Technology
Strange stories of the world of technology
Published
2 years agoon


Strange stories of the world of technology . The world of technology is full of strange and interesting adventures. In this article, we will mention twelve stories; From the story of choosing the word spam for unsolicited emails to the story of the same time in advertising Apple products.
Strange stories of the world of technology
The world of technology is wonderful. Although we are still at the beginning of the information age and we have a long way to go, many inventions and human achievements in the field of technology were unimaginable a century ago. Although we are still in the infancy of this path, we have made significant progress that has completely transformed our way of life.
However, perhaps what makes the world of technology more interesting is the origin story and interesting facts about each of the human technological achievements. In this article, we will mention strange stories of the world technology.
Read More: Google’s new artificial intelligence will put doctors out of work?
The computer bug was named after an insect stuck in the computer
One of the strange stories of the world of technology is the origin of the computer bug. Bug means “insect” in English and the world of technology, it refers to small faults and errors in software and systems. It is interesting to know that the reason for this name was a real insect. In 1947, Grace Hopper, an American scientist in the field of programming and the inventor of the first compiler, was working on the second version of the Mark computer at Harvard University when her assistants noticed a chipper that was stuck inside one of the computer’s relays and caused an error in the machine’s operation. After extracting the bug, they stuck it in their logbook and referred to it as “the first example of a real bug discovered” in a computer.


Very soon, the news spread in the department that the Harvard Mark project team “debugged” the computer; That is, they fixed the “bug”. From that day on, the process of fixing system and software problems is called “debug”. Hopper himself announced that he was not there when the team members noticed the bug stuck in the computer, But this is one of the popular stories that Hopper told many times.
The remains of this historic bug can be seen at the National Museum of American History in Washington, DC, along with the logbook of the Mark II project team. This incident was the first example of a computer bug; But the first time that this word was used in the general concept of a technical problem, goes back to 1878 and the person of Thomas Edison. Edison wrote in a letter that he was working on the quad telegraph and said that this device needed a “Bug Trap” to work properly.
The creator of Bitcoin is still unknown


Another one of the the strange stories of the world of technology is the name of the creator of the Bitcoin. Decentralized digital currency Bitcoin, which has been the headline in the financial and technology fields for years, was launched in early 2009. It is interesting to know that a year later, Laszlo Hanyecz made the first recorded purchase with Bitcoin when he paid ten thousand Bitcoins to buy two pizzas. Now more than ten years have passed since that day and the value of Bitcoin has increased from almost nothing to more than fifty thousand dollars; But with all these ups and downs in the value of Bitcoin, the identity of the creator of this cryptocurrency remains in an aura of uncertainty.
Needless to say, many theories have been proposed about Satoshi Nakamoto, the pseudonym of the person or persons involved in the creation of Bitcoin. Some have made many efforts to reveal Nakamoto’s identity, But there is still no evidence to authenticate the identity of the creator of Bitcoin. We may never discover the true identity of Bitcoin’s creator, and that may not be such a bad thing.
Some AMD processors can be overclocked with a pencil
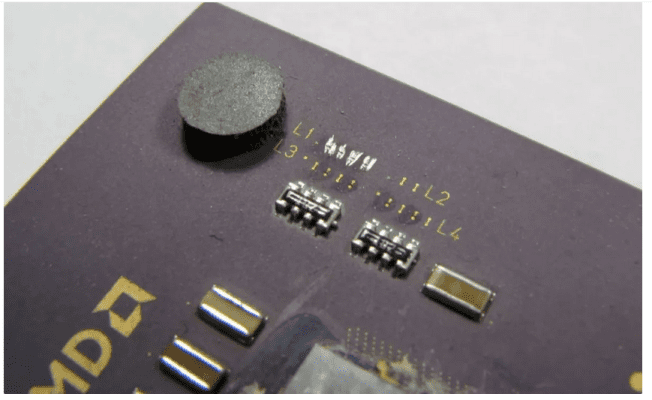

In this section of the strange stories of the world of technology we’re going to talk about the AMD processors. AMD was in a strange position in the early 2000s. The first generation of the company’s Athlon processors dominated the competing Pentium processors, and over time, it gained a lot of popularity among people who made more money by overclocking the chip.
AMD processors were so amenable to overclocking (that is, tampering with the chip to make it run faster) that some computer parts vendors overclocked slow chips and sold them to unsuspecting customers as premium chips for more profit.
This problem became so acute that AMD decided to deal with it by changing the design of the second-generation Athlon processors, called Thunderbird, in such a way that these cunning vendors could not manipulate the clock speed of the chips. However, it wasn’t long before overclockers realized that the graphite in the lead of a pencil or anything else that was conductive enough could be used to reconnect the bridges. Thus, it was possible to adjust the processor settings in the system BIOS and achieve higher processor speed.
It should be mentioned that this method became much more difficult after AMD switched from ceramic chips to a printed circuit board (PCB). Furthermore, it is not recommended for anyone to try this method; Because the smallest mistake will cause the processor to fail.
The American version of Super Mario 2 differs greatly from the Japanese version


Another story of the strange stories of the world of technology is about Super Mario 2. When the second version of the popular game Super Mario Bros. arrived in America, American gamers were overwhelmed by the level of difficulty of the game’s stages. The 1980s were not good days for the gaming industry in America, and now that they had barely managed to entertain gamers with Super Mario, they couldn’t let the frustration of gamers with the difficulty of this game deter them from playing. For this reason, Howard Phillips, consultant and spokesman for Nintendo of America, urged the Japanese company to prepare an easier and more gamer-friendly version of the Super Mario game for release in America.
In order to create an easier version of Super Mario, instead of starting a completely new project, Nintendo went to a game title that was already made for the Famicom console and turned it into a Mario game. Nintendo turned Yume Kojo: Doki Doki Panic into a Super Mario Bros. game with only a slight change. 2 conversion and released in October 1988 in America. The game became so popular that Nintendo brought it to Japan a few years later as Super Mario USA. The original version of Super Mario Bros. 2, released in Japan, eventually made its way to America as part of the Super Mario All-Stars series for the Super Nintendo in 1993 under the name The Missing Steps.
The first Apple logo is not what you think


Strange stories of the world of technology are great but here’s the greatest one which is about Apple’s logo.The Apple logo, the famous bitten apple, is one of the most well-known logos in the world. In 1977, Rob Janoff designed this logo and it has survived in various forms ever since. But did you know that this bitten apple was not the first design that Apple used to introduce its company’s products?
Ronald Wayne, who founded Apple with Steve Jobs and Steve Wozniak, also designed the first logo of this brand. Wayne’s black-and-white sketch shows Isaac Newton sitting under an apple tree, and around this image is a sentence from the famous English poet William Wordsworth: “Newton… a mind always wandering in a sea of strange thoughts… alone.”
Steve Jobs was not satisfied with this design and wanted the Apple logo to be easy to produce in small size and to match the company name and logo. In early 1977, Steve Jobs approached Janoff to design a new logo for Apple. In April of the same year, Apple’s rainbow logo was released with the Apple II computer.
The idea for Redbox movie rental kiosks came from McDonald’s


Here’s another one of the strange stories of the world of technology, the idea for Redbox movie rental kiosks came from McDonald’s. The trademark is the red kiosks on the street where you can rent movies. These kiosks were very popular in the late 2000s to early 2010s, and along with streaming services like Netflix and Hulu, they even caused the bankruptcy of Blockbuster, one of the largest and oldest movie rental companies.
By the end of 2012, more than 42,000 Redbox kiosks were active in the United States and Canada and rented nearly two million movies to users daily. Redbox even ranked 15th in Fortune magazine’s list of fastest-growing companies in 2012; But did you know that this brand was created by McDonald’s?
In 2012, McDonald’s business development department realized that customers prefer to work with a machine instead of a salesperson to make their purchases. Greg Kaplan, a member of McDonald’s early development team, said: “Customers like to be in complete control of their purchases; But when you interact with another person to make a purchase, you hand over some of this control to him
McDonald’s first used these kiosks to sell supermarket products; But the life of this project was short. Kaplan still believed that these devices have a lot of functionality and that’s why he used them for DVD rentals. The idea took off, and in 2005, Coinstar, whose kiosks exchange coins for bills and gift cards, bought 47 percent of Redbox for $32 million. In 2019, Coinstar bought the rest of the company for more than $169 million and now owns all of these red kiosks in the United States. For a while, Redbox kiosks even rented Xbox One and PlayStation 4 games.
There’s a reason why Apple products show the same amount of time in ads

Pointmeter users have noticed that Apple has been using photos to advertise its products for years, whereas the clock shows the same time in all of them. Apple has a reason for this. At the press event for the introduction of the first generation iPad, John Manning, an Australian iOS developer, asked Scott Forstall, then senior vice president of Apple’s iOS division, “Why did Apple’s promotional products first show 9:40 a.m. and then 9:41 a.m.?” »
Forstall explained as follows:
We adjust the text of the conference in such a way that when the product introduction time comes, forty minutes have passed since the conference. Therefore, when the big picture of the product appears on the screen, we want the time shown to be close to the real-time that is on the watch of the audience in the hall. Of course, we can’t always reach this moment exactly at forty minutes.”
Of course, there is an exception in the advertisements of Apple products, and that is the Apple Watch, which always shows the time 10:9 in the morning. In this context, Apple follows a long-standing tradition that believes that placing the hour hand a little after 10 and the minute hand a little before 2 will have a more attractive symmetrical appearance on the face of analog watches. Apple probably decided that placing the hands at 9:41 would not look attractive.
Credit card technology has been around since the 1970s
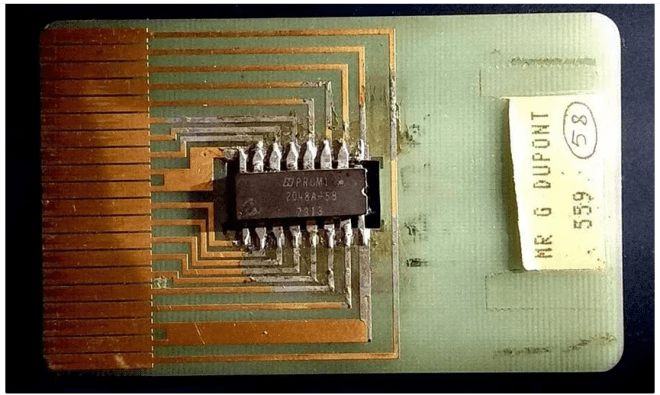

Chip and PIN-based credit cards are a relatively new technology in America. Only at the end of 2015, Visa and Mastercard started implementing this technology in America. Did you know that smart cards were used in other parts of the world decades ago? In fact, in the early 1970s, Roland Moreno, a French inventor, patented the world’s first smart card. According to some reports, two German engineers came up with a similar idea in the late 1960s; But it was Moreno who registered its patent in the patent office.
It took almost a decade for the idea of a smart card to be widely used in financial services, and it took even longer for the use of a smart card to take root in the world. Although Moreno did not become famous for his invention, he received a lot of money; Because according to a 2012 Guardian article, Moreno’s company had earned nearly 150 million euros in royalties for its invention. In 2006, Moreno told France Soir newspaper that the idea of a smart card came to him in a dream.
Some PlayStation 1 games were sold with scented labels


In the mid and late 1990s, Sony used interesting methods to advertise and encourage gamers to buy its products; From catchy slogans and hidden messages to pristine locations. One of these very creative methods was the use of scented stickers on CDs of PlayStation 1 games, which gave off a special smell when you swiped on them.
Among these games, we can mention Gran Turismo 2, which was released in 1999 as a “real driving simulator” and had nearly 650 cars and 30 trucks that could be raced. Some versions of the game had stickers that released the smell of “real pit stop” into the air when lightly swiped on.
EA also used the same advertising method for FIFA 2001; So that the disc of the PAL version of the game smelled like a football field. Using scented stickers to promote the game was very interesting, But only these two game titles used this method and Sony did not use it for any other titles.
Spam email is named after canned meat


Spam is the name of the canned meat brand that Hormel Food Company has been producing since 1937. During the Second World War, these canned meats were a big part of the soldiers’ diet due to their variety and shelf life. After the World War, the popularity of this canned product increased in the world.
Now, how did the word spam enter the email world from the food industry? In 1970, canned Spam was the subject of an episode of the comedy series Monty Python. In this episode, the word spam was repeated frequently, probably because of the popularity of this canned food around the world. In the early 1990s, when the first mass spam messages were sent to users, one Usenet user recalled the Monty Python spam episode. From that day on, this word is used for any unwanted message or action that is repeated regularly.
Domain registration was once free


In 1991, the US Defense Intelligence Agency asked Network Solutions to set up a domain name registration system (DNS) in a contract. In 1992, the company received funding from the National Science Foundation (NSF) to develop an Internet registration service, and a year later, it was the first and only company to register dotcom, dotnet, and dot org domains.
What many people probably don’t know is that until 1995, domain names were provided to users who wanted to register their websites on the Internet for free. Domain registration became monetized when Scientific Applications International Inc. (SAIC) bought Network Solutions for $4.7 million. After that, NSF allowed the new owner to charge users to register the domain name. Ultimately, this event led to the establishment of ICANN, which is responsible for managing the assignment of domain names and Internet Protocol addresses. With the establishment of Icon, competition in the domain registration market began.
Nintendo’s Punch Out still has some undiscovered secrets


In 1987, the popular Nintendo game Punch Out was released and quickly became one of the top video games in the history of the gaming industry. However, at the time of its release, no one was fully aware of the game’s capabilities or its hidden secrets. Some of these secret tips remain unknown to this day.
Punch Out is fun and challenging and has been enjoyed by almost everyone who has played it. Over the years, gamers, especially those who were interested in a speedrun and finishing the game in the shortest possible time, realized the complexities hidden in this seemingly simple Nintendo title.
In 2009, in a roundtable discussion with some of the creators of this game, it turned out that when fighting with the Bald Bull character, every time the opponent attacks, a camera flash can be seen in the background. If you time your punches with the flash of the camera, you can punch your opponent. Although gamers learned with a lot of play and practice when to punch Bald Bull to get a technical hit, they didn’t notice the camera flash in the background until this tip was revealed.
Manuta Wada, the whistleblower at the said round table, said that he had been waiting to talk about this issue for more than twenty years. He added that there are many hidden parts in the NES version of this game. Another one of these secret tips of this game was discovered in 2016. In order to be able to punch the Bald Bull or Piston Honda character, you have to punch him at the exact moment that one of the spectators (a bearded man sitting on the left of the first row) steals his head. How long will it take to discover other hidden hints in this game?


You may like
-




Biography of Geoffrey Hinton; The godfather of artificial intelligence
-




Everything about Cybercube and Robo Van; Elon Musk’s robotic taxis
-




How do we know that our phone is infected with malware?
-




The biography of Ida Lovelace; The first programmer in history
-




What is OBS Studio and how to use it?
-




Len Sassaman; The creator of Bitcoin
Technology
Biography of Geoffrey Hinton; The godfather of artificial intelligence
Published
3 hours agoon
17/10/2024

Biography of Geoffrey Hinton; The godfather of artificial intelligence
Geoffrey Hinton (Geoffrey Hinton), a scientist who has rightly been called the “Godfather of Artificial Intelligence”, created a revolution in the world of technology with his research. Inspired by the human brain, he built artificial neural networks and gave machines the ability to learn, think, and make decisions. These technologies that are everywhere in our lives today, from voice assistants to self-driving cars, are the result of the relentless efforts of Hinton and his colleagues.
Hinton is now recognized as one of the most influential scientists of the 20th century, having won the 2024 Nobel Prize in Physics. But his story goes beyond awards and honors.
Geoffrey Hinton’s story is a story of perseverance, innovation, and the constant search to discover the unknown. In this article, we will look at the life and achievements of Geoffrey Hinton and we will answer the question of how one person with a simple idea was able to revolutionize the world of technology.
From physical problems to conquering the digital world
Hinton has been working stand-up for almost 18 years. He can’t sit for more than a few minutes due to back disc problems, but even that hasn’t stopped him from doing his activities. “I hate standing and prefer to sit, but if I sit, my lower back bulges out and I feel excruciating pain,” she says.
Since driving or sitting in a bus or subway is very difficult and painful for Hinton, he prefers to walk instead of using a private car or public transportation. The long-term walks of this scientist show that he has not only surrendered to his physical conditions but also to what extent he is eager to conduct scientific research and achieve results.

For about 46 years, Hinton has been trying to teach computers like humans. This idea seemed impossible and hopeless at first, but the passage of time proved otherwise so much so that Google hired Hinton and asked him to make artificial intelligence a reality. “Google, Amazon, and Apple think artificial intelligence is what will make their future,” Hinton said in an interview after being hired by Google.

Heir to genius genes
Hinton was born on December 6, 1947, in England in an educated and famous family with a rich scientific background. Most of his family members were educated in mathematics and economics. His father, Howard Everest Hinton, was a prominent entomologist, and all his siblings had done important scientific research.
Hinton knew from the age of seven that he would one day reach an important position
Some of the world’s leading mathematicians, such as George Boole, the founder of Boolean logic, and Charles Howard Hinton, a mathematician known for his visualization of higher dimensions, were relatives of Hinton. So, from a young age, there was a lot of pressure on Hinton to be the best in education, so much so that the scientist was thinking about getting a doctorate from the age of seven.
 Geoffrey Hinton at seven years old
Geoffrey Hinton at seven years old
psychology, philosophy, and artificial intelligence; A powerful combination to create the future
Hinton took a diverse academic path; He began his primary education at Clifton College in Bristol and then went to Cambridge University for further studies. There, Hinton constantly changed his major, vacillating between the natural sciences, art history, and philosophy. Finally, he graduated from Cambridge University in 1970 with a bachelor’s degree in experimental psychology.
Hinton’s interest in understanding the brain and how humans learn led him to study artificial intelligence. Therefore, he went to the University of Edinburgh to continue his studies, where he began research in the field of artificial intelligence under his mentor, Christopher Longuet-Higgins. Finally, in 1978, Hinton achieved his seven-year-old dream and received his doctorate in artificial intelligence. The PhD was a turning point in Hinton’s career and prepared him to enter the complex and fascinating world of artificial intelligence.
Hinton’s diverse education, from psychology to artificial intelligence, gave him a comprehensive and interdisciplinary perspective that greatly contributed to his future research. This perspective enabled him to make a deep connection between the functioning of the human brain and machine learning algorithms.
Hinton decided to enter the field of physiology and study the anatomy of the human brain in his undergraduate course due to his great interest in learning about the workings of the human mind. After that, he entered the field of psychology and finally entered the field of artificial intelligence and completed his studies. His goal in entering the field of artificial intelligence was to simulate the human brain and use it in artificial intelligence.
If you want to learn about the functioning of a complex device like the human brain, you have to build one like it.
– Geoffrey Hinton
Hinton believed that in order to have a deep understanding of a complex device like the brain, one should build a device similar to it. For example, we normally think we are familiar with how cars work, but when building a car we will notice many details that we had no knowledge of before building it.
Only against the crowd, but victorious
While struggling with his ideas and thoughts and their opponents, Hinton met a number of researchers, such as Frank Rosenblatt (Frank Rosenblatt) in the field of artificial intelligence. Rosenblatt was an American scientist who created a revolution in the field of artificial intelligence in the 1950s and 1960s by inventing and expanding the perceptron model.
The perceptron model, one of the first machine learning models, is recognized as the main inspiration for the development of today’s artificial neural networks. Perceptron is a simple algorithm used to classify data. This model is inspired by the way brain neurons work. A perceptron is a mathematical model for an artificial neuron that receives various inputs, processes them using a weighted function, and decides on the output.

Rosenblatt’s hope was that one could feed a neural network a set of data, such as photographs of men and women, and the neural network, like humans, could learn how to separate the photographs; But there was one problem: the perceptron model didn’t work very well. Rosenblatt’s neural network was a single layer of neurons and was too limited to perform the assigned task of image separation.
Even when no one believed in artificial intelligence, Hinton didn’t lose hope
In the late 1960s, Rosenblatt’s colleague wrote a book about the limitations of Rosenblatt’s neural network. After that, for about ten years, research in the field of neural networks and artificial intelligence almost stopped. No one wanted to work in this field, because they were sure that no clear results would be obtained. Of course, nobody might not be the right word, and it is better to say almost nobody; Because the topic of artificial intelligence and neural network was completely different for Hinton.
Hinton believed that there must be a way to simulate the human brain and make a device similar to it. He had no doubt about it. Why did Hinton want to pursue a path that few would follow and almost no one saw a happy ending for? Thinking that everyone makes mistakes, this eminent scientist continued on his way and did not give up.
From America to Canada; A journey that changed the course of artificial intelligence
Hinton went to different research institutes in America during his research. At that time, the US Department of Defense funded many US research institutions, so most of the projects carried out or underway focused on military objectives. Hinton was not interested in working in the military field and was looking for pure scientific research and the development of technology for human and general applications. As a result, he was looking for a place where he could continue his research away from the pressures of the military and the limitations of dependent funds.
I did not want my research to be funded by military organizations, because the results obtained would certainly not be used for human benefit.
– Geoffrey Hinton
After searching for a suitable place to continue research, Canada seemed to be the most suitable option. Finally, Hinton moved to Canada in 1987 and began his research at the University of Toronto. In the same years, Hinton and his colleagues were able to solve problems that simpler neural networks could not solve by building more complex neural networks.
Hinton and his colleagues developed multilayer neural networks instead of building and expanding single-layer neural networks. These neural networks worked well and drew a null line on all disappointments and failures. In the late 80s, a person named Dean Pomerleau built a self-driving car using a neural network and drove it on different roads.
In the 1990s, Yann LeCun, one of the pioneers of artificial intelligence and deep learning, developed a system called “Convolutional Neural Networks” (CNNs). These networks became the basis for many modern techniques in machine vision and pattern recognition. One of the first important applications of these networks was to build a system that could recognize handwritten digits; But once again, after the construction of this system, researchers in the field of artificial intelligence reached a dead end.
In the 1990s, an interesting neural network was built, but it stalled due to insufficient data.
The neural networks built at that time did not work well due to the lack of sufficient data and the lack of necessary computing power. As a result, educated people in the fields of computer science and artificial intelligence once again concluded that neural networks and their construction were nothing more than a fantasy. In 1998, after 11 years at the University of Toronto, Geoffrey Hinton left Toronto to found and manage the Gatsby Computational Neuroscience Unit at University College London. During his research at this center, he studied neural networks and their applications.
AlexNet: A Milestone in the History of Artificial Intelligence
From the 1990s to 2000, Hinton was the only hopeful person on the planet who still believed in the development of neural networks and artificial intelligence. Hinton attended many conferences to achieve his goal but was usually met with indifference by the attendees and treated like an outcast. You might think to yourself that Hinton never gave up and moved on with hope, but that’s not the case. He was also sometimes disappointed and doubted reaching the desired result; But by overcoming despair, he continued his way no matter how difficult it was; Because this sentence kept repeating in Hinton’s mind: “Computers can learn.”
After returning to the University of Toronto in 2001, Hinton continued his work on neural network models and, together with his research group in the 2000s, developed deep learning technology and applied it to practical applications. In 2006, the world caught on to Hinton’s ideas and did not see them far away.
In 2012, Hinton, along with two of his PhD students, Alen Krizhevsly and Ilya Sotskever (the co-founder of OpenAI, the creator of ChatGPT), developed an eight-layer neural network program called AlexNet. The purpose of developing this program was to identify images in ImageNet, a large online database of images. AlexNet’s performance was stellar, outperforming the most accurate program up to that point by about 40 percent. The image below shows the architecture of Alexnet convolutional neural network.

In the image above, C1 to C5 are convolutional layers that extract image features. Each layer has convolutional filters of different sizes that are applied to the image or output of the previous layer to detect different features. Also, the number of channels in each layer (96, 256 and 384) shows the number of filters used in that layer.
After feature extraction, the image is sent to fully connected layers (FC6 to FC8). Each circle in these layers represents a neuron that is connected to the neurons of the previous layer.
FC8 is the final output layer and consists of 1000 neurons. Due to the high number of layers and the ability to learn complex image features, the AlexNet architecture was very accurate in image recognition and paved the way for further improvements in the field of neural networks.
After developing AlexNet, Hinton and two of his students founded a company called DDNresearch, which was acquired by Google for $44 million in 2013. That same year, Hinton joined Google’s artificial intelligence research team, Google Brain, and was later appointed one of its vice presidents and chief engineers.

From Backpropagation Algorithms to Capsule Networks: Hinton’s Continuous Innovations
Hinton has written or co-authored more than 200 scientific papers on the use of neural networks for machine learning, memory, perception, and symbol processing. While doing a postdoctoral fellowship at the University of California, San Diego, Hinton worked with David A. Rumelhart (David E. Rumelhart) and R. Wenald J. Williams (Ronald J. Williams) to implement a backpropagation algorithm on multilayer neural networks.
Hinton stated in an interview in 2018 that the main idea of this algorithm was from Rumelhart, But Hinton and his colleagues were not the first to propose the backpropagation algorithm. In 1970, Seppo Linnainmaa proposed a method called inverse automatic derivation, which the backpropagation algorithm is a special type of this method.
Hinton and his colleagues took a big step in their research after publishing their paper on the error backpropagation algorithm in 1986. This article is one of Hinton’s most cited articles with 55,020 citations.

In October and November 2017, Hinton published two open-access papers on capsule neural networks, which he says work well.
At the 2022 Neural Information Processing Conference, Hinton introduced a new learning algorithm called forward-forward algorithm for neural networks. The main idea of this algorithm is to use two forward steps instead of forward and backward steps in the error backpropagation method; One with positive (real) data and the other with negative data that only the network produces.
When the creator questions his creation
Finally, in May 2023, after about 10 years of working with Google, Hinton resigned from his job at the company because he wanted to speak freely about the dangers of the commercial use of artificial intelligence. Hinton was concerned about the power of artificial intelligence to generate fake content and its impact on the job market. Next, we read a part of Hinton’s words in an interview in 2023:
I think we’ve entered an era where, for the first time, we have things that are more talented than us. Artificial intelligence understands and has talent. This advanced system has its own experiences and can make decisions based on those experiences. Currently, artificial intelligence does not have self-awareness, but over time, it will acquire this feature. There will even come a time when humans are the second most talented creatures on earth. Artificial intelligence came to fruition after many disappointments and failures.
– Geoffrey Hinton
The supervisor of the doctoral course asked me to work on another subject and not to jeopardize my future work, but I preferred to learn about the functioning of the human brain and mind and simulate it, even if I fail. It took longer than I expected, about 50 years, to achieve the result.
At one point, the reporter asks Hinton at what point did you come to the conclusion that your idea about neural networks is right and everyone else is wrong? “I’ve always thought I was right, and I’m right,” Hinton replies with a pause and a smile.
With the advent of ultra-high-speed chips and the vast amount of data generated on the Internet, Hinton’s algorithms have reached magical power. Little by little, computers were able to recognize the content of photos, even later they were able to easily recognize sound and translate from one language to another. In 2012, words like neural networks and machine learning became the main words on the front page of the New York Times.
Read more: The biography of Ida Lovelace; The first programmer in history
From Turing to Nobel: The Unparalleled Honors of the Godfather of Artificial Intelligence
As one of the pioneers of artificial intelligence, Geoffrey Hinton has been recognized many times for his outstanding achievements. He has received numerous awards including the David E. Rommelhart of the Cognitive Science Society and Canada’s Gerhard Hertzberg Gold Medal, which is Canada’s highest science and engineering honor.
One of Hinton’s most notable honors was winning the Turing Award with his colleagues in 2018. This is a prestigious award in the field of computing, so it is referred to as the Nobel of Computing. This award was given in recognition of Hinton’s continuous efforts in the development of neural networks. In 2022, another honor was added to Hinton’s honors, when he received the Royal Society Medal for his pioneering work in deep learning.
2024 was a historic year for Geoffrey Hinton. He and John Hopfield won the Nobel Prize in Physics for their amazing achievements in the field of machine learning and artificial neural networks. The Nobel Committee awarded this valuable prize to these two scientists for their fundamental discoveries and inventions that made machine learning with artificial neural networks possible. When awarding the prize, the development of the “Boltzmann machine” was specifically mentioned.
When a New York Times reporter asked Hinton to explain in simple terms the importance of the Boltzmann machine and its role in pretraining post-propagation networks, Hinton jokingly referred to a quote from Richard Feynman :
Look, my friend, if I could explain this in a few minutes, it wouldn’t be worth a Nobel Prize.
– Richard Feynman
This humorous response shows that this technology is very complex and its full understanding requires extensive knowledge and study. Boltzmann machine is one of the first neural network models (1985), which as a statistical model helps the network to automatically find patterns in data.
Geoffrey Hinton is a man who turned the dream of machine intelligence into a reality by standing against the currents. From back pain to receiving the Nobel Prize in Physics, his life path was always full of ups and downs. With steely determination and perseverance, Hinton not only became one of the most influential scientists of the 20th century but also changed the world of technology forever with the invention of artificial neural networks. His life story is an inspiration to all who pursue their dreams, even when the whole world is against them.
Technology
Everything about Cybercube and Robo Van; Elon Musk’s robotic taxis
Published
5 days agoon
13/10/2024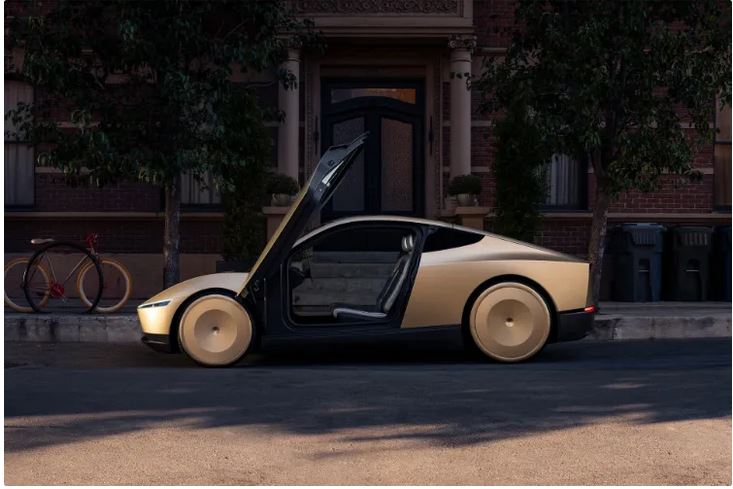

Everything about Cybercube and Robo Van; Elon Musk’s robotic taxis
After years of passionate but unfulfilled promises, finally on October 11, 2024 (October 20, 1403) at the WE, Robots event, Elon Musk unveiled Tesla’s robotic taxis.
Appearing on stage an hour late, Musk showed off the Cybercube self-driving taxi: a silver two-seater that moves without a steering wheel or pedals.
The CEO of Tesla further announced the presence of 21 Cybercubes and a total of 50 self-driving cars at the Warner Bros. studio (California), where Tesla hosted the event with special guests only.

Tesla
“We’re going to have a very glorious future ahead of us,” Musk said, but gave no indication of where the new cars will be built. According to him, Tesla hopes to offer Cybercubes to consumers at a price of less than 30,000 dollars before 2027.
The company will reportedly begin testing “unsupervised FSD” with Model 3 and Model Y electric vehicles in Texas and California next year.
Currently, the company’s self-driving cars operate with supervised FSD, meaning they require human support to take control of the steering wheel or brakes at any time. Tesla needs to get several permits from the regulators of different US states (or other countries) to offer cars without steering wheel and pedals.
But Cybercube was not the only product that was unveiled at this ceremony. Alongside the line-up of Optimus robots likely to launch as consumer work assistants in the coming months, the unveiling of an autonomous robotic van that can carry up to 20 passengers or be used to carry goods also generated more excitement among the audience.

According to Musk, Robovans and Cybercubes use inductive charging and do not need a physical power connection for recharging. He also stated that “robovans” would solve the problem of high density and pointed to the transportation of sports teams, for example.
The CEO of Tesla has been drawing the dream vision of the company’s self-driving public transportation fleet for the shareholders for years and sees the company’s future in self-driving vehicles.
It is not bad to remind you that the WE, Robots event was the first product introduction event after the introduction of Cybertrack in 2019; The product, which entered the market in late 2023, has since been recalled 5 times in the United States due to various problems.
The event ended with Elon Musk’s “Let’s party” and a video of Optimus robots dancing, while Tesla’s CEO invited guests to take a test drive with the on-site self-driving cars inside the closed-off film studios.
However, experts and analysts of the self-driving car industry believe that the release of cybercabs will take longer than the announced schedule because ensuring the safety of these cars in scenarios such as bad weather, complex road intersections and unpredictable behavior of pedestrians will require many permits and tests.
Tesla shareholders still balk at Musk’s vague timetable for the production and delivery of new cars, as he has a poor track record of promising robotic taxis. But we cannot deny that this unveiling breathed new life into the world of self-driving technologies.
But where did the idea of robotic taxis, which Tesla CEO claims are 10 to 20 times safer than human-driven cars and reduce the cost of public transportation, start?

Tesla
In 2019, during a meeting on the development of Tesla’s self-driving cars, Elon Musk suddenly made a strange prediction: “By the end of next year, we will have more than a million robot taxis on the road.”
Tesla’s investors were not unfamiliar with the concept of fully autonomous driverless cars, and what surprised them was the timing and short window of time of the plans that Musk was announcing. His prediction did not come true until the end of 2020, but has been postponed many times; But in recent months, with the decrease in Tesla’s interest rate, Elon Musk has tried in various ways to divert Wall Street’s attention from the company’s main activity and draw it to a new point. At every opportunity, he explains that the company’s future lies not in the production of electric cars, but in the very exciting world of artificial intelligence and humanoid robots.
According to him, one of the most profitable businesses in the field of AI will be driverless taxis or robotaxis that work almost anywhere and in any condition. Musk believes that Tesla’s market value will reach several trillion dollars after the release of these cars, although with this, Tesla will enter a highly competitive market.
Tesla’s technology will face fierce competition from Alphabet’s Waymo, Amazon’s self-driving unit Zoox, and General Motors’ Cruise. Also, ride-sharing companies such as Uber and Lyft and Chinese companies such as Baidu and BYD are considered serious competitors of Tesla.
Can robotaxis really save Tesla from declining profitability? How close is the company really to the production of driverless and fully autonomous car technology, and what guarantee is there for the success of Elon Musk’s plans to form a vast network of robotic taxis?
The start of the internal project of Tesla’s self-driving taxis

Business Insider
Although Elon Musk has implicitly raised the idea of robotaxis since 2016; the design and development operations of these cars took on a more serious color from 2022. At this time, during Tesla’s first-quarter earnings call, Musk once again announced that the company is building robotic taxis that do not have any steering wheel, pedals, or any other controller for physical human driving.
He also said that these cars will be fully self-driving and will be available to the public by 2024, when Tesla completes its self-driving car project. Sometime later, at the opening ceremony of the Gigafactory in Austin, he mentioned that the robotaxis would have a futuristic design and probably look more like a Cybertruck than a Tesla Model S.
Tesla’s robotic taxis have no steering wheel, pedals, or any other controls for physical human driving
During the same meeting, a Tesla investor asked Musk if the robot taxis would be offered to utilities or sold directly to consumers. Musk did not answer this question but continued to emphasize that robot taxis minimize the cost of a car per kilometer of distance, and the cost of traveling with these cars will be lower than a bus or subway ticket.
Sometime before Musk’s statement, Tesla announced that it is producing fully autonomous and self-driving vehicles at a cost of $25,000, which can have a steering wheel or not. For this reason, no one knows yet whether Musk’s robotaxis project refers to these cars or not.
According to the announced timeline, Tesla had 32 months to complete the construction, legal permits, and software required for the robot taxis and align with acceptable standards for “level 5 autonomy.”
At the beginning of 2024, the subject of robotic taxis made the news again. Elon Musk, who seemed fed up with Tesla’s usual car business, emphasized that Tesla’s future does not depend on selling more electric cars, but mainly on artificial intelligence and robotics.
Unlike Uber, which is Tesla’s main competitor in this project, Musk does not want to rely on Model 3 sedans and SUVs like the Model Y for the development of robot taxis. According to Tesla’s statement, the company is generally working on the production of new dedicated vehicles, which will probably be called Cybercab.
The supply of robotaxis depended on the completion of Tesla’s autopilot technologies and the so-called full self-driving systems, and exact statistics of how much consumers will accept this innovative product and what new rules will be imposed in this field were not announced.
Car design

Teslaoracle
In terms of design, the interior of the car was expected to have differences from other Tesla electric cars to meet the demands of passengers; For example, two rows of seats facing each other, or doors that open in a sliding manner and facilitate boarding of passengers. Also, a car that is used as a taxi should have provisions for simple and quick cleaning of the interior and even disinfection.
The idea of robotaxis also received interesting design proposals from enthusiasts: some said it would be better for Tesla to optimize its public self-driving cars depending on different uses; For example, some of them have a place to rest for long distances, or others come with a monitor and several accessories that are suitable for working along the way.
Supporters said that these facilities improve people’s quality of life and even if a passenger devotes his travel time to something useful, he has saved the same amount of time.
Continuing speculation about the design of the Cybercube, a group of experts in the field of car research also said that in the coming years, Tesla could produce other vehicles that are suitable for special entertainment, such as watching movies, or other amenities for users who want to hang out with friends and fellow travelers along the way. To socialize yourself, have: just like sitting in a limousine.
The design of the Cybercube is similar to the Cybertruck van, but with doors that open from the top
But the initial design of the Cybercube, which was published on the Tesla website, was somewhat reminiscent of the Cybertruck, and there was no special feature even to make it easier for people with disabilities to ride.
Forbes also wrote in its latest report comparing self-driving cars of different companies that Tesla’s robot taxi will probably be a two-seater car with side-by-side seats and a retractable steering wheel because eventually, users will need a steering wheel to drive outside the areas that have the company’s support services. had

However the final design of the Tesla Cybercube was not similar to the self-driving cars of the startup Zoox or Zeekr.
With doors that open up like butterfly wings and a small interior, this car only hosts two passengers. As we might have guessed, the Cybercube looks a lot like the Cybertruck, but it’s sleeker and more eye-catching than the controversial Tesla pickup.
Hardware

Sugar-Design
So far, Tesla has not disclosed any information about the set of sensors that will be used in the robotaxis. The company talks about Autopilot technologies on its website, but what Elon Musk has so far described as a fully self-driving, driverless car will require more advanced sensors, software and equipment than Autopilot.
Tesla Autopilot cars are equipped with multiple layers of cameras and powerful “machine vision” processing, and instead of radar, they use special “Tesla Vision” technology that provides a comprehensive view of the surrounding environment.
In the next step, Tesla Autopilot processes the data from these cameras using neural networks and advanced algorithms, then detects and groups objects and obstacles and determines their distance and relative position.
Tesla’s Autopilot system is equipped with multiple layers of cameras and powerful “machine vision” processing and uses “Tesla Vision” instead of radar.
Car driving functions also include two important eras: 1. adaptive cruise control with traffic detection that changes the car’s speed depending on the surrounding traffic; 2. The Autosteer steering system makes the car move on a certain line with the help of cruise control and continues the right path, especially when it encounters a curve in the road.
These cars can park automatically, recognize stop signs and other road signs as well as traffic lights, and slow down if necessary. Blind spot monitoring, automatic switching between road lanes, and intelligent summoning of the car by mobile application are some other features of these cars.
Despite all security measures, all Tesla Autopilot cars still require driver supervision according to national laws and the company’s own announcement. For this reason, until this company provides new specifications and information about the sensors, cameras, and systems of the robot taxis, no expert can check their efficiency or risk.
Introducing the Robotaxis application

Tesla
In April 2024, Tesla released a brief report on the mobile application of robotaxis, and Elon Musk also said that the first of these cars would be unveiled in August (this date was later postponed).
In the initial images of the robotic taxis application, a button to call or summon a taxi and a little lower, the message of waiting time for the car’s arrival could be seen. The second image showed a 3D map and a small virtual vehicle following a path toward a waiting passenger. These images were very similar to the Uber app, except that it looked like a Tesla Model Y car was driving in it.
According to Tesla, passengers can adjust the temperature of the car as they wish when they are waiting for the taxi to arrive. Of course, other details such as the waiting time and the maximum passenger capacity of the car were also seen in the images of the application.
Passengers can adjust the temperature inside the car and their favorite music through the Tesla application
According to the published screenshots, in the next step when the vehicle reaches the origin and the passenger boards, the map view changes to the destination. Passengers can control the car’s music through the mobile application.
The app looks like a standard online ride-hailing app, but there’s no mention of the robotic nature of the car, which does all the driving automatically and autonomously. Elon Musk said in the same meeting:
You can think of Tesla’s robotaxis as a combination of Uber and Airbnb.
According to Musk, part of the fleet of robotic cars will belong to Tesla and the other part will belong to consumers. The owners of this group of robotic cars can give their cars to the taxi fleet whenever they want and earn money in this way.
Legal restrictions on removing the steering wheel and pedals

independent
Despite all his previous promises, Tesla’s CEO has been evasive in past interviews when asked if the robotaxis will have traditional controls like pedals and steering wheels. Tesla’s Robotaxi plans have been heavily questioned due to delays in early prototype development, making the answer to the above question more important than ever.
The reality is that by mid-2024, in theory, it could take months or even years to approve a vehicle without pedals and a steering wheel for public roads, while a more traditional-looking vehicle could come much sooner.
In a letter addressed to its shareholders, Tesla emphasized that it would need the permission of the federal government to deploy and operate robotaxis with a more radical and progressive design. The statement also stated:
Scheduling robotaxis requires technological advances and regulatory approvals, but considering their very high potential value, we intend to make the most of this opportunity and are working hard on the project.
Elon Musk also did not respond to a question about exactly what type of regulatory approval Tesla is seeking.
He was then asked by reporters if Tesla was seeking an exemption from the Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards (FMVSS) to develop and market a car without traditional controls. In response, Musk compared Tesla’s new product to Waymo’s local self-driving cars and said that products that are developed for local transportation are very vulnerable and weak. He added:
The car we produce is a universal product that works anywhere. Our robotaxis work well on any terrain.
Currently, car manufacturers must comply with federal motor vehicle safety standards that require human controls such as steering wheels, pedals, side mirrors, and the like. These standards specify how vehicles must be designed before they can be sold in the United States, and if a manufacturer’s new product does not meet these requirements, manufacturers can apply for an exemption; But the US government has set a limit of 2,500 cars per company per year.
The regulatory exemption cap would theoretically prevent the mass deployment of purpose-built self-driving vehicles from any AV company, including Tesla. To date, self-driving car advocates have tried hard to pass legislation to cap the number of driverless cars on public roads; But the bill is apparently stalled in Congress due to questions about the technology’s “level of reliability” and readiness.
Tesla will need an FMVSS exemption if it wants to remove the steering wheel and pedals from its self-driving cars
So far, only Nuro has managed to obtain an FMVSS exemption, allowing it to operate a limited number of driverless delivery robots in the states of Texas and California.
For example, General Motors’ Cruise unit applied for a waiver for Origin’s steering-less and pedal-less shuttle, but it was never approved, and the Origin program was put on hold indefinitely.


Startup Zoox (a subsidiary of Amazon) also announced that its self-driving shuttles are “self-certified”, prompting the US National Highway Traffic Safety Administration to launch new research to understand this newly invented concept. Issues such as strict legal processes and approval of the license caused other companies in this field to completely ignore the issue of removing the steering wheel and pedals. For example, Waymo’s self-driving cars, although operating on public roads without a safety driver, have traditional controls. Some time ago, the company also announced that it would finally introduce a new driverless car, but did not specify an exact date for it, nor did it mention FMVSS exemptions.
Thus, now that it has been determined that the final Cybercube car will be produced without traditional controls, Tesla must also pass similar regulatory hurdles.
The challenges of mass production of Tesla robotaxis

Sugar-Design
Apart from persuading the regulators and getting a city traffic permit, there have been many other challenges standing in the way of the success of the robotaxis project, some of which Tesla has passed and has not found an answer for others.
For example, Tesla claims that it has reached a reliable milestone in terms of technologies and hardware infrastructure, but incidents such as the crash of Uber’s self-driving car in 2018, which killed a pedestrian, or two severe crashes of cruise cars in 2023, have a negative public view. It followed people into driverless cars.
On the other hand, the current infrastructure of most American cities is designed for conventional cars and must be updated and developed again to support the multitude of robotic taxis . For example, installing smart traffic lights that can communicate with self-driving cars and provide them with real-time information is one of the basic needs of robot taxis. Also, the presence of clear road lines and legible traffic signs is very important for self-driving car sensors.
The mass production of robotaxis requires changing the road infrastructure
Contrary to Musk’s claim that “the roads are ready for permanent robot taxis,” self-driving cars from other companies are still plying urban and intercity roads in certain parts of the United States. Until July 2024, Tesla had about 2.2 million cars on American roads, which is far from Elon Musk’s target of a fleet of 7 million cars.
In the second stage, Tesla’s self-driving cars are equipped with advanced technologies such as a variety of cameras and sensors and data processing systems, which, apart from the cost of production, also increase the cost of maintaining equipment and keeping software up-to-date.
In the past year alone, some Tesla customers have been forced to pay an extra $12,000 to upgrade their cars’ self-driving capabilities, while there’s still no news of new features.
If we consider the average price of robotaxis between 150,000 and 175,000 dollars, it is not clear how long Elon Musk’s promise to potential buyers about the revenue-generating potential of these cars will take. Unfortunately, Musk’s prediction regarding the annual gross profit of 30,000 dollars for the owners who give their cars to other passengers does not have statistical and computational support.
Developing new insurance models for self-driving cars will be one of Tesla’s serious challenges
The development of suitable insurance models for self-driving cars will also be one of Tesla’s serious challenges, because insurance companies must be able to correctly assess the risks and possible costs of robotaxis; Therefore, Tesla must cooperate with insurance companies from different angles to reach a comprehensive plan that both customers and companies are satisfied with.
In addition to paying attention to technological and legal issues, Tesla must gain people’s trust in its new series of fully automatic and driverless cars, and for this purpose, it will be necessary to hold advertising campaigns and extensive training programs to familiarize consumers with the company’s technologies and reduce the concerns of end users. was
The status of the project in 2024 and the concern of shareholders

Tesla
In 2024, Elon Musk postponed the unveiling date of robotaxis to August 8 and then to October 10. In April, he told Tesla’s investors, who were frustrated by the uncertain progress of production of the cars.
All the cars that Tesla produces have all the necessary hardware and computing for fully autonomous driving. I’ll say it again: all Tesla cars currently in production have all the prerequisites for autonomous driving. All you have to do is improve the software.
He also said that it doesn’t matter if these cars are less safe than new cars, because Tesla is improving the average level of road safety. A few weeks later, he released another video in which he summarized meeting Tesla’s goals in three steps:
- Completing the technological features and capabilities of fully autonomous vehicles
- Improving car technology to the point where people can ride driverless cars without any worries
- Convincing the regulators that the previous option is true!
While other companies producing self-driving cars go from city to city to obtain the necessary permits and try to expand the range of activities of cars by proving the safety of their products, NBC recently revealed in its report that Tesla even the states of California and Nevada, which employ the most employees. has not received a license to test these cars.
Tesla has not yet received permission to test robotaxis in the US states
In July, Musk told investors that anyone who does not believe in the efficiency and value of robotaxis should not be a Tesla investor. Meanwhile, the California Department of Motor Vehicles recently filed a lawsuit against Tesla, accusing the company of falsely advertising Autopilot and fully automated systems.
In addition to specifying the monthly cost and upfront payments for fully autonomous cars, the case also addresses the issue that both types of systems require drivers to be behind the wheel and control the vehicle’s steering and braking.
The unveiling of the Cybercubes in October 2024 seemed to ease the mind of Tesla shareholders somewhat, but during the night of the company’s big event, some of them expressed their concern about Musk’s uncertain timings to the media.
What do experts and critics say?
Some critics say that it is not possible for Elon Musk’s robot taxi to be produced and released according to his schedule. Referring to Waymo vehicles that make 50,000 road trips every week, this group considers Tesla’s silence regarding the request for technical information of the vehicles unacceptable. From their point of view, Musk is just continuing to make vague promises about this car.
In response to critics, Elon Musk emphasizes one sentence: that Tesla is basically an artificial intelligence and robotics company, not a traditional automobile company. So why doesn’t he try to clarify the obstacles that stand in the way of Tesla’s actions to realize the old idea?
On the other hand, the technology academies remind that Tesla’s systems have not reached level 5 autonomy, that is, conditions that do not require any human control. The MIT Technology Review writes:
After years of research and testing of robotic taxis by various companies on the road, mass production of these cars still has heavy risks. To date, these vehicles only travel within precise, pre-defined geographic boundaries, and although some do not have a human operator in the front seat, they still require remote operators to take over in an emergency.
R. Amanarayan Vasudevan , associate professor of robotics and mechanical engineering at the University of Michigan, also says:
These systems still rely on remote human supervision for safe operation, which is why we call them automated rather than autonomous; But this version of self-driving is much more expensive than traditional taxis.
Tesla is burning direct investor money to produce robotaxis, and it is natural that more pressure will be placed on the company to get more reliable results. The balance between costs and potential revenues will come when more robotaxis hit the roads and can truly compete with ride-sharing services like Uber.
Despite numerous legal, infrastructural and social challenges, the unveiling ceremony of Cybercube and RoboVon puts not only the technology levels of self-driving cars but the entire transportation industry on the threshold of a huge transformation. The entry of Tesla’s robotic taxis into the market can even affect the traditional taxi service model, but how long will it take for the transition from this unveiling to the actual launch
Technology
How do we know that our phone is infected with malware?
Published
6 days agoon
11/10/2024

How do we know that our phone is infected with malware?
Today’s smartphones are not just a means to communicate with others, for many of us, they are a personal notebook, a family photo and movie album, a mobile bank, and a device for storing important daily information. These cases clearly remind us of the high importance of taking care of the phone and paying attention to the security of the information stored in this device.
Android and iOS operating systems become more secure with each update; But again, it is possible that due to reasons such as rooting the Android phone or jailbreaking the iPhone phone, we expose our phone to malware that in many cases enters the victim’s devices with the aim of stealing information and causing financial losses. .
Although hackers very cleverly infect victims’ phones with their desired malware, after the device is infected, there are changes in the normal operation of your phone, and by identifying them and contacting a repairman in time, you can remove the malware from your phone and prevent serious damage. Next, join us to get to know the 7 signs that indicate your phone is infected with malware and learn how to get rid of it.
-
7 signs of phone virus infection
-
Abnormal increase in internet usage
-
Strange ads appear on the phone
-
Quick battery drain
-
Disabling phone apps and random device startup
-
Overheating of the phone body
-
Show unknown and new apps on the phone
-
Unstable internet connection or constantly dropping calls
-
How to remove malware from the phone?
-
How to prevent the phone from being infected with malware?
7 signs of phone virus infection
If your phone has recently experienced one or more of the following problems, it is likely that a malware is active on your phone:
Abnormal increase in internet usage
Many malware are usually designed to run permanently in the background of the phone and send personal information or files from the victim’s device to the hacker or download malicious files and hide them in certain parts of the phone. do This process is one reason for the phone’s internet to run out early because it increases the device’s internet usage unexpectedly to the point where, with a little precision, you can notice the difference between your usage in the current time period and, for example, the last week or month.

Adobe Stock
To find out how much data is being used on your mobile phone (SIM card internet), go to one of the two paths below and see exactly how much internet each app consumes and if this amount is in line with what you expect from that app’s functionality. Does it match or not?
Information about the amount of internet usage on the Android phone
- Enter Settings.
- Tap the Connections option.




- Go to Data usage and Mobile data usage respectively.
Information about the amount of internet usage on the iPhone
- Enter Settings.
- Tap on Cellular and Cellular Data respectively.
If the Internet consumption by an application is much more than you expect or that application should not connect to the Internet, it is better to consider the application as malware and delete it from your phone.
Strange ads appear on the phone
Most cybercriminals design mobile malware with the goal of making money. Part of this revenue is generated by displaying strange random ads (for example, immoral sites) on victims’ phones. This type of advertisement, known as adware, directs victims to certain sites that are either designed to steal more information from the person, are phishing in nature, or encourage the victim to download malicious software and install it on their phone or even computer.
-
What is malware and how to prevent it?
-
What is phishing? How to identify scam sites?
In addition, displaying multiple ads on your phone slows down the phone; A process that puts a lot of pressure on the battery and other hardware of the device; Of course, this is in the most optimistic scenario. If you click on these ads and don’t use IP masking tools (such as a VPN), there is a risk that your IP will be exposed to the cybercriminals behind this malware. Then, in addition to infecting your phone, you have to worry about the dangerous things hackers are doing with your IP.
Quick battery drain
If you have made sure of the health of your phone’s battery using Android or iPhone battery health testing methods, or if you have recently replaced the phone’s battery, but still have to charge it several times during the day, you should consider the possibility that the phone is infected with malware. The 24-hour running of malware in the background of the phone increases battery consumption to a great extent, and in addition to draining the battery quickly, it can increase the temperature of the device body.
Disabling phone apps and random device startup
It is normal for the apps installed on the phone to crash occasionally and it may happen for various reasons, including the app not being up-to-date; But this process should not be repeated constantly. If, in a short period of time, a significant number of apps on your phone freeze, don’t work as expected, close suddenly, or stop working completely, and won’t go back to their previous state even with an update, the hypothesis that your phone is a is infected with malware; is strengthened

In addition, if the phone restarts automatically and the process of loading the phone’s user interface after startup takes longer than before, it could be a sign of malware in your phone that restarts the phone every time it stops working and restarts in the background. The phone should run.
Overheating of the phone body
It doesn’t matter if you are doing simple tasks with your phone or playing games and heavy software is running; If your phone is infected with malware, the body of the phone will become abnormally hot. This heat will not only prevent you from working with the phone, but by damaging the hardware of the device, it will slow down its performance when running your favorite programs.
Sudden and excessive heat in the body is a very serious alarm about the possibility of malware in the phone
Unfortunately, in most cases, there is no uniform process to heat up a phone infected with malware, and you may face this excessive heat once when running a light messenger like WhatsApp, and another time even when running a heavy program, the heat generated in The body should not attract so much attention to itself.
In any case, sudden heat generation in the body of the device that was not there before or was not present at this intensity is a serious alarm about the possibility of malware in your phone and you should show your phone to a professional repairer as soon as possible.
Show unknown and new apps on the phone
Besides executing commands to send your information to their designers, malware may also download and install new apps on your phone. These programs may seem harmless on the surface (for example, they look like an exercise training program), but ultimately, they are not installed on your device with good intentions and often do things like track your traffic and display numerous advertisements intended by malware designers or in Worse, they steal your personal and sensitive information (such as passwords to social media accounts).

Adobe Stock
Be aware that most of these unknown and new apps usually have unreasonable permissions that allow them to access sensitive parts of the phone such as contacts, gallery, storage (phone and memory card), camera and microphone.
Unstable internet connection or constantly dropping calls
Malware communication on a phone or the malware designers’ server interferes with your phone’s ability to maintain a stable connection to the Internet or prevent call drops. If other devices that use the same Wi-Fi connection as you do not face the problem of unstable Internet connection, or if in the area where you are present, the SIM card antenna of other phones has no problem, you should suspect the possibility of your phone being infected with malware.
How do you remove malware from the phone?
If you see one or more of these symptoms on your phone and you suspect that your phone is infected with malware, you can identify the malware infecting your device and remove it through the following methods:
1. Removing malware from the phone through Safe Mode
Since most malware runs continuously in the background of the phone and closing them forcibly is not possible in some cases; It is better to delete the programs you suspect from your phone through Safe Mode. Android’s Safe Mode feature allows you to run the phone only with default system apps.
To enter Safe Mode on most Android phones, press and hold the Power button until the phone turns on and enters Safe Mode settings. In this mode, all the apps you have installed on the phone will be disabled and you can safely remove anything unusual and suspicious you see or apps you feel are infected from the phone.
-
The best antivirus for Android phones
-
Do you have an iPhone and are worried about being hacked? Enable Lockdown Mode
If you are using an iPhone, turn off the phone first to enter Safe Mode, similar to Android phones. After that, press and hold the power button for a few seconds. After the device turns on, press and hold the Volume Down button until the Apple logo appears on the screen, then release it to enter Safe Mode. Keep in mind that, unlike Android phones, different models of iPhones are equipped with a feature called Lockdown Mode, by which, if the phone is targeted by malware or hackers, the functionality of the device will be limited until you remove this malware.
2. Install antivirus
Installing a powerful antivirus on your phone is the easiest way to identify and remove malware
Sometimes, even after entering Safe Mode, you may not be able to identify and remove malicious programs from your phone. In such a situation, you can take the help of a good antivirus.
Be careful not to use free antiviruses as much as possible, as many of these programs either don’t provide the functionality you need or are just malware hiding behind the title of antivirus.

3. Restore the phone to factory settings
Some malware, for reasons such as being new, may not be detectable even by the most up-to-date versions of antiviruses, and despite installing several strong antiviruses, you may still struggle with one or more of the symptoms we mentioned at the beginning of the article. In this case, you will have no choice but to restore the phone to factory settings.
If you have important information and have already saved a backup copy of the phone data, to restore the iPhone to its factory settings, go to Settings > General > Transfer or Reset iPhone tap Reset, and select Reset All Settings to reset all the phone data. delete
In Android devices, the path to the factory reset option may be different in different brands. For example, if your phone is a Samsung, you can restore your phone to factory settings as follows:
- Go to Settings and click on Reset from the General Management section.
- Select the Factory Data Reset option.
How to prevent the phone from being infected with malware?
Contrary to what some people think, most malware is designed with the intention of causing serious harm to victims, and they usually do so within the first hours and days of entering the victim’s machine. Since many of us, due to ignorance of the signs of the phone being infected with malware, find out about the presence of malicious software in our phone late, sometimes even removing the malware does not have a special effect on the phone’s performance; Because this malware has already caused the damage desired by cybercriminals.
Being vigilant and careful to prevent malware from entering the phone is the most important step to prevent the phone from being infected with malware.
This shows the importance of being vigilant and careful to prevent malware from entering the phone. Observing these things can help you achieve such a goal so that you can better protect the security of your phone:
1. Download your favorite apps from Google Play or App Store
Many users, eager to use modded versions of a paid program, download that program from unknown sites and easily expose their phones to the risk of being infected by malware. Hence, it is essential to download Android and iOS apps only from Google Play or App Store. Fortunately, sometimes some paid apps become free for a limited time and you can install them instead of the modded version. At Zomit, we regularly feature paid Android and iPhone apps that have become free today.
2. Pay attention to the opinions of other users about a program
Showing excessive and unusual ads, not providing the functionality claimed by the creators, constantly crashing the program or directing the user to links outside the program are among the alarm bells of suspected malware programs that are often written by users in the comments section of a program. They can be a good clue to dissuade you from downloading that program.
3. Pay attention to the permissions of each program
Suspicious access that doesn’t need to be requested for certain apps can be a red flag for you. For example, if you download a reader app, it shouldn’t ask you to access the camera, audience, or gallery.

Adobe Stock
4. Do not download files from unknown devices
If you keep your phone’s Bluetooth on continuously due to using wireless headphones or Bluetooth hands-free, or the device’s AirDrop is always on, you should not accept files from unknown devices; Because this file (even in the form of a photo) may spread some kind of malware in your phone.
This includes receiving emails from unknown sources. Although you cannot prevent receiving these types of emails; if you receive them, you should not open these emails on your phone or computer and it is better to delete them immediately and block the sender of the email.
Read more: How to increase the security of Android phones?
5. Do not click on anonymous links
Many mobile phones get infected with malware by clicking on unknown links received through SMS or social media messages. You should note that you should never click on any unknown link, even from a familiar person. Or if you are determined, take help from reliable websites to determine if the link is safe.
Paying attention to the signs that your phone is infected with malware, as well as following the recommendations that can prevent malicious programs from entering your phone, are very important steps that keep your phone safe and prevent cybercriminals from stealing your personal and sensitive information.
Has your phone ever been infected? What solution did you use to fix it? Did you succeed in removing the virus?


Biography of Geoffrey Hinton; The godfather of artificial intelligence


The Secret of the Hummingbird’s Amazing Adaptation


Europa Clipper, NASA’s flagship probe was launched

How did accidental release cause the 1977 Russian flu?


Everything about Cybercube and Robo Van; Elon Musk’s robotic taxis


The biography of Andy Rubin, the creator of Android


The Strawberry Project; The OpenAI artificial intelligence model


Everything you need to know about the Windows Blue Screen of Death


Why doesn’t Jupiter have big and bright rings like Saturn?


How to prevent your location from being revealed through photos?
Popular
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoWho has checked our Whatsapp profile viewed my Whatsapp August 2023
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoSecond WhatsApp , how to install and download dual WhatsApp August 2023
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoHow to use ChatGPT on Android and iOS
-



 AI2 years ago
AI2 years agoUber replaces human drivers with robots
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoThe best Android tablets 2023, buying guide
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoThe best photography cameras 2023, buying guide and price
-


 Humans2 years ago
Humans2 years agoCell Rover analyzes the inside of cells without destroying them
-


 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoHow to prevent automatic download of applications on Samsung phones
