Technology
The planet Saturn; Features, number of moons, rings and wonders
Published
4 months agoon


The planet Saturn; Features, number of moons, rings, and wonders
Saturn is the sixth planet in terms of distance from the Sun and the second largest planet in the entire solar system. Saturn can be called the lord of the rings of the solar system due to its thousands of beautiful and unique rings. Like Jupiter, this planet is a gas giant with a radius 9 times that of Earth, while its density is one-eighth that of Earth.
Saturn’s internal structure is a mixture of iron, nickel, and rock (silicon and oxygen compounds). The core of the planet is surrounded by a layer of metallic hydrogen, the middle layer consists of liquid hydrogen and helium, and finally there is a gaseous outer layer. The reason for Saturn’s soft yellow color is the presence of ammonia crystals in its upper atmosphere. The electric current inside the metallic hydrogen layer has increased the magnetic field of this planet. The strength of Jupiter’s magnetic field is twenty-one times that of Saturn. The outer atmosphere of this planet is calm and without turbulence. The wind speed in some areas of Saturn reaches 1800 km/h, which is more than Jupiter.
From the collection of articles on the introduction of planets: The planet Mars; Everything you need to know
So far, at least 83 moons have been discovered in the orbit of Saturn, 53 of which have been officially named. The largest moon of Saturn, Titan, is the second largest moon in the solar system and is even larger than the planet Mercury. Titan is the only moon in the entire solar system that has a significant atmosphere. The most striking feature of Saturn is its ring system, which is a combination of ice particles and small pieces of rock.
-
What does the planet Saturn symbolize?
-
How was the planet Saturn formed?
-
Nucleus aggregation model
-
Disk instability model
-
Saturn is how many times the size of Earth?
-
Physical characteristics and internal composition of the planet Saturn
-
Saturn’s atmosphere and clouds
-
Saturn’s magnetic field
-
The orbit and rotation of Saturn
-
Rings of Saturn
-
How many moons does Saturn have?
-
Grouping of Saturn’s moons
-
Irregular moons
-
Alkeonides
-
Titan
-
The potential for life on Titan
-
Enceladus
-
Iaptus
-
Hyperion
-
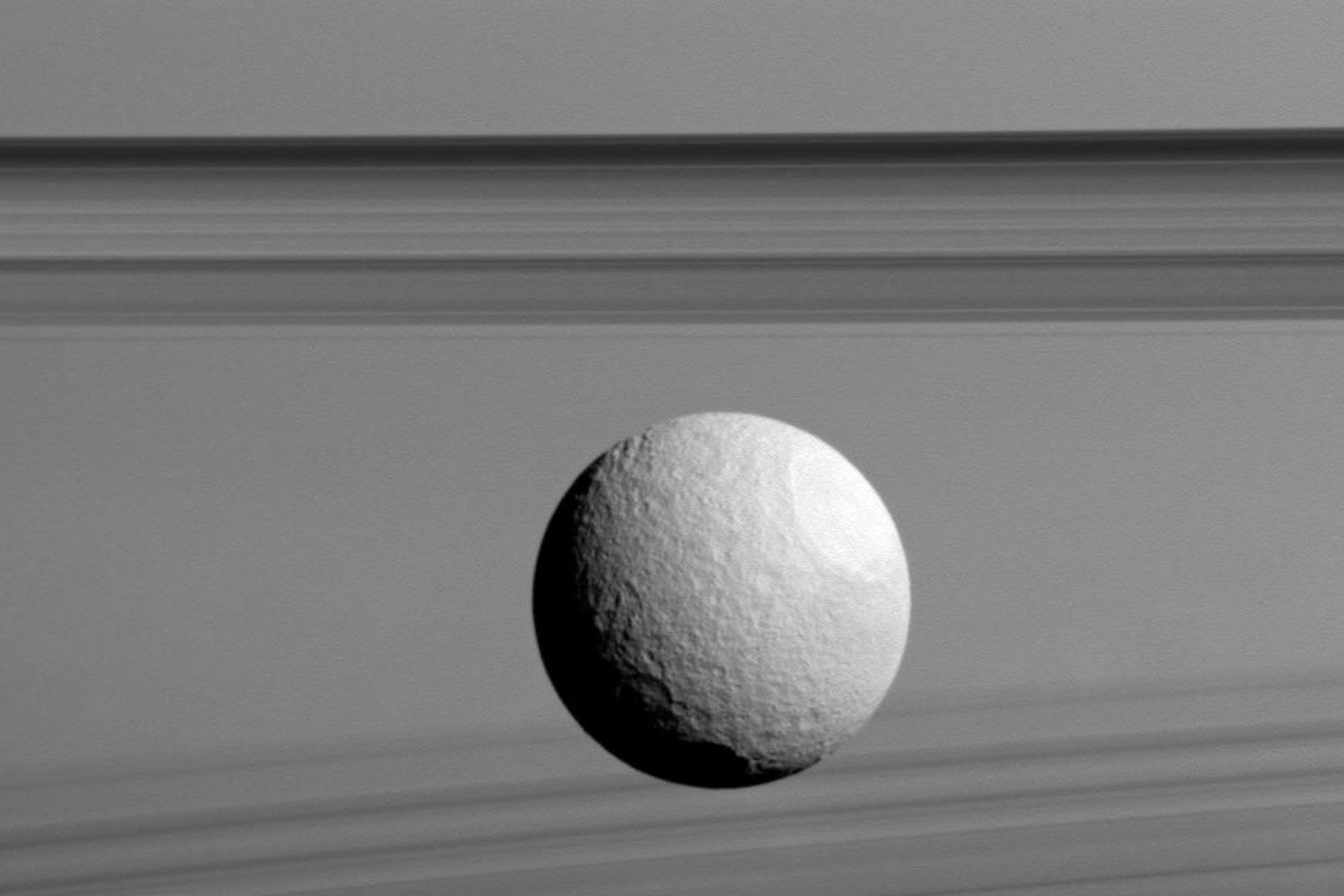
Mimas
-
Pan and Atlas
-
Rhea
-
debt
-
Tethys
-
The wonders of the planet Saturn
-
Seeing Saturn from Earth
-
Discoveries of Saturn in the Space Age
-
Pioneer discoveries 11
-
Voyager 1 and 2 discoveries
-
Cassini Huygens: Exploring the Saturn System
-
Farewell to Cassini
-
Future missions to Saturn
What does the planet Saturn symbolize?
The observation of the planet Saturn has a prehistoric age and has been recorded in myths since the first observation. Babylonian astronomers systematically observed Saturn and recorded its movements. The planet Saturn is known as Phainon in ancient Greece and as Saturn in Roman mythology.
Saturn is the Roman god of agriculture and equivalent to the Greek god Kronos, one of the Titans and the father of Zeus. The symbol of the planet Saturn is the scythe. Because Saturn is the god of agriculture and also time, this symbol is represented by a shape similar to the Greek letter eta, with a cross-like shape added on top of it, meaning the scythe of the gods. The Romans named the seventh day of the week Saturday, which stands for Saturn’s Day, and this day is named after this planet.

How was the planet Saturn formed?
Like other planets in the solar system, Saturn was formed from a solar nebula approximately 6.4 billion years ago. This nebula was a large cloud of cold gas and dust, which was probably formed by the impact of a supernova cloud or wave.
In general, there are two theories about the formation of planets in the solar system. The first and most acceptable theory is the core accretion theory, which is very close to reality in the case of rocky planets but faces problems in the case of gas giants such as Saturn. The second theory, the disc instability theory, could be true for gas giants.
Nucleus aggregation model
Approximately 6.4 billion years ago, the solar system was a cloud of gas and dust called the solar nebula. Gravity caused matter to begin to rotate. At the center of this rotation, the sun was created. With the emergence of the sun, the remaining materials joined together. Smaller particles were transformed into larger particles by the force of gravity. The solar winds carried smaller elements such as hydrogen and helium away from the regions near the sun, and in this way, heavy and rocky materials near the sun led to the formation of rocky worlds.
But at a further distance, the solar winds had less effect on the lighter elements, and thus gas giants like Saturn were born. Meteorites, comets, planets, and moons were formed in this way. It can be said that the planet Saturn is almost completely composed of light hydrogen gas, and of course, a significant part of it is helium. A small trace of other elements can be seen in its atmosphere. Saturn must have a large core to absorb these gases in this model. Thus, the gravity of the heavy core has attracted the lighter elements before they are blown away by the solar wind.

Disk instability model
However the need for a short time for the formation of gas giants is one of the problems of the core accretion model. According to the models, this process takes millions of years in the nuclear accumulation model. At the same time, the core accretion model also faces the problem of planetary migration, because small planets were placed in orbit around the Sun in a short period of time.
According to a relatively new theory known as disk instability, masses of gas and dust have joined each other in the early life of the solar system, and over time these masses have been compressed and formed gas giants. These planets are formed faster than their counterparts in the core accretion model, and their formation time even reaches several thousand years.
Saturn is how many times the size of Earth?
Saturn has 760 times the volume of Earth, it is the second heaviest planet in the entire solar system and has 95 times the mass of Earth. Saturn has the lowest density among the planets of the solar system. The density of this planet is even lower than water so if we drop Saturn in a large enough ocean, it will float on its surface.
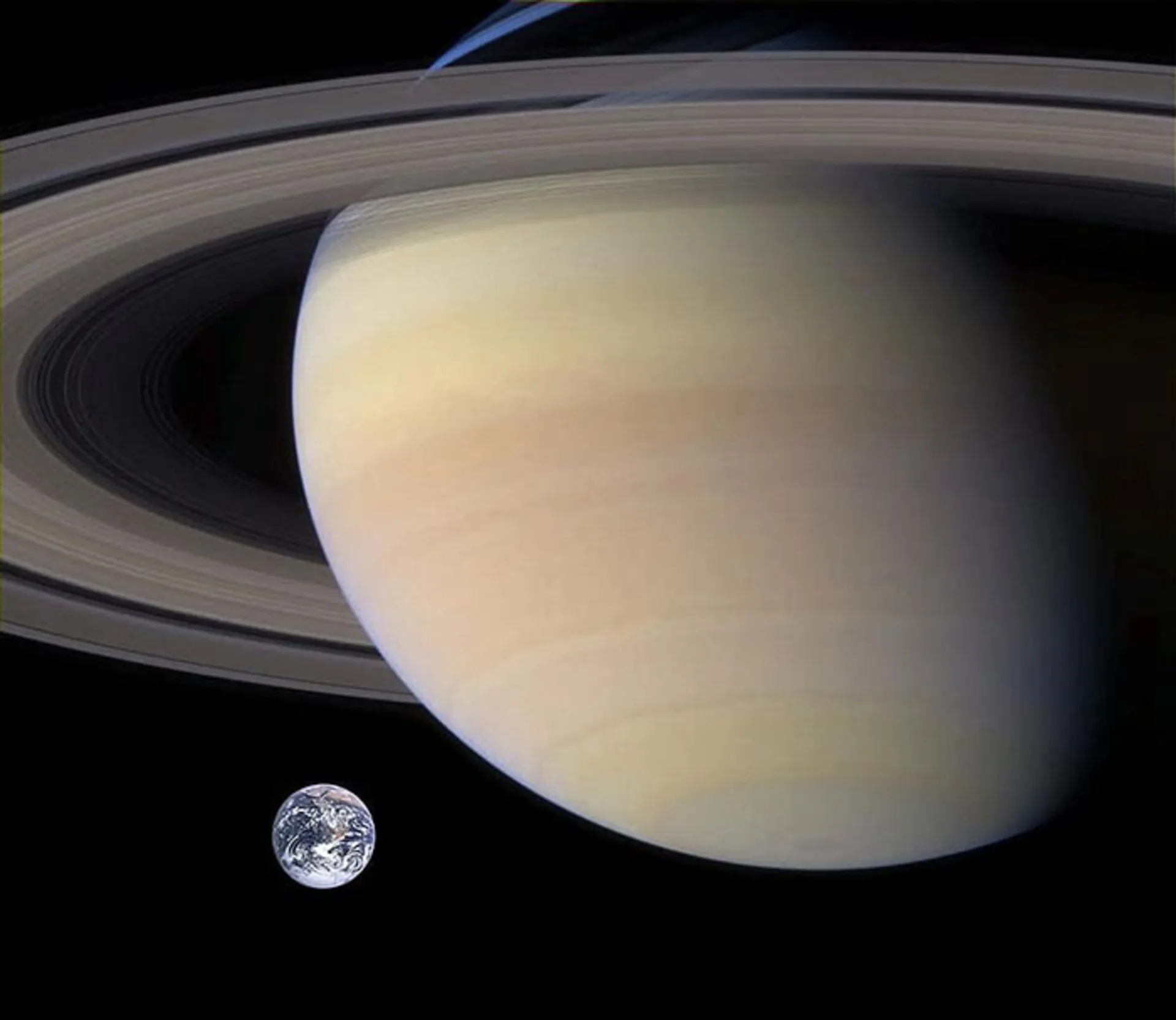

Saturn accommodates 760 Earths
Physical characteristics and internal composition of the planet Saturn
Hydrogen and helium are the dominant elements of Saturn, hence this planet is a gas giant. Like Jupiter, Saturn does not have a defined surface, although it may have a solid core. The rotation of the planet Saturn has made the shape of this planet widen at the poles and rise at the equator.
According to standard planetary models, the internal structure of Saturn is similar to the internal structure of Jupiter; It means a rocky core in the center surrounded by hydrogen and helium. The composition of Saturn’s core is similar to Earth’s, but it is more dense. In 2004, scientists estimated the mass of Saturn’s core to be 9 to 22 times that of Earth. Saturn’s core is surrounded by a thick layer of liquid metallic hydrogen, after this layer there is a liquid layer of molecular hydrogen, which gradually enters the gas phase with increasing altitude. The outermost layer is located at an altitude of 1000 km and consists of gas.
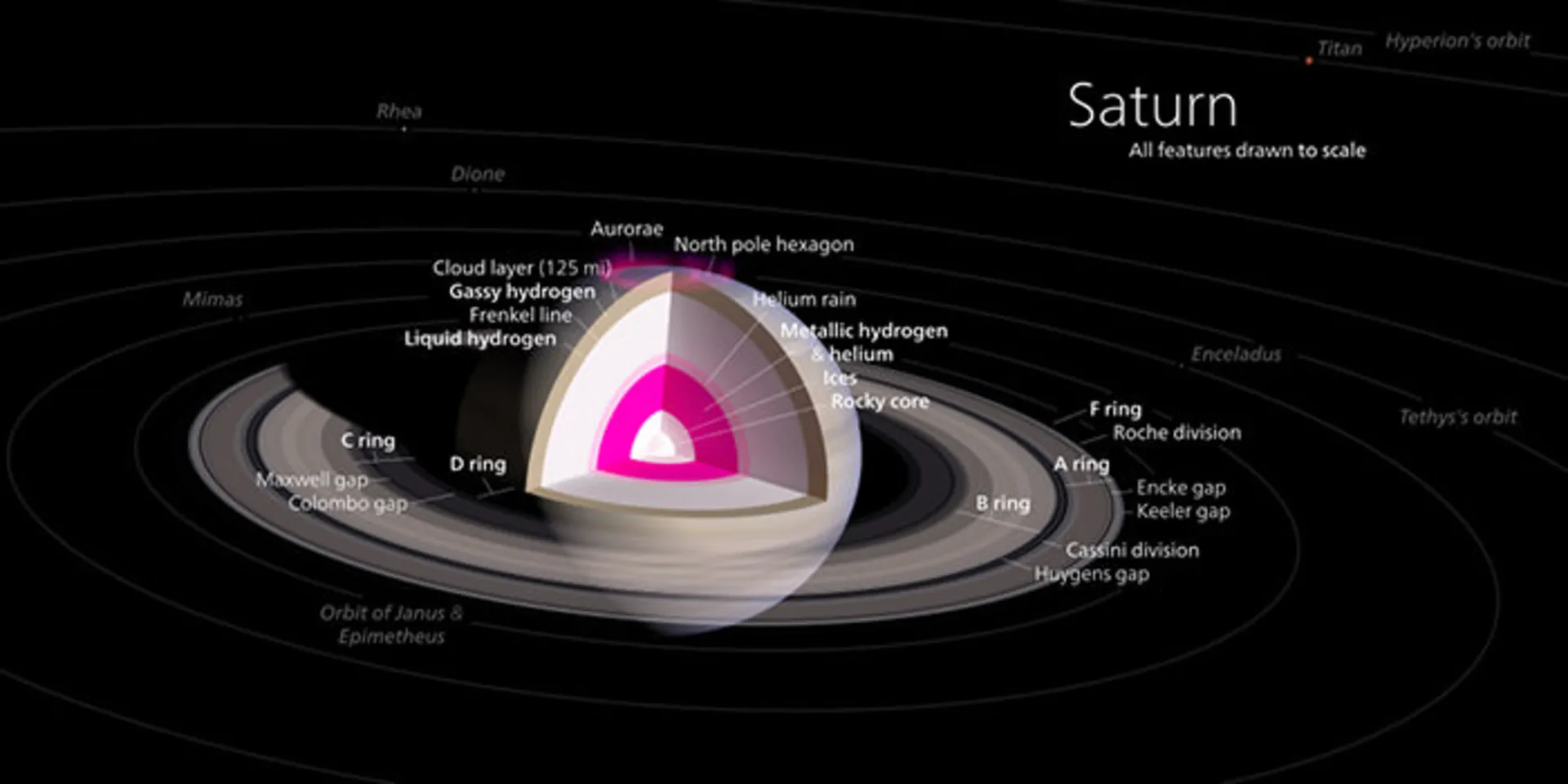
Composition diagram of Saturn: A layer of liquid hydrogen surrounds the core of this planet
The interior of Saturn is very hot and the temperature of its core reaches 11,700 degrees Celsius. Saturn releases 2.5 times the energy received from the Sun into space. Jupiter’s thermal energy is based on Kelvin Holmholtz’s slow gravitational compression mechanism (this mechanism occurs when the surface of a star or planet cools. The cooling process reduces the pressure and the star or planet shrinks), but this process is not sufficient to describe the heating of Saturn. . Another mechanism of heat production is the precipitation of helium droplets in the depths of Saturn. As the droplets fall on the low-density hydrogen, heat is released.
Saturn’s atmosphere and clouds
Saturn’s outer atmosphere contains 3.96% of molecular hydrogen and 25.3% of helium. In general, 75% of Saturn is hydrogen and 25% is helium and traces of other substances such as methane and frozen water can be found in its atmosphere. Amounts of ammonia, acetylene, ethane, propane, phosphine, and methane have also been discovered in Saturn’s atmosphere. The upper clouds are composed of crystalline ammonia, while the lower clouds are composed of ammonium hydrosulfide or water.
Although Saturn’s atmosphere is very similar to Jupiter’s, it appears uniform from a distance. Saturn’s atmosphere has a banded pattern similar to Jupiter’s. These bands become wider near the equator. The composition of clouds in different areas changes according to height and pressure increase. Saturn is one of the windiest places in the entire solar system and the wind speed in its equatorial regions reaches 1800 km/h. The yellow and gold bands in Saturn’s atmosphere are the result of super-fast winds in the planet’s upper atmosphere. Ultraviolet rays lead to the process of photolysis or photolysis in the upper atmosphere of Saturn, which leads to a series of hydrocarbon reactions. Saturn’s photochemical cycle also changes based on its seasonal cycle.
Saturn ranks second in terms of wind speed in the solar system
Saturn ranks second in terms of wind speed in the solar system after Neptune. Sometimes intense white storms disrupt the cloud layers. One of these storms was observed by the Hubble Space Telescope in 1994. To understand the characteristics of Saturn’s atmosphere, it is better to compare it with Earth. The atmosphere of Earth and Saturn have a major difference in terms of atmospheric pressure.
The radius of the planet Saturn is approximately 9 times the radius of the Earth, and the pressure increases as it penetrates into the deeper layers of the atmosphere. NASA’s observations of this planet show that the pressure of Saturn near the core is 1000 times the pressure on Earth, and this pressure is enough to convert hydrogen into liquid and then solid metal in the planet’s core. Atmospheric pressure levels common on Earth can only be found in the upper regions of Saturn’s atmosphere, where the ammonia ice clouds are located. The temperature of Saturn’s atmosphere varies from minus 130 degrees to plus 80 degrees Celsius.
Saturn’s magnetic field
Saturn has an internal magnetic field with a symmetrical and simple shape. Saturn’s magnetosphere is much smaller than Jupiter’s magnetosphere. The rings and many of Saturn’s moons are also within this magnetosphere, in this region the behavior of charged particles is more influenced by Saturn’s magnetic field than the solar wind.
The aurora phenomenon occurs when charged particles spiral in the planet’s atmosphere along the lines of the magnetic field. On Earth, these charged particles originate from the solar wind. Cassini showed that at least some of Saturn’s auroras are similar to Jupiter’s auroras and are not affected by the solar wind.
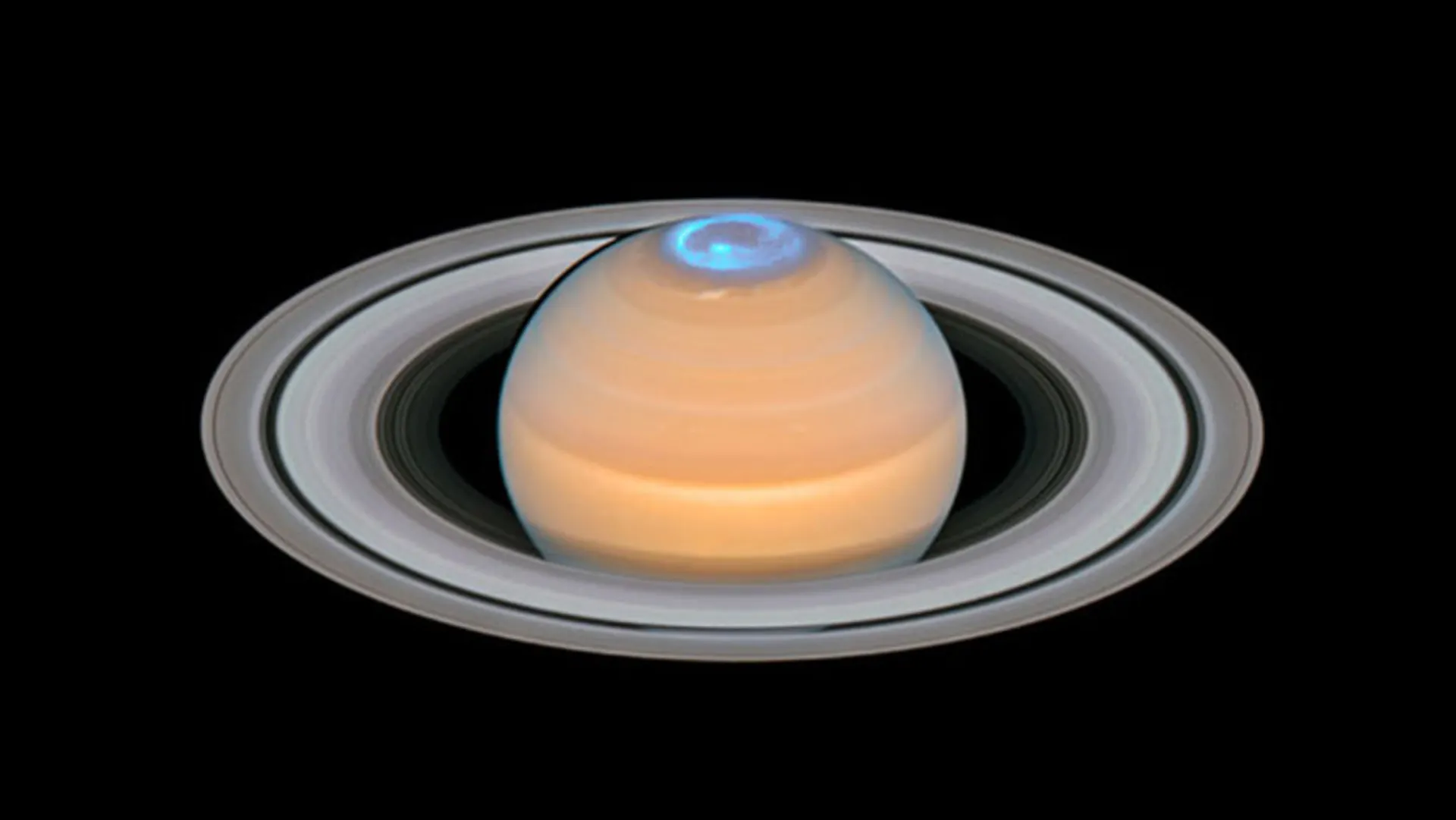

Saturn’s auroras are similar to Jupiter’s auroras
The orbit and rotation of Saturn
Compared to Earth, Saturn’s orbit around the Sun is slow, but its orbit around itself is faster. Saturn orbits the Sun at a speed of approximately 35,400 km/h. This speed is about one-third of the speed of the Earth’s movement around the sun. The length of Saturn’s year during a complete period of rotation around the Sun is equal to 29.5 years or 10,755 Earth days.
Although the movement of Saturn around the Sun is slow, its movement around its axis is much faster than that of the Earth, and it completes its rotation in less than half an Earth day. Because Saturn is about 10 times the diameter of Earth, any point on its equator moves 20 times faster than the corresponding point on Earth’s equator. This rapid rotation causes Saturn to form an oval shape so that it becomes flat at the poles and wide at the equator. Saturn’s day is equal to 10 hours and 38 minutes on Earth.
In 2007, it was found that the changes in radio emissions from Saturn do not correspond to its rotation speed. This variance may have occurred due to geyser activity on Saturn’s moon Enceladus. In this way, the water vapor released in the orbit of Saturn is charged and as a result, they cause stretching in the magnetic field of Saturn, and thus the rotation of the magnetic field becomes slower than the rotation of the planet itself.

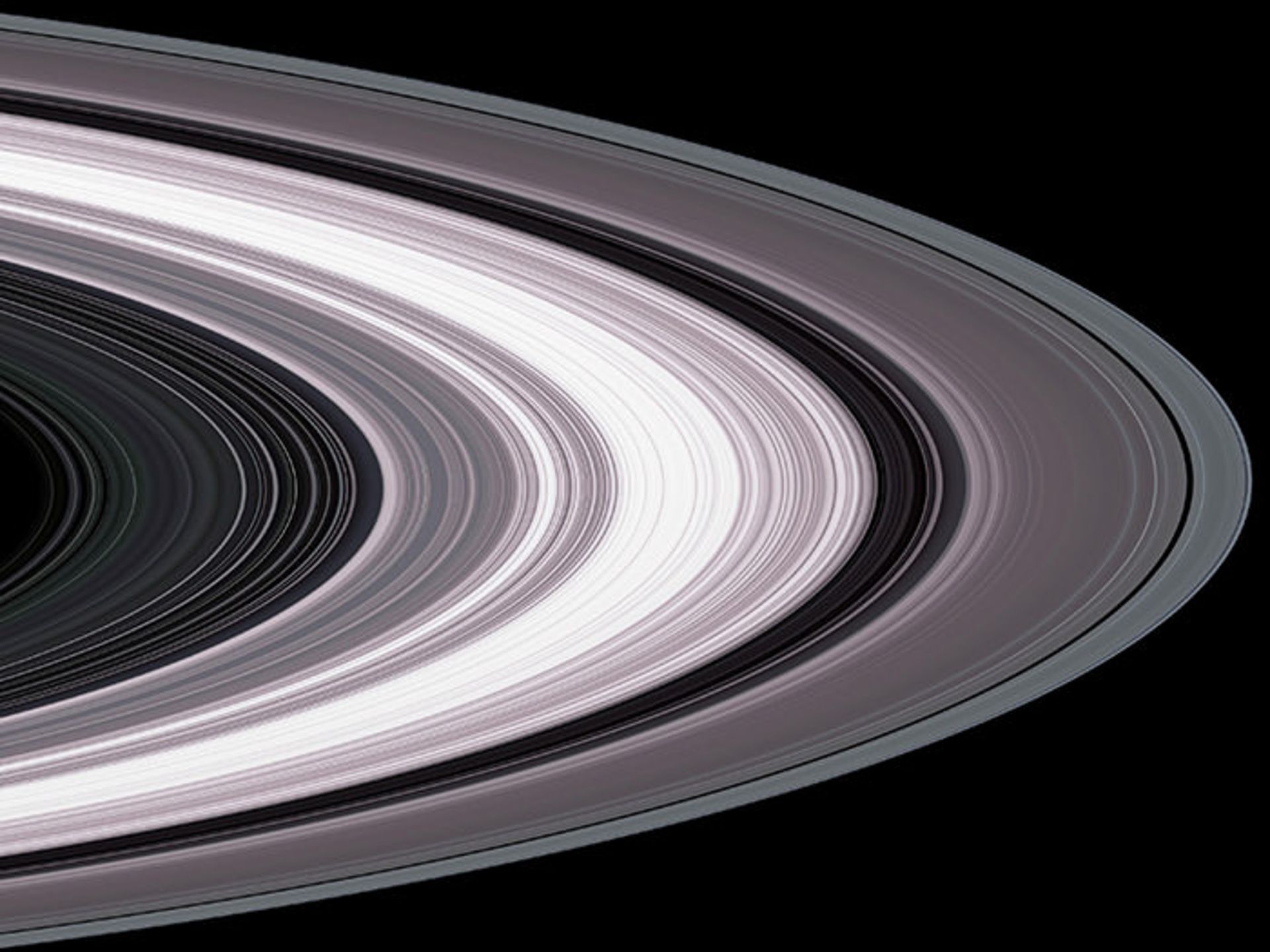
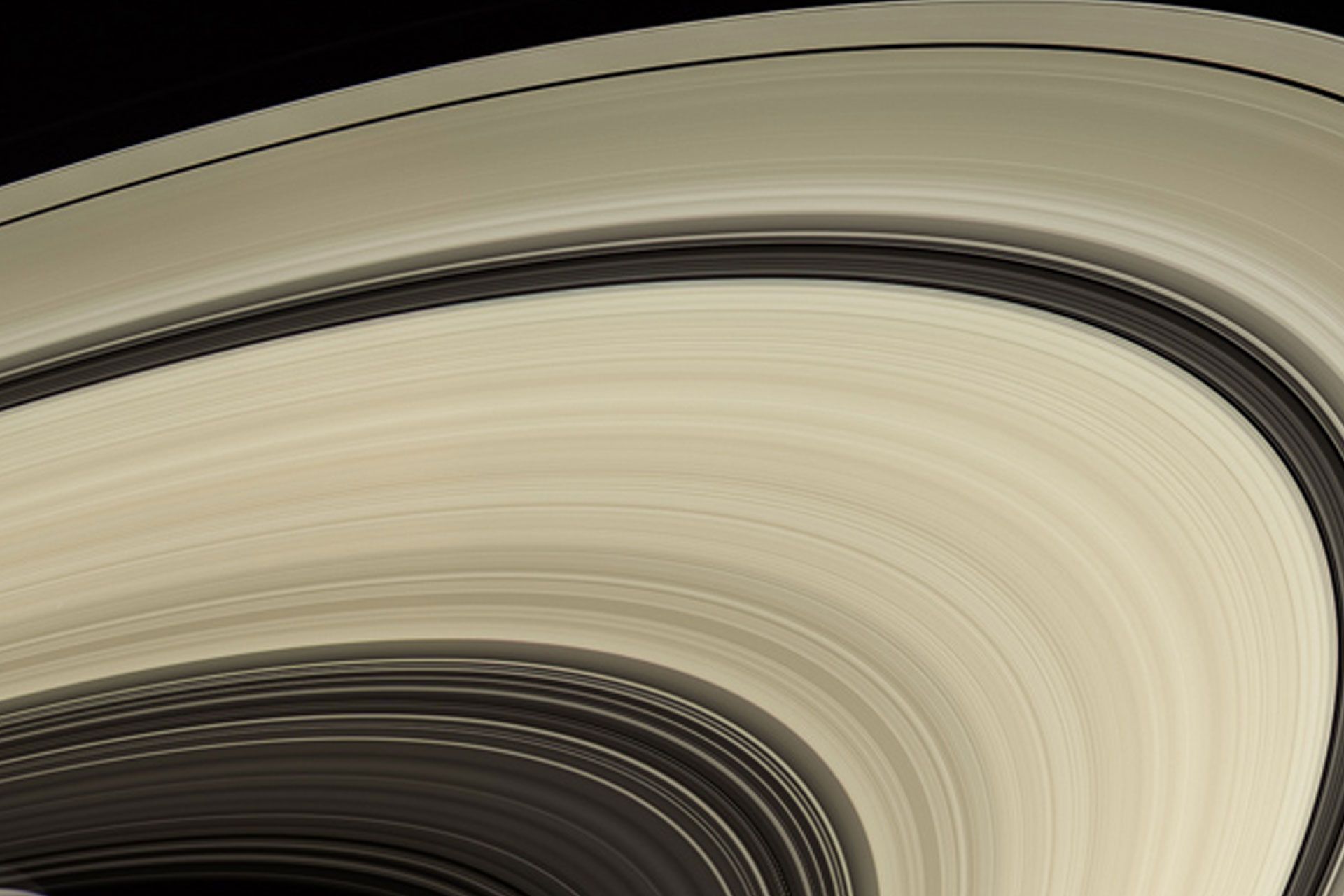
Rings of Saturn
Saturn’s prominent and bright rings make it a unique planet in the entire solar system. Saturn’s rings have fascinated astronomers for centuries. When Galileo first observed Saturn in 1610, he thought the rings were large moons on either side of the planet. During his seven years of observation and exploration, he recorded the rings changing shape and even disappearing (depending on the angle and declination with the Earth). ).
According to Galileo’s observations, Saturn’s equator has a 27-degree deviation from its orbit around the Sun (similar to the 23-degree deviation of the Earth). As Saturn revolves around the Sun, first one hemisphere and then the other hemisphere are facing the Sun. This deviation causes seasonal changes (similar to Earth) and when Saturn reaches the equinox, the equator and plane of the ring are aligned with the Sun. Sunlight hits the edges of the ring. The rings are generally 273,600 km wide, but only 10 meters thick.

In 1655, another astronomer, Christian Huygens, proved solid ring objects, and in 1660, another astronomer suggested that the rings were composed of satellites or small moons (a view that remained unconfirmed for 200 years).
In the modern era, Pioneer 11 passed through Saturn’s ring in 1979. In the 1980s, Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 investigated the planet’s ring system. In 2004, NASA’s Cassini Huygens mission became the first probe to enter Saturn’s orbit, recording detailed observations not only of the planet itself but of its ring system.
Saturn’s rings are made of billions of particles ranging from sand to large objects the size of mountains. Most of the particles are made of frozen water. When you look at Saturn with an amateur telescope, its ring appears to be one piece, but this ring is actually made up of several parts. The rings are named in order of discovery, so the main rings are named A, B, and C from farthest to closest. The width of the A gap is approximately 4700 km, which is also called the Cassini segment. This gap separates the A and B rings.
Other narrower rings were discovered as telescope technology improved. Voyager 1 discovered the innermost ring called D in 1980. The F ring is also placed outside the A ring. In contrast, the G and E rings are even further apart. The rings themselves are composed of a number of gaps and distinct structures. Some of them are very small moons of Saturn, while others confuse astronomers. Saturn is not the only planet in the solar system that has a ring system. Jupiter, Uranus, and Neptune also have rings, but Saturn’s ring is the most prominent type of ring.
There are different hypotheses about the formation of Saturn’s rings. Some scientists think that comets or passing meteorites are trapped by Saturn’s gravity and disintegrated before reaching it. The reason for the high brightness of Saturn’s rings is that a large part of the rings are made up of particles and ice pieces. The size of these particles varies from small pieces to large icebergs. These ice particles in Saturn’s rings form ice clusters and reflect a lot of light.
Another possibility suggests that the rings were once large moons orbiting the planet. Saturn has at least 83 moons. Only one of its moons, Titan, is a large moon. The rest of the moons are small objects and only 13 of them are more than 50 km. The gravity of these moons affects the structure of Saturn’s rings while providing clues about how the rings formed.
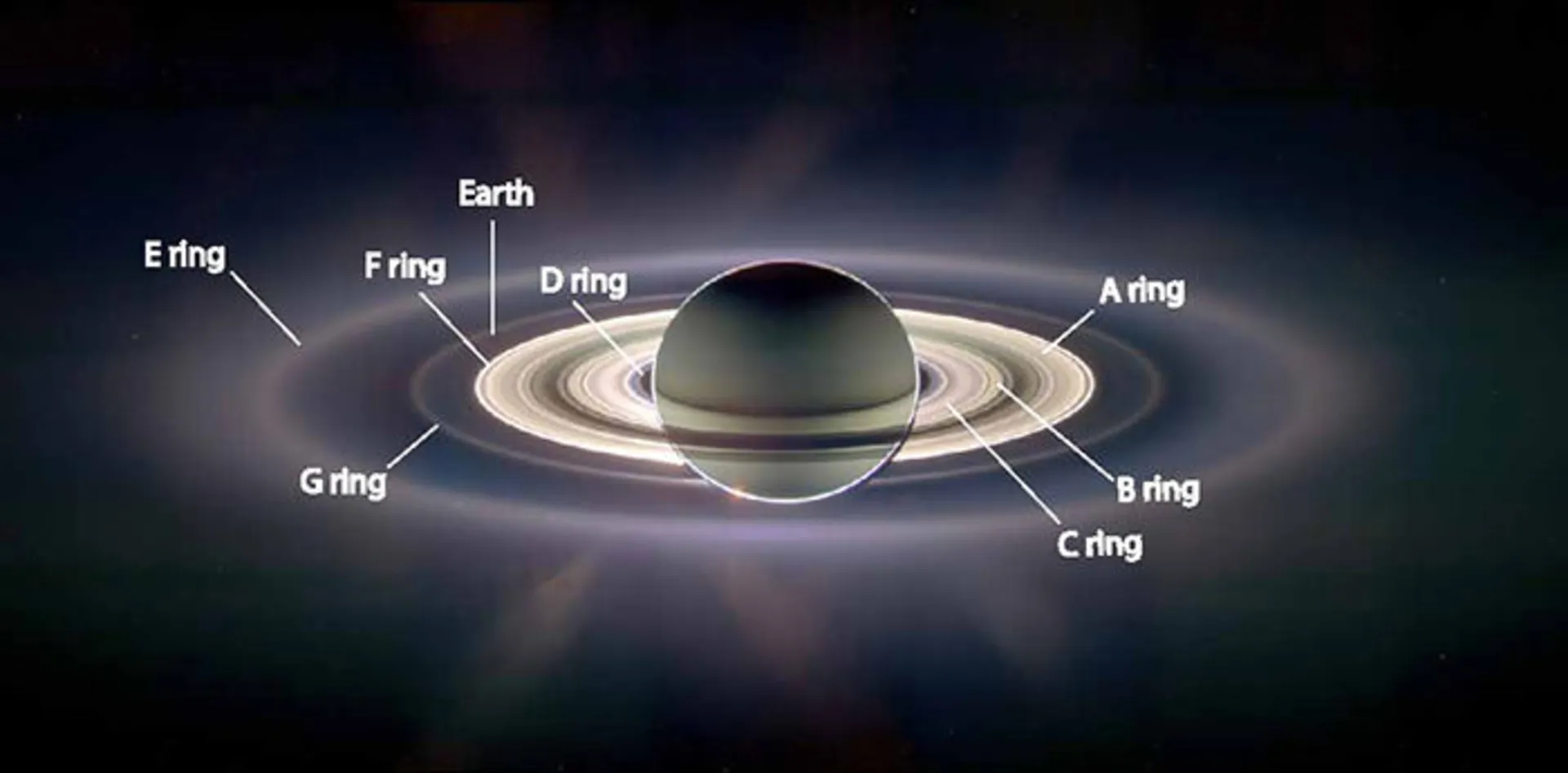
How many moons does Saturn have?
The planet Saturn has a large number of diverse moons, ranging from satellites with a diameter of tens of meters to large moons like Titan with dimensions larger than the planet Mercury. Saturn has 83 confirmed moons, only 13 of which have diameters greater than 50 km. Titan is the most prominent moon of Saturn and the second largest moon in the Solar System after Ganymede (Jupiter’s moon). The moon’s atmosphere, like Earth’s, is full of nitrogen and offers views of river networks and hydrocarbon lakes.
Twenty-four moons of Saturn are regular satellites and their progressive orbits are not inclined to Saturn’s equatorial plane. These twenty-four moons include seven main satellites, four small moons, two small co-orbiting moons, and two other moons that act as shepherds of Saturn’s F ring. The remaining 58 moons, which have a diameter varying from 4 to 213 km, are among the irregular moons whose orbits are at a greater distance from Saturn. These moons are probably trapped planets or parts of collapsed bodies after being trapped. Irregular moons are divided into Inuit, Norse, and Gaelic groups based on orbital characteristics. The names of these groups are taken from Greek mythology. The largest irregular moon Phoebe is the ninth moon of Saturn, which was discovered at the end of the 19th century. Saturn’s rings are a combination of microscopic variable bodies to satellites several hundreds of meters in diameter, each orbiting Saturn in its own orbit.
It is believed that the moon system of the planet Saturn was formed similar to the moons of the planet Jupiter, but in general, the details of the formation of the moons of Saturn are unclear. On June 23, 2014, NASA reported strong evidence that the nitrogen in Titan’s atmosphere came from material in the Oort Cloud, not from Saturn.


Comparison of Saturn’s moons in terms of size
Grouping of Saturn’s moons
Although the demarcation of Saturn’s moons is somewhat vague, they can be divided into ten groups based on their orbital characteristics. Many of these moons, including Penn and Daphnis, are in Saturn’s ring system, and their orbital period is slightly longer than that of Saturn. Inner moons and regular moons have an average orbital inclination ranging from 1° to 1.5°. On the other hand, the irregular moons in the outermost part of Saturn’s moon system, especially in the Norse group, have orbital radians of millions of kilometers and orbital periods of several years. The Norse moons also orbit Saturn in the opposite direction.
- Large inner moons: Saturn’s innermost large moons are located in Saturn’s thin E ring. These moons are Mimas, Enceladus, Tethys, and Dione.
- Large outer moons: These moons are located on the other side of the E ring, they are: Rhea, Titan, Hyperion, Iapetus
Irregular moons
Irregular moons are small satellites with high radians and inclinations and are thought to have been caught in Saturn’s gravitational trap in the past. The exact size of these moons is still unknown because their dimensions are so small that they are difficult to observe with a telescope.
Alkeonides
The three small moons between the moons of Mimas and Enceladus are called Alkeonids, which derives its name from Greek mythology. These three months are Matun, Ant, and Plan. Ant and Meton have a very thin circular arc in their orbit, while Plan has a completely thin ring. Among these moons, only Matun was photographed from a relatively close distance. This egg-shaped moon has a small number of impact craters.
Titan
Titan is the largest moon of Saturn and the second largest moon in the solar system (after Jupiter’s moon Ganymede). Titan is the only moon in the solar system with a dense and cloudy planet-like atmosphere. Scientists believe that the conditions on Titan are similar to the initial conditions on Earth, but the only difference is that the Earth is closer to the Sun and it is hotter. In many ways, Titan is the most similar to Earth.
Titan’s diameter reaches 2,575 km, which is almost 50% wider than the Earth’s moon. The distance between Titan and Saturn is about 1.2 million kilometers and 1.4 billion kilometers or 9.5 AU from the Sun. An astronomical unit is the distance from the Earth to the sun. It takes about 80 minutes for sunlight to reach Titan because of this distance, sunlight is about 100 times dimmer than sunlight on Earth.
It takes approximately 15 days and 22 hours for Titan to complete one orbit of Saturn. Titan is tidally locked to Saturn, which means that, like Earth’s moon, one side of it is always seen from Saturn. It takes approximately 29 Earth years for Saturn to complete an orbit around the Sun (Saturnian year) and Saturn’s axis of rotation, like Earth’s, has a deviation that creates seasons on this planet; But Saturn’s seasons are longer, typically lasting nearly seven Earth years each. Since Titan’s orbit is in line with Saturn’s equatorial plane and Titan’s deviation from the Sun is almost the same as Saturn’s, the seasons of this moon are the same as Saturn’s, that is, almost every season of Titan is seven Earth years and one year is equal to 29 Earth years.
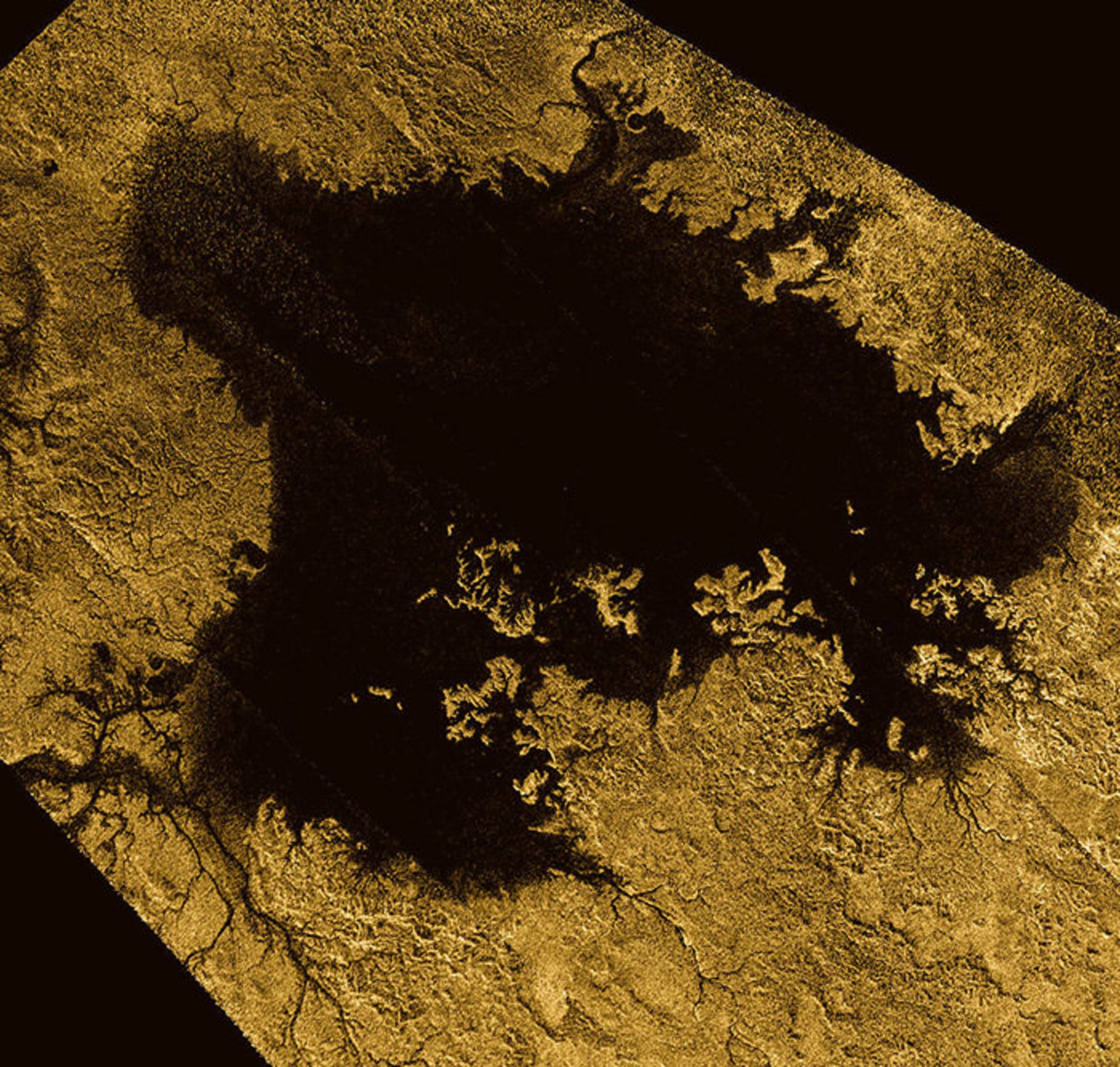
Cassini image of Titan’s north polar hydrocarbon lake
Scientists are not sure about the exact formation and origin of Titan. However, the atmosphere of this moon has clues. A number of Cassini Huygens probe instruments measured nitrogen-14 and nitrogen-15 isotopes in Titan’s atmosphere. According to the findings, the nitrogen isotope ratio found in Titan is very similar to the isotope of comets in the Everett cloud. The globular Oort cloud consists of hundreds of billions of icy bodies located between 5,000 and 100,000 AU from the Sun (each AU equals 150 million km). The nitrogen ratio of Titan’s atmosphere shows that the building blocks of this moon were formed in the same gas and dust cloud as the Sun in the early history of the solar system, and the origin of these blocks is not the hot disk of Saturn’s material.
Surface: Titan’s surface is one of the most similar to Earth in the entire solar system. Of course, its temperatures are lower and it has different chemical characteristics. The surface temperature of Titan reaches minus 179 degrees Celsius. Titan may also have volcanic activity. The surface of this moon is full of methane and ethane streams that form large river and lake channels. No other world in the entire solar system (except Earth) has surface liquid.
Titan’s rains are made of methane and form the moon’s seas and lakes
Atmosphere: Nearly 95% of Titan’s atmosphere is nitrogen and 5% is methane. Traces of carbon compounds can also be found in the atmosphere of this planet. At the heights of this moon, methane and nitrogen molecules are decomposed due to the impact of the ultraviolet light of the sun and energetic particles. Parts of this molecule are recombined and produce various biological chemicals such as materials containing carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, and other essential elements for life.
Some of the compounds are formed by decomposition and cycle of methane and nitrogen. Methane and nitrogen create a thick, orange cloud that covers the surface of this moon, which is why it is difficult to examine Titan’s surface from space. The origin of all the methane in the atmosphere still remains a mystery.
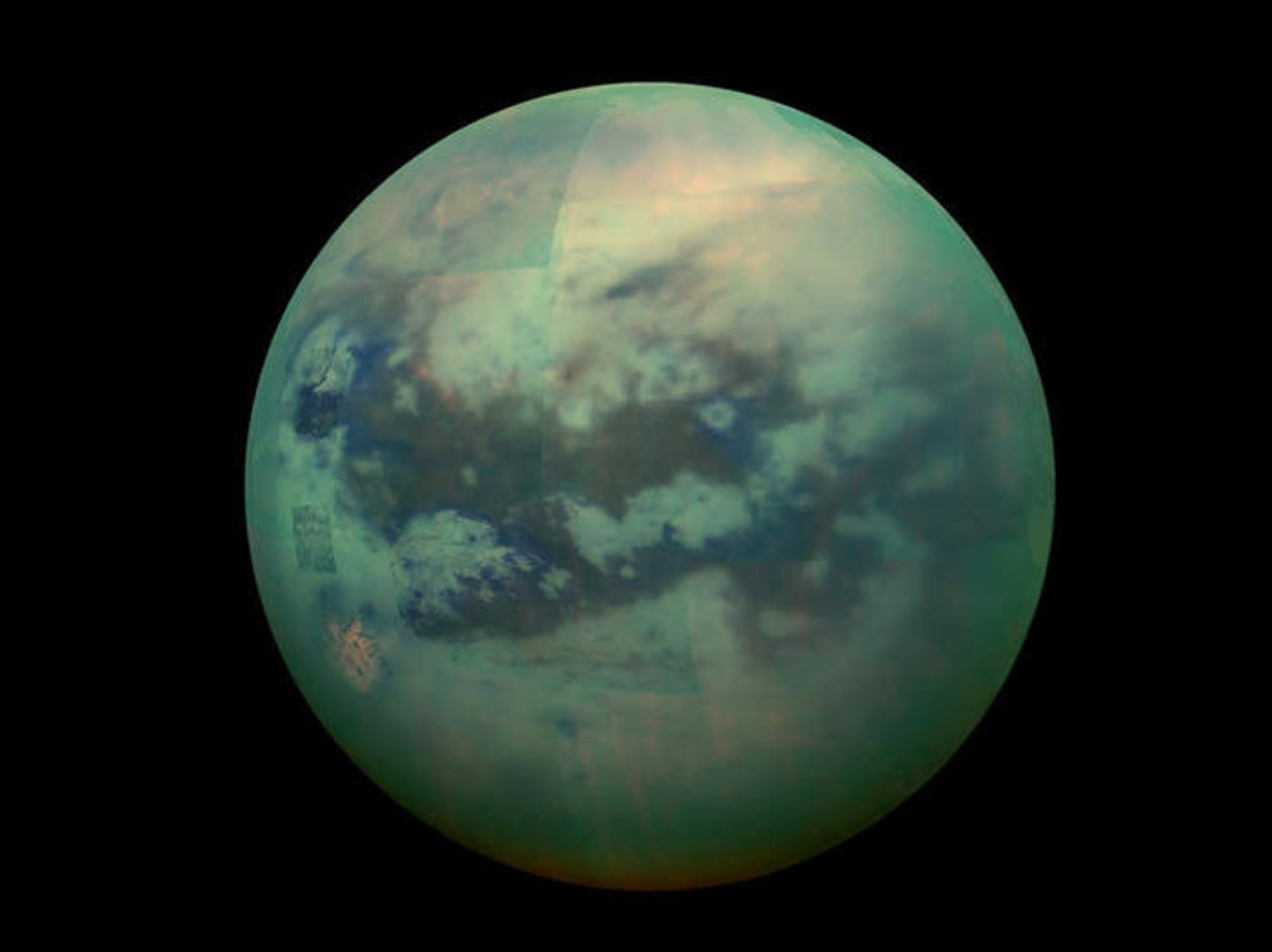

The presence of methane and nitrogen in Titan’s atmosphere causes orange clouds
The potential for life on Titan
Cassini’s numerous gravity measurements of Titan suggest that the moon has a subsurface ocean of liquid water, possibly mixed with salt and ammonia. The European Space Agency’s Huygens probe also measured radio signals from the moon’s surface in 2005, indicating oceans 55 to 80 kilometers below Titan’s icy surface. The discovery of a global ocean of liquid water also places Titan in the group of moons of the solar system that have the potential for life. In addition to these rivers, lakes, and seas of methane and liquid ethane on the surface of Titan, they could act as a habitable environment on the surface of this moon, although any possible life on this moon would be different from terrestrial life; Therefore, Titan can host habitats and suitable conditions for life, including life that we know (in the subsurface ocean) and life that we do not know (in surface hydrocarbon liquids). Although evidence of life on Titan’s surface has yet to be discovered, the moon’s complex and unique chemical nature are definitive findings that make it an ideal destination for exploration.
Enceladus
Few moons in the solar system are as fascinating as Enceladus. Some of these moons are thought to have oceans of liquid water beneath their frozen crusts, but one of the unique features of Enceladus is its glaciers. Based on samples obtained from space probes, Enceladus has the most chemical elements necessary for life and probably has hydrothermal or hydrothermal vents that transport hot mineral water from subsurface oceans.
About the size of Arizona, Enceladus has the whitest and most reflective surface in the Solar System. This moon has a ring system and releases ice fragments into its orbit in space. These fragments form Saturn’s E ring. The name Enceladus comes from Greek mythology. The images of the Voyager spacecraft in the 1980s show that this moon, despite its small size (approximately 500 km in diameter), has a relatively smooth ice surface in some places and has a high brightness. In fact, Enceladus is one of the most reflective bodies in the solar system, the reason for which scientists did not know for years.
Since Enceladus reflects a large part of the sunlight, its surface temperature is extremely low and reaches minus 201 degrees Celsius. Enceladus is located at a distance of 238 thousand kilometers from Saturn between the orbits of two other moons, Mimas and Tethys. The moon is tidally locked to Saturn, taking approximately 32.9 hours to complete one orbit in the densest part of Saturn’s E ring.
In 2005, NASA’s Cassini spacecraft revealed water ice, and gas particles ejected from the surface of Enceladus at speeds of approximately 400 meters per second. These eruptions appear to be continuous, creating a huge halo of icy dust around Enceladus that forms the material of Saturn’s E ring. Only a small fraction of this material enters the ring, and most of it falls on the surface of Enceladus as snow. For this reason, this moon has a white and bright surface.
Enceladus’ glaciers originate from relatively warm cracks in its crust, which scientists call tiger stripes. Several gases such as water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, and maybe a little ammonia, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen along with salt and silica make up the gas cover of Enceladus’ glacial channels. The density of biological material in glaciers is twenty times higher than expected by scientists.
Based on measurements of the Doppler effect and the very small amplitude of Enceladus’ wobble as it spins around, scientists have discovered a global ocean beneath the moon’s surface. They believe that the thickness of the ice shell of Enceladus in its south pole is close to 1 to 5 km. The average thickness of the entire crust is between 20 and 25 km.
Since the ocean of Enceladus has ice, and the glaciers form Saturn’s E ring, examining the E ring could mean examining the ocean of Enceladus. A large part of the E ring is made up of ice particles, but among them you can also find very small particles of silica. These particles are formed when liquid water and rock react with each other at temperatures above 90 degrees Celsius. This is another indication of the existence of warm blue channels under the icy crust of Enceladus, which are not dissimilar to the warm blue channels of the Earth’s oceans. Enceladus is one of the prime candidates for life in the solar system with features such as a global ocean, unique chemistry and internal heat.
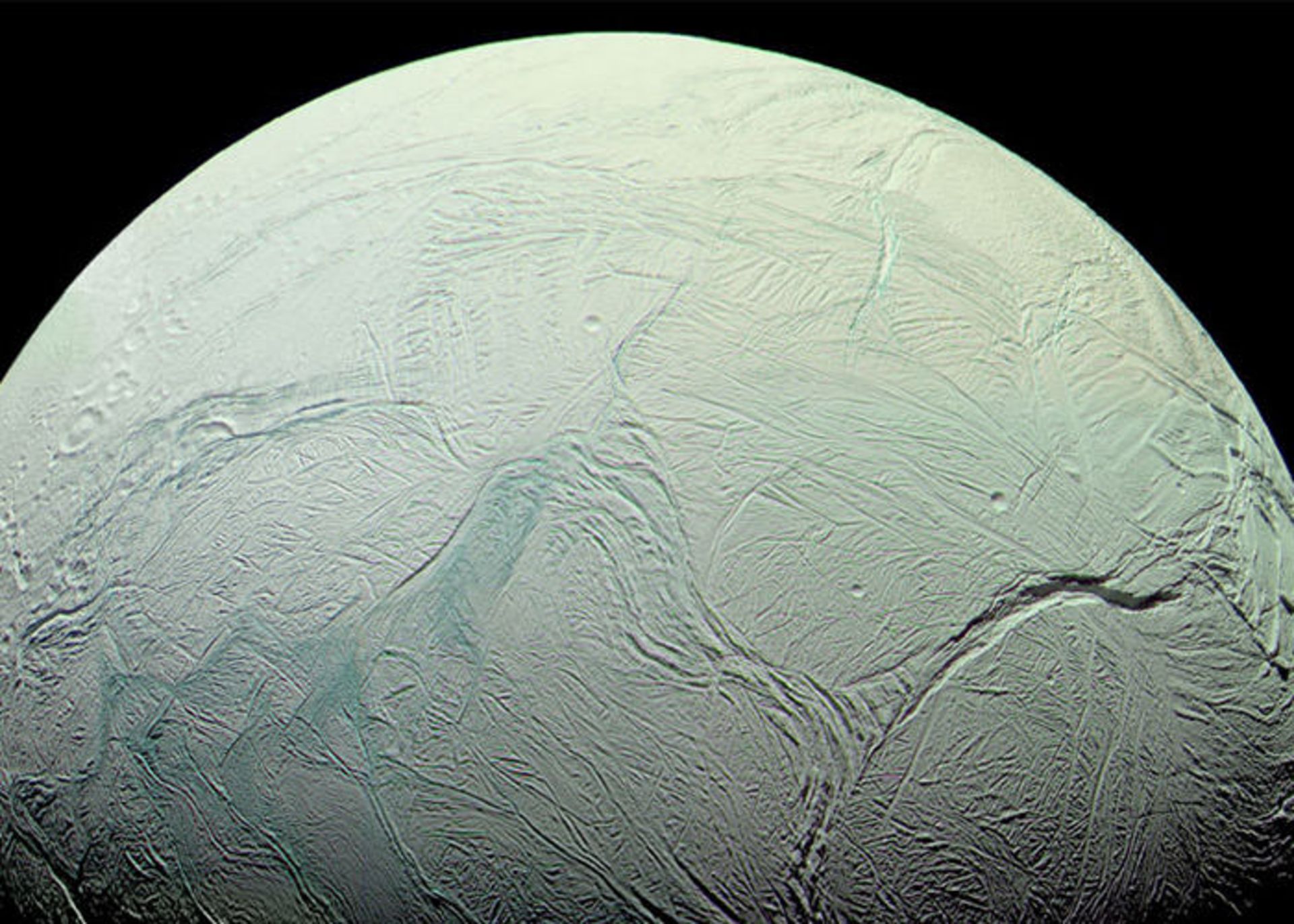
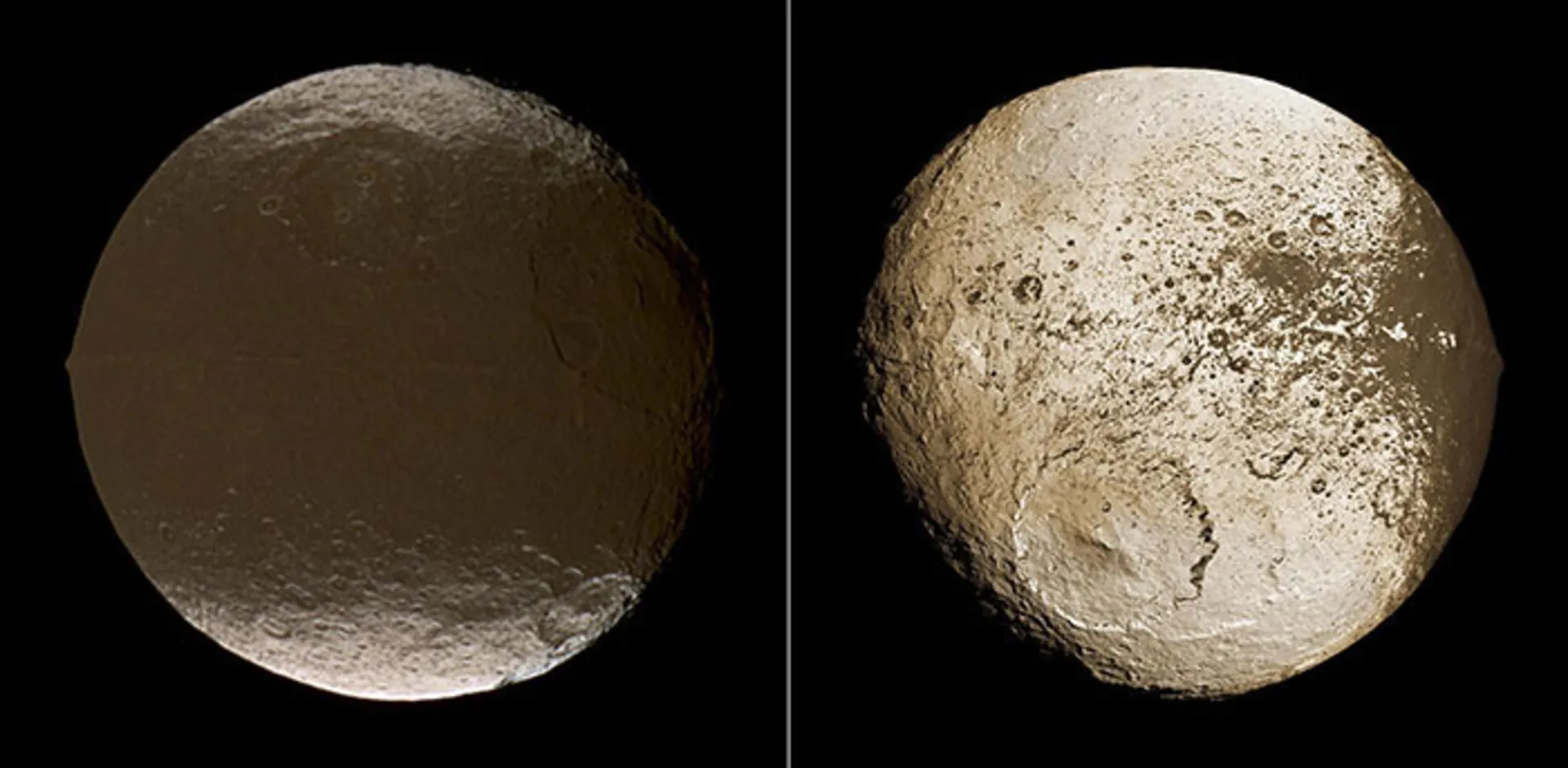
Iapetus
Iapetus is the third largest moon of Saturn and the eleventh largest moon in the entire solar system. The young Cassini discovered this moon on October 25, 1671. However, Iapetus was seen by astronomers as a point whose brightness changed during Saturn’s orbital period. Voyager 1 and 2 probes visited the Saturn system and this moon in the 1980s and revealed its strange features. The diameter of the Iapetus reaches 736 km. Like Rhea, three-fourths of Iapetus, the other moon of Saturn, is made of ice, and one-fourth of it is made of rock.
According to the two claims of Iapetus, Saturn’s moon is included in the list of strange moons of the solar system. This moon was discovered in 1671 and one side is dimmer than the other side. The part of the hemisphere facing Saturn’s orbit is dark brown in color; while the other hemisphere is light gray. According to a theory explaining the color difference of this moon, the side facing Saturn is covered with dust that was spread by small meteorite impacts on other small outer moons of Saturn.
Meanwhile, the Cassini images tell a more complicated story. Most of the dark material on the surface of Iapetus originates from inside this moon and leaves behind dark streaks by the sublimation of dusty ice from the moon’s surface (solid to vapor). This process probably begins with the accretion of dust from exoplanets.
Also, Iapetus has a mountain range 13 km high and 20 km wide at the equator, which gives it a distinctive walnut-like appearance. The origin of this mountain range is unknown. According to some theories, this mountain is a fossil from the time of the faster rotation of Iaptus, which arose in the equatorial part; While others believe that this mountain is the result of pebbles from the ancient ring system around this moon that collapsed and landed on the surface.

Hyperion
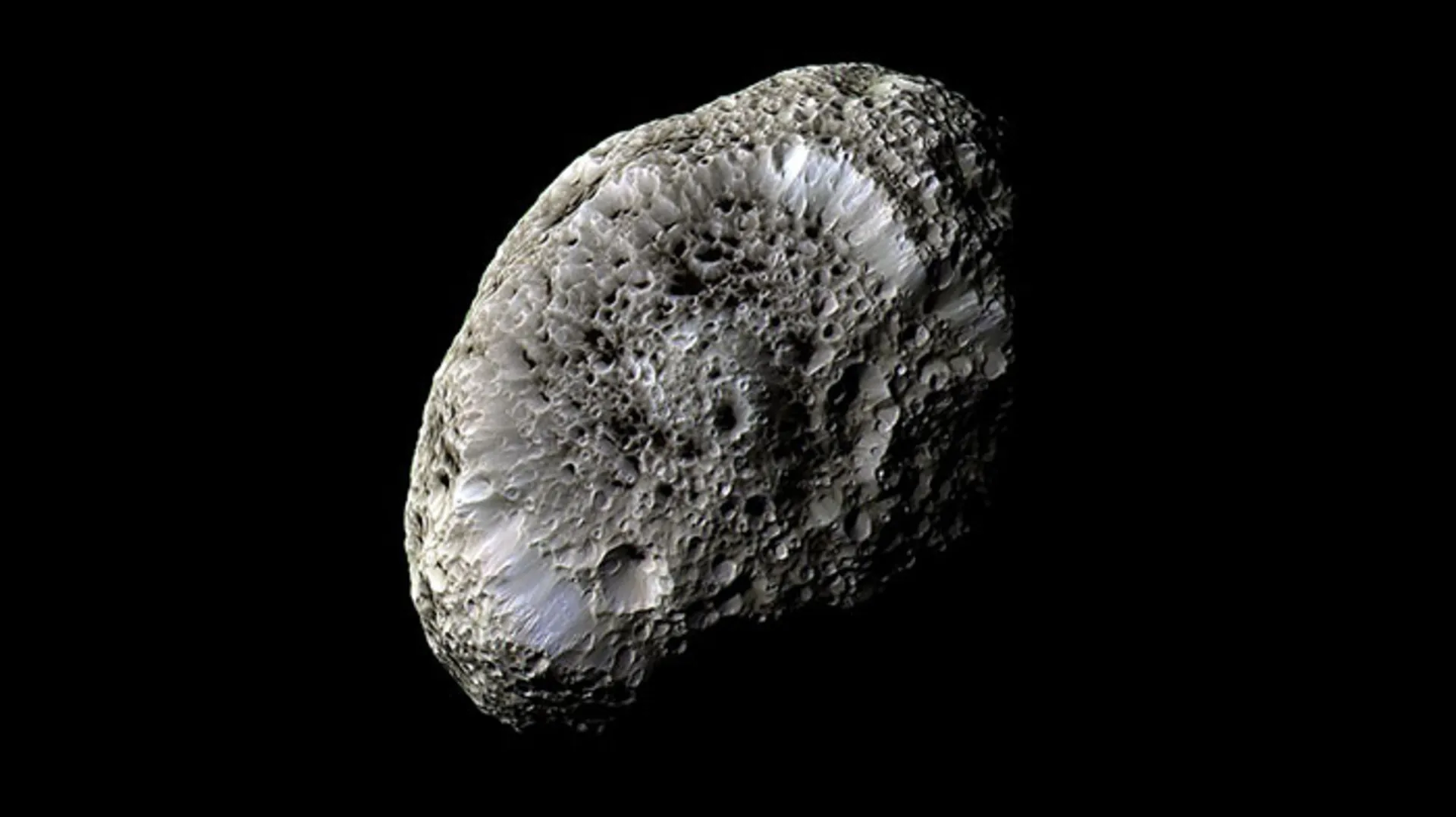
Hyperion is the largest non-spherical irregular moon of Saturn. Its average radius is 135 km, but since this moon is potato-shaped, its shape can be described based on its diameter along three axes. Hyperion has a strange appearance: its surface is like a sponge or coral with dark pits and sharp grooves formed by ice and lighter rocks. However, this is not the only strange feature of Hyperion: Hyperion was the first discovered non-spherical moon and has an eccentric orbit.
Hyperion’s rotation does not coincide with its orbital period and orbits Saturn in an irregular pattern; so that its rotation axis fluctuates unpredictably. Like other moons of the solar system, Hyperion is made of water ice; But its surface is strangely dark. According to Cassini spacecraft estimates, the density of Hyperion is 55% of that of water; As a result, a large part of its interior is empty.
According to a popular theory, one of the reasons for Hyperion’s strange properties is that it was a remnant of a larger moon that was probably located between Titan and Iapetus and was destroyed by a collision with a large comet. The remaining material condensed again and formed Hyperion.

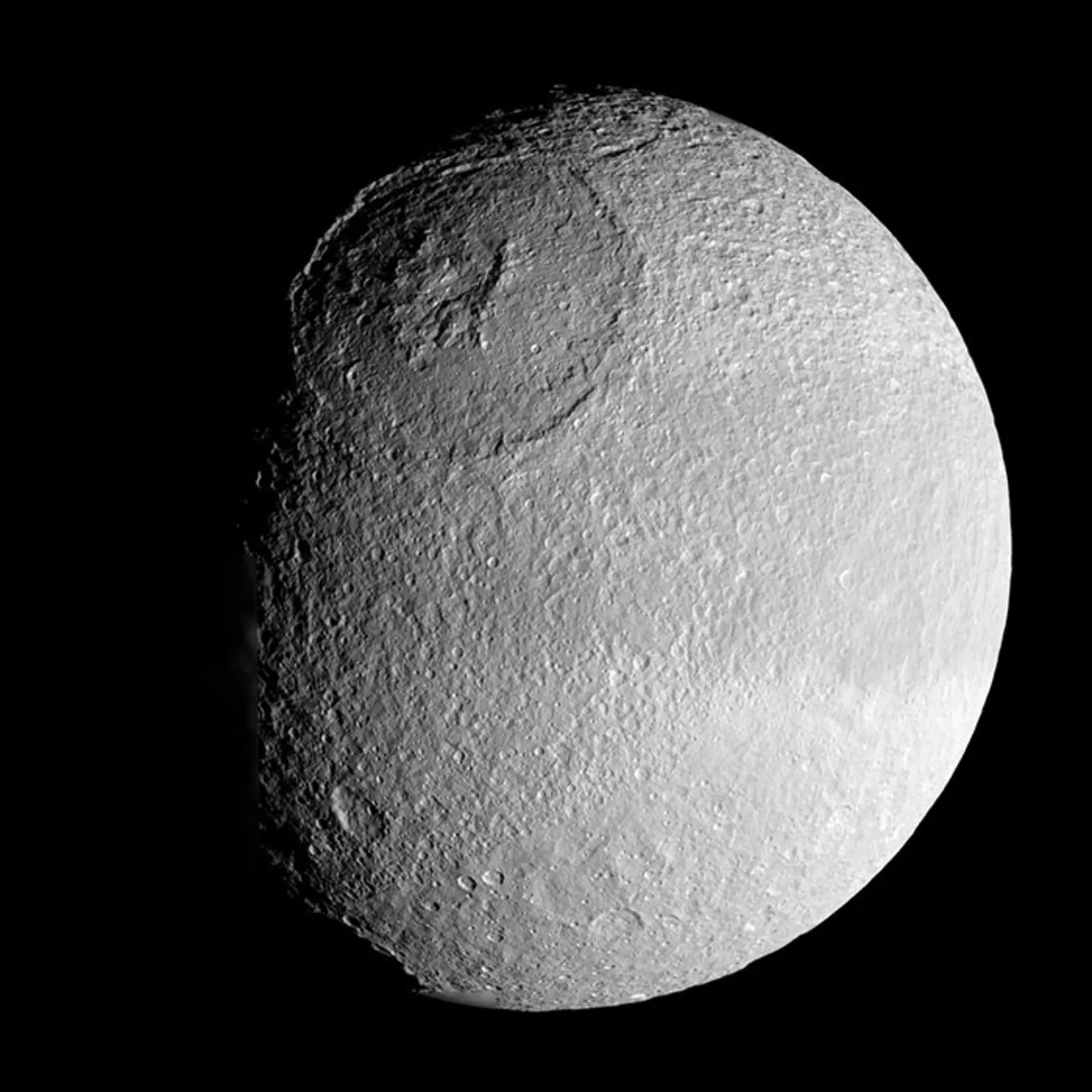
Mimas
The Voyager probes shocked scientists by capturing detailed images of Saturn’s moon Mimas in the 1980s. This moon is very similar to the Death Star in the sci-fi movie Star Wars. A large impact crater covers one of the hemispheres of this moon and is exactly the same size and similar to the destructive laser plate that George Lucas mentioned; But Mimas is more than just an element of popular culture.
Mimas is Saturn’s innermost moon, orbiting closer to Saturn than Enceladus and farther than Pan and Atlas. The diameter of this moon reaches 396 km; For this reason, the smallest object in the solar system is spherical in shape.
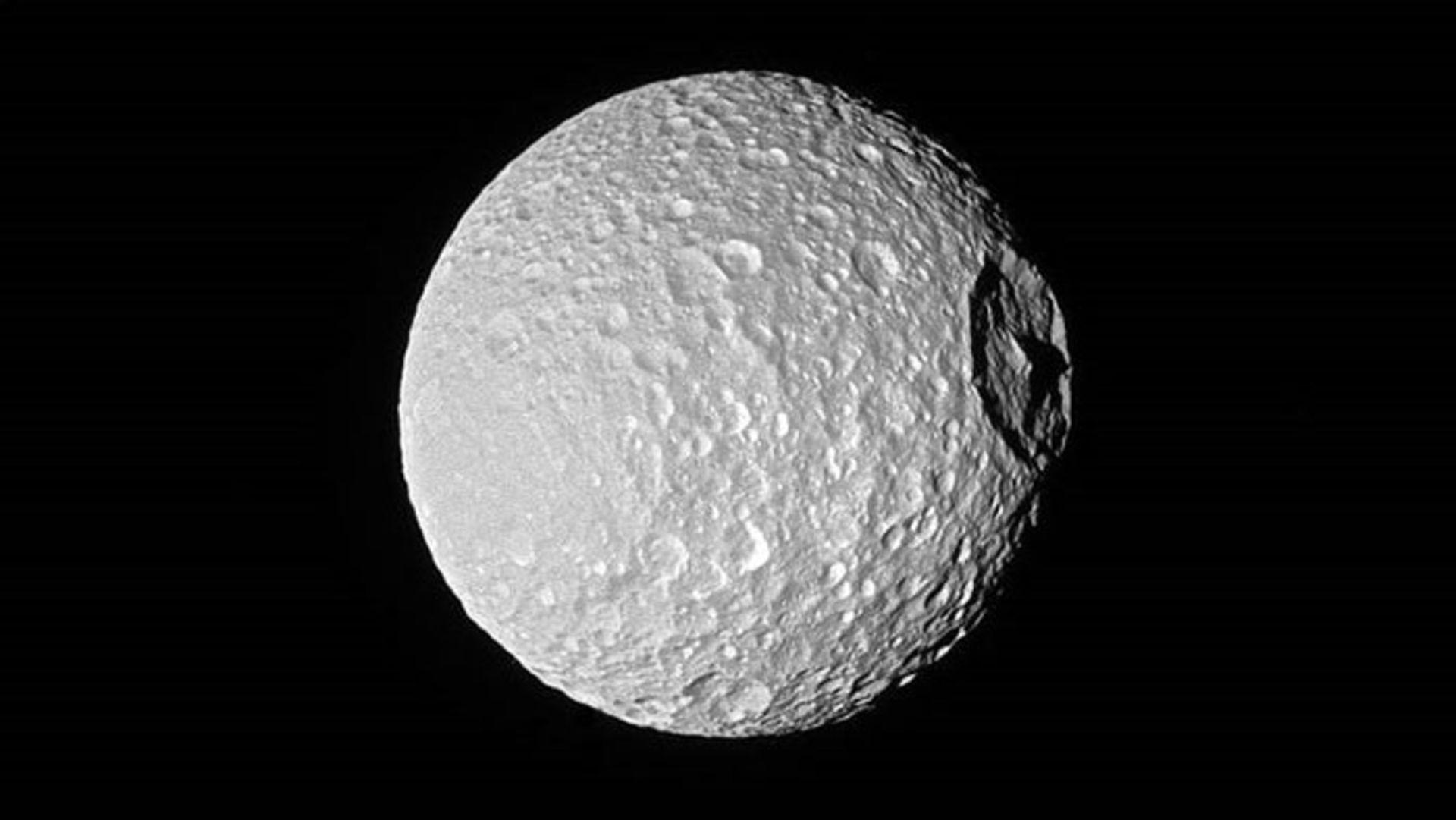

Herschel impact crater on the surface of Mimas. The name of this impact crater is derived from the name of William Herschel, who discovered this moon in 1789.
Pan and Atlas
Pan and Atlas are both Saturn’s innermost moons. Atlas orbits Saturn at the outer edge of the A ring. It takes approximately 14.4 hours for Atlas to complete one orbit of Saturn, and 8.13 hours for Pan. Saturn’s moons Pan and Atlas are the smallest moons in the solar system. Despite their small size, these moons can influence Saturn’s ring system. These small worlds are perhaps the best-known examples of shepherd moons. Shepherd moons are small moons that are located in the ring systems of giant planets. As their name suggests, these moons help particles in the Saturn system stick together, while also cleaning up other particles.
Pan causes Encke Gap; A prominent resolution is seen in the bright ring A; While Atlas is located outside the ring A. The most important feature of both moons is their smooth surface, which looks like a flying saucer or a walnut. Bonnie Borrati of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Experiment believes these moons are covered in tiny particles that clear the space between the rings.
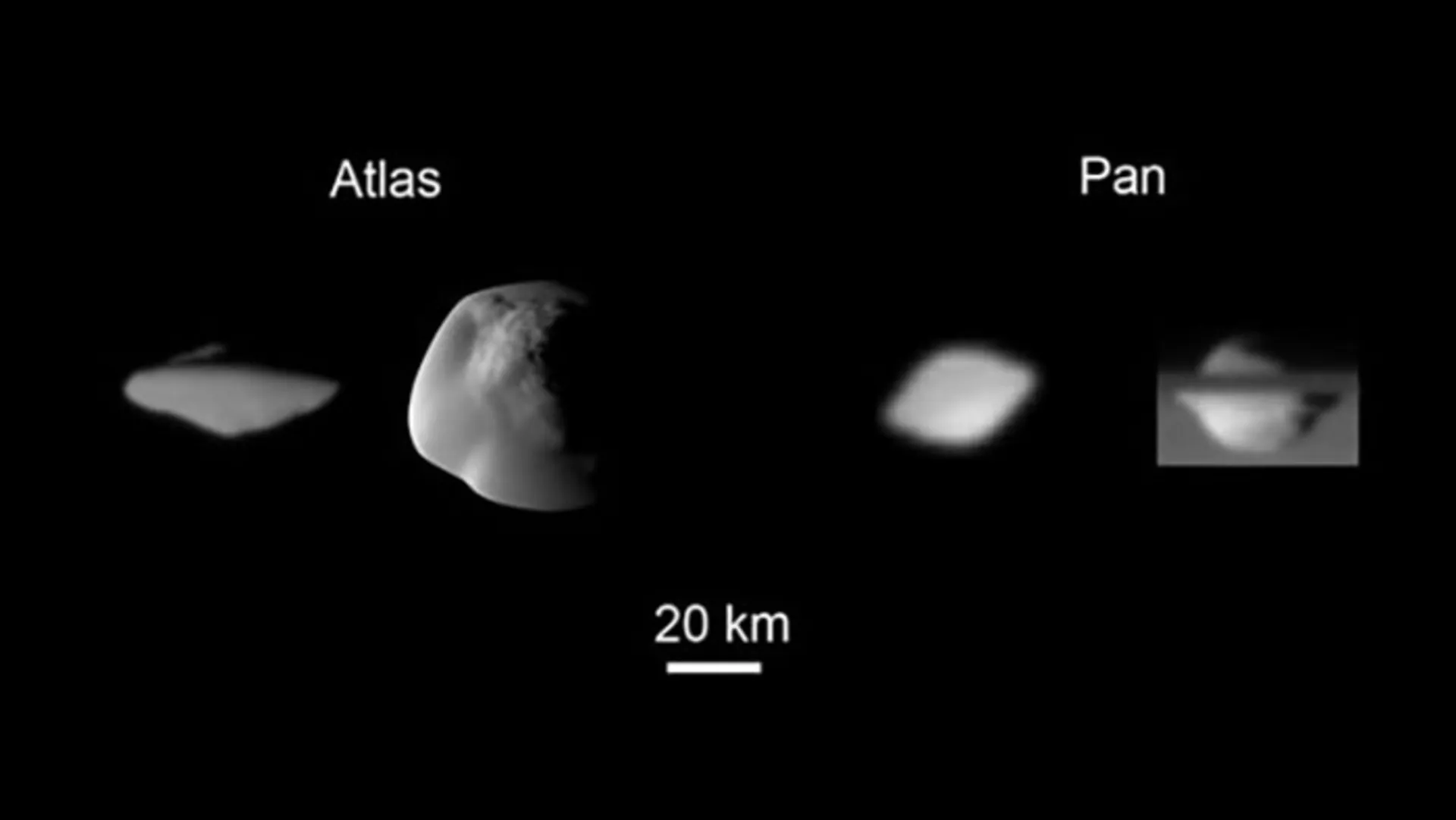

Pan and Atlas in the shape of a flying saucer
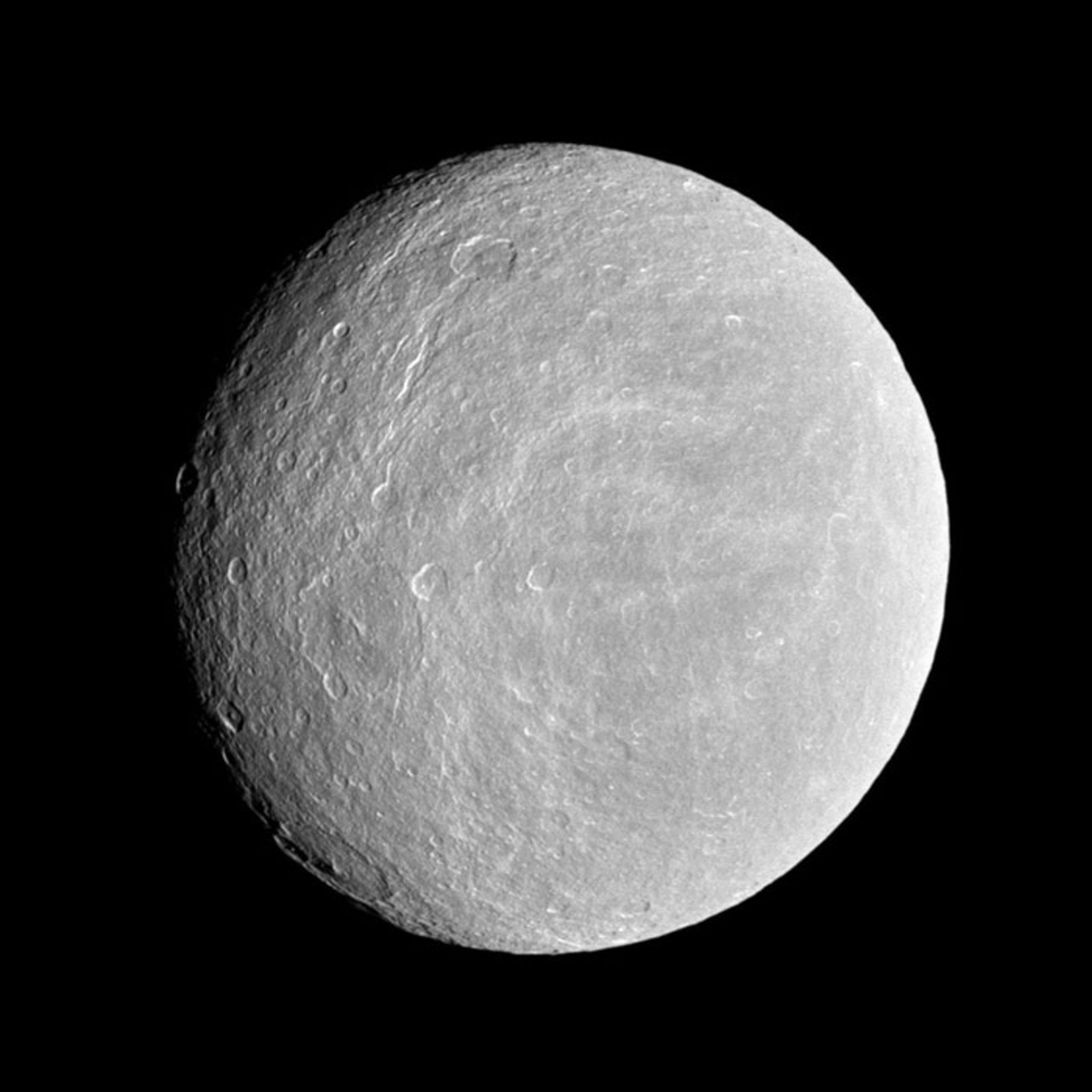
Rhea
Rhea is the second largest moon of Saturn, but its average radius is one-third that of Titan, Saturn’s largest moon. Rhea is a small, cold and airless world that is very similar to its moons, Dione and Tethys. Like the other two moons, Rhea has a tidal lock to Saturn, which means that one side of it is always seen from Saturn. It takes 4.5 Earth days for Rhea to complete one orbit of Saturn. The surface temperature of Rhea is similar to that of Dion and Tethys, which reaches minus 174 degrees Celsius in sunny areas and minus 220 degrees Celsius in shadow areas. Rhea, like Dion and Tethys, has a high reflectivity and shows that its surface is mainly composed of water ice.
Rhea is located at a distance of 527,000 km from Saturn and is a bit further from Dione and Tethys. In 2010, the Cassini spacecraft discovered a very thin atmosphere called the exosphere around Rhea, which is a mixture of oxygen and carbon dioxide. Cassini also detected signs of material in Rhea’s orbit in 2008. This was the first discovery of a ring around a moon.

Dione is a small moon with an average radius of 562 km that completes the orbit of Saturn once every 2.7 days. This moon is located at a distance of 377 thousand kilometers from Saturn, which is exactly equal to the distance between the moon and the Earth. The density of dione is 1.48 times that of liquid water, as a result, one-third of dione is made up of a dense core (probably of silicate rock), and the rest is made of ice.
Very fine icy powders (similar to smoke) from Saturn’s E ring bombard the surface of Dione. The E ring dust is formed from the icy moon Enceladus. The surface of Dion is full of impact craters so that the diameter of the craters reaches 100 km.
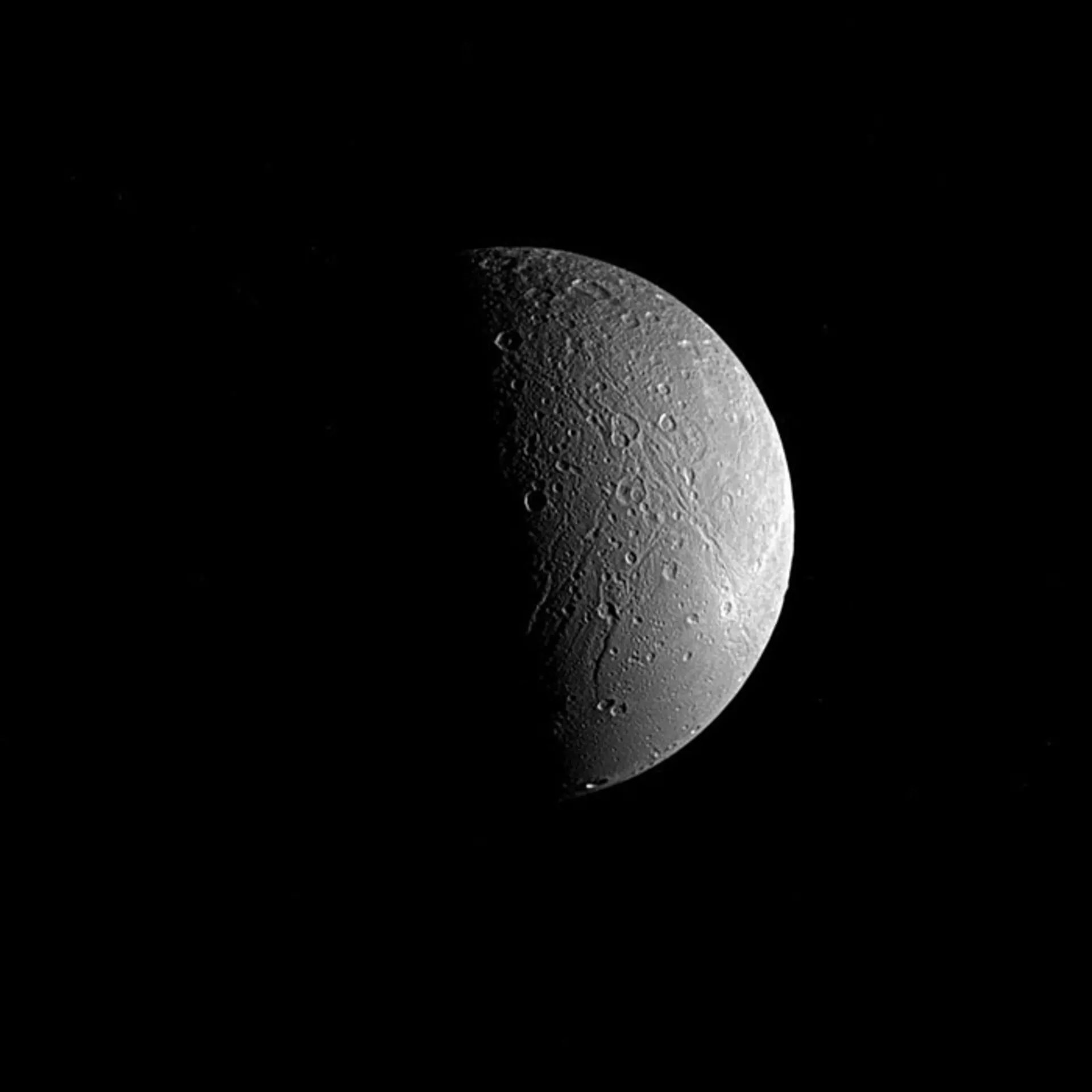

Tethys
Tethys is the fifth largest moon of Saturn. Its average radius reaches 633 km. This cold and airless moon is very similar to its sister moons, Dione and Rhea. Of course, with the exception that Tethys does not have many impact craters like the other two moons. A large part of Tethys is made up of water ice and a small part of it is made up of rock.
Tethys has a high reflectivity and this feature is another indication of its ice composition. The average temperature of Tethys reaches minus 187 degrees Celsius. Tethys appears as a small dot in the night sky, and its true nature was revealed after a visit by the Voyager probes. It takes 3.45 hours for Tethys to complete the orbit of Saturn.

The wonders of the planet Saturn
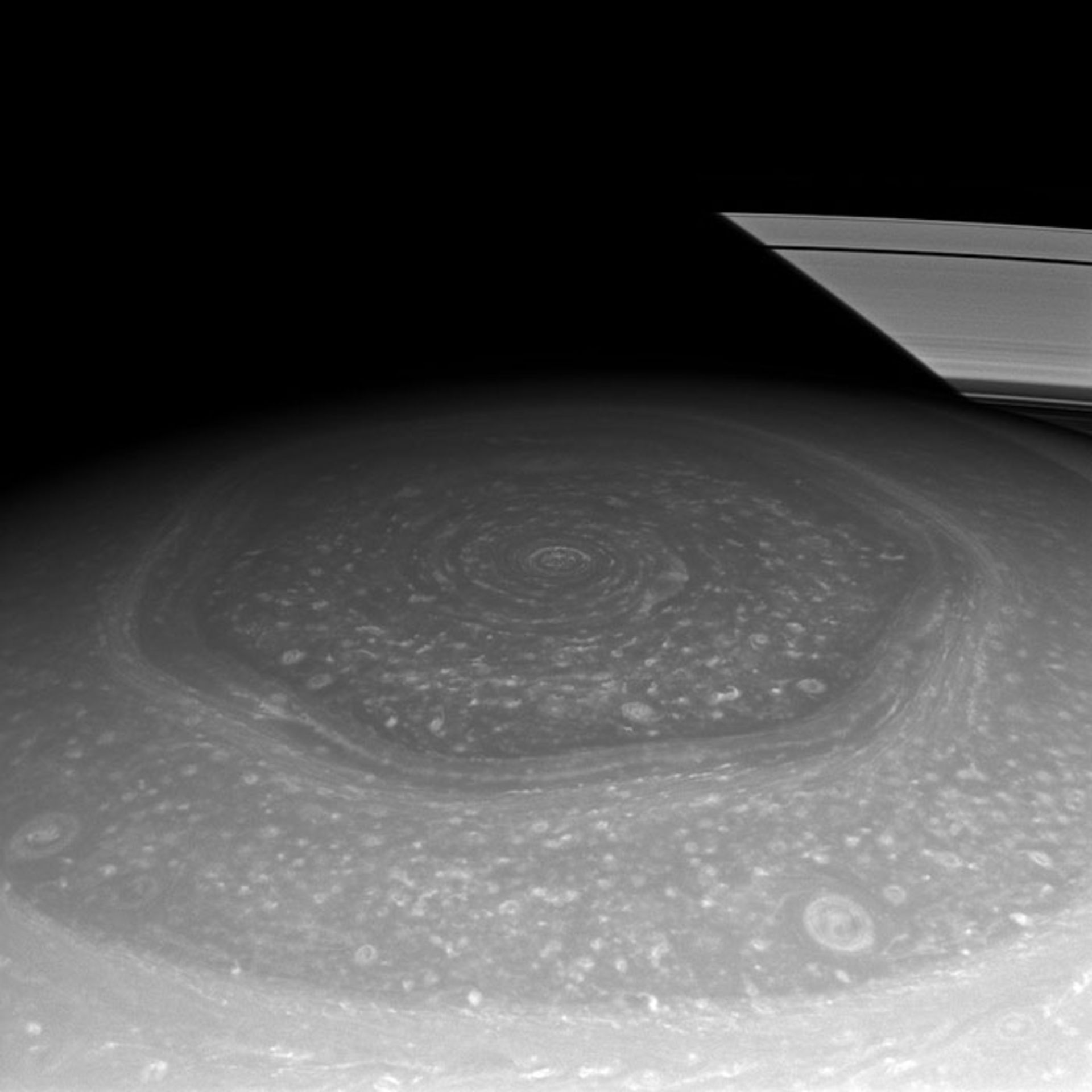
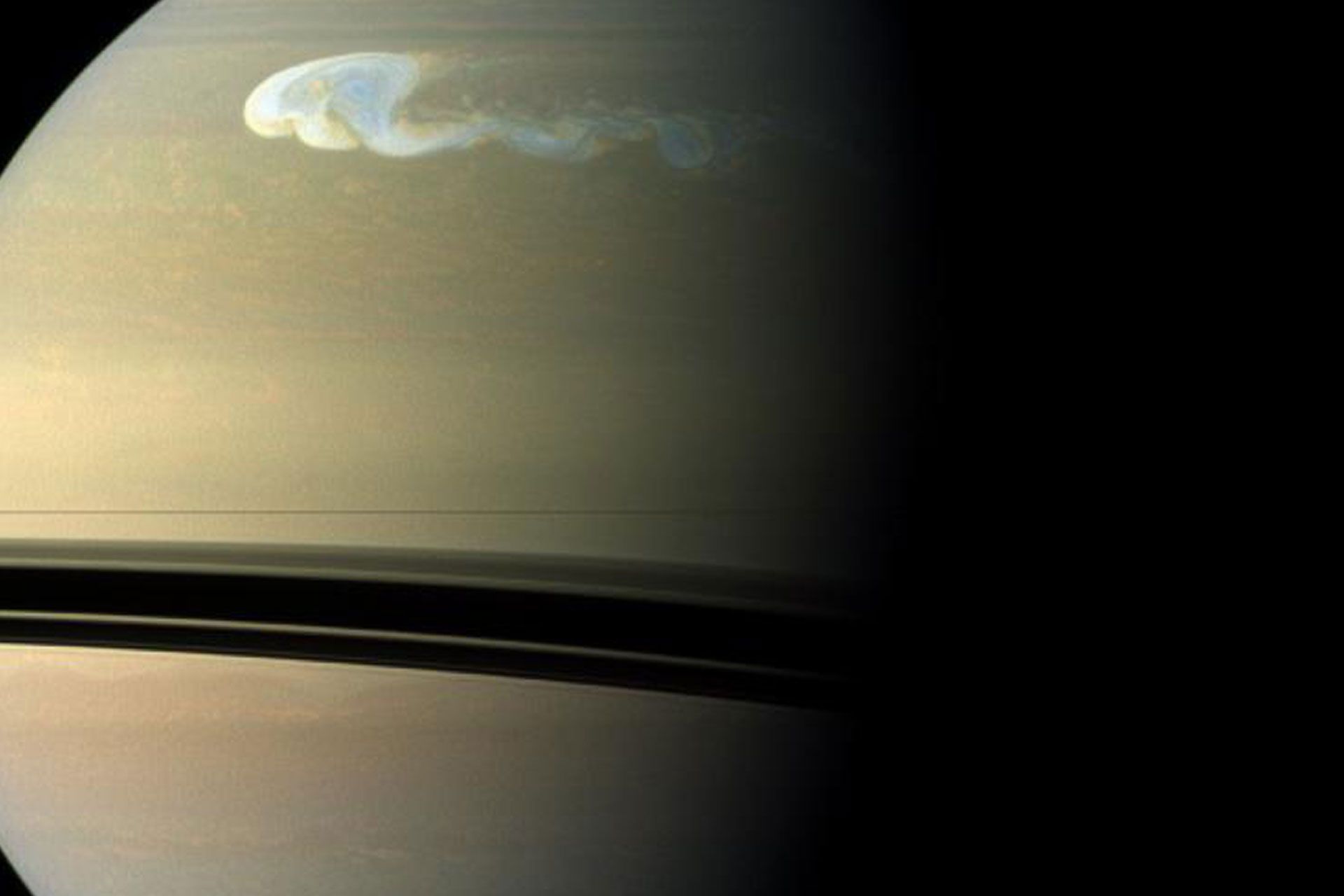
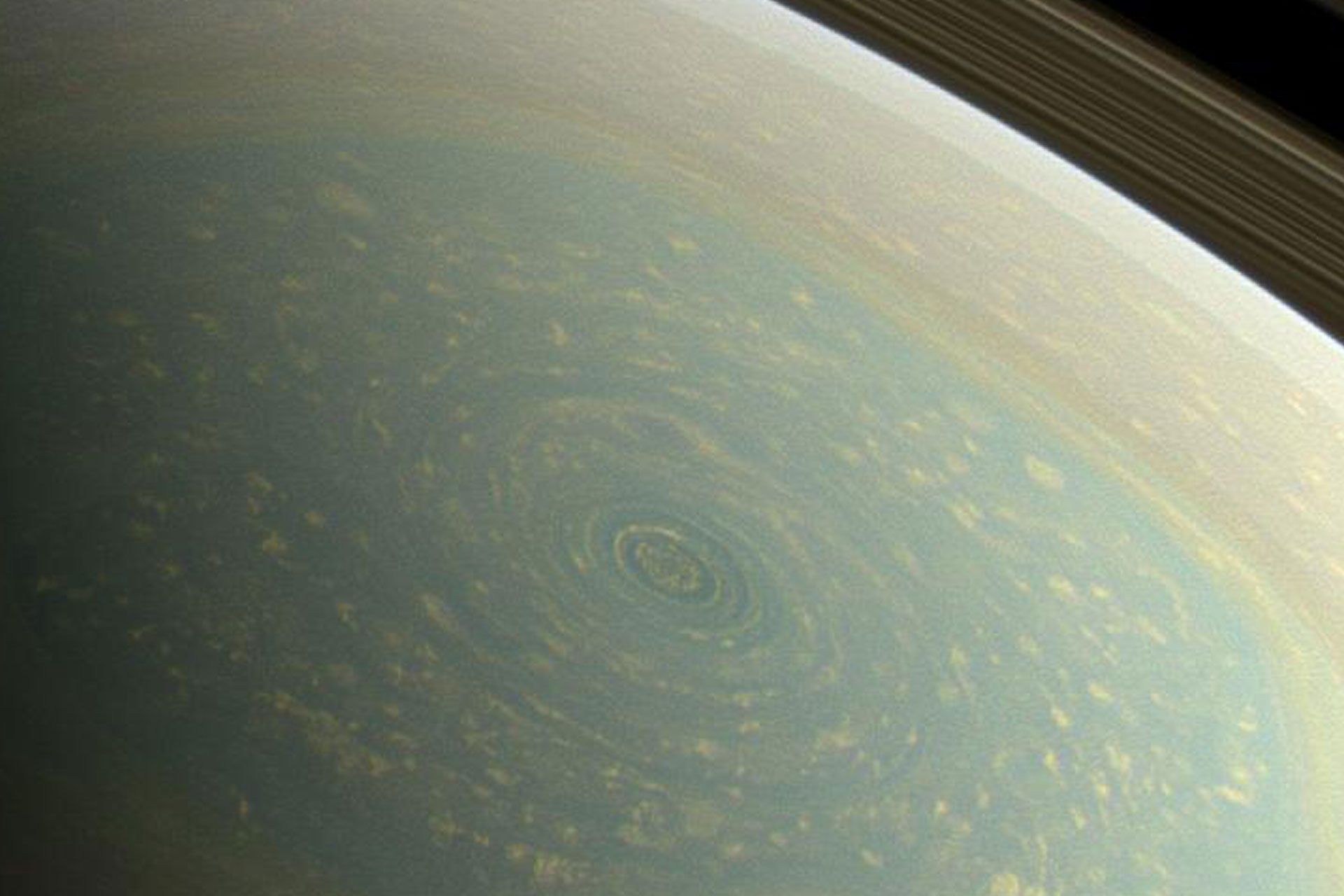
Hexagonal Storm: Saturn’s north pole has a fascinating feature called a hexagonal wind flow. This hexagonal pattern was first observed from images sent by the Voyager spacecraft and then observed from a closer distance by Cassini. This hexagon, whose diameter reaches 30,000 km, is a wavy current, whose wind speed reaches 322 km/h, and a storm is placed in its center. This storm is unique in the entire solar system. At the south pole of Saturn, there is also evidence of storm currents, but no hexagonal waves are seen. According to NASA reports from Cassini in November 2006, a tornado-like storm was observed at Saturn’s south pole.
Reduction of rings: According to NASA research, Saturn’s rings have been decreasing at a maximum speed since Voyager probes visited this planet. These rings were attracted towards this planet due to gravity and under the influence of Saturn’s magnetic field. According to scientists, Saturn’s rings will be completely destroyed in three hundred million years, on the other hand, according to Cassini’s findings, Saturn’s rings are relatively young and their life is less than one hundred million years. As a result, the rings of Saturn are much younger compared to the life of this planet (4 billion years).
Long seasons: Saturn has seasonal changes like Earth, but Saturn’s seasons have a major difference from Earth’s seasons. It takes one year for the Earth to complete the orbit of the sun, during this time the Earth experiences cold and hot seasons. But since Saturn is far from the Sun, it takes 29 Earth years to complete the orbit of the Sun. As a result, one Saturn year is equal to 29 Earth years. Therefore, the seasons also get longer and the duration of each Saturnian season is approximately seven years.
Diamond rain: Since the internal structure of Saturn is completely different from the structure of Earth, its rains are not made of water but of diamonds. According to scientists, ten million tons of diamonds are produced in Saturn’s atmosphere every year. This phenomenon occurs thanks to the combination of methane gas (CH4) with the wind activities of this planet. Saturn’s rays have a high temperature and are 10,000 times stronger than Earth’s rays, and when they are emitted, they break molecular bonds and separate hydrogen and carbon.
Ten million tons of diamond rain falls on Saturn every year
The carbon atoms join together to form larger molecules that result in a soot-like compound. This black cloud is far from a diamond, but the story does not end there. The new molecule is relatively heavy and will fall down when caught in the planet’s gravity trap. By falling to greater depths, the temperature and pressure on the molecules also increase. These conditions lead to carbon transformation. At first, carbon is converted to graphite. The same stuff that’s inside your pencils and then turns into one-centimeter-diameter diamonds and they keep falling.
Seeing Saturn from Earth
The observation and exploration of Saturn can be divided into three phases. The first period of ancient observations (including observations with the naked eye) is before the invention of the telescope. Advanced ground-based telescopic observations began in the 17th century. According to written history, the planet Saturn has been one of the main elements of many myths. Babylonian astronomers systematically observed and recorded the movements of Saturn.
The third phase was the visit of space probes, simultaneously with this period of ground-based observations (including the Hubble Space Telescope) continued. To see Saturn’s rings, you need a telescope with a diameter of at least 15 mm. Christian Huygens was able to achieve this success in 1659. Before that, Galileo had observed Saturn with his early telescope and thought that Saturn was not completely spherical. Until Huygens was able to observe Saturn’s rings for the first time with a more advanced telescope. Huygens also discovered Titan, Saturn’s largest moon. Later, the young Domenico Cassini discovered four more moons of Saturn: Iapetus, Rhea, Tethys, and Dione.
William Herschel discovered two other moons, Mimas and Enceladus, in 1789. A British team also discovered Hyperion in 1848. William Henry Pickering discovered Phoebe in 1899, which is an irregular moon that does not rotate perfectly in sync with Saturn and its other moons. In the 20th century, studies of Titan proved the existence of a thick atmosphere on this moon.
Discoveries of Saturn in the Space Age
In the modern era, Hubble Space Telescope observations continued. Pioneer 11 was the first spacecraft to observe Saturn from a close distance, later Voyager 1 and 2 provided more detailed observations. But Cassini was the only orbiter that provided more detailed and comprehensive information about Saturn, and the Huygens probe of this spacecraft landed on the surface of Titan for the first time in 2005.
Pioneer discoveries 11
Pioneer 11 passed through the upper clouds of Saturn for the first time in September 1979. Pioneer 11 photographed Saturn and several of its moons, although the quality of the images is low and does not show much detail. The spacecraft also examined Saturn’s rings and revealed the thin F ring.
Pioneer 11 also showed that dark gaps in Saturn’s rings appear bright and contain light-scattering material when viewed from a high phase angle (towards the Sun). Another achievement of Pioneer in the exploration of Saturn was to measure the temperature of Titan.

Pioneer 11 low quality image of Saturn
Voyager 1 and 2 discoveries
Voyager 1 visited the Saturn system in November 1980. The probe released the first high-quality images of the planet, its rings, and its moons. The surface features of Saturn’s moons were first revealed by Voyager. Voyager 1 approached the moon Titan and sent back a lot of information about the moon’s atmosphere. According to the data of this probe, Titan’s atmosphere is impenetrable in visible wavelengths, as a result, none of its surface details were seen.
Almost a year later, in August 1981, Voyager 2 continued its survey of the Saturn system. More detailed images of Saturn’s moons were sent, as well as evidence of atmospheric changes and its rings. Unfortunately, the probe’s rotatable camera malfunctioned for several days during the Saturn survey, and many views were not recorded. Operators used Saturn’s gravity to redirect the spacecraft toward Uranus. The two Voyager probes discovered a number of moons near and inside Saturn’s rings, as well as the small Maxwell fissure (a gap in the C ring) and the Keeler fissure (a wide, 42 km gap in the A ring).
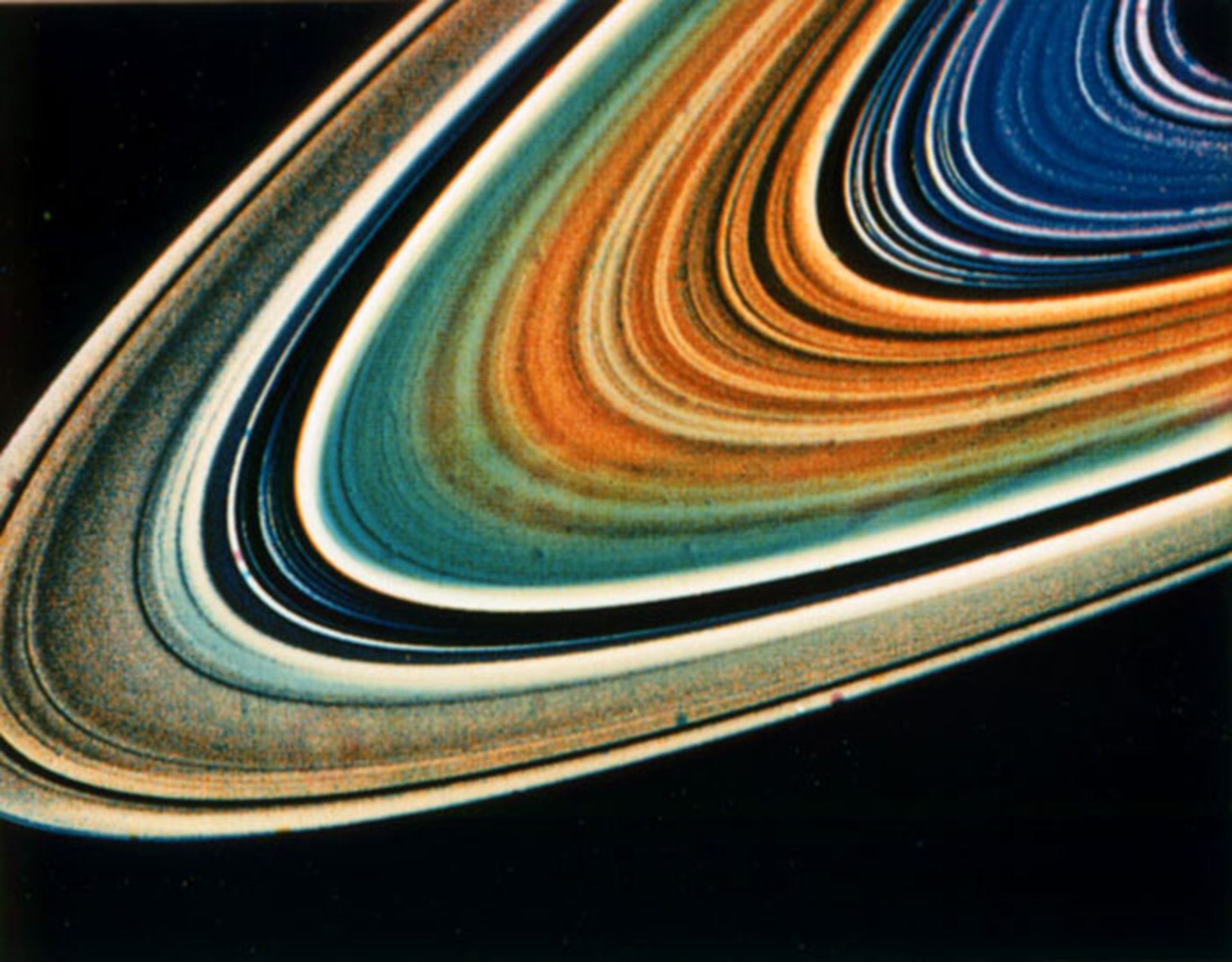

Image captured by Voyager 2
Cassini Huygens: Exploring the Saturn System
The Cassini spacecraft began orbiting Saturn on June 30, 2004 and continued its mission until September 15, 2017, when the probe ended its life by hitting the planet’s atmosphere. The destruction of Cassini was intentional and to ensure that the moons Enceladus and Titan were not contaminated. Cassini’s achievements include the discovery of the glaciers of Enceladus and the discovery of new moons for Saturn. Cassini was a joint project of multiple space agencies and was pitted against NASA’s older and larger probes, including Pioneer and Voyager. Cassini’s partners were NASA, the European Space Agency, and the Italian Space Agency.
Cassini was the first spacecraft dedicated entirely to studying Saturn and its ring system. The orbiter was named after Giovanni Cassini, an astronomer of the 17th century. Cassini was not launched directly at Saturn. Rather, its mission was a little more complicated. Before reaching Saturn, he checked the planets Venus (twice), Earth, and Jupiter and thus used the gravity of each planet to increase his speed. This 5700 kg spacecraft was launched on October 15, 1997. It reached Venus in April 1998, Earth in August 1999, and Jupiter in December 2000.
Cassini finally entered Saturn’s orbit on July 1, 2004. One of the main goals of this mission was to discover more moons for Saturn and to discover the structure and color of the rings, as well as to get more information about the moons of this planet. Cassini carried a passenger called the Huygens probe. Huygens landed on the surface of Titan on January 14, 2005, and transmitted data to Earth for 2.5 hours.
In this short period of time, the researchers obtained images of the surface as well as information about the gases and winds in the atmosphere and on the surface of Titan. Cassini discovered two new moons for Saturn and discovered the presence of liquid water on the surface of Enceladus and its glaciers. It also published more details about Titan’s methane lake. Other Cassini discoveries include the following:
- Debris 80 km from the surface of Iapetus
- A close-up view of the Rhea moon and its impact craters.
- The discovery of a large ring approximately 12 million kilometers from Saturn, which is probably composed of particles from the moon Phoebe.
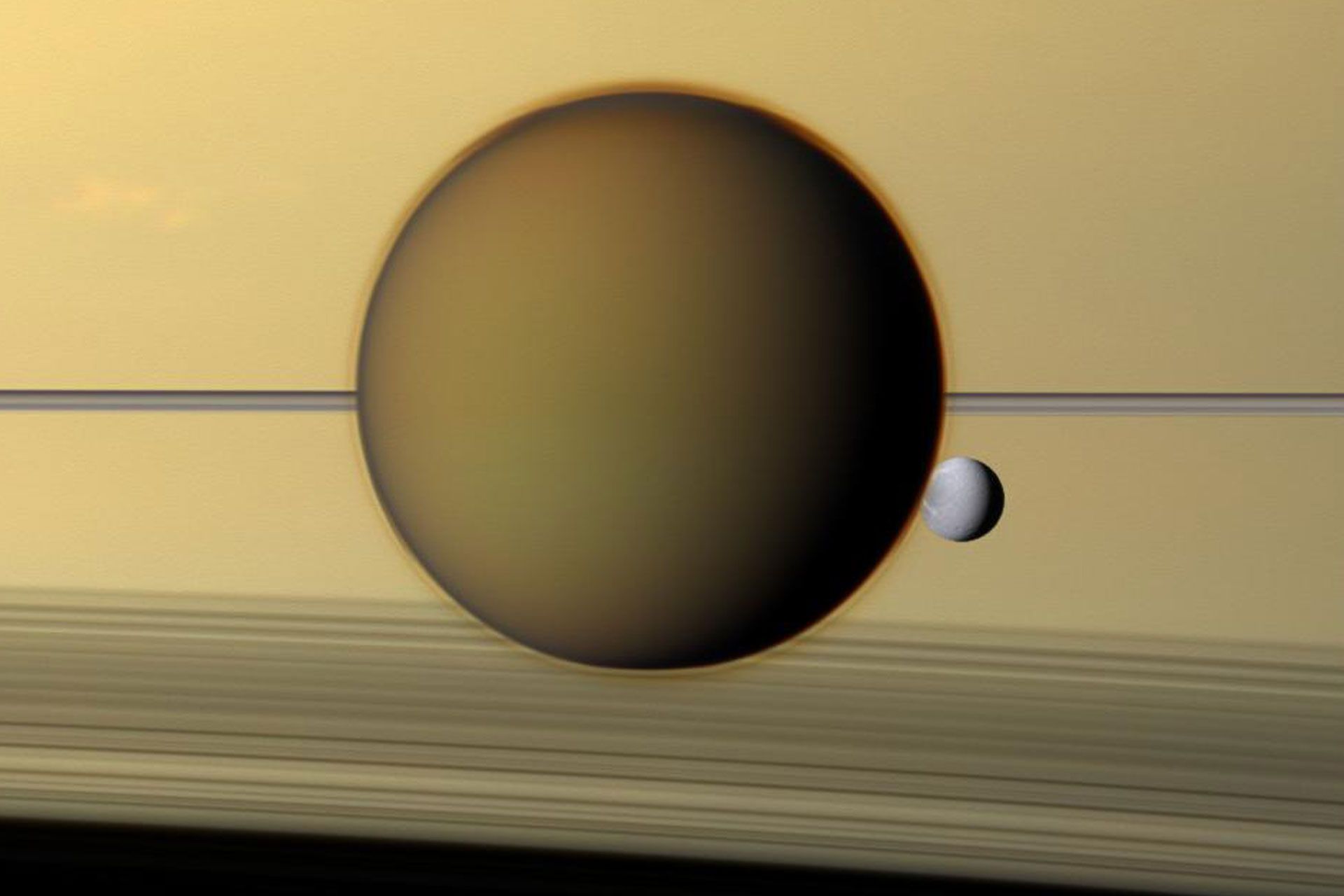
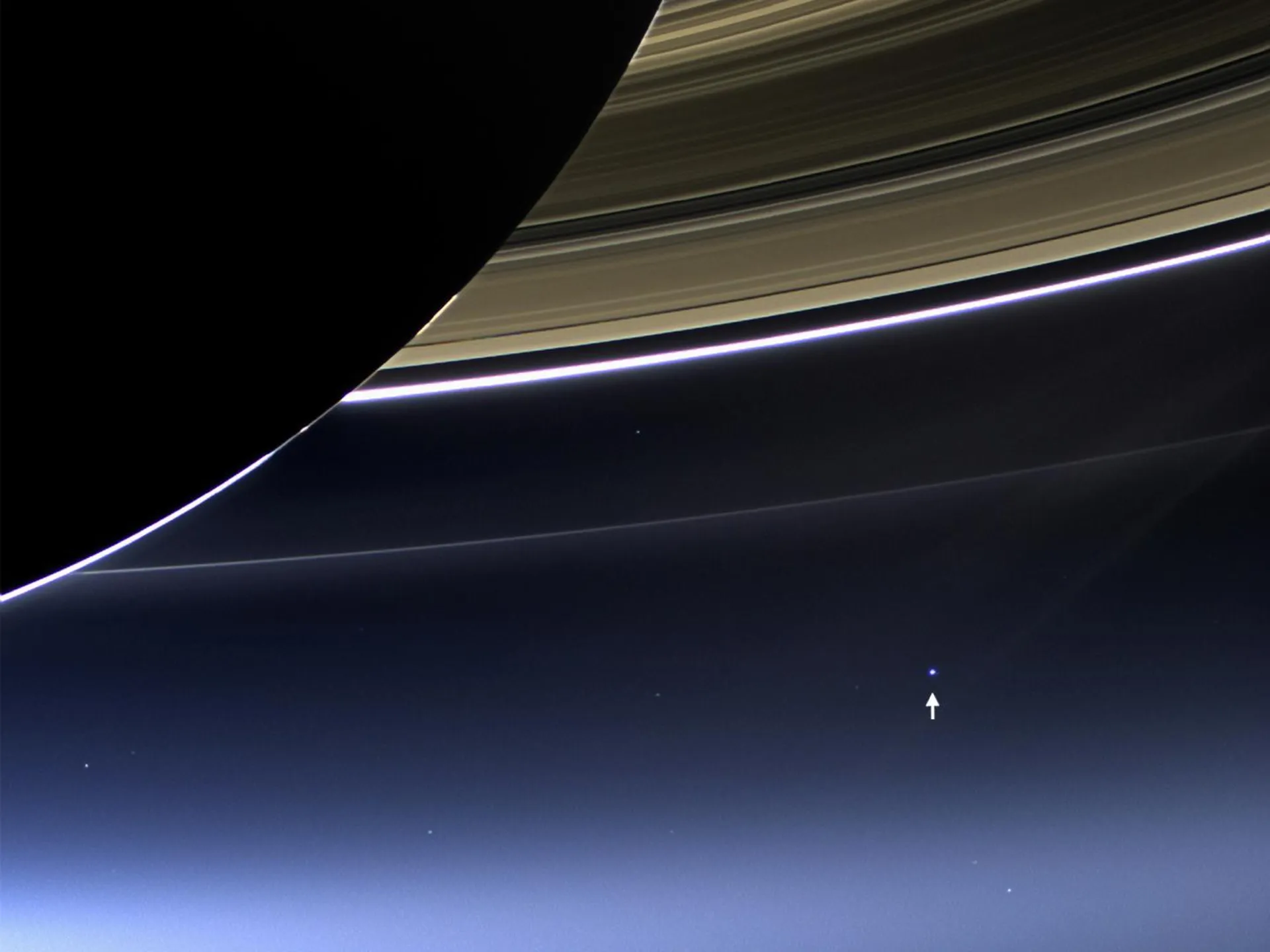




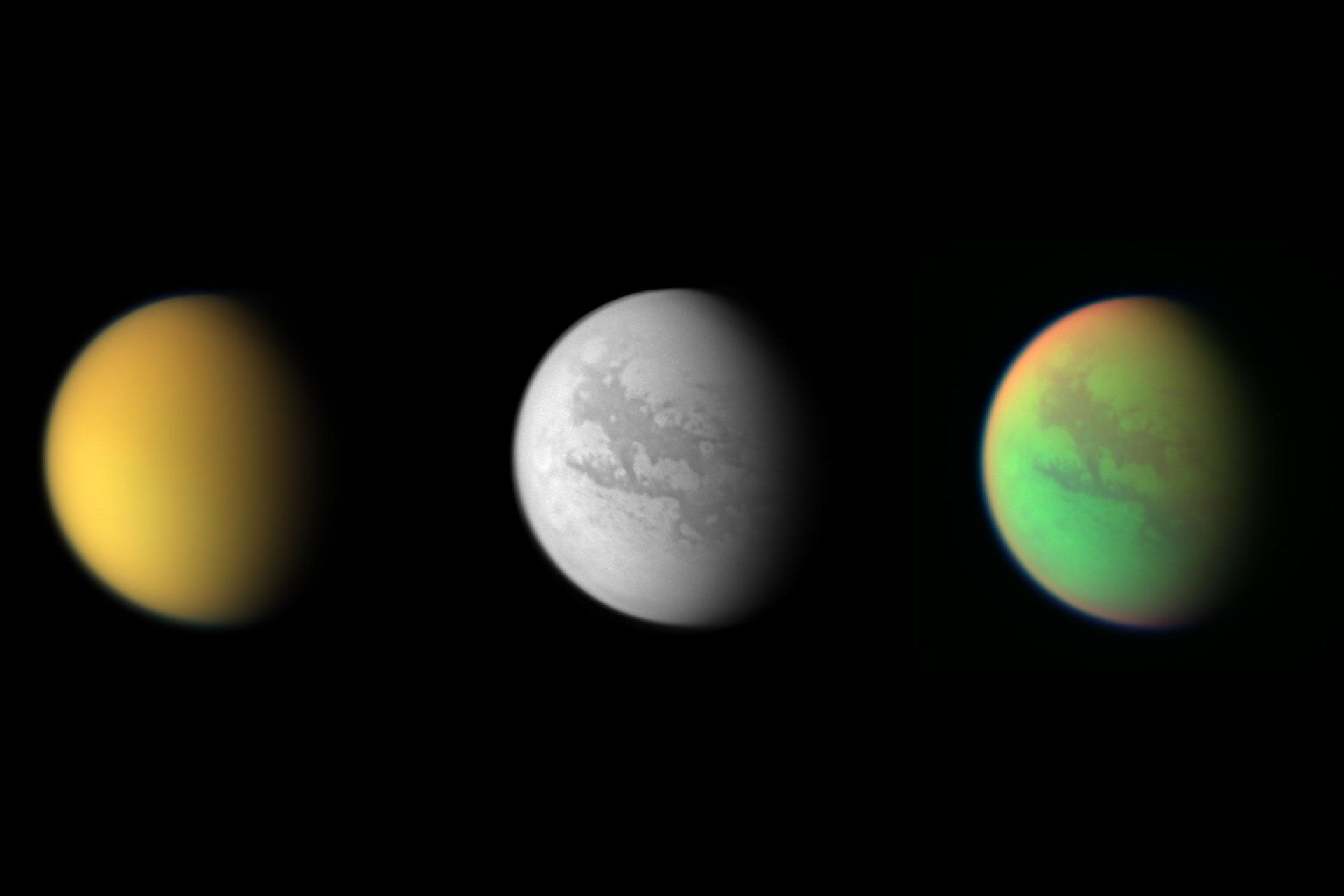



A selection of images captured by the Cassini Huygens spacecraft
Farewell to Cassini
Cassini’s last data was transmitted to Earth on September 15, 2017; Then this probe was destroyed by collision with Saturn’s atmosphere. This was Cassini’s last orbit around Saturn after 13 years of exploration and investigation. According to NASA experts, Cassini disintegrated 45 seconds after its last transmission due to the heat and friction of the fall.
Shortly after Cassini broke up, its mission planner Eric Sturm outlined his plan to report on his and his team’s experiences on the mission. The mission is over, but its scientific results will be published for decades to come because the entire data has not yet been analyzed.
Future missions to Saturn
Among the proposed plans for explorations on the planet Saturn, the robotic probe Dragonfly has reached the approval stage of NASA. The probe is in the form of a drone and will investigate hundreds of locations on Titan, Saturn’s moon. It will also sample and measure the composition of biological materials on the surface of Titan and search for life on this moon. Dragonfly will launch in 2026 and reach Saturn in 2034.


You may like


iPhone 16 Pro Review
We usually know Apple as a company that refuses to release half-assed products or software features and prefers not to enter a new field at all or to enter with a product that provides a reliable and efficient experience to the user. Accordingly, the iPhone 16 Pro is the most imperfect product in Apple’s history; I will explain further.
-
iPhone 16 Pro video review
-
Camera and Camera Control
-
Ultrawide camera
-
Main camera
-
Telephoto camera
-
Portrait photography
-
selfie camera
-
Performance and battery
-
Design and build quality
-
Display and speaker
-
Summary and comparison with competitors
Apple is marketing the iPhone 16 Pro with a focus on Apple Intelligence and its artificial intelligence capabilities; But now, even to experience Apple’s artificial intelligence half-and-half, you have to wait until the official release of iOS 18.1 in late October, more than a month after the iPhone 16’s launch. There is not even news of the attractive animation of the new Siri; The animation that inspired Apple to name the iPhone 16 event It’s Glowtime.

For those who have been unaware of the technology world since the early months of 2024, I must say that Apple Intelligence is Apple’s answer to Google’s Gemina, Samsung’s Galaxy AI, and even Microsoft’s Copilot. According to Apple Intelligence, Siri is going to be what was promised 13 years ago, during its unveiling; A full-fledged digital assistant that speaks to the user in natural language; Of course, apart from the advanced Siri, capabilities such as creating photos and emojis with AI, text writing and photo editing tools will also be added to iOS.
Note that we have to wait for iOS 18.4 to fully experience Apple Intelligence with all its features; This update will be released in the early months of 2025. iPhone 16 comes with iOS 18 by default; So it is not surprising that Apple lags behind its competitors with such a delay, and the iPhone 16 Pro is not a perfect device either.
Camera and Camera Control
Now that Apple Intelligence is out of the question, and as per Zoomit’s policy, we don’t review a device based on the promise of future updates, let’s leave AI out of the iPhone 16 Pro review headlines and start straight from the part that has changed the most. : Camera or rather, camera button.




While it was said that Apple is working on removing the physical buttons of the iPhone, this year surprisingly, another button was added to the iPhone 16 family; Although Apple insists on calling it Camera Control. Unfortunately, camera control is crude and incomplete both in terms of implementation and capabilities; I will explain further.
As usual with Apple, the camera control has a complex engineering behind its simple appearance. The surface of the control camera is made of sapphire and is surrounded by a stainless steel ring of the same color as the body. Under this surface, there is a precise force detection sensor with haptic feedback along with a touch sensor so that the camera control can simulate the shutter of DSLR cameras and recognize the swipe of the finger on the button surface.

Apple says that by the end of this year, with a software update, it will add a feature to the camera control that will allow the user to focus on the subject by half-pressing the button and record the photo by fully pressing it, just like professional cameras and Xperia phones. On the other hand, after the release of Apple Intelligence, the user will have access to Siri’s image search function with the camera control.
control camera; An interesting idea, but very immature
Currently, with the camera control, you can take photos, record videos, or change camera parameters; Thus, by pressing the button once, the camera application is launched, now if you press the button again, a photo will be taken, and if you hold it, the video will start, and as soon as you lift the finger, the video will stop.
In the camera environment, if you gently press the button twice without lifting your finger, the photography parameters will appear, you can switch between the options by swiping on the button surface, and you can enter the desired parameter settings with another gentle press. Among the photography parameters available are exposure, depth of field, zoom, switching between cameras, Style, and Tone, and we will talk more about the last two in the following.



To be honest, for me and many of my colleagues at Zoomit, it was much easier and more straightforward to touch the screen to navigate through the camera menu than to use the camera controls. Still, after 10 days of working with iPhone 16 Pro, it is very difficult and time-consuming to go to the photography parameters section and swipe to adjust the parameters; For example, it often happens that while swiping to adjust the value of a parameter such as Tone, the phone decides to exit the Tone settings and move between parameters.
One of the problems of the camera control comes back to the firmness of its button; Therefore, when taking pictures with this button, the phone shakes; An issue that may end up blurring the details of photos in the dark.
Apart from the safety of the button, the placement of Camera Control is also not optimal in my opinion; When using the phone in portrait mode, especially with the Pro Max model, you are likely to have trouble and need to use both hands; If you use the phone with your left hand, sometimes your fingers may press the button and disrupt the phone’s functionality.

If Apple fixes the problems and bugs of the control camera, maybe it can be used in two cases; First, during zooming, because you can have more precise control over the zoom level, and second, for faster access to Apple’s new settings for the camera called Style and Tone, which are very useful for photography enthusiasts; Now I will explain the reason.
iPhones usually have their own style of photography; iPhone photos usually have colors close to reality with a relative tendency towards warmth, and there is no mention of saturated and high-contrast colors; Of course, Apple introduced the Photographic Styles feature with iPhone 13 to satisfy the fans of high-contrast photography in the style of Google Pixels by providing different photography styles.
iPhone 16 Pro? Pixel 9 Pro XL or Galaxy S24 Ultra? Which phone has the best camera? The result will surprise you.
With the iPhone 15, Apple adopted a policy that was not very pleasant for the public; In short, in order to use all the capacities of the powerful Photonic Engine with the aim of preserving the details of the shadows and highlights, the iPhone goes a little too far in the implementation of HDR to the point where the colors and shadows lose their power and do not have the previous dramatic sense.
The bad news is that the iPhone 16 Pro follows Apple’s previous policy and, so-called, records the shadows weakly; But the good news is that now with the evolved version of Photographic Styles, you can breathe new life into shadows and colors. With the new version of Photographic Styles, you can change the type of skin color processing and shadows, even after taking photos, you can change the photography style.
Discover your photography style with the iPhone 16 Pro
Before we see the effect of photographic styles on photos, let’s talk about their different modes first. iPhone photography styles are now divided into two general categories: Mood and Undertone; Apart from the standard photography mode, 5 Undertone styles and 9 Mood styles are available. Undertone styles adjust the skin tone of human subjects more than anything else, and Mood styles offer functionality similar to Instagram filters.
Undertone styles are as follows:
- Standard: iPhone’s default photography mode
- Amber: Intensifies the amber tone in photos
- Gold: Intensifies the golden tone in photos
- Rose Gold: Intensifies the pink-gold tone in photos
- Neutral: Neutralizes warm undertones in photos
- Cool Rose: Intensifies cool-toned color in photos






Mood styles are as follows:
- Vibrant
- Natural
- Luminous
- Dramatic
- Quiet
- Cozy
- Ethereal
- Muted B&W
- Stark B&W









All styles can be customized with three new parameters: Palette, Color, and Tone; The Palette parameter changes the range of applied colors, Color adjusts the intensity of color saturation, and most importantly, Tone can change the intensity of shadows and contrast and bring freshness back to iPhone photos.
While the Palette parameter is adjusted with a simple slider, you have to use a control pad to adjust color and tone. Working with this pad is very difficult and boring; Because to change the value of each of the two parameters, you have to put your finger on the head pad and since you have no feeling about the exact location of the finger, it is difficult to change the other parameter by keeping one parameter constant.
The iPhone 16 Pro photography experience is slightly different from the previous generation
If, like me, you don’t feel like messing around with the control pad and slider, you can directly access the styles or the Tone parameter with the camera control button and believe that you can increase the attractiveness of iPhone photos just by changing the Tone; For example, pay attention to the following two photos:
As you can see in the photos above, without changing the styles and simply by reducing the intensity of the tone, both the shadows have returned to the photo, and the black color of Mohammad Hossein’s t-shirt is visible better than before thanks to the improvement of the contrast of the image.
Ultrawide camera
Leaving aside the discussion of photography styles, the iPhone 16 Pro camera itself has undergone several major changes, the most important of which is the upgrade of the telephoto camera sensor from 12 to 48 megapixels; The new sensor uses a Quad-Bayer filter and 0.7-micrometer pixels; Therefore, it seems that the dimensions of the sensor itself are not different from the 1.2.55-inch sample of the previous generation with 1.4-micrometer pixels.
|
camera |
Sensor |
Lens |
capabilities |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Wide camera (main) |
48-megapixel Sony IMX903 Dimensions 1/1.28 inches 1.22 µm pixels Phase detection autofocus Sensor-shift optical stabilizer |
24 mm Aperture f/1.78 |
12, 24 and 48-megapixel photography 4K120 video recording Dolby Vision, ProRes, and Log Portrait photography |
|
Telephoto camera |
12-megapixel Sony IMX913 Dimensions 1/3.06 inches 1.12 µm pixels Dual Pixel phase detection autofocus Sensor-shift optical stabilizer |
120 mm Aperture f/2.8 5x optical zoom |
12-megapixel photography 4K60 video recording Dolby Vision, ProRes, and Log Portrait photography |
|
Ultrawide camera |
48 megapixels Dimensions 1/2.55 inches 0.7 µm pixels Phase detection autofocus |
13 mm Aperture f/2.2 |
12 and 48-megapixel photography 4K60 video recording Dolby Vision, ProRes, and Log Macro photography |
|
selfie camera |
12-megapixel Sony IMX714 Dimensions 1/3.6 inches 1.0 µm pixels Phase detection autofocus |
23 mm Aperture f/1.9 |
12-megapixel photography 4K60 video recording Dolby Vision, ProRes, and Log |
In order for the pixels to capture the right light, the ultrawide camera by default captures 12MP photos by combining 4:1 pixels and achieving 1.4 micrometer pixels; But with the HEIF Max photography format, it is possible to shoot with 48 megapixels, so that the user has more freedom to zoom in on the photos.




As you can see in the images above, the ultrawide 48 megapixel photo of the iPhone is somewhat more detailed in some parts; But it is generally softer than the 12-megapixel model. We also took photos of the same subject with iPhone 16; There is no noticeable difference between the 12 megapixel photos of the two phones.

Ultrawide iPhone 16 Pro camera with 1/25 second exposure

iPhone 16 ultrawide camera with 1/10 second exposure
 Crop ultrawide camera photos in the dark
Crop ultrawide camera photos in the dark
iPhone 16 Pro goes to Night mode and long exposure much less than the iPhone 16 in dark environments; Therefore, sometimes its ultrawide night photos are less detailed than the iPhone 16; For example, in the photos above, the iPhone 16 is exposed for one-tenth of a second; While the exposure of the iPhone 16 Pro was 60% less and equivalent to one twenty-fifth of a second; So it is not surprising that the cheaper iPhone photo is more attractive!
iPhone 16 Pro ultrawide camera photo gallery












The ultrawide camera of the iPhone 16 Pro generally takes attractive photos, But maybe it cannot be considered on par with competitors. The difference in performance with the best in the market is more noticeable in the dark; The iPhone 16 Pro’s ultrawide camera doesn’t appear so amazing in dark environments and records relatively soft photos. To evaluate the performance of the iPhone’s ultrawide camera against the competitors, I suggest that you read the comprehensive article comparing the 2024 flagship cameras.
Main camera
On paper, the main 48-megapixel camera of the iPhone 16 is no different from the previous generation in terms of sensor dimensions and pixels or lens specifications; But Apple calls this camera Fusion and claims that the sensor itself has become faster, and thanks to a new architecture called Apple Camera Interface, image data is transferred from the sensor side to the chip for processing at a faster rate; So now the main camera of the iPhone has the ability to record 4K120 Dolby Vision.
Record stunning videos with 120 frames per second video recording
HDR filming at a rate of 120 frames per second and 4K resolution requires very heavy processing; Because to implement the HDR effect, several 4K frames with different exposures must be compared and aggregated every second. If you have an external SSD and a high-speed USB 3 cable, you can also save 4K120 videos in professional ProRes and log formats, which give you more freedom when editing videos and correcting colors.
4K120 video sample 1
4K120 video sample 2
The 4K120 iPhone 16 Pro videos are very attractive and detailed and bring a wonderful visual experience to Armaghan. Since none of the 4K120 iPhone 16 Pro videos were uploaded properly to the app platform, you must refer to the YouTube links to watch the videos.
Thanks to the faster sensor and Apple’s new interface, 48-megapixel photos with HEIF Max format are recorded almost without pause and at a rate of about 4 frames per second. Like the previous generation, the iPhone combines multiple 12- and 48-megapixel frames, by default, it shoots at 24-megapixel resolution to provide a balanced combination of contrast, color, and detail; Of course, it is possible to take 12-megapixel photos alongside 48-megapixel HEIF Max photos.



 Crop photos of 48, 24, and 12 megapixels
Crop photos of 48, 24, and 12 megapixels
As you can see in the photos above, the 48-megapixel mode improves the details to some extent at the cost of overall softening of the photo and gives you more freedom to zoom into the photo; But the contrast and concentration of its colors are at a lower level than the 24 and 12-megapixel modes. The 24MP photos seem to have a good balance of detail, color and contrast.

iPhone 16 Pro main camera

iPhone 16 main camera

The main camera of the iPhone 16 Pro has recorded a little more detail in the photos above compared to the iPhone 16; But as you can see, the iPhone 16 Pro photo has a lower contrast, its colors are more warm than the iPhone 16, and the black color of Mohammad Hossein’s T-shirt does not match black enough.
iPhone 16 Pro main camera photo gallery
















The photos of the iPhone 16 Pro’s main camera have the same feeling as the iPhone 15 Pro; They are full of details, the colors appear relatively natural, and tend to be a little warm. The iPhone does not artificially remove noise as much as possible; Therefore, even in the dark, it pulls out a high level of fine and intricate details from the subjects. The large dimensions of the sensor allow the iPhone to record 2x high-quality photos by creating a 12-megapixel crop from the middle of the full-sensor image of the main camera.
Telephoto camera
In addition to the renewed ultrawide camera, another big change is the addition of a 5x telephoto camera to the iPhone 16 Pro; Last year, this camera was exclusive to the iPhone 15 Pro Max. The new telephoto camera uses the same 12-megapixel sensor as the previous generation and provides the user with digital zoom up to 25 times.
iPhone 16 Pro telephoto camera photo gallery












The iPhone 16 Pro telephoto camera records 5x high-quality photos; The level of detail and colors of the telephoto camera are very similar to the main camera and match its mood. The telephoto camera also excels in low-light environments and takes good photos in the dark. But as we said in the comprehensive comparison of 2024 flagship cameras, the competitors perform better in this field.

1x photo

Double photo

3x photo

5x photo

10x photo

25x photo
The combination of the iPhone 16 Pro’s 48-megapixel main camera and its 5x telephoto camera allows us to record relatively high-quality zoomed photos in the range of 1-10x; Apart from the 5x optical zoom, the iPhone looks quite satisfactory at 2x and 10x levels.
Portrait photography
The iPhone 16 Pro relies on the main and telephoto cameras for portrait photography and uses the ToF sensor to accurately separate the subject from the background. 1x and 2x portrait photos are recorded with the main camera and 5x portrait photos are also recorded with the telephoto camera.

1x portrait photo

2x portrait photo

5x portrait photo

1x portrait photo

2x photo with natural bokeh

5x portrait photo
The iPhone had a poor performance in portrait photography several years ago, and the iPhone 16 Pro follows the same rule. Portrait photos are detailed and the bokeh effect implementation is gradual and similar to professional cameras. As we saw in the 2024 flagship camera comparison article, the iPhone beats even tough competitors like the Pixel 9 Pro and S24 Ultra in portrait photography.
selfie camera
The selfie camera of the iPhone 16 Pro is no different from the previous generation, and it still captures eye-catching photos with many details and true-to-life colors.


iPhone 16 Pro with all its cameras is capable of recording 4K60 videos with Dolby Vision HDR standard; Of course, you can also choose 24 and 30 frames per second for filming. Videos are pre-recorded with h.265 codec, But it is also possible to switch to the more common h.264 codec.
We shot at 30 and 60 fps and h.265 codecs, and the iPhone 16 Pro recorded very detailed videos in both modes with vivid colors, high contrast, and decent exposure control; If you want to see the video recording performance in competition with other flagships, don’t miss the iPhone 16 Pro vs. Pixel 9 Pro and Galaxy S24 Ultra camera comparison article.
Performance and battery
The next big change to the iPhone 16 Pro comes back to its chip. A18 Pro uses the familiar combination of 2 high-power cores and 4 low-power cores as a CPU, and this unit is accompanied by a 6-core graphics processor and a 16-core neural processing unit. Apple’s new chip is produced with TSMC’s improved 3nm lithography called N3E.
|
Technical specifications of the A18 Pro chip compared to the previous generation |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Specifications/Chip |
A17 Pro |
A18 |
A18 Pro |
|
Central processor |
2 powerful 3.78 GHz cores with 16 MB cache 4 low-power 2.11 GHz cores with 4 MB cache 24 MB system cache |
2 powerful 4.04 GHz cores with 8 MB cache 4 low-power 2.0 GHz cores with 4 MB cache 12 MB system cache |
2 powerful 4.04 GHz cores with 16 MB cache 4 low-power 2.2 GHz cores with 4 MB cache 24 MB system cache |
|
A set of instructions |
ARMv8.6-A |
ARMv9.2-A |
ARMv9.2-A |
|
Graphics |
6-core 1398 MHz 768 shading units Ray tracing |
5-core 1398 MHz 640 shading units Ray tracing |
6-core 1450 MHz 768 shading units Ray tracing |
|
Memory controller |
4 16-bit channels RAM 3200 MHz LPDDR5X The bandwidth is 51.2 GB |
4 16-bit channels RAM 3750 MHz LPDDR5X The bandwidth is 58.6 GB |
4 16-bit channels RAM 3750 MHz LPDDR5X The bandwidth is 58.6 GB |
|
Record and play video |
4K60 10-bit H.265 |
8K24 / 4K120 10-bit H.265 |
8K24 / 4K120 10-bit H.265 |
|
Wireless connection |
Bluetooth 5.3 and Wi-Fi 7 |
Bluetooth 5.3 and Wi-Fi 7 |
Bluetooth 5.3 and Wi-Fi 7 |
|
modem |
X70 modem Download 7500 MB in the UK Upload is 3500 megabits per second |
X75 modem Download 10,000 megabits per second Upload is 3500 megabits per second |
X75 modem Download 10,000 megabits per second Upload is 3500 megabits per second |
|
manufacturing process |
3-nanometer TSMC |
3-nanometer TSMC (Enhanced: N3E) |
3-nanometer TSMC (Enhanced: N3E) |
Apple says it uses new cores in the CPU, which results in 15% faster performance than the A17 Pro and achieves the same level of performance as this chip with 20% less power consumption. Apple claims that the A18 Pro uses more cache memory compared to the A18 chip.
The A18 Pro chip has faster single-core performance than even multi-100W desktop processors.
According to Apple, the 6-core A18 Pro graphics is 20% faster than the previous generation. Apple says the ray tracing accelerator in the new GPU is also a 100% improvement over the previous generation.

The 16-core A18 Pro neural processing unit, like the previous generation, is capable of performing 35 trillion operations; But thanks to the 17% increase in bandwidth between the RAM and the chip, the new NPU performs better than before in real-world applications. The A18 Pro chip is connected to 8 GB LPDDR5x-7500 RAM with a high-speed memory controller.
|
iPhone 16 Pro performance against competitors |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Product/benchmark |
chip |
Speedometer 2.1 |
GeekBench 6 |
GFXBench |
|
|
Web browsing experience |
GPU computing power |
CPU computing power |
Game simulator |
||
|
Vulkan/Metal |
Single/Multi |
Aztec Ruins Onscreen/1440p |
|||
|
Vulkan/Metal |
|||||
|
iPhone 16 Pro |
A18 Pro |
572 |
33105 |
3542 8801 |
59 70 |
|
iPhone 16 |
A18 |
554 |
28025 |
3440 8406 |
59 61 |
|
iPhone 15 Pro |
A17 Pro |
475 |
27503 |
2960 7339 |
59 46.8 |
|
Piura 70 Ultra (Performance Mode) |
Kirin 9010 |
235 |
1528 (Failed) |
1452 4494 |
32 30 |
|
Pixel 9 Pro |
Tensor G4 |
221 |
6965 |
1945 4709 |
70 44 |
|
Galaxy S24 Ultra |
Snapdragon 8 Gen 3 for Galaxy |
240 |
17012 |
2262 7005 |
75 81 |
iPhone 16 Pro is noticeably faster than current Android flagships; The difference of about 60% in single-core CPU performance with the Galaxy S24 Ultra clearly shows how fast the iPhone 16 Pro appears in everyday use.
Apple’s 2024 flagship dictates its 95% advantage over a rival such as the Galaxy S24 Ultra when using the GPU for calculations such as blurring the background of photos and face recognition; However, in the rendering of games, the advantage is still with the Galaxy and the Snapdragon 8 generation 3 chip.
|
The performance of the neural processing unit of the iPhone 16 Pro against competitors |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
|
phone/parameters |
framework |
intermediary |
Single count accuracy score (FP32) |
|
iPhone 16 Pro |
Core ML |
Neural Engine |
4647 |
|
iPhone 15 Pro |
Core ML |
Neural Engine |
3862 |
|
Piura 70 Ultra |
TensorFlow Lite |
NNAPI |
235 |
|
Pixel 9 Pro |
TensorFlow Lite |
NNAPI |
347 |
|
Galaxy S24 Ultra |
TensorFlow Lite |
NNAPI |
477 |
The neural processing unit of the iPhone 16 Pro outperforms the Galaxy S24 Ultra in the GeekBench AI benchmark by an astronomical 870%; Now we have to wait until the release of Apple’s artificial intelligence capabilities to see if such a difference is reasonable or just a bug in the benchmark software.
Like the previous generation, Apple sells the iPhone 16 Pro in versions of 128, 256, 512 GB and 1 TB with NVMe storage; While the base model of the iPhone 16 Pro Max uses 256 GB of storage space. Benchmarks show that the storage speed of the iPhone 16 Pro is no different from the previous generation.
|
iPhone 16 Pro storage speed compared to competitors |
||
|---|---|---|
|
phone model |
Sequential reading rate |
Sequential write rate |
|
iPhone 16 Pro |
1636 megabytes |
1340 megabytes |
|
iPhone 15 Pro |
1652 MB UK |
1380 megabytes |
|
Pixel 9 Pro XL |
1350 megabytes |
171 megabytes |
|
Galaxy S24 Ultra |
2473 megabytes |
1471 megabytes |
If we leave the numbers aside, we will face the fact that the feeling of using the iPhone 16 Pro in everyday use is not much different from the iPhone 15 Pro or even the iPhone 14 Pro. The performance gap between the new iPhone and the previous generations is the reason that the phone can still provide good performance with the standard of a few years later, and of course, it can handle the heavy processing of Apple Intelligence.
Apple says that with the changes made in the internal structure of the iPhone 16 Pro; Including the metal shell of the battery (pro model only), the phone can now perform up to 20% more stable in heavy usage. This performance stability improvement is felt to some extent; The phone does not get hot while playing graphic games and its performance drops less than before; In the Zomit stability test, the iPhone 16 Pro dropped less than the Galaxy S24 Ultra and the previous generation; The maximum temperature of his body reached 47 degrees Celsius.
In order to measure the performance stability of the iPhone 16 Pro in applications other than playing heavy games, we went to the CPU stress test; This test involves all CPU cores for 20 minutes and at the end shows what level of performance capacity the CPU provides after heating up under heavy processing load.

In our tests, the iPhone 16 Pro was able to provide 84% of its performance level to the user after 20 minutes; Therefore, the iPhone probably rarely lags and drops frames during very heavy use. In the CPU stress test, the body of the device reached about 45 degrees Celsius.
This year, Apple has increased the battery capacity of the iPhone 16 Pro and 16 Pro Max by about 10%; This issue, along with the A18 Pro chip’s excellence, makes the new flagships have very good charging; In such a way that Apple considers the iPhone 16 Pro Max as “the best iPhone in history in terms of charging”.

Cupertino residents announce the charging time of the new iPhones with the duration of video playback and say that the iPhone 16 Pro has 4 hours more charging time compared to the previous generation with 27 hours of video playback. Zomit tests also show 26 hours and 5 minutes of charging time for the new iPhone, which is more or less consistent with Apple’s claim.
|
iPhone 16 Pro battery life against competitors |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Product/benchmark |
Display |
battery |
Play video |
Everyday use |
|
Dimensions, resolution, and refresh rate |
milliampere hour |
minute: hour |
minute: hour |
|
|
iPhone 16 Pro |
6.3 inches, 120 Hz 2622 x 1206 pixels |
3582 |
26:05 |
— |
|
iPhone 15 Pro |
6.1 inches, 120 Hz 2556 x 1179 pixels |
3274 |
21:11 |
— |
|
iPhone 15 Pro Max |
6.7 inches, 120 Hz 2796 x 1290 pixels |
4441 |
24:43 |
— |
|
Pixel 9 Pro XL |
6.8 inches, 120 Hz 2992 × 1344 pixels (Native) |
5060 |
25:00 |
13:25 |
|
Piura 70 Ultra |
6.8 inches, 120 Hz 2844 x 1260 pixels |
5200 |
25:00 |
17:00 |
|
Galaxy S24 Ultra |
6.8 inches, 120 Hz 3088 x 1440 pixels |
5000 |
27:41 |
14:05 |
Another change of the iPhone 16 Pro goes back to increasing the charging speed; Apple’s new flagship now supports wired charging with a power of 30 watts, and if the same charger is connected to the Magsafe wireless charging pad, the wireless charging power reaches 25 watts, which, according to Apple, can charge the battery from zero to 50% within 30 minutes.
Very good charging and beyond the last generation
Although the wired charging speed of the iPhone 16 Pro has increased from 20 to 30 watts; again, it takes about 100 minutes to fully charge the battery; Because both the battery capacity has increased by 10%, and the iPhone charges between 85 and 100% at a very low speed; Even with the optimal battery charging function turned off, the phone needs about 35-40 minutes to complete the remaining 15% of the battery capacity.
Design and build quality
Leaving aside the fundamental and significant changes of the iPhone, what you will notice at first glance is the increase in the size of the phone, especially in the iPhone 16 Pro Max, and the narrowing of the edges around the screen.

iPhone 16 Pro and Pro Max use 6.3 and 6.9-inch screens with an increase of 0.2 inches in screen diameter compared to several previous generations; So it is not strange that the physical dimensions and weight also increase; Both phones are about 3 mm longer and 1 mm wider and 12 and 6 grams heavier, respectively; Therefore, the increase in the weight of the iPhone 16 Pro is more significant, and the 16 Pro Max sits worse in the hand than before and requires constant two-handed use.

The borders around the display have become noticeably narrower; Now, around the screen of the iPhone 16 Pro, a border with a thickness of a little more than one millimeter (1.15 millimeters to be exact) is covered; While the thickness of the edges of the iPhone 15 Pro is about 1.5 mm, and it reaches more than 2 mm for the iPhone 16; Of course, you should pay attention that by putting the cover on the phone, the narrowness of the edges is less noticeable.


Another change in the appearance of the iPhone 16 Pro is the addition of the Desert Titanium color option to the device’s coloring and the removal of the Blue Titanium option. The new color is more similar to cream with a golden frame; But unfortunately, we didn’t have this color to review. Other color options are limited to neutral and understated Black Titanium, White Titanium, and Natural Titanium.

The design of the iPhone 16 Pro is no different from the previous generation in the rest of the parts; We see the same flat titanium frame with flat glass panels on the back and front of the phone, which are mounted with high precision and form a solid structure with IP68 certification. Unlike the iPhone 16, there has been no change in the painting process of the back panel and the arrangement of the cameras, only the screen cover has been upgraded to the third-generation ceramic shield, which, according to Apple, is twice as strong as the previous generation.

We talked about Camera Control and its not very ergonomic location on the right side of the frame at the beginning of the article. Apart from this new button, the rest of the buttons are the same as the previous generation, the volume control buttons and Side button are in the right place and provide very good feedback, and the Action button, like the previous generation, allows you to personalize it.
Read more: Reviews of iPhone 14 Plus, price and technical specifications
Display and speaker
Finally, another not-so-variable part is the iPhone 16 Pro display, which uses the same 120 Hz OLED panel with LTPO technology; Of course, this year, due to the 0.2-inch increase in the diameter of the screen, its resolution reaches 2622 x 1206 pixels with a very good density of 460 pixels. As before, the display supports HDR standards including HDR10 and Dolby Vision; Therefore, like a few generations ago, we are either with a 10-bit panel or 8-bit + FRC.

Thanks to the LTPO technology, the iPhone 16 Pro display can change the refresh rate of the display between 1 and 120 Hz depending on the type and movement rate of the content, so that the phone can display smooth and smooth animations, and match the frame rate of games and videos. Do not damage the battery charging.
|
iPhone 16 Pro display performance against competitors |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Product/Test |
Minimum brightness |
Maximum brightness |
contrast ratio |
sRGB |
DCI P3 |
Adobe RGB |
|||
|
manual automatic |
local |
cover |
Average error |
cover |
Average error |
cover |
Average error |
||
|
iPhone 16 Pro |
1.35 |
1044 1950 (HDR) |
∞ |
99.7 percent |
0.98 |
— |
— |
— |
— |
|
iPhone 15 Pro |
2.21 |
1052 1947 (HDR) |
∞ |
99.7 percent |
1.0 |
— |
— |
— |
— |
|
iPhone 15 Pro Max |
2.15 |
1041 1950 (HDR) |
∞ |
99.7 percent |
0.9 |
— |
— |
— |
— |
|
Pixel 9 Pro XL |
4 |
1300 2650 (HDR) |
∞ |
97.2 percent (Natural) |
1.1 |
81.6 percent (Adaptive) |
3 |
— |
— |
|
Piura 70 Ultra |
2.5 |
740 1500 (HDR) |
∞ |
99.7 percent (Natural) |
1.9 |
79.7 percent (Vivid) |
5.3 |
— |
— |
|
Galaxy S24 Ultra |
0.7 |
914 2635 (HDR) |
∞ |
102 percent (Natural) |
3.5 |
81.8 percent (Vivid) |
4.4 |
— |
— |
Apple says that the iPhone 16 Pro display, like the previous generation, supports the wide color space of P3, achieves a brightness of 1000 nits in manual mode, and its maximum brightness reaches 2000 nits in automatic mode or during HDR video playback; But the important difference between the iPhone 16 Pro panel and the iPhone 15 Pro comes back to the minimum single-purpose brightness.
Zoomit measurements confirm Apple’s claims about the iPhone’s brightness; We measured the iPhone 16 Pro’s minimum brightness at 1.35 nits, which is significantly lower than the previous generation’s 2.15 nits; But the maximum brightness in manual mode and while displaying HDR videos is no different from the iPhone 15 Pro and is equal to 1044 and 1950 nits, respectively. It goes without saying that the iPhone 16 Pro achieved a brightness of 1296 nits in automatic mode while displaying SDR content (uses other than HDR video playback); But probably exposed to strong ambient light, it can approach the same range of 2000 nits.

iPhone 16 Pro uses stereo speakers, the main channel of which is located at the bottom edge of the frame, and the conversation speaker also plays the role of the second channel. Maybe the volume of the iPhone does not reach the level of competitors such as Pixel 9 Pro or Galaxy S24 Ultra, But the output quality of the speakers is at a higher level; The iPhone’s sound is clearer and its bass is much stronger than its competitors.
Summary and comparison with competitors
If we assume that the government will finally act rationally and start working on the iPhone registry, in this situation, it is not very logical for iPhone 15 Pro and even iPhone 14 Pro users to buy the iPhone 16 Pro with a few 10 million additional costs; Unless the 5x telephoto camera (for iPhone 15 Pro and both 14 Pro models), 15-30% faster chip performance, or Apple Intelligence (for iPhone 14 Pro users) is critical to them.
Users of iPhone 13 Pro or older models have more reasons to buy the iPhone 16 Pro; Better charging, more RAM, a more efficient camera, a brighter screen with Dynamic Island, a faster chip, and perhaps finally artificial intelligence capabilities, can all justify spending money to upgrade from the iPhone 13 Pro to the 16 Pro.
If the ecosystem is not a limiting factor for you, the Galaxy S24 Ultra, even a year after its launch and at a much lower price, offers you more or less the same experience promised by Apple Intelligence with Galaxy AI, and in most cases, in terms of photography and videography, it is on par with the iPhone 16 Pro and even better than It appears.
Naturally, we could not check the competitive advantage of the iPhone 16 Pro; Apple Intelligence is the focus of Apple’s marketing for this phone; But to experience all its capabilities, we have to wait until early 2025; However, a significant part of these features will be available on the iPhone 15 Pro with basically the same experience.

iPhone 16 Pro is a very attractive phone; But at least in the first month of its release, it is not in line with Apple’s philosophy; We know Apple as a company that provides mature and efficient functions and features to the user from the very beginning; But apparently, in the age of artificial intelligence, we have to get used to rudeness and delays; First it was the turn of Google, Microsoft and Samsung; Now Apple.
Technology
Biography of Geoffrey Hinton; The godfather of artificial intelligence
Published
5 days agoon
17/10/2024

Biography of Geoffrey Hinton; The godfather of artificial intelligence
Geoffrey Hinton (Geoffrey Hinton), a scientist who has rightly been called the “Godfather of Artificial Intelligence”, created a revolution in the world of technology with his research. Inspired by the human brain, he built artificial neural networks and gave machines the ability to learn, think, and make decisions. These technologies that are everywhere in our lives today, from voice assistants to self-driving cars, are the result of the relentless efforts of Hinton and his colleagues.
Hinton is now recognized as one of the most influential scientists of the 20th century, having won the 2024 Nobel Prize in Physics. But his story goes beyond awards and honors.
Geoffrey Hinton’s story is a story of perseverance, innovation, and the constant search to discover the unknown. In this article, we will look at the life and achievements of Geoffrey Hinton and we will answer the question of how one person with a simple idea was able to revolutionize the world of technology.
From physical problems to conquering the digital world
Hinton has been working stand-up for almost 18 years. He can’t sit for more than a few minutes due to back disc problems, but even that hasn’t stopped him from doing his activities. “I hate standing and prefer to sit, but if I sit, my lower back bulges out and I feel excruciating pain,” she says.
Since driving or sitting in a bus or subway is very difficult and painful for Hinton, he prefers to walk instead of using a private car or public transportation. The long-term walks of this scientist show that he has not only surrendered to his physical conditions but also to what extent he is eager to conduct scientific research and achieve results.

For about 46 years, Hinton has been trying to teach computers like humans. This idea seemed impossible and hopeless at first, but the passage of time proved otherwise so much so that Google hired Hinton and asked him to make artificial intelligence a reality. “Google, Amazon, and Apple think artificial intelligence is what will make their future,” Hinton said in an interview after being hired by Google.

Heir to genius genes
Hinton was born on December 6, 1947, in England in an educated and famous family with a rich scientific background. Most of his family members were educated in mathematics and economics. His father, Howard Everest Hinton, was a prominent entomologist, and all his siblings had done important scientific research.
Hinton knew from the age of seven that he would one day reach an important position
Some of the world’s leading mathematicians, such as George Boole, the founder of Boolean logic, and Charles Howard Hinton, a mathematician known for his visualization of higher dimensions, were relatives of Hinton. So, from a young age, there was a lot of pressure on Hinton to be the best in education, so much so that the scientist was thinking about getting a doctorate from the age of seven.
 Geoffrey Hinton at seven years old
Geoffrey Hinton at seven years old
psychology, philosophy, and artificial intelligence; A powerful combination to create the future
Hinton took a diverse academic path; He began his primary education at Clifton College in Bristol and then went to Cambridge University for further studies. There, Hinton constantly changed his major, vacillating between the natural sciences, art history, and philosophy. Finally, he graduated from Cambridge University in 1970 with a bachelor’s degree in experimental psychology.
Hinton’s interest in understanding the brain and how humans learn led him to study artificial intelligence. Therefore, he went to the University of Edinburgh to continue his studies, where he began research in the field of artificial intelligence under his mentor, Christopher Longuet-Higgins. Finally, in 1978, Hinton achieved his seven-year-old dream and received his doctorate in artificial intelligence. The PhD was a turning point in Hinton’s career and prepared him to enter the complex and fascinating world of artificial intelligence.
Hinton’s diverse education, from psychology to artificial intelligence, gave him a comprehensive and interdisciplinary perspective that greatly contributed to his future research. This perspective enabled him to make a deep connection between the functioning of the human brain and machine learning algorithms.
Hinton decided to enter the field of physiology and study the anatomy of the human brain in his undergraduate course due to his great interest in learning about the workings of the human mind. After that, he entered the field of psychology and finally entered the field of artificial intelligence and completed his studies. His goal in entering the field of artificial intelligence was to simulate the human brain and use it in artificial intelligence.
If you want to learn about the functioning of a complex device like the human brain, you have to build one like it.
– Geoffrey Hinton
Hinton believed that in order to have a deep understanding of a complex device like the brain, one should build a device similar to it. For example, we normally think we are familiar with how cars work, but when building a car we will notice many details that we had no knowledge of before building it.
Only against the crowd, but victorious
While struggling with his ideas and thoughts and their opponents, Hinton met a number of researchers, such as Frank Rosenblatt (Frank Rosenblatt) in the field of artificial intelligence. Rosenblatt was an American scientist who created a revolution in the field of artificial intelligence in the 1950s and 1960s by inventing and expanding the perceptron model.
The perceptron model, one of the first machine learning models, is recognized as the main inspiration for the development of today’s artificial neural networks. Perceptron is a simple algorithm used to classify data. This model is inspired by the way brain neurons work. A perceptron is a mathematical model for an artificial neuron that receives various inputs, processes them using a weighted function, and decides on the output.

Rosenblatt’s hope was that one could feed a neural network a set of data, such as photographs of men and women, and the neural network, like humans, could learn how to separate the photographs; But there was one problem: the perceptron model didn’t work very well. Rosenblatt’s neural network was a single layer of neurons and was too limited to perform the assigned task of image separation.
Even when no one believed in artificial intelligence, Hinton didn’t lose hope
In the late 1960s, Rosenblatt’s colleague wrote a book about the limitations of Rosenblatt’s neural network. After that, for about ten years, research in the field of neural networks and artificial intelligence almost stopped. No one wanted to work in this field, because they were sure that no clear results would be obtained. Of course, nobody might not be the right word, and it is better to say almost nobody; Because the topic of artificial intelligence and neural network was completely different for Hinton.
Hinton believed that there must be a way to simulate the human brain and make a device similar to it. He had no doubt about it. Why did Hinton want to pursue a path that few would follow and almost no one saw a happy ending for? Thinking that everyone makes mistakes, this eminent scientist continued on his way and did not give up.
From America to Canada; A journey that changed the course of artificial intelligence
Hinton went to different research institutes in America during his research. At that time, the US Department of Defense funded many US research institutions, so most of the projects carried out or underway focused on military objectives. Hinton was not interested in working in the military field and was looking for pure scientific research and the development of technology for human and general applications. As a result, he was looking for a place where he could continue his research away from the pressures of the military and the limitations of dependent funds.
I did not want my research to be funded by military organizations, because the results obtained would certainly not be used for human benefit.
– Geoffrey Hinton
After searching for a suitable place to continue research, Canada seemed to be the most suitable option. Finally, Hinton moved to Canada in 1987 and began his research at the University of Toronto. In the same years, Hinton and his colleagues were able to solve problems that simpler neural networks could not solve by building more complex neural networks.
Hinton and his colleagues developed multilayer neural networks instead of building and expanding single-layer neural networks. These neural networks worked well and drew a null line on all disappointments and failures. In the late 80s, a person named Dean Pomerleau built a self-driving car using a neural network and drove it on different roads.
In the 1990s, Yann LeCun, one of the pioneers of artificial intelligence and deep learning, developed a system called “Convolutional Neural Networks” (CNNs). These networks became the basis for many modern techniques in machine vision and pattern recognition. One of the first important applications of these networks was to build a system that could recognize handwritten digits; But once again, after the construction of this system, researchers in the field of artificial intelligence reached a dead end.
In the 1990s, an interesting neural network was built, but it stalled due to insufficient data.
The neural networks built at that time did not work well due to the lack of sufficient data and the lack of necessary computing power. As a result, educated people in the fields of computer science and artificial intelligence once again concluded that neural networks and their construction were nothing more than a fantasy. In 1998, after 11 years at the University of Toronto, Geoffrey Hinton left Toronto to found and manage the Gatsby Computational Neuroscience Unit at University College London. During his research at this center, he studied neural networks and their applications.
AlexNet: A Milestone in the History of Artificial Intelligence
From the 1990s to 2000, Hinton was the only hopeful person on the planet who still believed in the development of neural networks and artificial intelligence. Hinton attended many conferences to achieve his goal but was usually met with indifference by the attendees and treated like an outcast. You might think to yourself that Hinton never gave up and moved on with hope, but that’s not the case. He was also sometimes disappointed and doubted reaching the desired result; But by overcoming despair, he continued his way no matter how difficult it was; Because this sentence kept repeating in Hinton’s mind: “Computers can learn.”
After returning to the University of Toronto in 2001, Hinton continued his work on neural network models and, together with his research group in the 2000s, developed deep learning technology and applied it to practical applications. In 2006, the world caught on to Hinton’s ideas and did not see them far away.
In 2012, Hinton, along with two of his PhD students, Alen Krizhevsly and Ilya Sotskever (the co-founder of OpenAI, the creator of ChatGPT), developed an eight-layer neural network program called AlexNet. The purpose of developing this program was to identify images in ImageNet, a large online database of images. AlexNet’s performance was stellar, outperforming the most accurate program up to that point by about 40 percent. The image below shows the architecture of Alexnet convolutional neural network.

In the image above, C1 to C5 are convolutional layers that extract image features. Each layer has convolutional filters of different sizes that are applied to the image or output of the previous layer to detect different features. Also, the number of channels in each layer (96, 256 and 384) shows the number of filters used in that layer.
After feature extraction, the image is sent to fully connected layers (FC6 to FC8). Each circle in these layers represents a neuron that is connected to the neurons of the previous layer.
FC8 is the final output layer and consists of 1000 neurons. Due to the high number of layers and the ability to learn complex image features, the AlexNet architecture was very accurate in image recognition and paved the way for further improvements in the field of neural networks.
After developing AlexNet, Hinton and two of his students founded a company called DDNresearch, which was acquired by Google for $44 million in 2013. That same year, Hinton joined Google’s artificial intelligence research team, Google Brain, and was later appointed one of its vice presidents and chief engineers.

From Backpropagation Algorithms to Capsule Networks: Hinton’s Continuous Innovations
Hinton has written or co-authored more than 200 scientific papers on the use of neural networks for machine learning, memory, perception, and symbol processing. While doing a postdoctoral fellowship at the University of California, San Diego, Hinton worked with David A. Rumelhart (David E. Rumelhart) and R. Wenald J. Williams (Ronald J. Williams) to implement a backpropagation algorithm on multilayer neural networks.
Hinton stated in an interview in 2018 that the main idea of this algorithm was from Rumelhart, But Hinton and his colleagues were not the first to propose the backpropagation algorithm. In 1970, Seppo Linnainmaa proposed a method called inverse automatic derivation, which the backpropagation algorithm is a special type of this method.
Hinton and his colleagues took a big step in their research after publishing their paper on the error backpropagation algorithm in 1986. This article is one of Hinton’s most cited articles with 55,020 citations.

In October and November 2017, Hinton published two open-access papers on capsule neural networks, which he says work well.
At the 2022 Neural Information Processing Conference, Hinton introduced a new learning algorithm called forward-forward algorithm for neural networks. The main idea of this algorithm is to use two forward steps instead of forward and backward steps in the error backpropagation method; One with positive (real) data and the other with negative data that only the network produces.
When the creator questions his creation
Finally, in May 2023, after about 10 years of working with Google, Hinton resigned from his job at the company because he wanted to speak freely about the dangers of the commercial use of artificial intelligence. Hinton was concerned about the power of artificial intelligence to generate fake content and its impact on the job market. Next, we read a part of Hinton’s words in an interview in 2023:
I think we’ve entered an era where, for the first time, we have things that are more talented than us. Artificial intelligence understands and has talent. This advanced system has its own experiences and can make decisions based on those experiences. Currently, artificial intelligence does not have self-awareness, but over time, it will acquire this feature. There will even come a time when humans are the second most talented creatures on earth. Artificial intelligence came to fruition after many disappointments and failures.
– Geoffrey Hinton
The supervisor of the doctoral course asked me to work on another subject and not to jeopardize my future work, but I preferred to learn about the functioning of the human brain and mind and simulate it, even if I fail. It took longer than I expected, about 50 years, to achieve the result.
At one point, the reporter asks Hinton at what point did you come to the conclusion that your idea about neural networks is right and everyone else is wrong? “I’ve always thought I was right, and I’m right,” Hinton replies with a pause and a smile.
With the advent of ultra-high-speed chips and the vast amount of data generated on the Internet, Hinton’s algorithms have reached magical power. Little by little, computers were able to recognize the content of photos, even later they were able to easily recognize sound and translate from one language to another. In 2012, words like neural networks and machine learning became the main words on the front page of the New York Times.
Read more: The biography of Ida Lovelace; The first programmer in history
From Turing to Nobel: The Unparalleled Honors of the Godfather of Artificial Intelligence
As one of the pioneers of artificial intelligence, Geoffrey Hinton has been recognized many times for his outstanding achievements. He has received numerous awards including the David E. Rommelhart of the Cognitive Science Society and Canada’s Gerhard Hertzberg Gold Medal, which is Canada’s highest science and engineering honor.
One of Hinton’s most notable honors was winning the Turing Award with his colleagues in 2018. This is a prestigious award in the field of computing, so it is referred to as the Nobel of Computing. This award was given in recognition of Hinton’s continuous efforts in the development of neural networks. In 2022, another honor was added to Hinton’s honors, when he received the Royal Society Medal for his pioneering work in deep learning.
2024 was a historic year for Geoffrey Hinton. He and John Hopfield won the Nobel Prize in Physics for their amazing achievements in the field of machine learning and artificial neural networks. The Nobel Committee awarded this valuable prize to these two scientists for their fundamental discoveries and inventions that made machine learning with artificial neural networks possible. When awarding the prize, the development of the “Boltzmann machine” was specifically mentioned.
When a New York Times reporter asked Hinton to explain in simple terms the importance of the Boltzmann machine and its role in pretraining post-propagation networks, Hinton jokingly referred to a quote from Richard Feynman :
Look, my friend, if I could explain this in a few minutes, it wouldn’t be worth a Nobel Prize.
– Richard Feynman
This humorous response shows that this technology is very complex and its full understanding requires extensive knowledge and study. Boltzmann machine is one of the first neural network models (1985), which as a statistical model helps the network to automatically find patterns in data.
Geoffrey Hinton is a man who turned the dream of machine intelligence into a reality by standing against the currents. From back pain to receiving the Nobel Prize in Physics, his life path was always full of ups and downs. With steely determination and perseverance, Hinton not only became one of the most influential scientists of the 20th century but also changed the world of technology forever with the invention of artificial neural networks. His life story is an inspiration to all who pursue their dreams, even when the whole world is against them.
Technology
Everything about Cybercube and Robo Van; Elon Musk’s robotic taxis
Published
1 week agoon
13/10/2024

Everything about Cybercube and Robo Van; Elon Musk’s robotic taxis
After years of passionate but unfulfilled promises, finally on October 11, 2024 (October 20, 1403) at the WE, Robots event, Elon Musk unveiled Tesla’s robotic taxis.
Appearing on stage an hour late, Musk showed off the Cybercube self-driving taxi: a silver two-seater that moves without a steering wheel or pedals.
The CEO of Tesla further announced the presence of 21 Cybercubes and a total of 50 self-driving cars at the Warner Bros. studio (California), where Tesla hosted the event with special guests only.

Tesla
“We’re going to have a very glorious future ahead of us,” Musk said, but gave no indication of where the new cars will be built. According to him, Tesla hopes to offer Cybercubes to consumers at a price of less than 30,000 dollars before 2027.
The company will reportedly begin testing “unsupervised FSD” with Model 3 and Model Y electric vehicles in Texas and California next year.
Currently, the company’s self-driving cars operate with supervised FSD, meaning they require human support to take control of the steering wheel or brakes at any time. Tesla needs to get several permits from the regulators of different US states (or other countries) to offer cars without steering wheel and pedals.
But Cybercube was not the only product that was unveiled at this ceremony. Alongside the line-up of Optimus robots likely to launch as consumer work assistants in the coming months, the unveiling of an autonomous robotic van that can carry up to 20 passengers or be used to carry goods also generated more excitement among the audience.

According to Musk, Robovans and Cybercubes use inductive charging and do not need a physical power connection for recharging. He also stated that “robovans” would solve the problem of high density and pointed to the transportation of sports teams, for example.
The CEO of Tesla has been drawing the dream vision of the company’s self-driving public transportation fleet for the shareholders for years and sees the company’s future in self-driving vehicles.
It is not bad to remind you that the WE, Robots event was the first product introduction event after the introduction of Cybertrack in 2019; The product, which entered the market in late 2023, has since been recalled 5 times in the United States due to various problems.
The event ended with Elon Musk’s “Let’s party” and a video of Optimus robots dancing, while Tesla’s CEO invited guests to take a test drive with the on-site self-driving cars inside the closed-off film studios.
However, experts and analysts of the self-driving car industry believe that the release of cybercabs will take longer than the announced schedule because ensuring the safety of these cars in scenarios such as bad weather, complex road intersections and unpredictable behavior of pedestrians will require many permits and tests.
Tesla shareholders still balk at Musk’s vague timetable for the production and delivery of new cars, as he has a poor track record of promising robotic taxis. But we cannot deny that this unveiling breathed new life into the world of self-driving technologies.
But where did the idea of robotic taxis, which Tesla CEO claims are 10 to 20 times safer than human-driven cars and reduce the cost of public transportation, start?

Tesla
In 2019, during a meeting on the development of Tesla’s self-driving cars, Elon Musk suddenly made a strange prediction: “By the end of next year, we will have more than a million robot taxis on the road.”
Tesla’s investors were not unfamiliar with the concept of fully autonomous driverless cars, and what surprised them was the timing and short window of time of the plans that Musk was announcing. His prediction did not come true until the end of 2020, but has been postponed many times; But in recent months, with the decrease in Tesla’s interest rate, Elon Musk has tried in various ways to divert Wall Street’s attention from the company’s main activity and draw it to a new point. At every opportunity, he explains that the company’s future lies not in the production of electric cars, but in the very exciting world of artificial intelligence and humanoid robots.
According to him, one of the most profitable businesses in the field of AI will be driverless taxis or robotaxis that work almost anywhere and in any condition. Musk believes that Tesla’s market value will reach several trillion dollars after the release of these cars, although with this, Tesla will enter a highly competitive market.
Tesla’s technology will face fierce competition from Alphabet’s Waymo, Amazon’s self-driving unit Zoox, and General Motors’ Cruise. Also, ride-sharing companies such as Uber and Lyft and Chinese companies such as Baidu and BYD are considered serious competitors of Tesla.
Can robotaxis really save Tesla from declining profitability? How close is the company really to the production of driverless and fully autonomous car technology, and what guarantee is there for the success of Elon Musk’s plans to form a vast network of robotic taxis?
The start of the internal project of Tesla’s self-driving taxis

Business Insider
Although Elon Musk has implicitly raised the idea of robotaxis since 2016; the design and development operations of these cars took on a more serious color from 2022. At this time, during Tesla’s first-quarter earnings call, Musk once again announced that the company is building robotic taxis that do not have any steering wheel, pedals, or any other controller for physical human driving.
He also said that these cars will be fully self-driving and will be available to the public by 2024, when Tesla completes its self-driving car project. Sometime later, at the opening ceremony of the Gigafactory in Austin, he mentioned that the robotaxis would have a futuristic design and probably look more like a Cybertruck than a Tesla Model S.
Tesla’s robotic taxis have no steering wheel, pedals, or any other controls for physical human driving
During the same meeting, a Tesla investor asked Musk if the robot taxis would be offered to utilities or sold directly to consumers. Musk did not answer this question but continued to emphasize that robot taxis minimize the cost of a car per kilometer of distance, and the cost of traveling with these cars will be lower than a bus or subway ticket.
Sometime before Musk’s statement, Tesla announced that it is producing fully autonomous and self-driving vehicles at a cost of $25,000, which can have a steering wheel or not. For this reason, no one knows yet whether Musk’s robotaxis project refers to these cars or not.
According to the announced timeline, Tesla had 32 months to complete the construction, legal permits, and software required for the robot taxis and align with acceptable standards for “level 5 autonomy.”
At the beginning of 2024, the subject of robotic taxis made the news again. Elon Musk, who seemed fed up with Tesla’s usual car business, emphasized that Tesla’s future does not depend on selling more electric cars, but mainly on artificial intelligence and robotics.
Unlike Uber, which is Tesla’s main competitor in this project, Musk does not want to rely on Model 3 sedans and SUVs like the Model Y for the development of robot taxis. According to Tesla’s statement, the company is generally working on the production of new dedicated vehicles, which will probably be called Cybercab.
The supply of robotaxis depended on the completion of Tesla’s autopilot technologies and the so-called full self-driving systems, and exact statistics of how much consumers will accept this innovative product and what new rules will be imposed in this field were not announced.
Car design

Teslaoracle
In terms of design, the interior of the car was expected to have differences from other Tesla electric cars to meet the demands of passengers; For example, two rows of seats facing each other, or doors that open in a sliding manner and facilitate boarding of passengers. Also, a car that is used as a taxi should have provisions for simple and quick cleaning of the interior and even disinfection.
The idea of robotaxis also received interesting design proposals from enthusiasts: some said it would be better for Tesla to optimize its public self-driving cars depending on different uses; For example, some of them have a place to rest for long distances, or others come with a monitor and several accessories that are suitable for working along the way.
Supporters said that these facilities improve people’s quality of life and even if a passenger devotes his travel time to something useful, he has saved the same amount of time.
Continuing speculation about the design of the Cybercube, a group of experts in the field of car research also said that in the coming years, Tesla could produce other vehicles that are suitable for special entertainment, such as watching movies, or other amenities for users who want to hang out with friends and fellow travelers along the way. To socialize yourself, have: just like sitting in a limousine.
The design of the Cybercube is similar to the Cybertruck van, but with doors that open from the top
But the initial design of the Cybercube, which was published on the Tesla website, was somewhat reminiscent of the Cybertruck, and there was no special feature even to make it easier for people with disabilities to ride.
Forbes also wrote in its latest report comparing self-driving cars of different companies that Tesla’s robot taxi will probably be a two-seater car with side-by-side seats and a retractable steering wheel because eventually, users will need a steering wheel to drive outside the areas that have the company’s support services. had

However the final design of the Tesla Cybercube was not similar to the self-driving cars of the startup Zoox or Zeekr.
With doors that open up like butterfly wings and a small interior, this car only hosts two passengers. As we might have guessed, the Cybercube looks a lot like the Cybertruck, but it’s sleeker and more eye-catching than the controversial Tesla pickup.
Hardware

Sugar-Design
So far, Tesla has not disclosed any information about the set of sensors that will be used in the robotaxis. The company talks about Autopilot technologies on its website, but what Elon Musk has so far described as a fully self-driving, driverless car will require more advanced sensors, software and equipment than Autopilot.
Tesla Autopilot cars are equipped with multiple layers of cameras and powerful “machine vision” processing, and instead of radar, they use special “Tesla Vision” technology that provides a comprehensive view of the surrounding environment.
In the next step, Tesla Autopilot processes the data from these cameras using neural networks and advanced algorithms, then detects and groups objects and obstacles and determines their distance and relative position.
Tesla’s Autopilot system is equipped with multiple layers of cameras and powerful “machine vision” processing and uses “Tesla Vision” instead of radar.
Car driving functions also include two important eras: 1. adaptive cruise control with traffic detection that changes the car’s speed depending on the surrounding traffic; 2. The Autosteer steering system makes the car move on a certain line with the help of cruise control and continues the right path, especially when it encounters a curve in the road.
These cars can park automatically, recognize stop signs and other road signs as well as traffic lights, and slow down if necessary. Blind spot monitoring, automatic switching between road lanes, and intelligent summoning of the car by mobile application are some other features of these cars.
Despite all security measures, all Tesla Autopilot cars still require driver supervision according to national laws and the company’s own announcement. For this reason, until this company provides new specifications and information about the sensors, cameras, and systems of the robot taxis, no expert can check their efficiency or risk.
Introducing the Robotaxis application

Tesla
In April 2024, Tesla released a brief report on the mobile application of robotaxis, and Elon Musk also said that the first of these cars would be unveiled in August (this date was later postponed).
In the initial images of the robotic taxis application, a button to call or summon a taxi and a little lower, the message of waiting time for the car’s arrival could be seen. The second image showed a 3D map and a small virtual vehicle following a path toward a waiting passenger. These images were very similar to the Uber app, except that it looked like a Tesla Model Y car was driving in it.
According to Tesla, passengers can adjust the temperature of the car as they wish when they are waiting for the taxi to arrive. Of course, other details such as the waiting time and the maximum passenger capacity of the car were also seen in the images of the application.
Passengers can adjust the temperature inside the car and their favorite music through the Tesla application
According to the published screenshots, in the next step when the vehicle reaches the origin and the passenger boards, the map view changes to the destination. Passengers can control the car’s music through the mobile application.
The app looks like a standard online ride-hailing app, but there’s no mention of the robotic nature of the car, which does all the driving automatically and autonomously. Elon Musk said in the same meeting:
You can think of Tesla’s robotaxis as a combination of Uber and Airbnb.
According to Musk, part of the fleet of robotic cars will belong to Tesla and the other part will belong to consumers. The owners of this group of robotic cars can give their cars to the taxi fleet whenever they want and earn money in this way.
Legal restrictions on removing the steering wheel and pedals

independent
Despite all his previous promises, Tesla’s CEO has been evasive in past interviews when asked if the robotaxis will have traditional controls like pedals and steering wheels. Tesla’s Robotaxi plans have been heavily questioned due to delays in early prototype development, making the answer to the above question more important than ever.
The reality is that by mid-2024, in theory, it could take months or even years to approve a vehicle without pedals and a steering wheel for public roads, while a more traditional-looking vehicle could come much sooner.
In a letter addressed to its shareholders, Tesla emphasized that it would need the permission of the federal government to deploy and operate robotaxis with a more radical and progressive design. The statement also stated:
Scheduling robotaxis requires technological advances and regulatory approvals, but considering their very high potential value, we intend to make the most of this opportunity and are working hard on the project.
Elon Musk also did not respond to a question about exactly what type of regulatory approval Tesla is seeking.
He was then asked by reporters if Tesla was seeking an exemption from the Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards (FMVSS) to develop and market a car without traditional controls. In response, Musk compared Tesla’s new product to Waymo’s local self-driving cars and said that products that are developed for local transportation are very vulnerable and weak. He added:
The car we produce is a universal product that works anywhere. Our robotaxis work well on any terrain.
Currently, car manufacturers must comply with federal motor vehicle safety standards that require human controls such as steering wheels, pedals, side mirrors, and the like. These standards specify how vehicles must be designed before they can be sold in the United States, and if a manufacturer’s new product does not meet these requirements, manufacturers can apply for an exemption; But the US government has set a limit of 2,500 cars per company per year.
The regulatory exemption cap would theoretically prevent the mass deployment of purpose-built self-driving vehicles from any AV company, including Tesla. To date, self-driving car advocates have tried hard to pass legislation to cap the number of driverless cars on public roads; But the bill is apparently stalled in Congress due to questions about the technology’s “level of reliability” and readiness.
Tesla will need an FMVSS exemption if it wants to remove the steering wheel and pedals from its self-driving cars
So far, only Nuro has managed to obtain an FMVSS exemption, allowing it to operate a limited number of driverless delivery robots in the states of Texas and California.
For example, General Motors’ Cruise unit applied for a waiver for Origin’s steering-less and pedal-less shuttle, but it was never approved, and the Origin program was put on hold indefinitely.


Startup Zoox (a subsidiary of Amazon) also announced that its self-driving shuttles are “self-certified”, prompting the US National Highway Traffic Safety Administration to launch new research to understand this newly invented concept. Issues such as strict legal processes and approval of the license caused other companies in this field to completely ignore the issue of removing the steering wheel and pedals. For example, Waymo’s self-driving cars, although operating on public roads without a safety driver, have traditional controls. Some time ago, the company also announced that it would finally introduce a new driverless car, but did not specify an exact date for it, nor did it mention FMVSS exemptions.
Thus, now that it has been determined that the final Cybercube car will be produced without traditional controls, Tesla must also pass similar regulatory hurdles.
The challenges of mass production of Tesla robotaxis

Sugar-Design
Apart from persuading the regulators and getting a city traffic permit, there have been many other challenges standing in the way of the success of the robotaxis project, some of which Tesla has passed and has not found an answer for others.
For example, Tesla claims that it has reached a reliable milestone in terms of technologies and hardware infrastructure, but incidents such as the crash of Uber’s self-driving car in 2018, which killed a pedestrian, or two severe crashes of cruise cars in 2023, have a negative public view. It followed people into driverless cars.
On the other hand, the current infrastructure of most American cities is designed for conventional cars and must be updated and developed again to support the multitude of robotic taxis . For example, installing smart traffic lights that can communicate with self-driving cars and provide them with real-time information is one of the basic needs of robot taxis. Also, the presence of clear road lines and legible traffic signs is very important for self-driving car sensors.
The mass production of robotaxis requires changing the road infrastructure
Contrary to Musk’s claim that “the roads are ready for permanent robot taxis,” self-driving cars from other companies are still plying urban and intercity roads in certain parts of the United States. Until July 2024, Tesla had about 2.2 million cars on American roads, which is far from Elon Musk’s target of a fleet of 7 million cars.
In the second stage, Tesla’s self-driving cars are equipped with advanced technologies such as a variety of cameras and sensors and data processing systems, which, apart from the cost of production, also increase the cost of maintaining equipment and keeping software up-to-date.
In the past year alone, some Tesla customers have been forced to pay an extra $12,000 to upgrade their cars’ self-driving capabilities, while there’s still no news of new features.
If we consider the average price of robotaxis between 150,000 and 175,000 dollars, it is not clear how long Elon Musk’s promise to potential buyers about the revenue-generating potential of these cars will take. Unfortunately, Musk’s prediction regarding the annual gross profit of 30,000 dollars for the owners who give their cars to other passengers does not have statistical and computational support.
Developing new insurance models for self-driving cars will be one of Tesla’s serious challenges
The development of suitable insurance models for self-driving cars will also be one of Tesla’s serious challenges, because insurance companies must be able to correctly assess the risks and possible costs of robotaxis; Therefore, Tesla must cooperate with insurance companies from different angles to reach a comprehensive plan that both customers and companies are satisfied with.
In addition to paying attention to technological and legal issues, Tesla must gain people’s trust in its new series of fully automatic and driverless cars, and for this purpose, it will be necessary to hold advertising campaigns and extensive training programs to familiarize consumers with the company’s technologies and reduce the concerns of end users. was
The status of the project in 2024 and the concern of shareholders

Tesla
In 2024, Elon Musk postponed the unveiling date of robotaxis to August 8 and then to October 10. In April, he told Tesla’s investors, who were frustrated by the uncertain progress of production of the cars.
All the cars that Tesla produces have all the necessary hardware and computing for fully autonomous driving. I’ll say it again: all Tesla cars currently in production have all the prerequisites for autonomous driving. All you have to do is improve the software.
He also said that it doesn’t matter if these cars are less safe than new cars, because Tesla is improving the average level of road safety. A few weeks later, he released another video in which he summarized meeting Tesla’s goals in three steps:
- Completing the technological features and capabilities of fully autonomous vehicles
- Improving car technology to the point where people can ride driverless cars without any worries
- Convincing the regulators that the previous option is true!
While other companies producing self-driving cars go from city to city to obtain the necessary permits and try to expand the range of activities of cars by proving the safety of their products, NBC recently revealed in its report that Tesla even the states of California and Nevada, which employ the most employees. has not received a license to test these cars.
Tesla has not yet received permission to test robotaxis in the US states
In July, Musk told investors that anyone who does not believe in the efficiency and value of robotaxis should not be a Tesla investor. Meanwhile, the California Department of Motor Vehicles recently filed a lawsuit against Tesla, accusing the company of falsely advertising Autopilot and fully automated systems.
In addition to specifying the monthly cost and upfront payments for fully autonomous cars, the case also addresses the issue that both types of systems require drivers to be behind the wheel and control the vehicle’s steering and braking.
The unveiling of the Cybercubes in October 2024 seemed to ease the mind of Tesla shareholders somewhat, but during the night of the company’s big event, some of them expressed their concern about Musk’s uncertain timings to the media.
What do experts and critics say?
Some critics say that it is not possible for Elon Musk’s robot taxi to be produced and released according to his schedule. Referring to Waymo vehicles that make 50,000 road trips every week, this group considers Tesla’s silence regarding the request for technical information of the vehicles unacceptable. From their point of view, Musk is just continuing to make vague promises about this car.
In response to critics, Elon Musk emphasizes one sentence: that Tesla is basically an artificial intelligence and robotics company, not a traditional automobile company. So why doesn’t he try to clarify the obstacles that stand in the way of Tesla’s actions to realize the old idea?
On the other hand, the technology academies remind that Tesla’s systems have not reached level 5 autonomy, that is, conditions that do not require any human control. The MIT Technology Review writes:
After years of research and testing of robotic taxis by various companies on the road, mass production of these cars still has heavy risks. To date, these vehicles only travel within precise, pre-defined geographic boundaries, and although some do not have a human operator in the front seat, they still require remote operators to take over in an emergency.
R. Amanarayan Vasudevan , associate professor of robotics and mechanical engineering at the University of Michigan, also says:
These systems still rely on remote human supervision for safe operation, which is why we call them automated rather than autonomous; But this version of self-driving is much more expensive than traditional taxis.
Tesla is burning direct investor money to produce robotaxis, and it is natural that more pressure will be placed on the company to get more reliable results. The balance between costs and potential revenues will come when more robotaxis hit the roads and can truly compete with ride-sharing services like Uber.
Despite numerous legal, infrastructural and social challenges, the unveiling ceremony of Cybercube and RoboVon puts not only the technology levels of self-driving cars but the entire transportation industry on the threshold of a huge transformation. The entry of Tesla’s robotic taxis into the market can even affect the traditional taxi service model, but how long will it take for the transition from this unveiling to the actual launch


Ancient humans survived the last ice age just fine


iPhone 16 Pro Review

Why is the colon cancer increasing in people younger than 50?

Why is it still difficult to land on the moon?


Biography of Geoffrey Hinton; The godfather of artificial intelligence


The Strawberry Project; The OpenAI artificial intelligence model


Everything you need to know about the Windows Blue Screen of Death


Starlink; Everything you need to know about SpaceX Satellite Internet


iOS 18 review: A smart update even without Apple’s intelligence


There is more than one way for planets to be born
Popular
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoWho has checked our Whatsapp profile viewed my Whatsapp August 2023
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoSecond WhatsApp , how to install and download dual WhatsApp August 2023
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoHow to use ChatGPT on Android and iOS
-



 AI2 years ago
AI2 years agoUber replaces human drivers with robots
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoThe best Android tablets 2023, buying guide
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoThe best photography cameras 2023, buying guide and price
-


 Humans2 years ago
Humans2 years agoCell Rover analyzes the inside of cells without destroying them
-


 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoHow to prevent automatic download of applications on Samsung phones