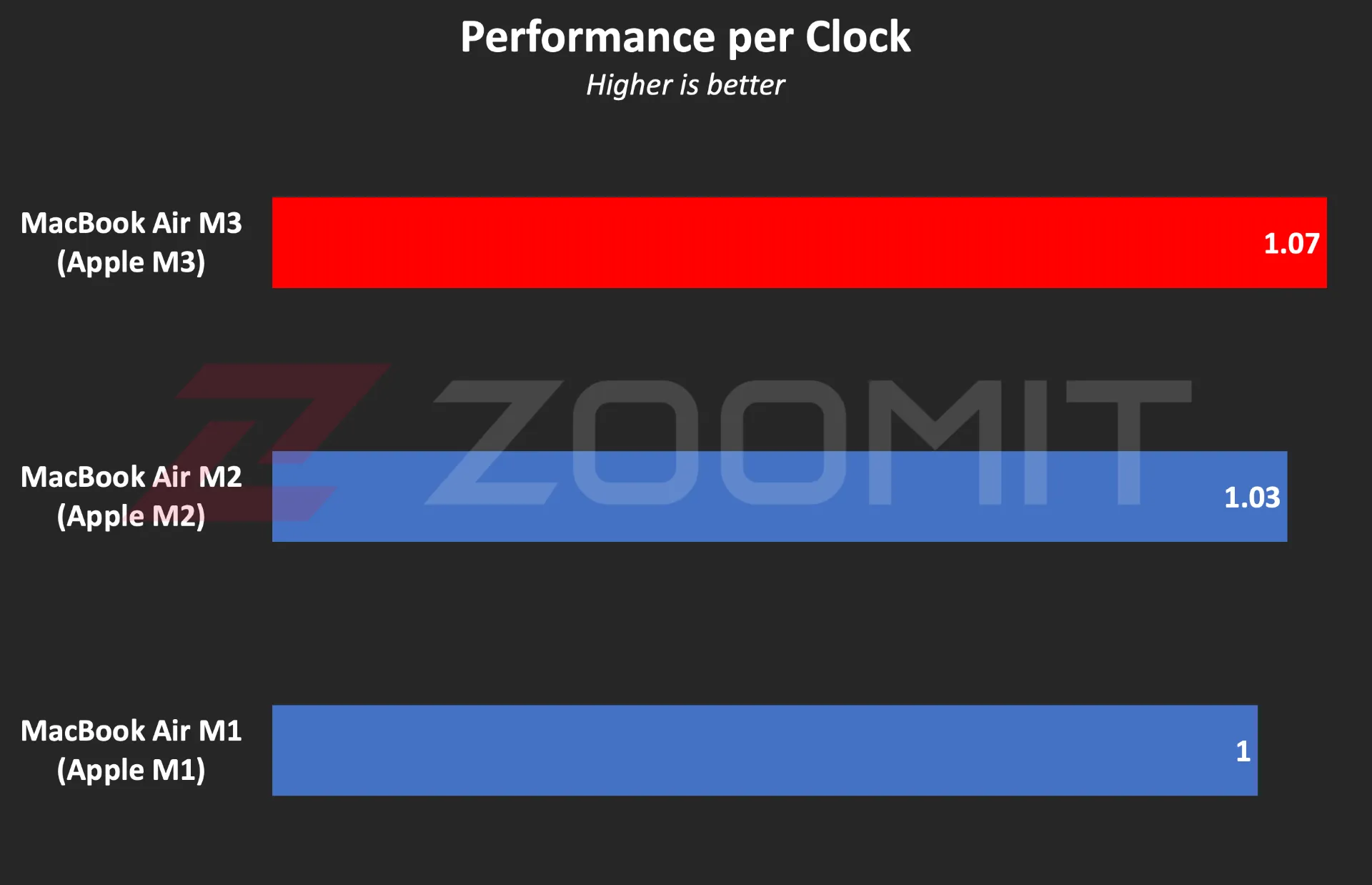 Ratio of performance to CPU frequency
Ratio of performance to CPU frequency
To be more precise, what you see in the graph above is the ratio of single-core performance to CPU frequency in three generations of MacBook Air laptops with M1, M2, and M3 chips. In this chart, I have considered the MacBook Air M1 as a benchmark so that we can compare the other two chips relatively. The numbers say that the architectural changes in M3 have a 4 and 7 percent impact on the performance of this chip compared to M2 and M1, which is not a significant improvement.
In the graph below, you can see the ratio of M3’s performance to its power consumption compared to previous generations and the Core Ultra 7 155H chip. Note that the amount of power consumed by the chips is not stable and after a few seconds, it deviates from its maximum value; Therefore, the graph below was created by running CineBench R23 once and based on the average power consumption during the benchmark execution period, so that we can obtain the ratio of performance to power consumption in the best performance condition of the laptop.
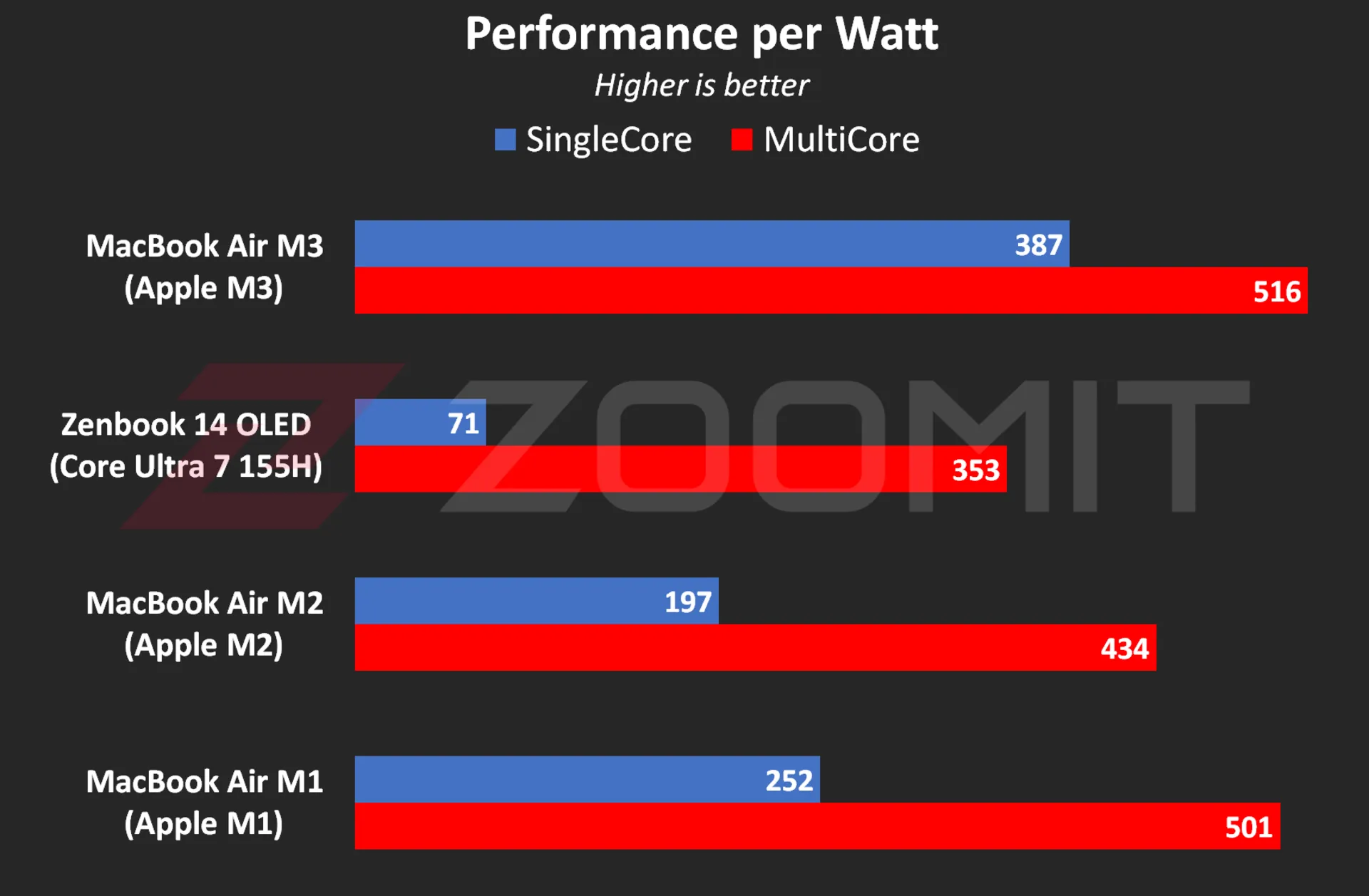 The ratio of performance to CPU power consumption
The ratio of performance to CPU power consumption
My measurements show that the M3 consumes an average of 4.9 and 19.1 watts when running the CineBench R23 single-core and multi-core benchmarks, respectively; While these numbers are equal to 8 and 20.2 watts for the M2 and 23 and 37.8 watts for the Core Ultra 7 155H, respectively, this shows the stunning efficiency of the M3; But if you consider the numbers obtained in the previous chart, you will realize that TSMC’s optimized manufacturing process has more influence on this amazing productivity than IPC and Apple’s architecture improvements.
The M3’s incredible efficiency also contributes to the MacBook Air M3’s excellent charging performance. Apple uses the same 52.6-watt-hour battery as the MacBook Air M2 in its new ultrabook and says that this laptop can charge for about 18 hours, just like the previous generation.
|
MacBook Air 2024 battery life compared to other laptops |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Laptop/Test |
Functional profile |
hardware |
Display |
Battery capacity |
Play offline video |
Everyday use |
|
Processor and graphics |
Dimensions, resolution, and refresh rate |
watt-hours |
720p Video |
PCMark 10 |
||
|
minute: hour |
minute: hour |
|||||
|
MacBook Air 2024 |
— |
Apple M3 8 core GPU |
13.6 inches and 60 Hz 1664 x 2560 pixels |
52.6 |
14:13 |
— |
|
Zenbook 14 |
Performance |
Core Ultra 7-155H Intel Arc |
14 inches and 120 Hz 1800 x 2880 pixels |
75 |
17:25 |
9:09 |
|
Galaxy Book 3 Ultra |
Performance |
Core i7-13700H RTX 4050 |
16 inches and 120 Hz 1880 x 2880 pixels |
76 |
11:00 |
6:21 |
|
MacBook Pro 2022 |
— |
Apple M2 10-core GPU |
13.3 inches and 60 Hz 1600 x 2560 pixels |
58.2 |
26:18 |
— |
|
MacBook Air 2022 |
— |
Apple M2 8 core GPU |
13.6 inches and 60 Hz 1664 x 2560 pixels |
52.6 |
14:11 |
— |
|
MacBook Pro 2020 |
— |
Apple M1 8 core GPU |
13.3 inches and 60 Hz 1600 x 2560 pixels |
58.2 |
16:47 |
— |
|
MacBook Pro 14-inch 2021 |
— |
M1 Max 24Core GPU |
14.2 inches and 120 Hz 1964 x 3024 pixels |
70 |
18:14 |
— |
The MacBook Air 2024 was able to play our benchmark HD video for a little over 14 hours, just like the previous generation, in standard Zoomit conditions, which includes 200 nits brightness (about 70% brightness) and flight mode activation, which is an impressive result; But it is about 3 hours less than the Asus Zenbook 14 Ultrabook with a larger 75 watt-hour battery.
… and 8GB RAM for everyone
Unfortunately, this year Apple did not fall short either, and in 2024, it released the basic version of its $1,100 ultrabook with 8 GB of RAM and 256 GB of SSD. If you buy from Apple’s website, you can order 16GB or 24GB of RAM and 512GB, 1TB, and 2TB of SSD; Of course, to go to each higher step, you have to pay 200 dollars more; For example, the MacBook Air 2024 with 16 GB RAM and 512 GB SSD will cost you about $1,500.
If the base version of the 8GB MacBook Air disappointed you, you can be glad that Apple has moved away from the cowardly strategy of using a NAND chip for the SSD of the base version of the MacBook Air, which ended up halving the read and write speeds, and this year all models with 2 sells NAND chips; The maximum speed of 4 and 3.5 GB/s for reading and writing is lower than Windows competitors; But it’s not bad either.
|
The average SSD speed of the base model MacBook Air 2024 compared to other MacBooks |
||
|---|---|---|
|
Models / Performance |
Sequential reading rate (UK gigabytes) |
Sequential write rate (UK gigabytes) |
|
MacBook Air M3 |
2.63 |
2.58 |
|
MacBook Air M2 |
1.03 |
2.32 |
|
MacBook Pro M1 |
2.28 |
2.46 |
There is a lot of debate on social networks about whether 8GB of RAM is sufficient or not. A number of Apple fans, with the logic that “MacBook RAM has high speed and memory swap technology is available to help SSD as RAM”, say that in many applications, 8 GB of RAM is enough; But you should pay attention to several points:
1. The data is not just traveling between the chip and RAM, which can compensate for the low capacity of the RAM by just having a high data exchange rate; In some applications, such as modeling or graphic work, several gigabytes of data may be stored in RAM for a relatively long time. Let’s say that the data exchange rate between the RAM and the M3 or M2 chip is no longer the best, and some chips such as the Core Ultra 7 155H offer a higher rate.
2. Memory swap is not a magical and new technology; The rest of the operating systems, such as Windows, also have similar technology; But it should be noted that swap memory reduces the useful life of SSD and the speed of SSD is not at the level of RAM that can fully play its role; For example, in MacBook Air M3, the data exchange rate between RAM and chip also reaches 102 GB/s; While the Mac SSD read and write rate is maybe one twentieth of this number.
3. Software tools are constantly developing, and their need for hardware resources, including RAM, also increases day by day. On the other hand, the user also buys the MacBook for a few years of use; Therefore, due to the lack of ability to upgrade RAM, one may face problems over time.
Aside from all the talk about Rome, a number of domestic sellers are also taking advantage of the opportunity; For example, Apple charges the same amount for a MacBook Air with 16 GB of RAM and 256 GB of SSD as for an 8 | 512 GB considered; But in Iran, configuring MacBook with more RAM is much more expensive than configuring with more SSD.
MacBook Air M3; Attractive and not very valuable
The MacBook Air M3 is by no means a bad product; But what makes buying this ultrabook illogical is the great value of its predecessors, especially the MacBook Air M1, especially if we consider their significant price difference.
For a person who does not have a laptop and is looking for a compact and well-made ultrabook for daily and light use, the base model of MacBook Air M1, which is currently sold at a price of 47-48 million Tomans, is a very desirable option; A device with an integrated metal body, a high-quality display, a very good keyboard and trackpad, excellent charging and fast performance that meets all the needs of an individual with daily use, journalism or light content production; Without the need to take an irrational action, about 25 million Tomans more will be spent to buy M3.

A person who already has a MacBook Air M2 and uses it for daily use should not go for the MacBook Air M3; Because it will not experience any significant changes; Except for the faster SSD, which is hardly noticeable in everyday use. For a current Mac M1 user, it might make more sense to upgrade to the M3.
For people who use laptops for tasks such as programming or video editing, the 8GB version of the MacBook Air M3 is not really a rational choice. If these people prefer macOS, it is better to go for used models with a budget of 70-75 million tomans, such as M1 Pro with 16 GB RAM, or if they are comfortable with Windows, high-quality options such as HP Envy with Core i9-13900H processor. And 16 GB of RAM will be a reasonable option for them.


What are the obstacles on the way for humans to reach Mars?


Unveiling of OpenAI new artificial intelligence capabilities


Samsung S95B OLED TV review


Discovery of the brain circuit that manages inflammation


History of the world; From the Big Bang to the creation of the planet Earth


Xiaomi Pad 6S Pro review


Is Telegram really safe?


The biography of Pavel Durov


AI PC; revolutionary technology of the future?


Motorola Edge 50 Pro review, technical specifications
Popular
-



 Technology10 months ago
Technology10 months agoWho has checked our Whatsapp profile viewed my Whatsapp August 2023
-



 Technology11 months ago
Technology11 months agoHow to use ChatGPT on Android and iOS
-



 Technology10 months ago
Technology10 months agoSecond WhatsApp , how to install and download dual WhatsApp August 2023
-



 Technology11 months ago
Technology11 months agoThe best Android tablets 2023, buying guide
-



 AI1 year ago
AI1 year agoUber replaces human drivers with robots
-


 Humans1 year ago
Humans1 year agoCell Rover analyzes the inside of cells without destroying them
-



 Technology11 months ago
Technology11 months agoThe best photography cameras 2023, buying guide and price
-


 Technology11 months ago
Technology11 months agoHow to prevent automatic download of applications on Samsung phones