Technology
Google brand story; From a small startup to ruling the web world
Published
1 week agoon


Proper noun: A search engine that popularized the company of the same name.
Preposition: For each; per.
Noun: A topology name.
Adverb: Beyond all others.
Preposition: For each; per.
Noun: A topology name.
Adverb: Beyond all others.
Preposition: For each; per.
Noun: A topology name.
Proper noun: A particular Internet company.
Proper noun: A search engine that popularized the company of the same name.
Proper noun: A particular Internet company.
Proper noun: A search engine that popularized the company of the same name.
Proper noun: A particular Internet company.
Proper noun: A search engine that popularized the company of the same name.
Proper noun: A particular Internet company.
Proper noun: A search engine that popularized the company of the same name.
Proper noun: A particular Internet company.
Proper noun: A search engine that popularized the company of the same name.
Google brand story; From a small startup to ruling the web world
The general public of the world cannot imagine removing Google services from their lives today. Regardless of the search engine or the Chrome browser, most of us set our programs on Google Calendar, and using Gmail, Google Drive, Google Docs, Google Maps, Google Photos, YouTube, and the like has become a daily habit for us.
Google’s role in shaping our relationship with the Internet world is undeniable. Many of this company’s products have known alternatives, But Google has designed its comprehensive and integrated ecosystem in such a way that we cannot easily abandon the use of all its applications and services.
This article was updated on the occasion of the anniversary of the establishment of Google on 14 September 1403.
But how dangerous will it be for technology companies to gain power at this level? Today’s opponents of Google are divided into several groups: some believe that Google is acting against the direction of freedom of expression by prioritizing certain search results. One group also argues that Google collects user data in a variety of ways that people are unaware of and that this data is not necessarily used in advertising.
For example, some activists of the de-Google movement say: “Spying on people at this level is not acceptable and should not be. “We need to control the technologies we interact with, not the other way around.”
But 26 years ago, before it came under the microscope of US antitrust cases and its empire was in danger of being disintegrated, the initial idea for founding the company was formed with a student project with the aim of facilitating people’s access to web information.
Back then, finding specific content on websites was more like exploring a disorganized library. Even the algorithms of the best search engines, such as Xcite and Altavista, often displayed scattered links in response to user queries that may or may not be related to the user’s search. In fact, finding what you were looking for was more like a game of chance. But Google changed everything.
Join us to review the story of the origin of the Google brand and its evolution.
Getting to know the founders of Google and the BackRub project
Larry Page and Sergey Brin met in the summer of 1995 at Stanford University’s doctoral student induction program, which included a tour around San Francisco. Both of them had just finished their master’s degree in computer science and were about to enter the doctoral degree with brilliant academic records.
Sergi Brin, who had a more social spirit, had volunteered to lead one of the student teams during the event. He had to show the university campus to the students and also lead the said recreational tour. Larry Page happened to be his bandmate and, contrary to expectations, their association during the camp was not pleasant for either of them.
According to Larry Page, Sergey Brin was too proud, while Sergey Brin considered Larry Page to be an unbearable person. They talked about urban infrastructure and social order for almost the entire camp and did not agree at any point.
Page later said in an interview: “We were arguing for a long time, Sergi had strong ideas and I think I was the same.” Sergiy Brin also confirmed his words and continued: “Both of us considered the other party hateful!” But the fact that we took time to discuss with each other showed that we also value thoughts.” They clearly complemented each other.
By the start of the first semester of their Ph.D., Page and Breen were no longer in contact and were working on their own projects and research. Page had learned from his father, a computer science professor at Michigan State, that a doctoral dissertation could determine the ultimate path of one’s academic career. When he approached his advisor, Terry Winograd, to decide on a thesis topic, he put more than 10 interesting ideas on his desk.
Larry Page had more than 10 different topics in mind for his thesis
However, Larry Page’s work did not start with researching the web search engine. Although Stanford graduates were getting rich founding Internet companies, Larry Page found the Web primarily interesting for its mathematical properties: each computer was a node, and each link on a Web page established a connection between nodes, something that a structure It showed classic graphics.
He says:
Computer scientists love graphs, and the World Wide Web could be the largest graph ever created.
Finally, with the consent of his mentor, Terry Winograd, Page began to examine the structure of web links. The point that disturbed his mind in the first stages of research was that although surfing the web from one page to another by following links was a simple and trivial task, few people paid attention to the reverse process, that is, the number of links behind each web page.
Larry Page in the BackRub project was looking for a way to count and determine the importance of each backlink on the web
Page thought that knowing which pages were linking to which pages would have many potential uses. This research led him to BackRub, a project focused on backlinks: perhaps if he could find a way to count and determine the importance of each backlink on the web, the web would become a more valuable place.
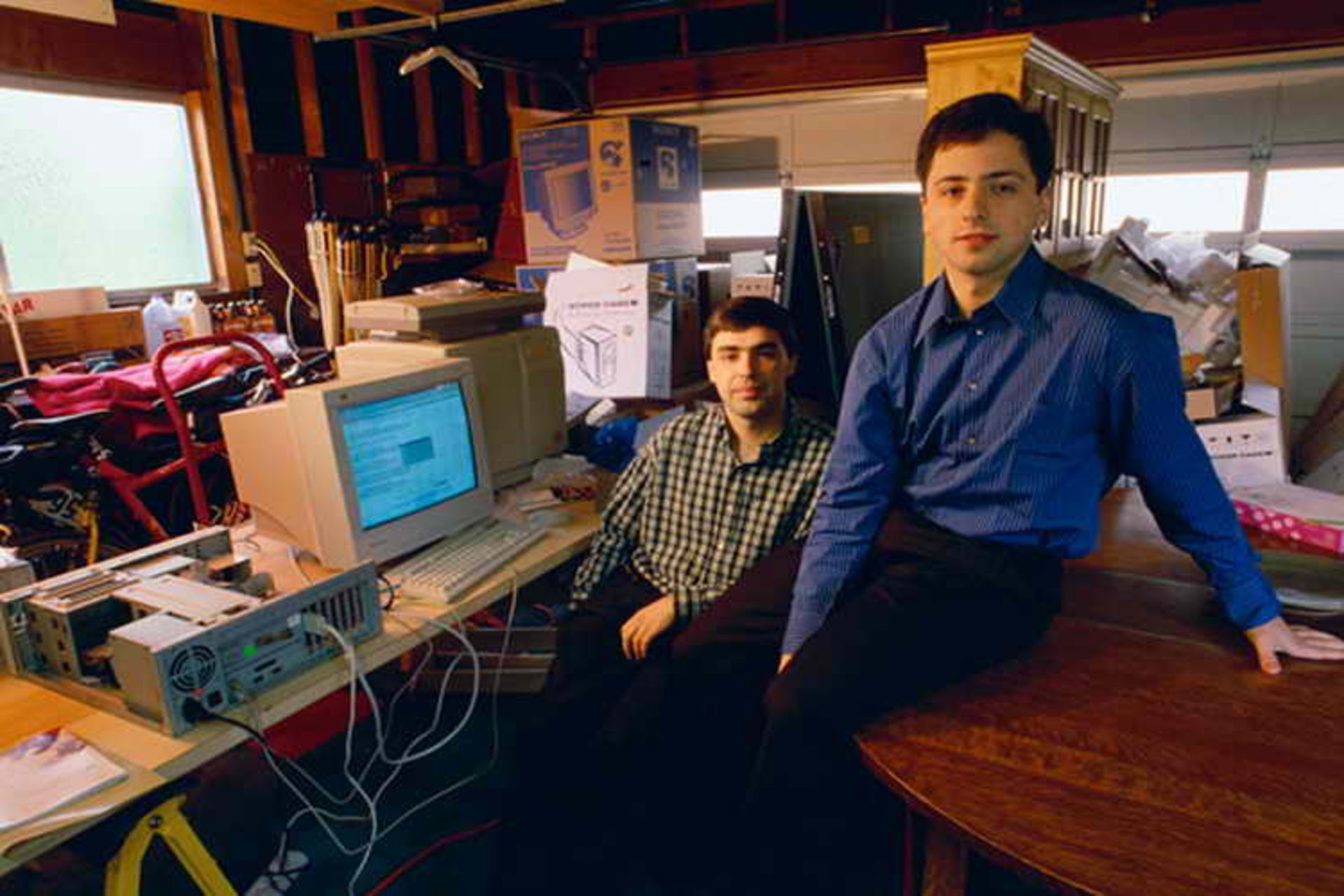

At that time, the web contained about 10 million documents with countless links between them. The computing resources of such a project were estimated far beyond student theses, and the dimensions and complexity of the project attracted the attention of Sergey Brin, who had worked on data mining articles and algorithm analysis during his PhD.
Sergey Brin joined the BackRub project and took over the mathematical side of the research, while Larry Page worked on link weighting and backlinks.
The weight of the links, in simple words, indicated that each link is from which source and with what degree of importance it targets another website. For example, the importance of the link that Intel’s website gave to IBM’s website was very different from the link that a teenager’s diary-blog gave to IBM’s website.
Sergey Brin handled the mathematical part of the research and Larry Page focused on link weighting
On the other hand, each link was placed in a different position and ranked according to the number of links on its home page. In other words, they counted not only the number of links on a page but also the links that were attached to each particular link. As the project progressed, its mathematical dimensions became more surprising and complex.
Sergey Brin says:
I loved data mining, which means analyzing huge amounts of data and finding patterns and trends. At the same time, Larry wanted to download the entire Internet, which contained the most interesting data possible for analysis.
Based on the results of their research, Page and Brin designed an algorithm called PageRank, which sent more popular sites to the top of the list and less important sites to the bottom of the list.
While investigating the work, they realized that the outputs of this model act somewhat similar to the search engine. In fact, BackRab was already a search engine that took a URL and provided a list of backlinks ranked by importance.
In addition, BackRub’s results outperformed those of other existing search engines such as AltaVista and Excite, which often listed irrelevant sites. By focusing on keywords, these search engines only looked at the text of the websites and ignored the most important factor, the ranking of the web pages.
Page and Brin developed the first search tool experimentally. This software only considered the headlines and page titles of the websites and then used the PageRank algorithm to rank and sort the websites. The results were significantly better than popular search engines.
Search engine development
At this point, Sergey Brin and Larry Page realized that they had taken a big step: the backrub engine not only performed well but also scaled as the Internet expanded. In other words, since the algorithm worked by analyzing links, the bigger the web, the more powerful the search engine.

For this reason, Page and Brin chose the name Googol (meaning the number one and 100 zeros in front of it) for their search engine, which was a symbol of processing the endless amount of information on the web. They published the first version of Google in August 1996 on the Stanford website with the domain google.stanford.edu, a year after they first met and got to know each other.
Page and Brin released the first version of Google for Stanford students with the domain google.stanford.edu
Its initial version was a success among a small group of Stanford users, and the two classmates quickly began improving the service to monitor the entire content of websites in addition to titles, while indexing more pages.
After Page’s room was filled, Brain’s room became their programming center and management office. Before long, the former BackRab was a legendary project in Stanford’s computer science department, consuming nearly half of the university’s network bandwidth. By the fall of 1996, it had gotten to the point where the search engine was regularly disconnecting Stanford’s Internet connection.
Larry Page later recalled:
We were lucky that there were so many forward-thinking people at Stanford who didn’t blame us too much for the resources we used.
The founding of Google: A Star rises
Page and Brin registered the google.com domain in September 1997. They knew that they could no longer rely on university resources to continue. In August 1998, one of the university advisors suggested that they meet Andy Bechtolsheim, the founder of Sun Microsystems. The meeting was held on the porch of this consultant’s house with a demonstration of the Google search engine.
Andy Bechtolsheim wrote a check for $100,000 to Google Inc. But the problem was that there was no company called Google yet. Page and Breen kept the check in their dorm room for several weeks while they went through the business registration process and opened new bank accounts for their business.
 Andy Bechtolsheim, Google’s first investor
Andy Bechtolsheim, Google’s first investor
Google was officially registered on September 4, 1998, and according to the previous agreement, Larry Page became the CEO and Sergey Brin became the company’s president. The two defined the company’s mission in one phrase: “Organizing the world’s information and making it accessible and useful to all people.”
Google’s mission: “Organizing the world’s information and making it accessible and useful for everyone.”
Page and Breen moved their tools and equipment to the company’s first office, which was the garage of their friend Susan Wojitsky’s house in Menlo Park, and by the end of the year, they had hired six more software engineers to work with them. By the end of 1999, the number of Google employees reached 21 people, among whom the names of Salar Kamangar, Omid Kurdestani, Suzan Vejitsky, and Marisa Mir stand out.
While Google’s daily searches were growing exponentially, the development of the company’s infrastructure required more capital.
 Google’s first office in the garage of Suzanne Wojitsky’s house
Google’s first office in the garage of Suzanne Wojitsky’s house
At the end of the first year of its establishment, it held its first fundraising round and received a total of one million dollars from three angel investors, Amazon CEO Jeff Bezos, Stanford University computer science professor David Cheriton, and Ram Shriram, one of the entrepreneurs of the technology world.
Andy Bechtolsheim, the founder of Sun Microsystems, was Google’s first investor
Many investors thought that the idea of a search engine startup would go nowhere, because the effort of technology companies was to keep users on their websites longer, and the search engine made people go from one website to another.
 Google page in 1998
Google page in 1998
But the potential and early success of Google in the second round of fundraising attracted the attention of two famous venture capitalists: John Doerr of Kleiner Perkins and Michael Moritz of Sequoia Capital, after carefully examining Google, they decided to invest a total of $50 million in this fledgling startup. .
The interesting point is that before these investments, Larry Page and Sergey Brin had offered Excite to buy their startup for one million dollars, but Excite refused to pay more than 750,000 for Google, and thus the contract was canceled.
 Google team in 1999 Palo Alto office
Google team in 1999 Palo Alto office
After raising capital, Google moved to its second office in Palo Alto, home to many famous Silicon Valley startups. In 2000, the Google team launched Google AdWords with the idea of Susan Wojitsky, which optimally changed the company’s revenue stream.
The AdWords service allowed companies to show their ads precisely to those who were looking for related products or services. This service was a revolutionary example in the world of online advertising and allowed Google to have a powerful money-making machine in addition to the search engine.
While the number of Google searches increased daily, with these changes, Google employees found a better mood and focused strongly on the path of progress.
At this time, John Doerr and Michael Koritz, the main investors of the company, according to their long-term experiences in the technology world, suggested to the founders of Google to hire a more experienced manager to lead their startup. Sergey Brin and Larry Page conducted complex interview sessions with several candidates but found none of them aligned with Google’s vision and long-term horizon.
In 2001, Eric Schmidt went to the interview meeting of the founders of Google with his hands full: he had detailed plans for developing Google internationally, diversifying products, sales, and accounting strategies, and managed to get on the Google board. A few months later, Page and Brin tapped him to become Google’s CEO, seeing Schmidt as the best fit for the company’s IPO event.
CEO Eric Schmidt’s tenure: Google’s explosive growth
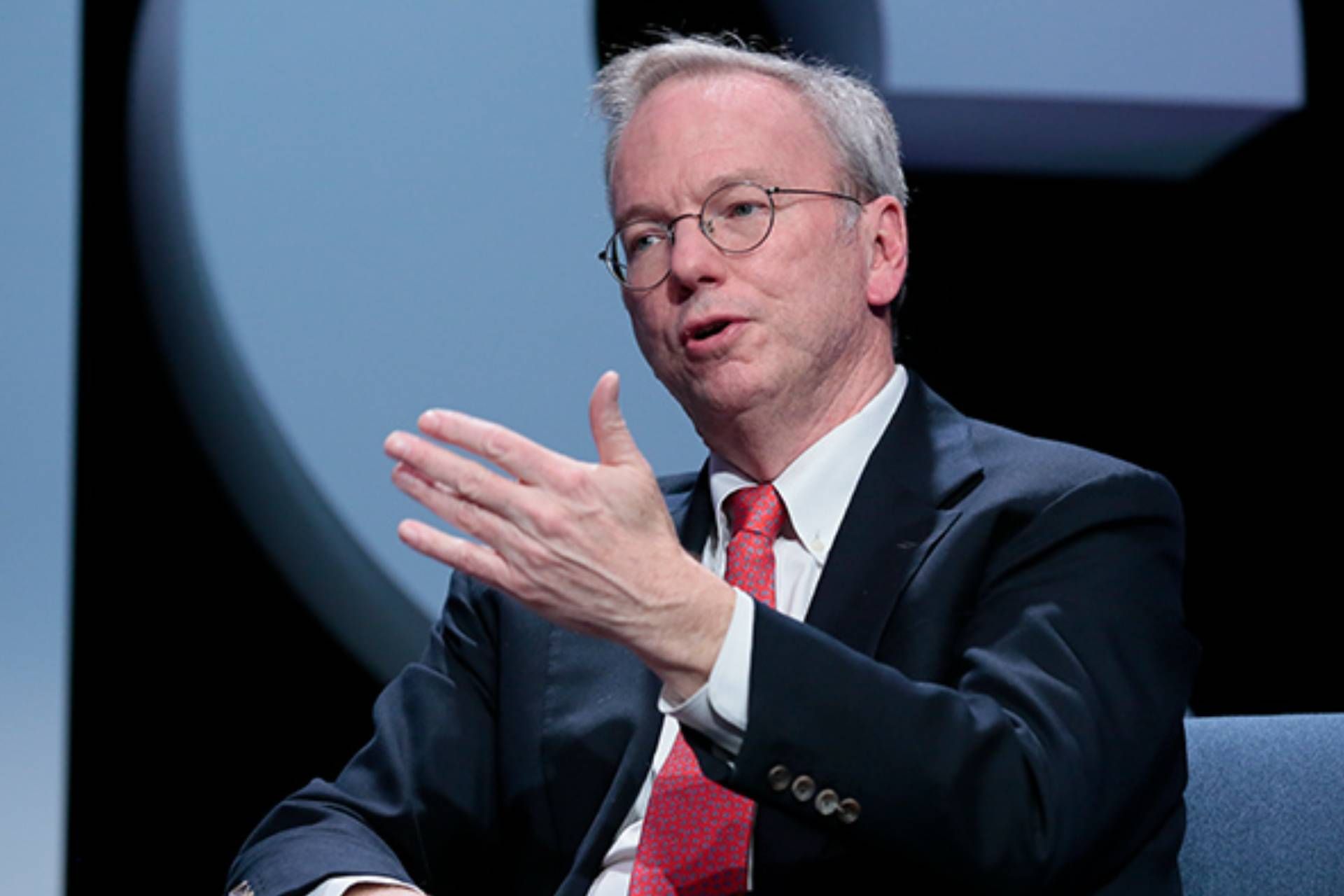

Eric Schmidt was appointed CEO of Google in August 2001 and remained in this position for 10 years. The joint idea of Sergey Brin, Larry Page, and Eric Schmidt was to create a comprehensive ecosystem that would meet all the digital needs of users through Google.
In the product development department, Schmidt had Merissa Meyer by his side, who had previously managed web products with user interface changes and the introduction of Google Doodles. One of the first developments of Google in the search engine side was the addition of the image search section.
In 2002, Yahoo planned to buy Google for $3 billion
In 2002, Yahoo tried to buy Google for $3 billion, but Page and Brin rejected the offer; Because they believed that their startup has more value.
Google executives wanted this company to be a symbol of the endless power of innovation; For this reason, they adopted a policy that allowed Google employees to dedicate 20% of their working time to projects that interest them, even if it is outside the scope of their official duties. This policy led to the emergence of some of Google’s most popular products in the following years.
In 2003, the Google News division was launched, and the board of directors purchased a building complex in Mountain View, California, to provide a suitable space for the company’s operations until they employed a thousand employees.
 Google Camp in Mountain View
Google Camp in Mountain View
This office, known today as “Google Plex”, expanded over time by purchasing the surrounding buildings and became the largest company camp in the world.
From Gmail to Chrome: The products that changed the web market forever
In 2004, the Gmail service created a storm in the world and raised the company’s position among users to a new level.
With 1 gigabyte of storage space, Gmail allowed users to quickly search for any email they had sent or received. In addition, this service provided users with new ways to automatically organize emails by topic. Many people thought that Gmail was Google’s April fool, but luckily it was not.
Gmail’s features far exceeded other free email services
In this era, Google’s revenue-generating strategies worked well, so that a few days before the initial offering of Google shares, stock market experts considered the company’s future to be very profitable.
 Gmail in 2004
Gmail in 2004
Finally, on August 19, 2004, Google’s IPO event took place at a price of $85 per share, bringing a fortune of about $1.7 billion to the company’s founders and early investors. In addition, the value of the company was estimated at 27 billion dollars.
 Google IPO on Nasdaq with Eric Schmidt and Larry Page
Google IPO on Nasdaq with Eric Schmidt and Larry Page
The introduction of the Google Maps service in 2005 marked another success in Google’s career and became a background for the company’s research collaboration with NASA. Google Maps evolved over time and became one of the most valuable features of Google to facilitate people’s daily lives.
Google started working with NASA after the introduction of Google Maps
But no one expected the company’s next revolutionary product to impact the entire tech world.
In September 2008, Google introduced the Chrome browser to the world. Interestingly, Eric Schmidt was against Google’s entry into the web browser market from the beginning, and this product was developed at the insistence of Sundar Pichai, one of the company’s forward-looking executives who was supposed to play a key role in the company’s future.
To create Chrome, Google hired some of the original Firefox engineers and developed the browser first for Windows and then for other operating systems. The first version of Chrome came with a 40-page visual guide to show users how to work with the browser. In just 4 years, the popularity of Google’s browser surpassed Firefox and Internet Explorer.
Schmidt later said in an interview:
I told Larry Page and Sergey Brin that we shouldn’t think about browser or operating system development, we shouldn’t compete with Microsoft. They told me they were hiring people to improve Firefox, and six months later they showed me Chrome. To be honest, I was so excited to see the Chrome demo that I had no choice but to admit I was wrong.
At the same time, Google’s organizational culture was still at the center of attention. This company was known as one of the best working environments in the world by maintaining a creative work environment. In such an environment that was based on the freedom of creativity and innovation, Google could attract the best talents and encourage them to create new and efficient products.
Strategic purchases: Doubleclick, YouTube and Android
At a time when Google was improving the level of user experience by offering various products that often had better performance than competitors, it was also preparing the ground for building an inclusive ecosystem by buying leading startups.
For example, the company took the biggest step toward expanding its pervasive advertising empire across the Internet with its $3.1 billion purchase of DoubleClick, the company’s most expensive acquisition at the time. In 2006, Google also bought YouTube for 1.65 billion dollars to give its plans in the field of video content a more serious color.
Under the leadership of Salar Kamangar and then Susan Wojitsky, YouTube became one of Google’s most valuable assets and one of the best online video content platforms, used by millions of users every day.
One of the other decisive actions of Google is the purchase of the Android operating system for 50 million dollars in 2005, which was released in 2008 for the T-Mobile G1 phone known as the HTC Dream. Open source software and integration with the Google ecosystem and the highest levels of notification capabilities were the most important features of Android that made it the most popular mobile operating system in the world.
So far, there has been no news of Google’s serious presence in the smartphone market.
Founding of Alphabet and CEO Larry Page: Reorganizing the company
Between 2010 and 2014, Google was trying to create a new chapter in its history. Delving into fields beyond the search engine and web browser, the company had become a global innovation laboratory pursuing ideas ranging from driverless cars to projects in healthcare, renewable energy, and artificial intelligence.
In April 2011, Eric Schmidt resigned, saying that Google no longer needed the supervision of veteran executives like him, and Larry Page took his place. Larry Page and Sergey Brin realized a long time ago that they needed structural changes to better manage a company as big as Google and focus more on their ambitious projects. For this reason, in 2015, they made a bold decision.
They established a new holding company called Alphabet and brought Google and their other projects and companies under its umbrella. This move was not only a structural rearrangement but also reflected a profound philosophical change in Page and Breen’s approach. In this way, Google found a different position and at the same time in sync with a set of independent companies, each of which was looking for its specific and sometimes ambitious goals.
For example, the Google X division managed modern projects such as self-driving cars and smart cities. Meanwhile, Calico oversaw research related to increasing human lifespan and improving quality of life, and Verily focused on medical and biotechnology research.
In May 2011, Google reached a record of one billion visitors
Larry Page remained the CEO of Google until 2015, after which he took over the management of Alphabet. During his CEO tenure, Google experienced many ups and downs.
In May 2011, Google reached a record of one billion unique visitors. In the same year, “Chrome OS” was also introduced, which was mainly used in Chromebook laptops. These laptops were manufactured by Acer and Samsung and were first released to the general public in some retail stores, but in later years were made available to students and teachers in schools for educational purposes.
 Google+ circles page
Google+ circles page
This period coincided with the introduction of one of Google’s famous and failed projects, namely Google Plus. The fact was that Google managers wanted to compete with Facebook by launching a social network, and in this regard, they replaced Google Plus with the Google Buzz microblogging service. Despite repeated redesigns, Google Plus never achieved success.
Google wanted to compete with Facebook by launching Google Plus
Another unfinished project of the company was Google Glass, whose experimental hardware was developed in the Google X and ATAP divisions. Despite the good idea and design, Google Glass needed technologies to process information that had not yet been developed at that time. In addition, some companies considered this product to be against their privacy and banned employees from using Google Glass.
July 2013, when Google announced the end of the Google Reader service, fans of this popular feed reader looked at this decision in disbelief. Shutting down Google Reader required courage, as we later saw in removing the headphone jack from iPhones. But this action made many Google users move to Twitter and search for daily news in tweets.
Finally, the purchase of DeepMind, an artificial intelligence laboratory based in London, was one of the most important steps taken by Google in this era, which later played a significant role in gaining the power of Google’s artificial intelligence department.
CEO Sundar Pichai’s era: the season of fighting with rivals
In 2015, together with the founding of Alphabet, Sundar Pichai, the company’s senior vice president under Eric Schmidt, replaced Larry Page as Google’s new CEO. Pichai, who joined Google in 2004, had proven his ability in leading the Google search bar, Google Gears, Google Pack, and Google Drive projects.
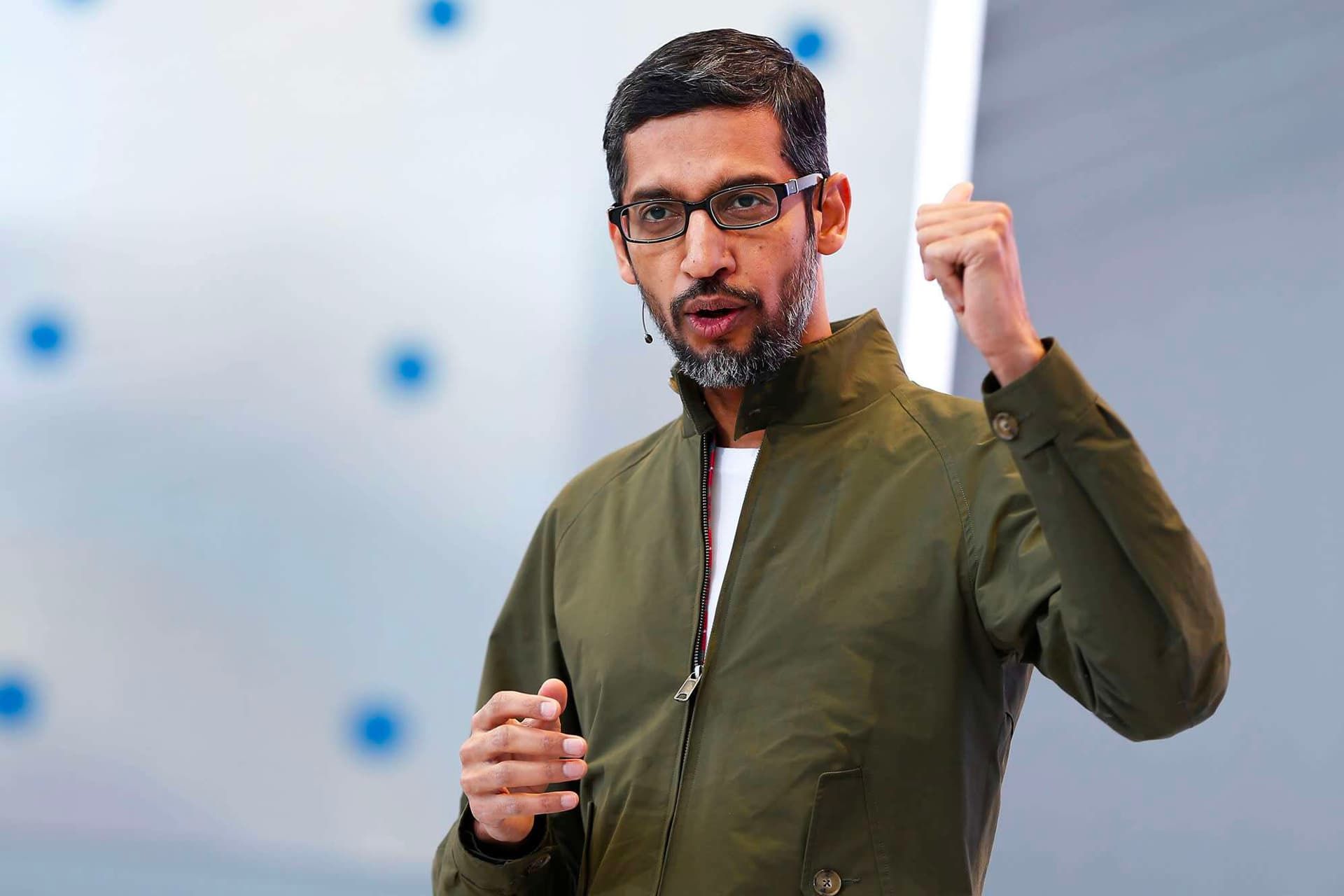

Pichai soon became one of the well-known faces of Google due to the idea of the Chrome browser and the management of the team that was responsible for the development of this software, and he became the deputy CEO of the company. He also played a significant role in the development of Android and the development of Google Apps.
One of the most important products that was introduced in the early days of Pichai’s CEO was Google Assistant. Google Assistant was introduced two years later than Amazon’s Alexa and 5 years after Apple’s Siri, But very soon it found its right place among users.
The wish of the founders of Google for the development of an inclusive and integrated ecosystem was realized during the management of Sundar Pichai
The strength of this virtual assistant was its synchronization with other products of the Google ecosystem, such as Google Home speakers, smart TVs, and most importantly, Android systems. Also, in 2016, Google announced the production of tensor processing units.
In October 2016, Google was at the forefront of the competition of flagship phones in the hardware sector with the introduction of Pixel phones, and two months later, the self-driving car project, which was considered one of the most successful projects of the Google X laboratory, was transferred to Waymo as an independent company after 6 years of testing. Guide the alphabet.
Sundar Pichai, unlike Eric Schmidt, was not afraid of competing with powerful technology companies, although now Google had also found a different face and no one considered it a new Silicon Valley player.
For example, Sundar Pichai had a special focus on the company’s cloud services, and despite long-standing competitors in this field such as Amazon and Microsoft, he invested heavily in building new data centers and developing cloud networks. With his efforts, Google Cloud became one of the top three cloud service providers in the world.
By introducing artificial intelligence tools and platforms in its cloud platform, Google was able to support corporate customers in various fields, including data analysis, machine learning, and process automation. During this period, the development and expansion of Nest smart home products also reached its peak. Although Google bought Nest in 2014, in recent years the integration of these products with the Google ecosystem has provided customers with an unparalleled user experience.
Some Google products, such as Google Translate, Google Lens, and Google Mate, found an undeniable role in people’s daily lives, and some projects, such as Google DeepMind projects, with every development and news, surprise the world beyond the technology world. Also, under the effective leadership of Sundar Pichai, Google has become one of the most powerful companies in the highly competitive market of generative artificial intelligence.
Google’s presence in the mobile market: from Nexus to Pixel
In the early 2010s, Google executives decided that they needed to enter the mobile market to improve the Android user experience and ensure timely updates for users.
At that time, Android was available as an open-source operating system to different manufacturers, and each company released its own version with desired changes and different user interfaces. But by producing Nexus phones, Google intended to provide users with a pure and integrated Android experience.

The first Nexus phone, named Nexus One, was introduced in January 2010 in collaboration with HTC. After that, Google introduced new Nexus models every year in partnership with one of the smartphone manufacturing companies:
- Nexus S: Samsung manufacturer, Android 2.1 Eclair operating system can be updated to Android 2.2 Froyo and Android 2.3 Gingerbread
- Galaxy Nexus: manufactured by Samsung, the operating system Android 4.0 Ice Cream Sandwich can be updated to Android 4.1 Jelly Bean
- Nexus 4: manufactured by LG, the Android 4.2 Jelly Bean operating system can be updated to Android 5.1
- Nexus 5: manufactured by LG, the Android 4.4 KitKat operating system can be updated to Android 6.0.1 Marshmallow
- Nexus 6: Motorola manufacturing company, Android 5 operating system before update to Android 7.1.1 Nougat
- Nexus 5X: manufactured by LG, operating system Android 6.0 Marshmallow updatable to Android 8.1.0 Oreo
- Nexus 6P: Huawei manufacturer, Android 6.0 Marshmallow operating system
The production of Nexus phones continued until 2015, but Google gradually realized that this series of phones, despite the loyal fans, could not compete well with other flagships in the market.

The production of the first series of Pixel phones began in 2016, and Google played the main role in the design and development of this series. The company optimized pure Android for Pixel phones to provide a smoother experience to the audience.
Since Google’s main goal was to compete with the flagships of Google and Samsung, it used better hardware and especially improved cameras in these products, which consequently raised their prices higher than the Nexus series. Also, the peak of Android integration with Google platforms was also seen in these phones.
However, since 2019, Google has tried to gain popularity among mid-range phone users by adding the Pixel series to its product series. Also, in 2023, the first Pixel Fold was introduced to compete with foldable phones of competing brands.
Google and artificial intelligence
Google was aware of the power of algorithms and machine learning from the beginning of its activities, and one of the most important areas in which it continuously invested was artificial intelligence.
As we said, in 2014, Google bought DeepMind Lab, which had advanced research in the field of artificial intelligence. Among the achievements of this laboratory, we can mention Alphago and AlphaFold projects.
 Demis Hessabis, co-founder of Deepmind
Demis Hessabis, co-founder of Deepmind
Researchers at the AlphaGo project developed neural network models specifically for video games and game boards, and in 2016 AlphaGo beat the world champion Go player in a competition. Alphafold also made a significant contribution to the pharmaceutical industry by accurately predicting the three-dimensional structure of proteins using a deep learning system.
On the other hand, Google had opened a special account on the development of neural processing units. TPUs, or tensor processing units, were custom-designed silicon chips developed specifically for machine learning and optimized for TensorFlow. According to Google, TPUs train and run AI models much faster than traditional chips.
In 2019, Google used Bert algorithms in its search engine, which understood the meaning of words in the text instead of understanding words separately. According to Google, Bert greatly improved the responsiveness of the search engine, because users could ask Google their questions naturally instead of listing their desired keywords.

In 2023, Google finally made Bard’s generative artificial intelligence system available to users, which was based on the large conversational language model LaMDA. Google Bard was integrated into many everyday Google services such as Drive, Maps, Docs, Gmail, and YouTube.
With the increasing popularity of ChatGPT, in May 2023, Google introduced the next generation of its artificial intelligence language model called PaLM 2, which had more capabilities in the field of understanding different languages and the power of reasoning and coding. Google Jumnai based on this model was developed and replaced Bard.

Getty Images
Google’s noticeable speed and effort in the field of productive artificial intelligence can be considered one of the most obvious competitive manifestations of this company to obtain a greater share of various technology markets. After Microsoft’s huge investment in the startup OpenAI, Google also invested 500 million dollars in the startup Entropic.
The challenges of Google Jamnai photo production caused Sundar Pichai to invite Sergey Brin and Larry Page to have a closer relationship with this company by declaring an emergency (code red). Following this event, Sergey Brin officially confirmed his return to Google.
Also, in 2024, Google showed its readiness to compete with Apple by completely redesigning Android and took great steps towards local processing of artificial intelligence features in phones, such as Circle to Search.
Google Antitrust Cases: Growing Challenges
The flow of legal cases and complaints related to Google’s monopoly started in 2010; That is when the European Union Commission started a wide-ranging investigation into the anti-competitive behavior of this company. At that time, one of the main accusations was that Google placed its products and services above competitors in the search results, thereby marginalizing other companies.
This investigation became one of the longest and most complex antitrust cases in the history of technology, and finally, in 2017, the European Union sentenced Google to pay a heavy fine of 2.4 billion euros for prioritizing its shopping services (Google Shopping). .
A year later, the European Union condemned Google to pay a fine of 4.34 billion euros; But this time because of the Android operating system. Now Google was accused of encouraging mobile phone manufacturers to install their own apps (such as Google Maps, Gmail, and Play Store) and thus keeping competitors out of the market.
Read more: Amazon brand story; A store for everything
In this case, Microsoft, Nokia, and Oracle were influential in the final verdict and condemnation of Google by participating in the research group called FairSearch. In 2019, Google was fined another 1.5 billion euros by the European Commission. Google Adsense service was the main focus of these accusations.
 Judge Amit Mehta in the Google monopoly case
Judge Amit Mehta in the Google monopoly case
After this case, it was the turn of the US Department of Justice to file a new and detailed complaint regarding Google’s monopolistic actions in the search engine and advertising market. In this lawsuit, more than 30 US states were on the opposite side of Google and sided with the judiciary.
In response to the accusations of the United States Department of Justice, Google announced that the online search and advertising market is a competitive market and different companies operate in this market. According to Google, users choose the company’s products and services because of their high quality, and this does not indicate exclusivity.
But in August 2024, Google finally lost its biggest antitrust case and was convicted by a Colombian court that it illegally monopolized the search market.
The Department of Justice and US prosecutors say that Google pays billions of dollars annually to mobile phone manufacturers such as Apple and Samsung to install the company’s search engine as the default application on their products in order to maintain its 95% share of mobile searches.
The consequences of this ruling can be very heavy for Google, while Google still has several other antitrust cases pending.
On the eve of the 26th year of Google’s establishment, this company with a market value of 2.02 trillion dollars is known as the fourth most valuable company in the world.
However, Google has never faced such serious challenges. Will it break up as US government and judicial officials say? Will the emergence of new artificial intelligence search systems such as SearchGPT diminish the popularity of Google’s search engine? How do you see the future of it?


You may like
-




What is Kali Linux? Everything you need to know about this popular but mysterious distribution
-




Sony Brand Story; From the production of rice cookers to becoming one of the most famous companies in the world
-




How did the people of the past imagine the future?
-




The story of the Yahoo brand, the story of the fall of a unicorn startup
-




Samsung brand story; Full-view mirror of Korea’s commercial history
-




How to recognize the name of the font from its picture?
Technology
What is Kali Linux? Everything you need to know about this popular but mysterious distribution
Published
2 days agoon
15/09/2024

What is Kali Linux? Everything you need to know about this popular but mysterious distribution
In today’s technology era, as devices and tools become more advanced, their negative and destructive side also become more complex, and as a result, interaction with them requires more care. Currently, with the pervasiveness of the Internet the strong dependence of our daily lives on it, and the emergence of artificial intelligence, cyber threats have also increasingly spread, and the news of hacking various platforms is heard from left and right.
Considering the cyberization of part of people’s lives (entertainment, chat, and earning), the importance of strong cyber security measures cannot be ignored. Kali Linux or in English Kali Linux is a powerful and open-source Linux distribution that is specifically used for penetration testing and digital research and is considered one of the most important tools in the field of cyber security.
 Kali Linux 2024.3
Kali Linux 2024.3
Every techie has probably thought of installing Kali Linux, even via a virtual machine, to poke around and entertain their inner little scientist.
When users first encounter Kali tools, they see strange names such as BeFF Bettercap Hashcat Metasploit, or Nmap, which are almost difficult to guess their use from the name. Overall, Kali is a powerful distribution, and working with it requires a deep understanding of its tools.
What is Kali Linux?
Kali Linux, formerly known as BackTrack Linux, is a Debian-based Linux distribution developed by Offsec. This Linux distribution hosts hundreds of different tools used for penetration testing, reverse engineering, and vulnerability detection of networks and websites.

Due to the fact that Kali is developed based on Debian, it has high stability and security, and its Debian base allows it to benefit from vast software repositories and a similar package management system. In addition, if you are in the category of users who are already familiar with Debian Linux distributions such as Ubuntu, navigating Kali will not be difficult for you; But for users of other operating systems to enter the world of Linux, learning Kali takes more time.
Another important goal of Kali developers is to give the user unlimited freedom to have an open-source and ever-evolving platform and not just be limited to the tools available on the platform. Thus, even the most detailed parts of the software on Kali are open to optimization by the user.
Who uses Kali?
If you are imagining a sequence of Mr. You’re Robot, which depicts a hall full of professional hackers, and the hackers are sitting behind their systems in hoodies, you’re completely wrong. The use of Kali Linux does not require special clothing and there are professional and skilled experts who appear in their company and workplace every day and are responsible for simulating attacks on the network and discovering and fixing its vulnerabilities.
Other people for whom the use of Kali Linux is useful are instructors who plan to train the next generation of white hat hackers and ethical hackers, and Kali Linux is considered the best toolbox for training.
Key features of Kali Linux
Kali Linux has a variety of tools in various categories, including intelligence gathering tools, vulnerability analysis tools, wireless attacks, password mining, and social engineering tools. Do not forget that one of the main foundations of hacking and penetration is social engineering.
 Kali Linux tools menu
Kali Linux tools menu
In Kali Linux, you can use Nmap to scan a network and identify its open ports, Metasploit tool is also provided to exploit a vulnerability, and Wireshark should be used to go deep into the traffic of a network.
Tools like Wifite and Airgeddon are also pre-installed on the Kali platform to check the security of your Wi-Fi network. In fact, Wifite automates the process of cracking WiFi passwords, while Airgeddon provides a convenient environment for assessing wireless network security.
Regardless of the tools and programs that are available by default on the platform immediately after installation, users can install other programs they need by connecting to the Internet by learning how to install the program on Linux.
 Metasploit tool on Kali Linux
Metasploit tool on Kali Linux
The Kali developers have paid attention to every detail and even included a custom kernel kernel for packet injection, which plays a key role when working with Wi-Fi. In addition, all packages are signed with GNU Privacy Guard to assure the user about the security of the platform.
Features of Kali based on the introduction on the official website:
- It is free and will always be free.
- Git is open source.
- It conforms to the Filesystem Hierarchy Standard.
- It is compatible with a wide range of devices.
- It is developed in a safe environment.
- Supports multiple languages; Of course, the platform tools are in English.
- Compatible with ARMEL and ARMHF.
Why is Kali Linux not suitable for everyone?
Kali tools are very powerful and require the same amount of knowledge and experience to use them properly. For example, a normal user might want to scan his home Wi-Fi network and find possible vulnerabilities by installing Kali. But in this process, with Kali’s tools, he creates a problem that has serious consequences for him.
 Installing the program in Kali Linux through the terminal
Installing the program in Kali Linux through the terminal
Suppose you try to execute a script without sufficient knowledge and because Kali is connected to the Internet, this script affects the computer of a certain person or organization. Do not forget that Kali is not designed and optimized for the everyday use of ordinary people and common tasks such as web browsing, editing documents and watching movies.
Go to Ubuntu to satisfy your curiosity and experience the Linux environment
If you are just curious about working with Linux and getting to know the environment of Linux distributions, better options can be found compared to Kali. Usually, the most recommended migration from other platforms to Linux ends up with the Ubuntu distribution, which has a user-friendly interface and a huge support community and runs everyday processes like any other operating system.
Linux Mint is another option recommended for beginners, especially for users who are used to traditional desktops. On the other hand, Windows users usually associate more with Zorin OS. These distributions are all developed for everyday use and perform tasks such as web browsing, editing documents and even running games very well.
Getting started with Kali
Finally, if you decide to install Kali Linux, you should download it from the official Kali website. On the Kali website, you can see different versions of Kali for installation in different ways, and according to your conditions and desired installation method, you can download the desired version.
To install Linux distributions, it should be noted that it is possible to install Linux on Flash or that the user can install the desired distribution on the virtual machine. Installing Kali on a virtual machine has the advantage that all events are kept in isolation and no damage is done to the user’s main operating system.
The Kali Linux distribution is considered the most popular platform for hackers and is designed for specific purposes where everyday use is not among its goals; Therefore, it is not necessary to install it for specialized work and of course to meet the needs of curiosity, but for normal use it is recommended to go for other distributions of Linux.
Dear Zomit users, what is your opinion about the user experience with Kali Linux? Do you recommend installing it?
fashion
Sony Brand Story; From the production of rice cookers to becoming one of the most famous companies in the world
Published
2 days agoon
15/09/2024

Noun: Someone who assists () a goal.
Sony brand story; From the production of rice cookers to becoming one of the most famous companies in the world
Sony is a Japanese multinational company headquartered in Minato, Tokyo. This company provides electrical services, gaming, entertainment, and financial services.
Sony is known as one of the pioneers in the production of electrical products and in recent years it has improved its position among the top companies in the world. Sony consists of many subsidiaries, the most famous of which are Sony Pictures, Sony Music, Sony Mobile, Sony Entertainment, and Financial Holding.
The story of the formation of the Sony brand
Masaru Ibuka returned to Tokyo from World War II in September 1945 to start a new job in the Japanese capital. He set up his workshop in an old, war-torn building with only eight employees. Their initial office walls were full of cracks and had no windows, but over time as their business progressed, the office building also improved.
In October of that year, Ibuka and his group launched a new company called Tokyo Tsushin Kogi, or Tokyo Institute of Communications Research. At that time, everyone was eager to work in the new company and wanted to use their engineering knowledge to rebuild Japan. However, no one knew where to start. Most of the employees were paid from Ibuka’s small savings and they had to work hard to survive.
The story of the formation of Sony goes back to 1945; When Masaru Ibuka returned from World War II
At that time and during the Second World War, people were thirsty to hear the news of the day. As a result, they came up with an interesting idea that changed the fate of the company forever. Most of the radios at that time were either destroyed by the war or could not receive radio waves due to police interference.
The Ibuka company repaired broken radios and also made it possible to receive waves using a series of converters. It didn’t take long for this model of radio to gain many fans among people.
Their business was in the center of attention and for this reason one of the Japanese newspapers published an article about them. This article not only got them more customers but also brought Ibuka’s old friend, Akio Morita, closer to him.
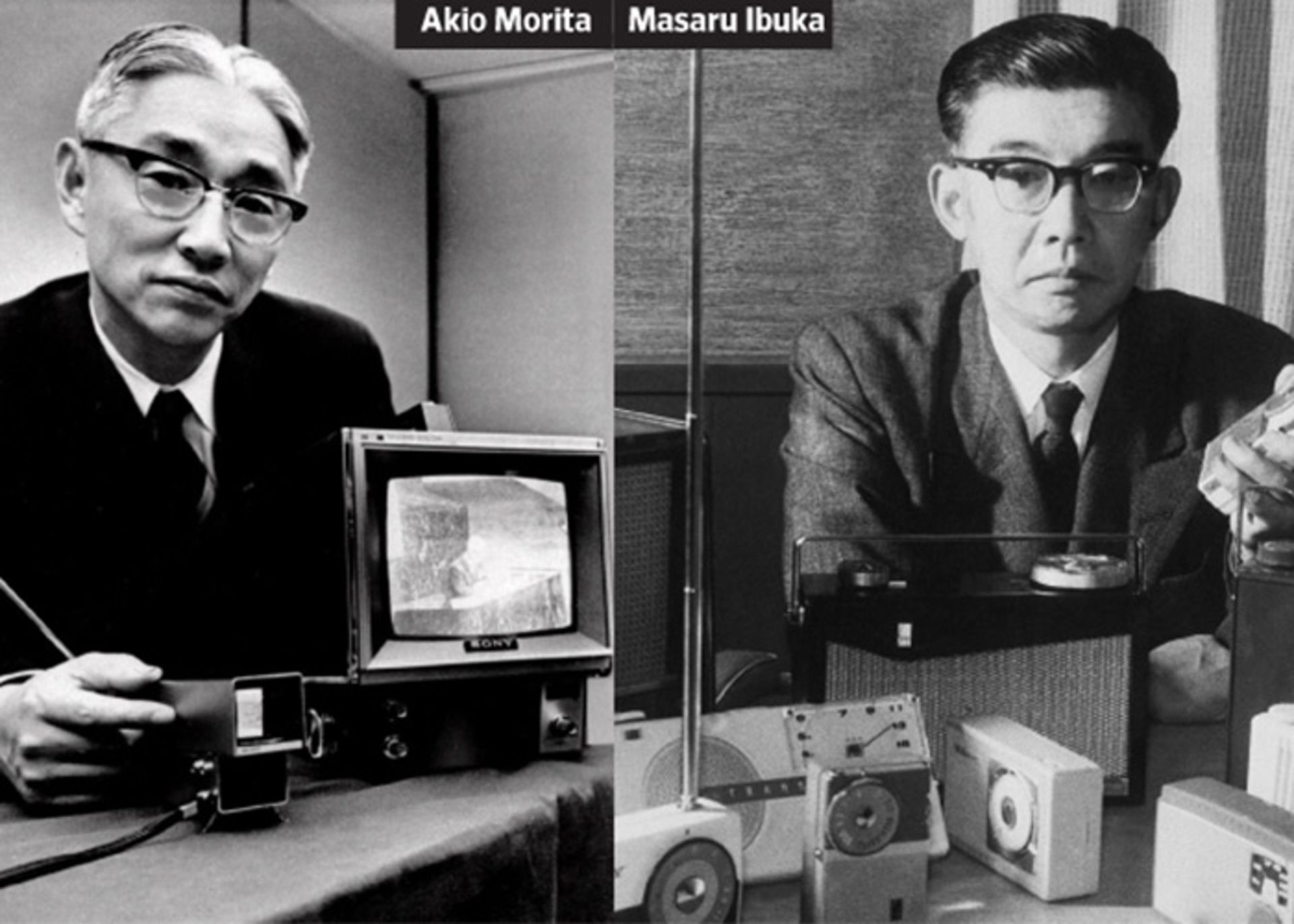

Ibuka and Morita, the founders of Sony Corporation, first met on a research committee studying new types of war weapons.
After some time passed, despite the big age difference, a deep friendship between Ibuka and Morita was formed. After the end of the war, Morita returned to his hometown and the communication between them was cut off. Until one day he read his friend’s name in a newspaper article and called Ibuka. Ibuka also asked him to get to Tokyo as soon as possible to start working with him again.
Sony’s brand name was originally supposed to be TTK or Totsuko
They were looking for a new name to advertise their company globally. Their intention was to choose the abbreviation of the company’s name, TTK, for advertising, but this name was already used. The word Totsuko was also another suggested name. But during his trip to America, Morita realized that it is difficult for Americans to pronounce this name.
They finally chose the name Sony from the combination of 2 words Sonus meaning sound and Sonny meaning young boy. Their purpose in choosing this name was to pronounce it in the same way in all languages of the world.
The company’s first product was a rice cooker, which, contrary to expectations, failed to meet expectations and failed. They did not get discouraged after their first failure and devoted more money to research. They focused on developing products that would benefit the Japanese people.
Sony; The first brand
During 77 years of operation, Sony has been able to launch the first product in many markets of the world. From Japan’s first tape recorder to Japan’s first transistor radio and other products.
Tape recorder
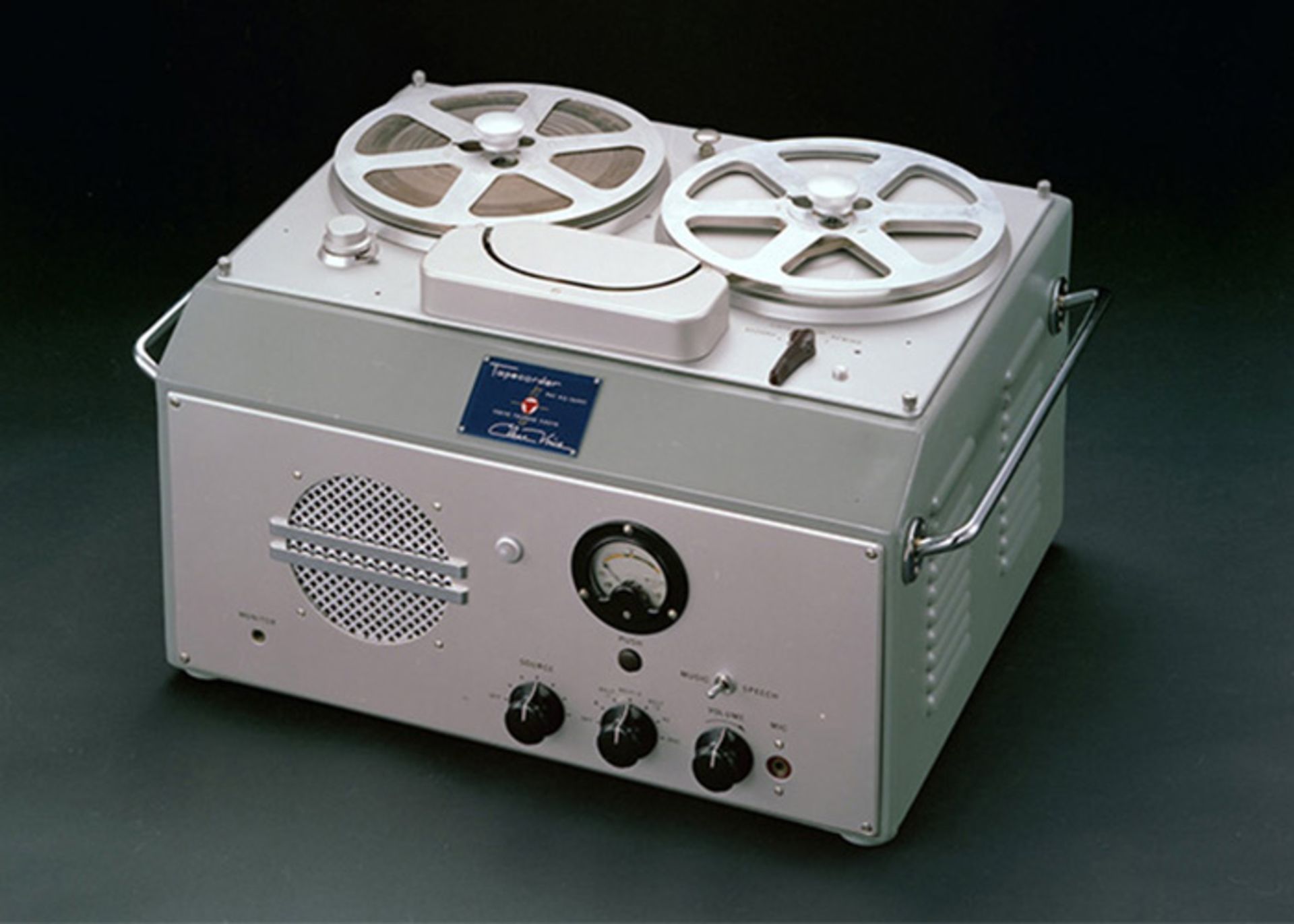

In 1950, the first Japanese tape recorder was made from its American model. This device was also not well received until Sony released a translated version of 999 Ways to Use the tape recorder.
After people became familiar with the product’s uses, the purchase request increased and the Sony tape recorder sold well. The demand for this product increased so much that the company had to expand its facilities to produce orders.
Transistor radio
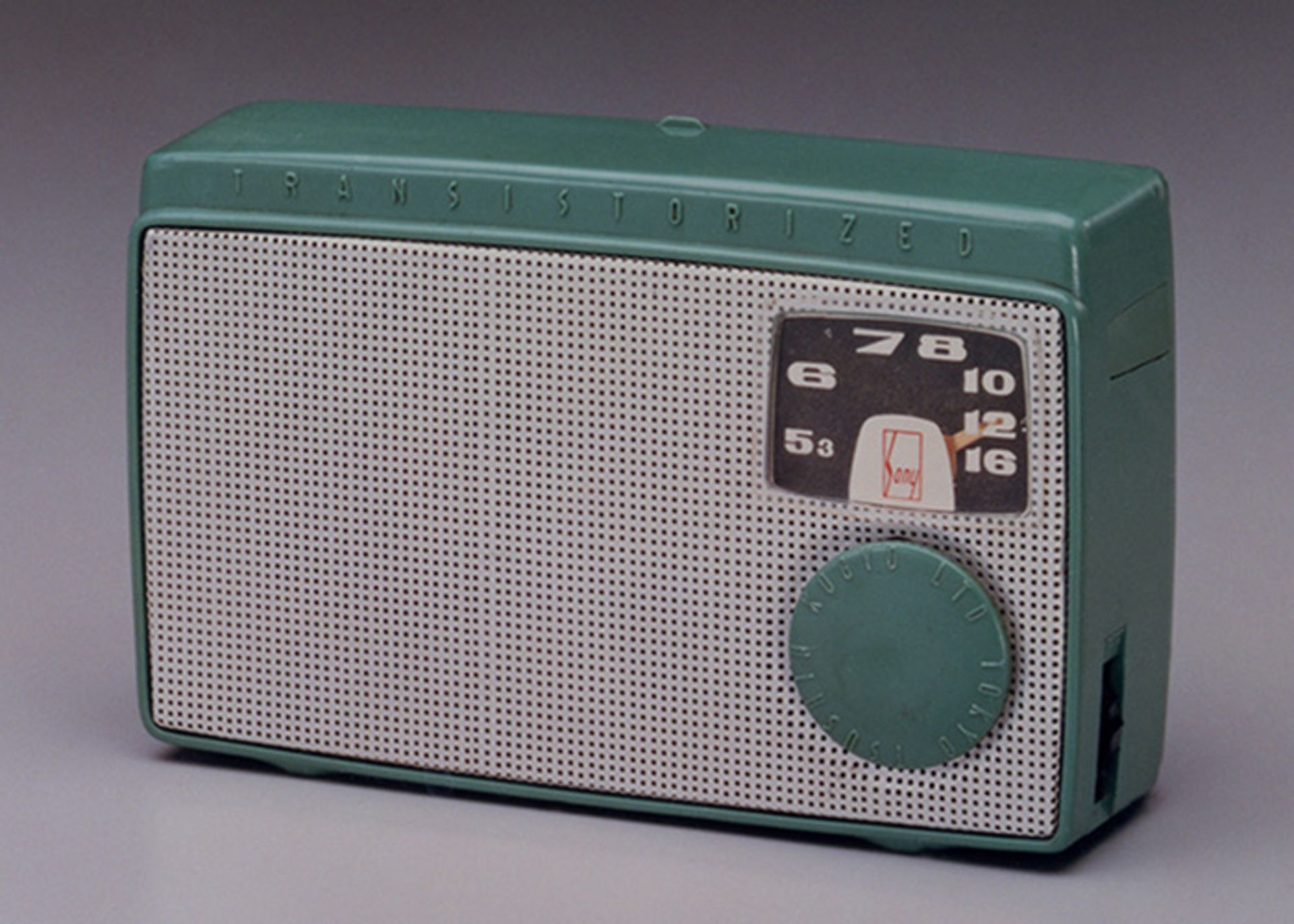

Japan’s first transistor radio was introduced in 1955 by Sony.
Portable TV
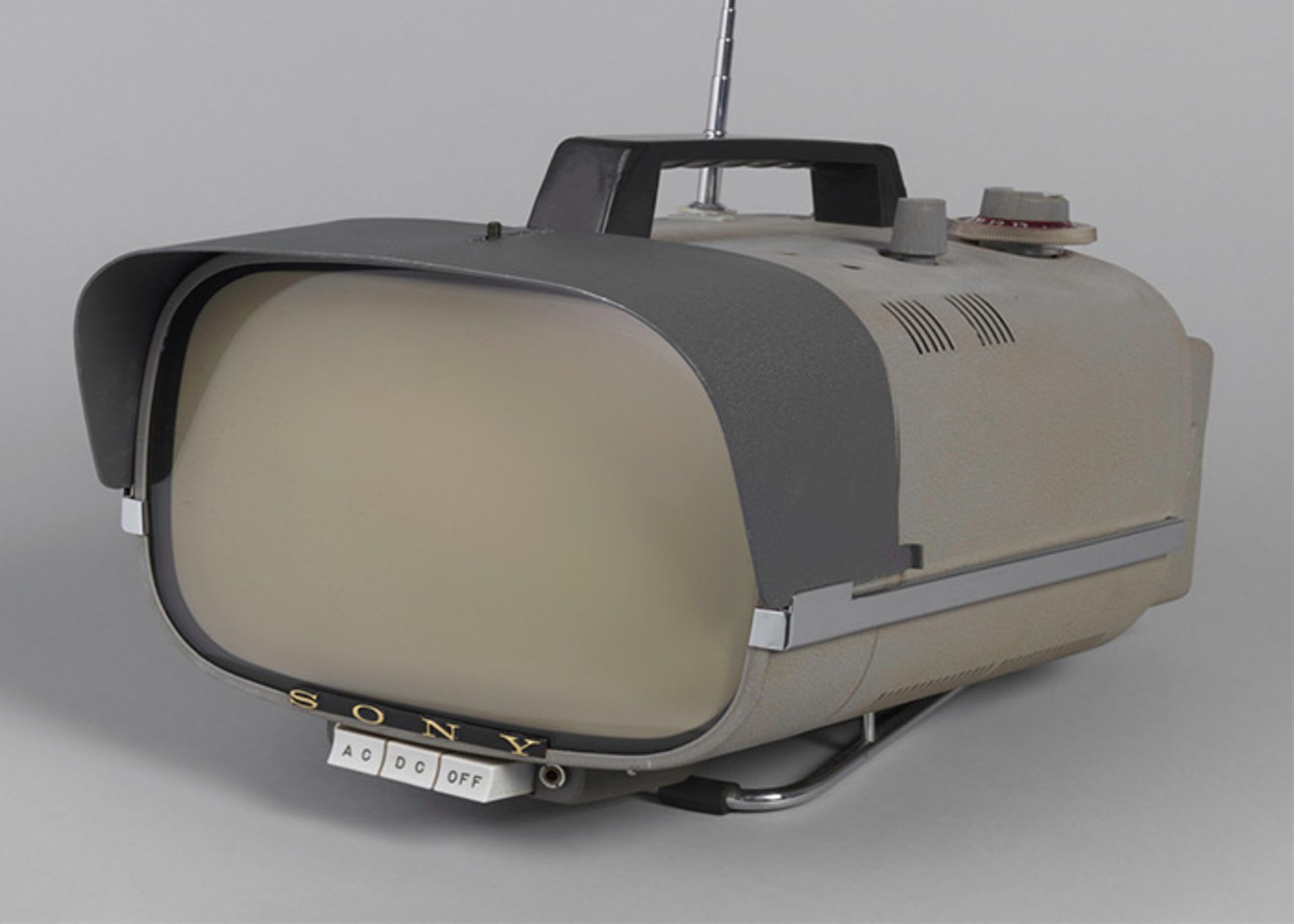

In 1960, Sony released the world’s first portable transistor TV. Sony used radio technology to produce this device.
The televisions of that time were big and in every house, a specific room was reserved for them. But these products brought a new definition of personal televisions to the market.
Video tape player
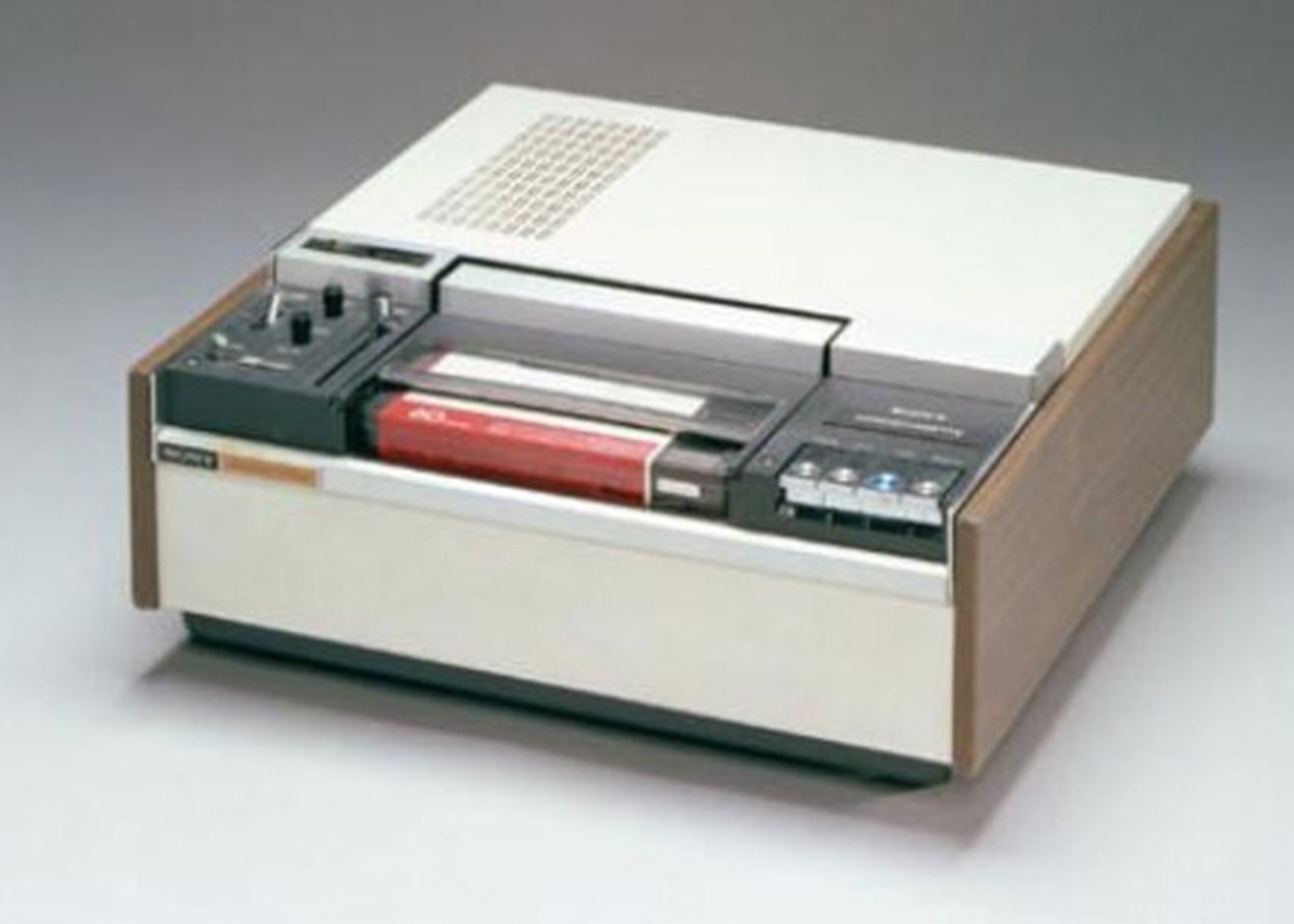

In 1971, Sony unveiled another product. This player was able to show videotapes in color inside the TV.
Masaru Ibuka retired in 1976 and was succeeded by Akio Morita as CEO.
The first generation Walkman
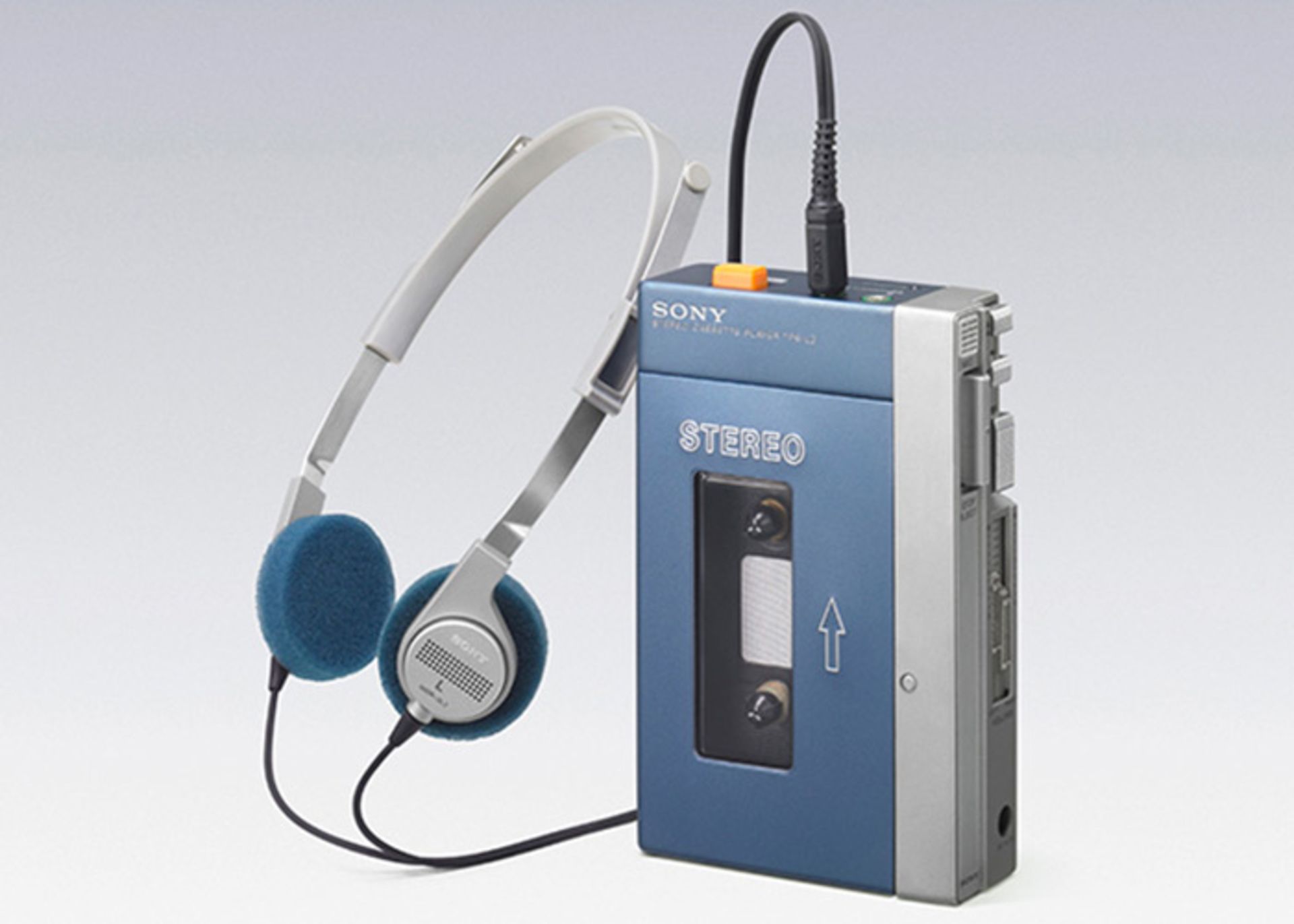

In 1979, Sony launched the first generation of Walkmans. These devices were portable and customers could listen to their favorite cassettes anywhere.
Many employees of the company believed that this device could not become popular among people without the ability to record sound. But contrary to their belief, this device introduced a new and successful lifestyle among people and achieved remarkable success.
The first CD player
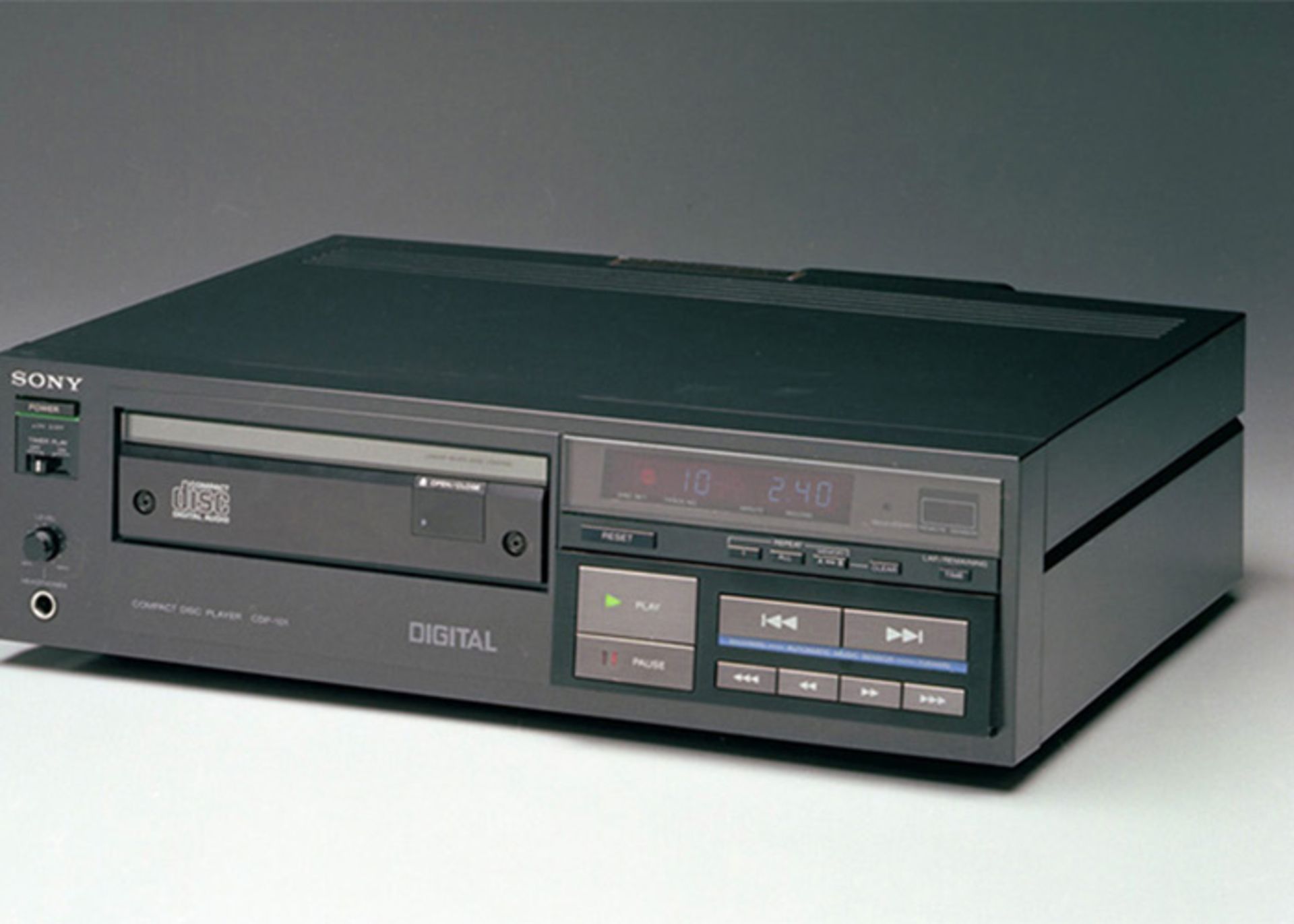

The world’s first CD player was launched in 1982 by Sony.
One of Sony’s senior managers, Norio Oga, was elected as the company’s CEO in 1989. Sony bought Columbia Pictures in the same year. This action was considered the biggest purchase of a Japanese company at that time.
PlayStation
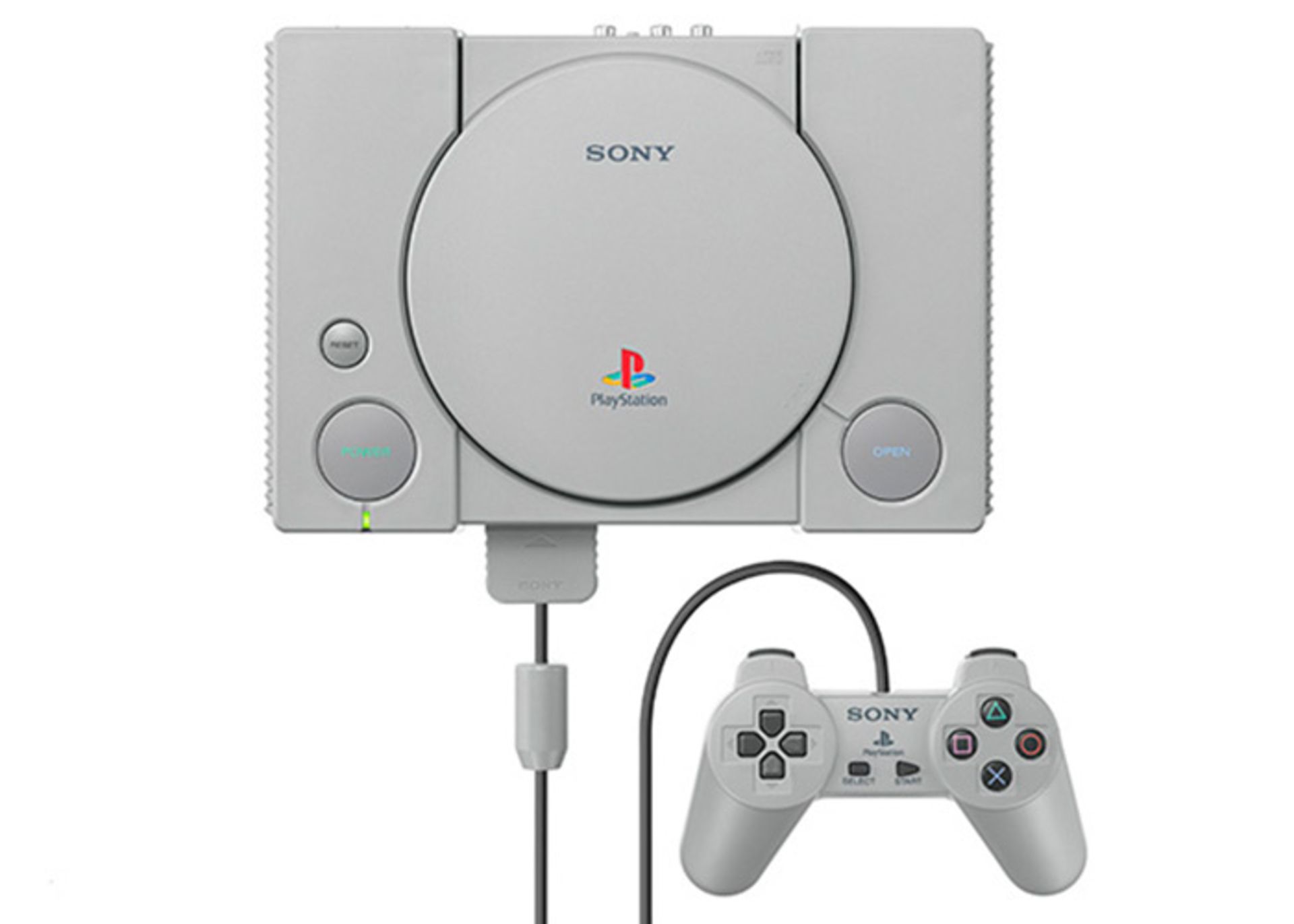

PlayStation is another important product of Sony. This product was sold in the Japanese market in 1994 and entered America and Europe in 1995.
PlayStation became so popular among people that its sales reached 10 million units by the end of 1996, and in 1998, about 50 million of this console had been sold. The production of new models of this product continues and today PlayStation 5 is considered the newest Sony console.
Digital camera
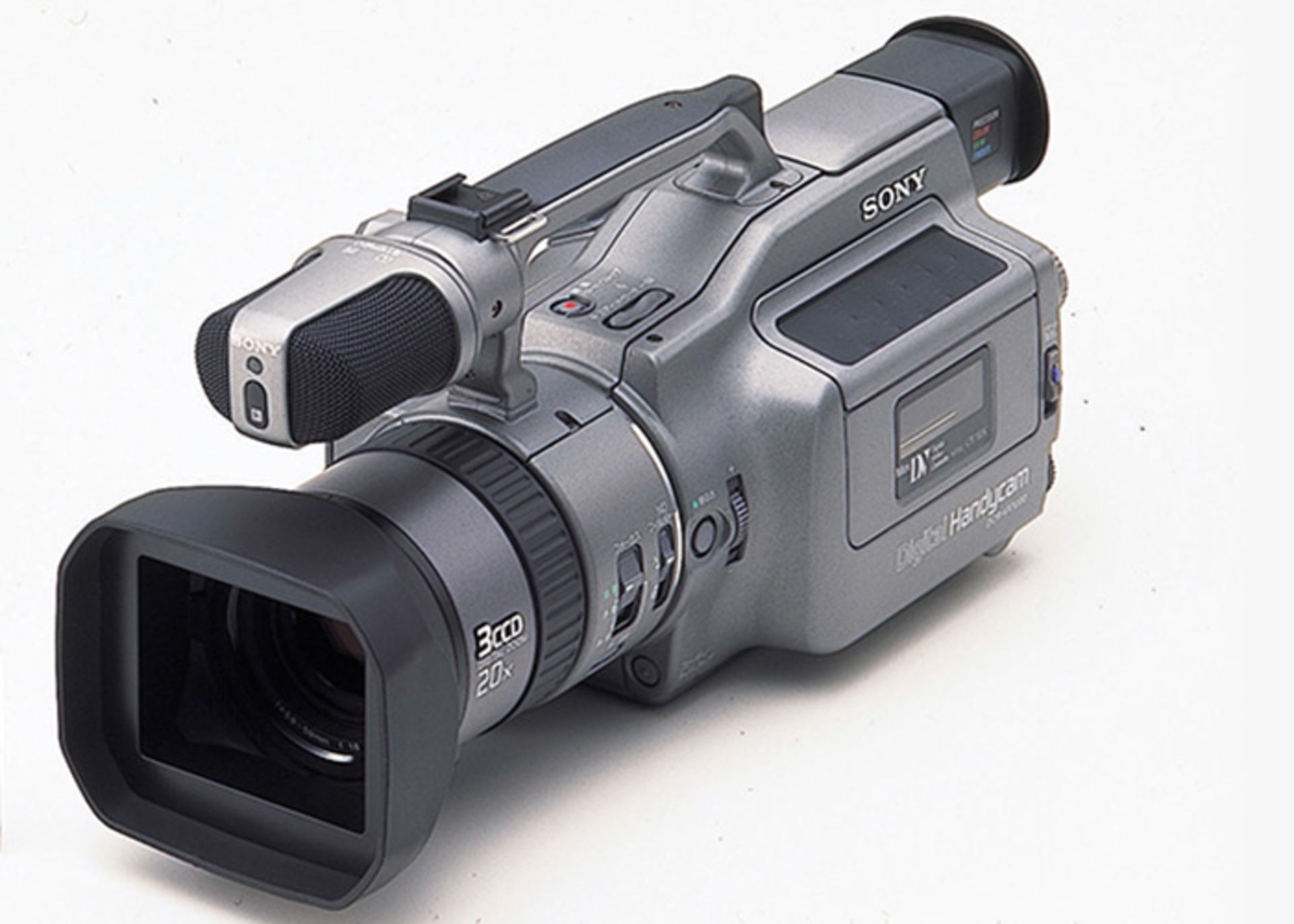

The first digital camera was launched by Sony in 1995. This device was very well built and recorded high-quality videos.
Sony Mobile
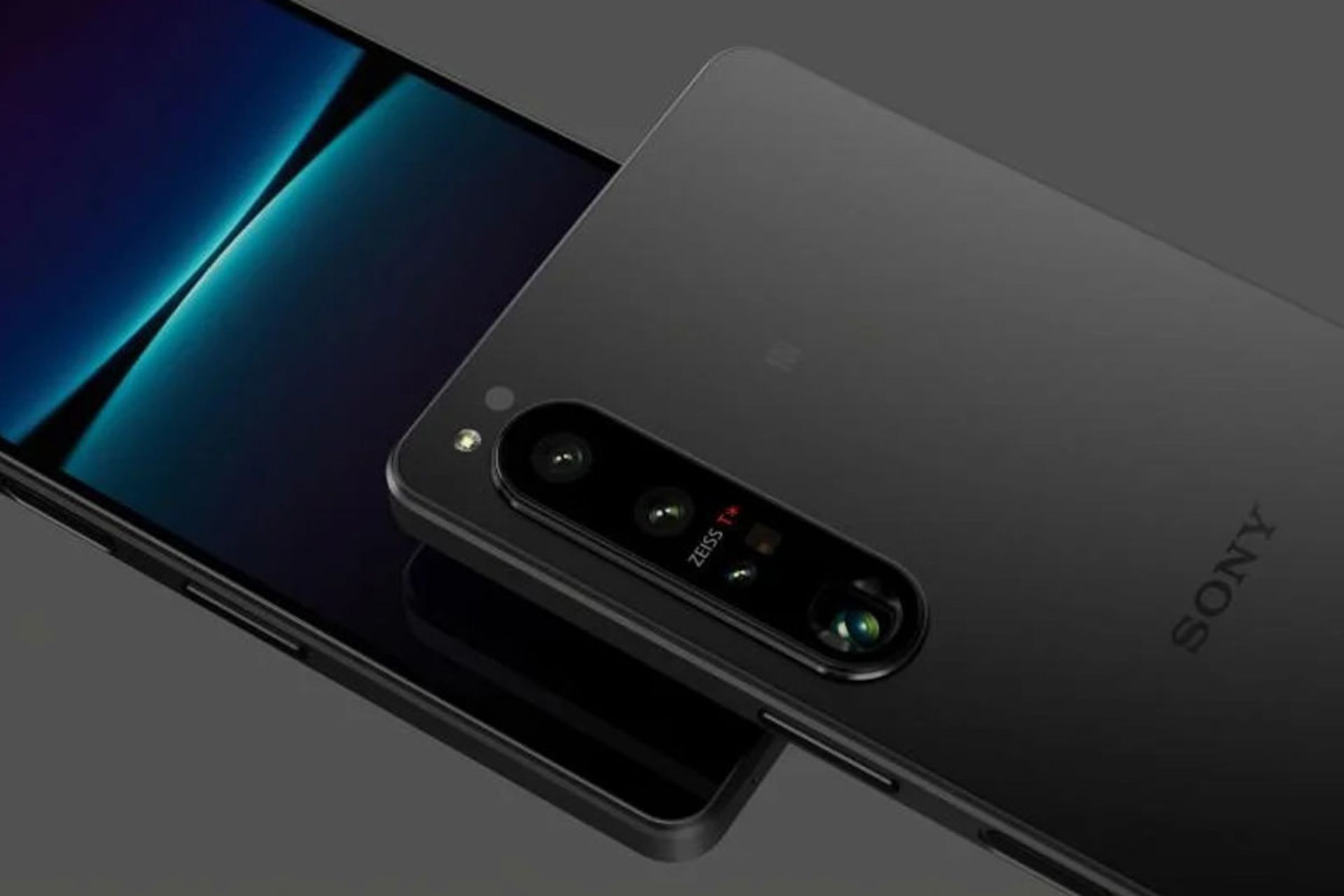

Sony Mobile Company started working in 2001 in cooperation with Ericsson. The company’s products were first marketed under the name of Sony Ericsson until Sony bought Ericsson’s shares in 2012. Since then, the phones of this company have entered the market under the name of Sony.
In 2012, Sony was able to win the title of the fourth mobile phone manufacturer. Xperia series mobile phones are the current flagships of this company. The Xperia brand doesn’t sell much at the moment, but Sony continues to produce products.
Vaio laptop

The first generation of Vaio laptops was launched in 1997. These laptops had a slim body and introduced a new concept of personal computers to the world.
Personal life of Masaru Ibuka
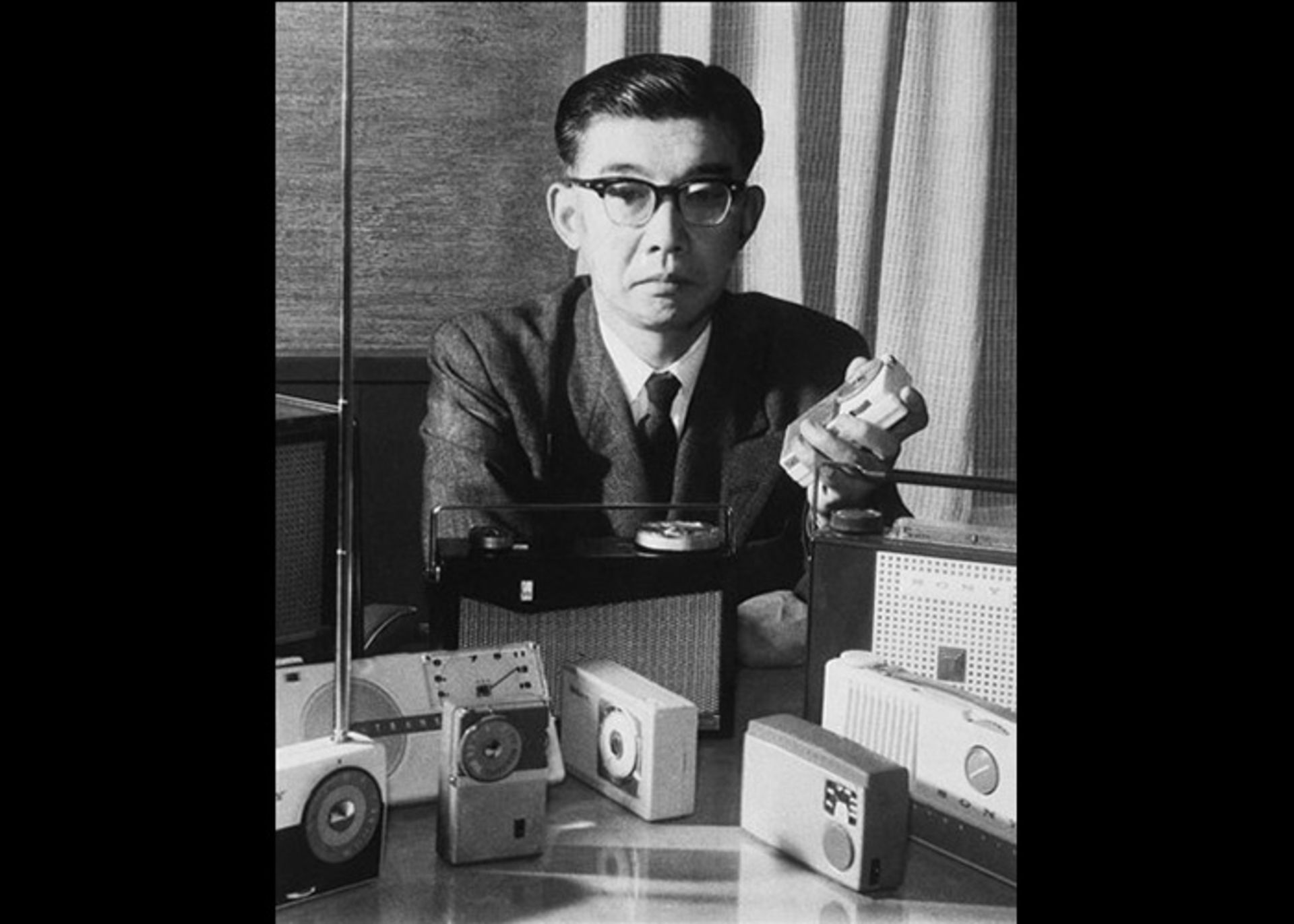

Masaru Ibuka was born on April 11, 1908 in Nikko, Japan. He graduated from the university in 1933 and worked in a film production company. Ibuka joined the Navy during World War II and was a member of the investigative committee; But after some time in 1945, he left the war to start his own radio repair workshop in Tokyo.
At that time, people followed the news of the world through the radio. As a result, starting a radio-related business was a good idea for a company. Ibuka and Akio founded Sony in 1946. Ibuka used transistors to make his company’s products. Therefore, Sony was introduced to the world as one of the first companies to use this technology for non-combat purposes.
Ibuka was a member of the Navy during World War II
In 1976, Ibuka was awarded an honorary doctorate from the University of Tokyo. He received two other honorary doctorate degrees in 1979 and 1994 from Tokyo and American universities.
Ibuka published a book titled “Kindergarten is Too Late” in 1971. In this book, he claimed that the most important time for human learning is from birth to three years old. As a result, he has suggested ways to teach skills to children at this time.
Ibuka was the leader of Sony until 1976 and then he retired; But even after that, he had a close relationship with company managers and guided them. He died in 1997 at the age of 89 due to heart failure.
Personal life of Akio Morita
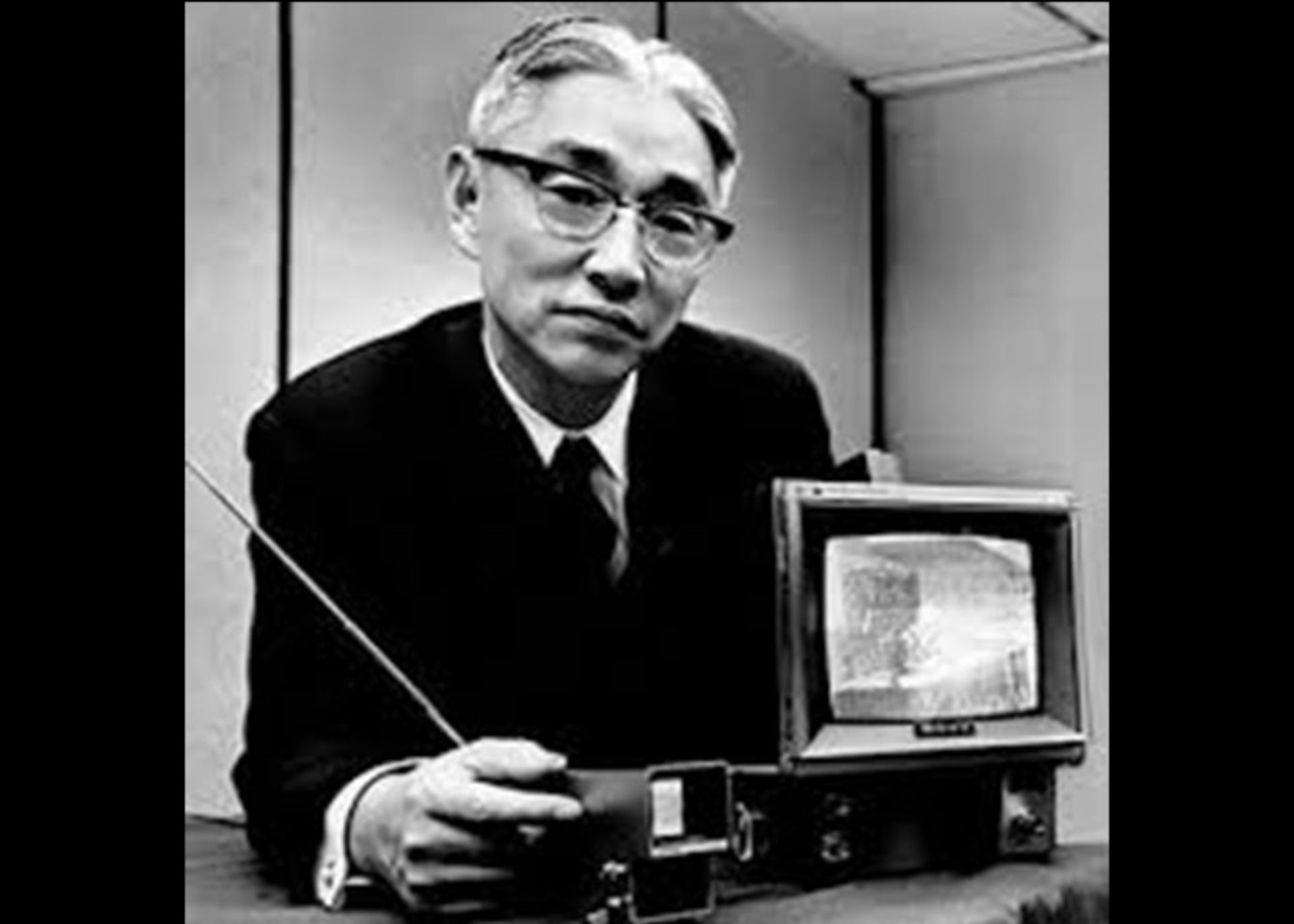

Akio Morita was born on January 26, 1921 in Japan. He was the eldest of his four siblings. As a result, his father trained him to manage the family business.
Akio was very interested in mathematics and physics and graduated from university with a degree in physics. During World War II, he became a member of the Japanese Army’s Research Committee, and while serving, met his future business partner, Masaru Ibuka.
Morita was a huge fan of all Sony products and worked hard to promote them. For example, the size of their first production radios was slightly larger than the standard shirt pocket size. Because they wanted to market their products as pocket radios, Morita made shirts for their employees with larger pockets to show customers that these radios were pocket radios.
Sony established its first branch in America in 1960. Sony was the first Japanese company to enter the US stock market. In 1994, Morita suffered a stroke while playing tennis and resigned from the chairmanship of Sony. He finally died of pneumonia in 1999 at the age of 78.
Sony failures

Since its establishment in 1964, Sony has produced successful and innovative products. Many of these products were entering the market for the first time, and as a result, they introduced a new concept of technology to the world; But no success story is without failures.
Sony Aibo
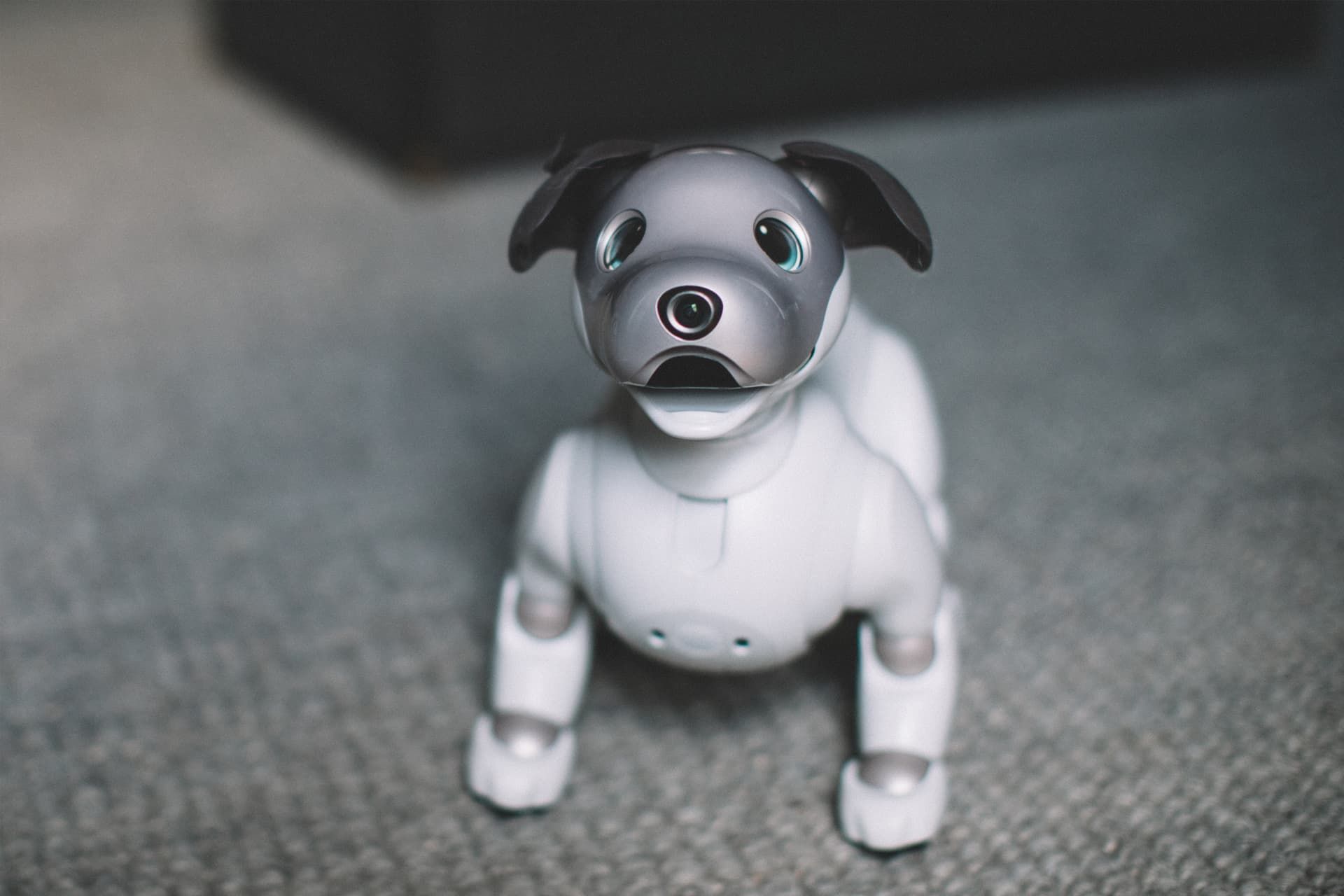

Sony robots were launched in 1999. These robots were in the form of cute dogs and had the power to learn. These robots could show emotions such as happiness, sadness, anger, surprise, fear and disinterest.
Sony robots were sold at a price of $2,500 and were very popular among their owners. But its high price prevented it from increasing its popularity and eventually, Sony stopped production.
Vaio music device
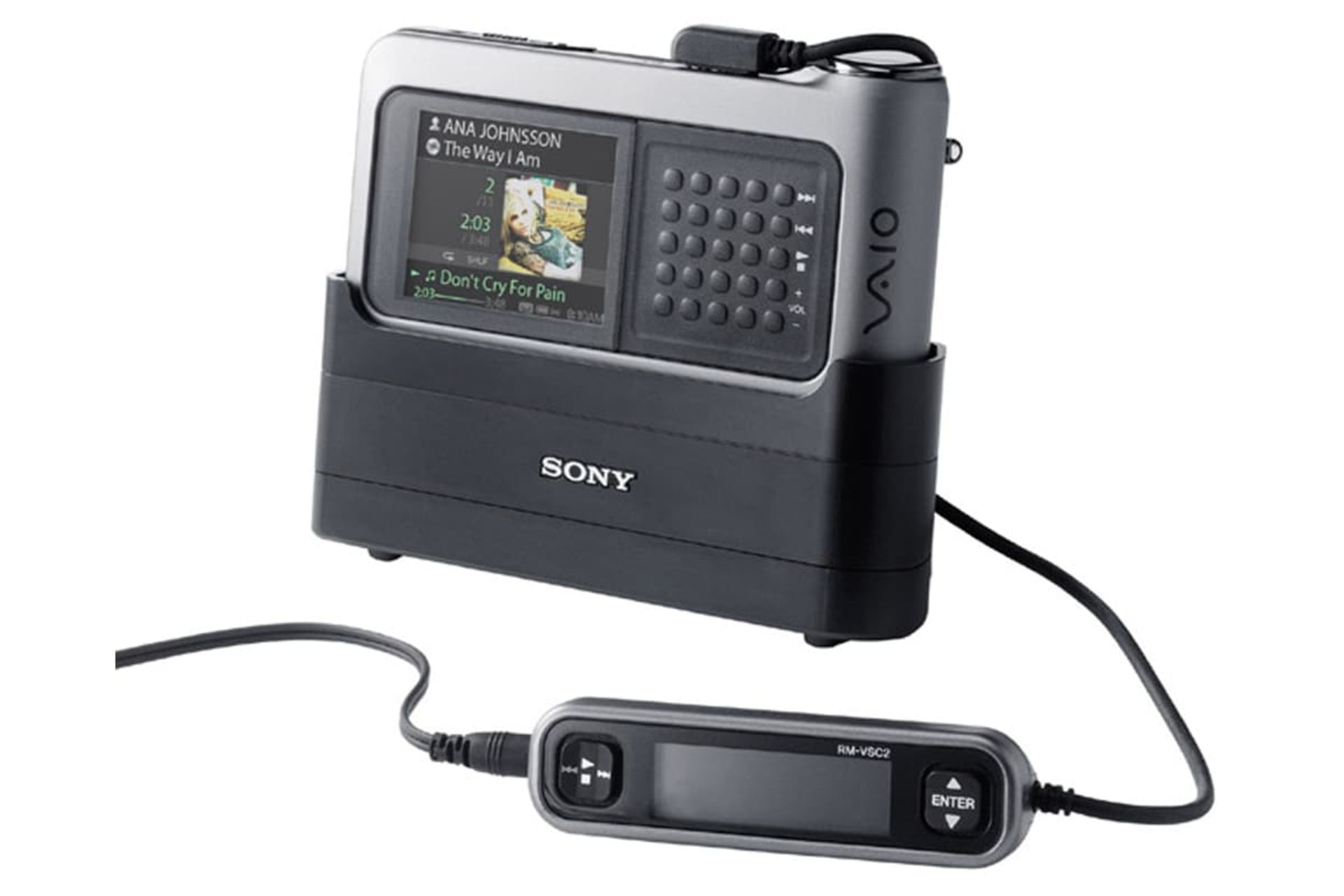

In 1979, Sony introduced a new concept of portability to the market by presenting its Walkman. The company had been Apple’s fierce competitor in digital music for two years, but its first product did not perform well.
The biggest mistake of the company was the dependence of files on the ATRACT format. Files with this format could only be used in Sony minidiscs. The ability to share files was the first word in digital music in 2000, and all files were released in MP3 format. As a result, this issue became a big challenge for Sony.
Sony e-Villa
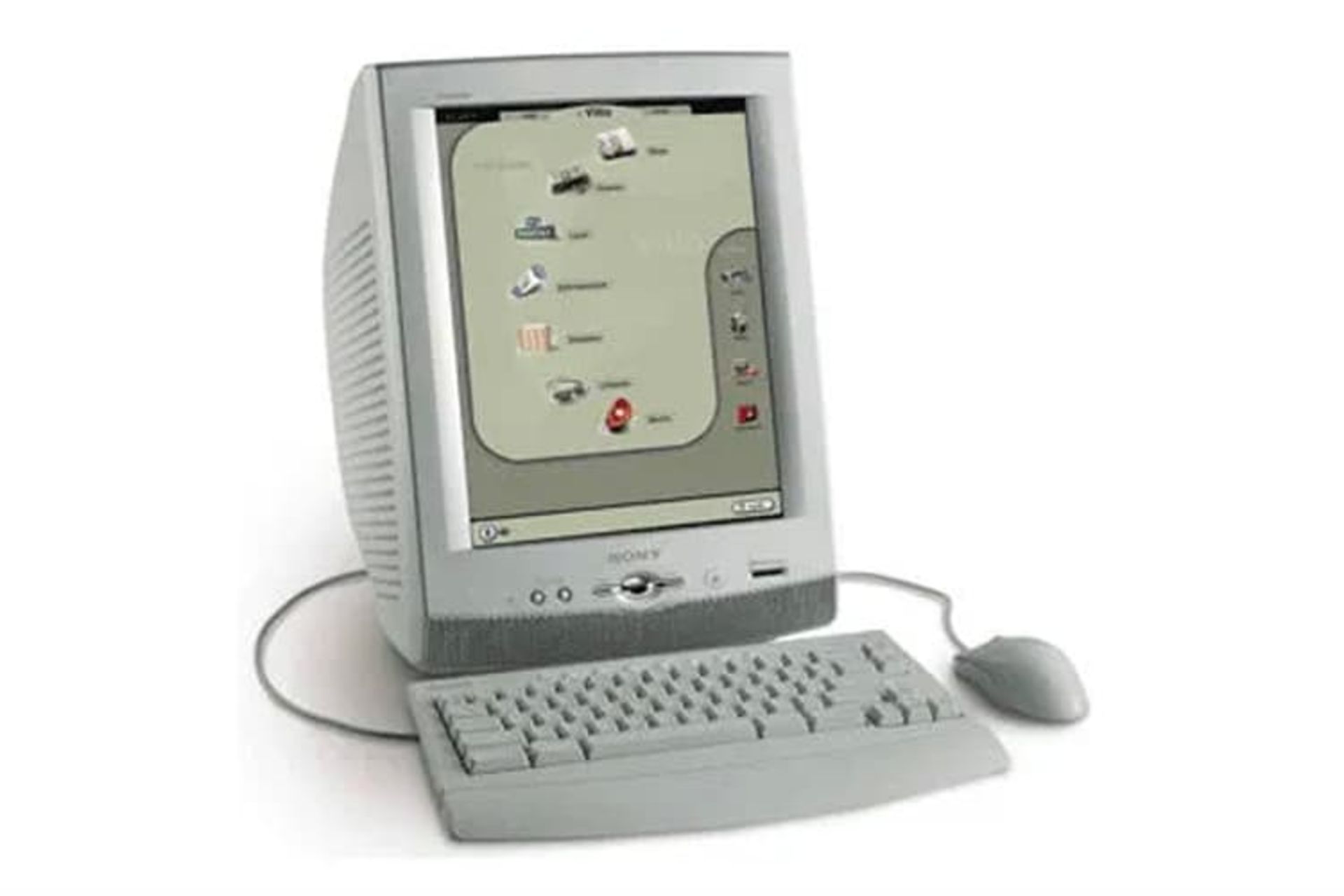

In 2001, many companies were offering Internet home appliances, including dedicated terminals for accessing the Internet and web browsers. Sony e-Villa was also a product that was launched with the same purpose.
The e-villa had a 15-inch monitor and a 56 kbps dial-up modem. e-Villa was designed to have access to email services and websites. At that time, there was a lot of competition between these devices and people preferred to use devices with Windows XP. As a result, Sony stopped the production of these products after three months.
Sony Airboard
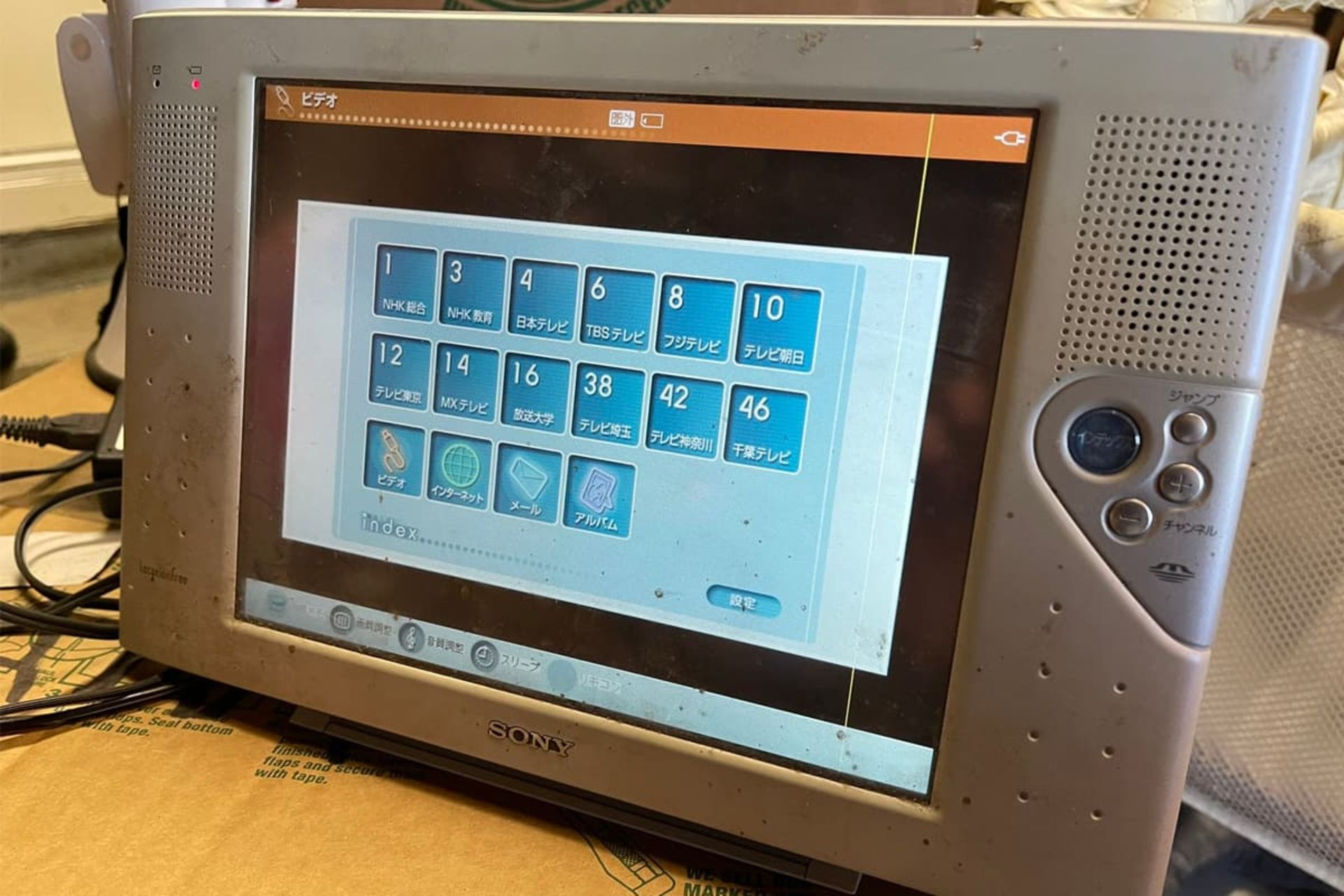

10 years before people became interested in watching videos on tablets, Sony launched a device called Airboard. The tablets of this family were 10 inches and had the possibility to connect to Wi-Fi and broadcast TV channels.
Using the picture-in-picture feature, users could search the Internet and watch TV. This device never caught on because people thought it was just a portable and expensive TV. Therefore, its production was stopped before entering the American market.
Sony PSX
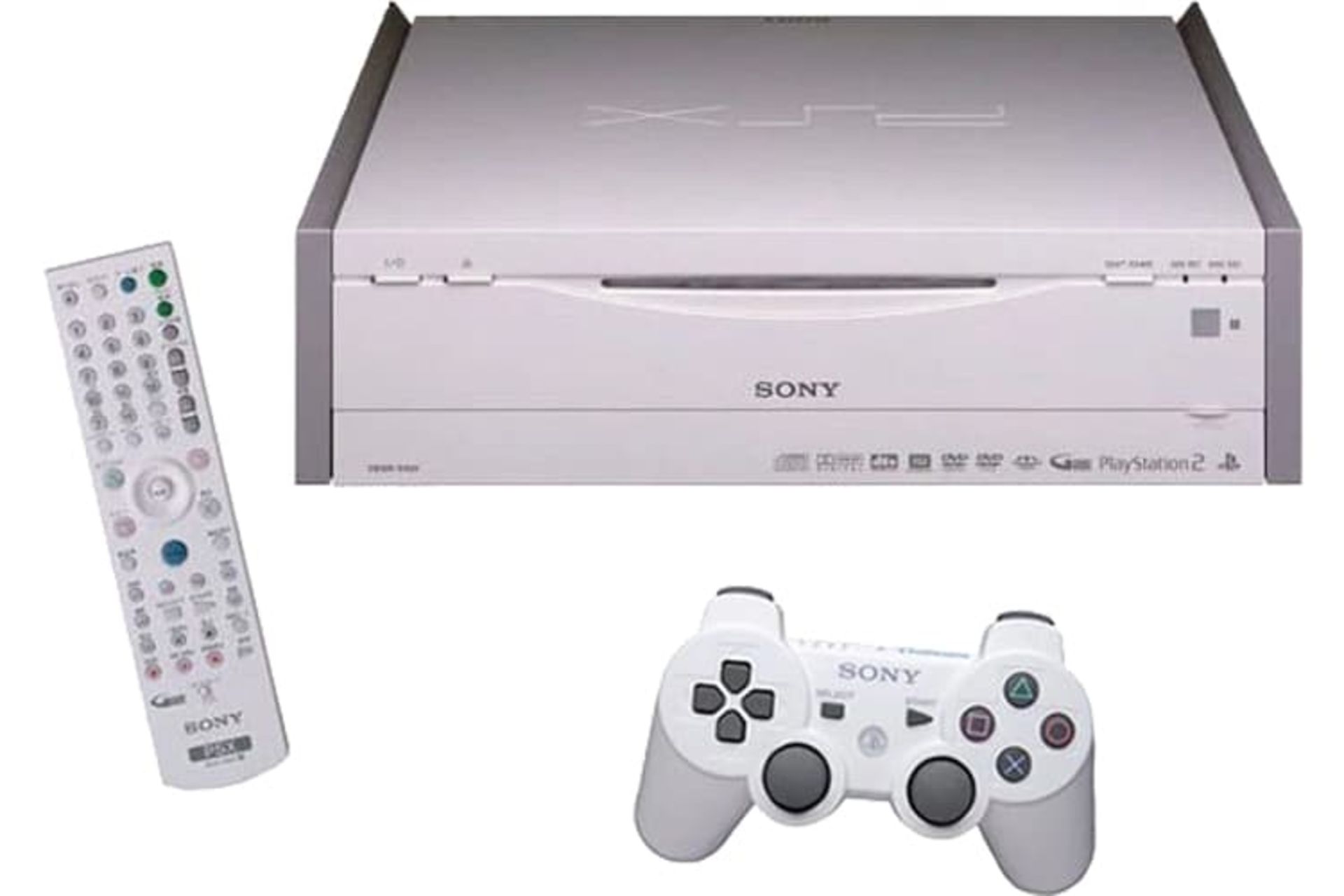

In 2003, Sony combined its two products, the PlayStation 2 and the video recorder, and marketed it as a single product. Using this product, customers could record the TV show on the storage memory or DVD at the same time as the game experience.
But the PSX, which was released only in Japan, was much larger and heavier than the PlayStation. Although this product did not have a high price, it could never attract many customers.
The current state of the Sony brand

Sony is one of the largest Japanese companies by revenue. The company reached the peak of profitability in the 1990s and 2000s due to the launch of its PlayStations, but faced financial problems in the late 2000s.
Read more: Samsung brand story; Full-view mirror of Korea’s commercial history
The global financial crisis, increased competition with PlayStation, and the earthquake in Japan in 2011 went hand in hand with Sony experiencing major failures for three years.
Due to the negative effects caused by natural disasters and exchange rates, the Times magazine called Sony a lack of flexibility and inability to measure the economy, but Sony was able to overcome all the crises in all these years by using innovation and became one of the top companies in the world. become in the television industry.
Sony’s current slogan is Be Moved, and the company aims to emotionally excite its customers with every product it offers.
Sony was able to pocket an operating profit of 1.21 trillion yen (about 8.9 billion dollars) in fiscal year 2022, which is a new record. Sony’s revenue in the final quarter of last year grew by 35 percent to about 3.06 trillion yen ($22.5 billion).

Adjective: The greatest; the best.
Pronoun: The greater part of a group, especially a group of people.
Noun: The greatest amount.
Noun: The greater part.
Noun: A record-setting amount.
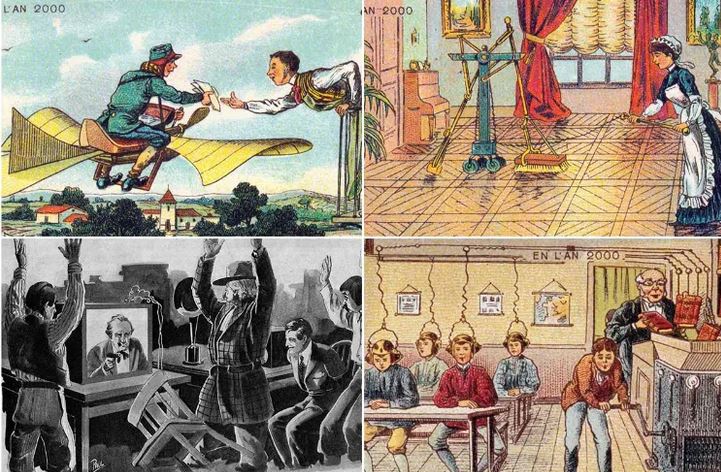
How did the people of the past imagine the future?
How can you explain to people in the 1900s that a robot can sweep floors and carpets without any intervention by drawing a map of your house without sounding crazy?
To people of the last century, our technology today seems like magic; But that doesn’t mean they didn’t fantasize about what the future would be like. Many inventors and artists have depicted their own predictions of future technology. Let’s look at these paintings and then comment on their scope.
 Bird postman – 1892
Bird postman – 1892
The potential of human flight was one of the concerns of futurists. It is true that aviation has revolutionized our world, but the type of flying equipment and “flying cars” that captured the imagination a century ago will remain for the future.
One of the important innovations that the minds of the ancients often did not imagine is the Internet and modern wireless communications. In today’s world, the flying postman pictured here would probably be out of a job thanks to plain old email.
 Electric floor washer (electric scrubber) – 1899 | The vacuum cleaner was invented just two years after this image was made.
Electric floor washer (electric scrubber) – 1899 | The vacuum cleaner was invented just two years after this image was made.
The idea of a robot vacuum cleaner, now a reality in millions of homes, was apparently beyond imagination in the late 19th century.
 Machine learning-1901
Machine learning-1901
According to this prediction, teaching was supposed to become a very easy job by the year 2000. The principal simply feeds the history books into the machine, while an assistant (or perhaps a student being punished?) turns the handle and somehow wires the contents of the books to the headsets the students are wearing, and from there into their minds. sends Do you understand the necessity of the presence of the school principal in this process?
 Phone with photo – 1918
Phone with photo – 1918
The arrival of video-calling technology was predicted more than a century ago. The Electrical Experimenter magazine wrote in 1918: “Many inventors have attempted to invent a device or machine by which one person can see another while talking on the telephone.” According to the author of the magazine, such a device, which should naturally be called a “telephot”, will be invented sooner or later, because “everyone would like to have such a device.”
 Video call – 1942
Video call – 1942
Another article in the magazine Practical Electrics in 1942 predicted a similar device with moving pictures so interesting it is admirable.
 wheel of destruction
wheel of destruction
During World War I, specialized technology magazines were full of ideas that were hoped to bring an end to the long conflict. One of these inventions was the gyro-electric destroyer. “This 45-foot monster is steered by a large gyroscope wheel,” Electrical Experimenter magazine reported. “The destroyer travels at a speed of 40 to 60 miles per hour and because of its large diameter it easily rolls over trenches and other obstacles.”

The vision envisions a robot dog that readers can build for themselves; A wheeled device that operates with batteries and follows its owner’s metal cane through a magnet. It may have a cute face but don’t expect this dog to roll over, play, or react if something bad happens to you.
The idea of artificial pets doesn’t seem so strange nowadays. This is a concept that exists mostly in the field of cyberspace, exemplified by digital home assistants and artificial intelligence-based video game characters.
 Climate control – 1954
Climate control – 1954
The dramatic image above shows how future humans will be able to control the weather. This article describes an airplane that is dispatched to disperse a cloud that threatens to form a tornado. “In the age of the hydrogen bomb and supersonic flight, it’s possible that science will find ways not only to destroy tornadoes and hurricanes but also to influence weather conditions in ways that will boggle the imagination,” the magazine reports.
Read more: The future of generative artificial intelligence from its own language
 Food planning by computer – 1967
Food planning by computer – 1967
In 1967, Philco-Ford, a maker of electrical goods, produced a short film called 1999AD, showing how its future products might transform ordinary homes. The family in the film owns a space-age car, a large wall-filling television, and a large home computer that helps the family (specifically the mother) plan their meals. In the film, we see the father of the family using the computer to check the invoice for the clothes he bought online.


Do animals have an understanding of the concept of death?


What is Kali Linux? Everything you need to know about this popular but mysterious distribution


Sony Brand Story; From the production of rice cookers to becoming one of the most famous companies in the world


How did the people of the past imagine the future?


Mammoth and dodo return to nature


How to use iMessage on Android?

Can humans endure the psychological torment of living on Mars?


Xiaomi Glorimi M2 Max watch review; Alternative economic option for iPhone owners


Artificial intelligence problems; Frauds based on artificial intelligence and methods to deal with them


Why do we humans sleep?
Popular
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoWho has checked our Whatsapp profile viewed my Whatsapp August 2023
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoSecond WhatsApp , how to install and download dual WhatsApp August 2023
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoHow to use ChatGPT on Android and iOS
-



 AI2 years ago
AI2 years agoUber replaces human drivers with robots
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoThe best Android tablets 2023, buying guide
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoThe best photography cameras 2023, buying guide and price
-


 Humans2 years ago
Humans2 years agoCell Rover analyzes the inside of cells without destroying them
-


 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoHow to prevent automatic download of applications on Samsung phones
