Technology
Everything you need to know about the Windows Blue Screen of Death
Published
3 days agoon

Everything you need to know about the Windows Blue Screen of Death
Blue Screen of Death or BSOD (abbreviation of Blue Screen of Death), which is also called stop screen or stop error; It is one of the most famous and unpleasant effects of Windows. A Windows blue screen appears when the operating system encounters an unsolvable error and cannot continue to operate.
In the latest and perhaps most pervasive case, a flawed update to CrowdStrike’s cyber security software caused one of the most catastrophic events in tech history to occur, leaving thousands of businesses around the world using Windows systems with the Windows Blue Screen of Death.
A Windows blue screen indicates a computer stroke to prevent serious damage to the operating system, stored data, or hardware components. In this situation, the system will automatically restart or shut down. However, sometimes this may need to be done manually.
When the computer restarts, it will start the troubleshooting process automatically. If Windows can’t fix the blue screen of death problem, the user has to do it himself.
-
The history of Windows blue screen
-
What is the reason for the blue screen of death?
-
View the Blue Screen of Death errors
-
Troubleshoot the Blue Screen of Death
-
Safe mode boot
-
Update drivers or install drivers without problems
-
Use System Restore
-
Malware scan
-
Checking hardware problems
-
Analysis of Minidump files
-
Reinstall Windows
-
Recommendations to prevent Windows blue screen
The history of Windows blue screen
The Windows death screen originated from the first beta versions of Windows 1 and 2, which were actually MS-DOS graphical shells. In Windows 1.01 and 2.1, a large number of characters were displayed consecutively on this screen.

Windows 1

Windows 3

Windows NT

Windows 95
From Windows 3.0 onwards, the Blue Screen of Death appeared more serious and displayed system errors in more detail. In different versions of Windows, there were gradual changes in the appearance of this page; For example, the death page error text changed from many sentences with small font in Windows NT to a shorter and larger text in Windows 8 and 10.

windows xp

Windows 7
Microsoft introduced Safe Mode in version 2000 to solve the Windows blue screen problem, allowing users to boot the system with minimal drivers and programs to troubleshoot the system.
Windows XP, released in 2001, brought about a significant change in the look and feel of Windows Blue Screen. While the famous blue background was retained, the error messages were presented in a more user-friendly form and provided basic information about why the Windows death screen was displayed. However, the blue screen of death kept happening and was usually caused by hardware incompatibility, driver issues, or software conflicts.
Windows Vista and 7 introduced stronger error-handling mechanisms to make the Windows Blue Screen of Death appear less frequently. At this time, Microsoft made it possible to store and report blue screen error information. This data was very helpful in fixing the Windows Blue Screen of Death problem. Hardware compatibility issues, especially graphics cards, were the most common reasons for this.
With the release of Windows 8, Microsoft made radical changes to the Blue Screen of Death. The page was redesigned with a modern, minimalist look, including a sad emoticon and simpler, more readable error messages with a pale blue background. This approach was designed to reduce user anxiety and provide a more error-tolerant experience.
 Blue screen of death in Windows 8
Blue screen of death in Windows 8
Behind the scenes, significant improvements were made to solve the Windows blue screen and system recovery. Windows generally became more fault-tolerant and often reverted automatically without requiring a reboot.
The Blue Screen of Death is much less likely to occur in Windows 10 than in previous versions and is usually caused by hardware failures, driver issues, or more complex software conflicts. In Windows 10 and 11, a QR code was added to the blue screen of death so that users could scan it to get more information about the error.
 Blue screen of death in Windows 10
Blue screen of death in Windows 10
What is the reason for the blue screen of death?
Several hardware or software causes can cause the user to face the blue screen of death. Installing software or drivers incompatible with the system, faulty update patches, incorrect settings in BIOS or UEFI, and the presence of malware and viruses are among the most common software causes of this problem.
In addition to software problems, some hardware issues such as RAM corruption, CPU and graphics card overheating, bad sectors in the hard disk, and insufficient power can lead to the blue screen of death.
Normal software is rarely capable of causing a blue screen, but software with a higher level of access to the Windows kernel, including antivirus and security software, if they get an error in their driver, can trap Windows in a vicious loop that may eventually lead to a blue screen. to be
According to Microsoft: “There is no simple explanation for why stop errors occur. Various factors may be involved in this matter. Our analysis of the main causes of Windows crashes shows that 70% are caused by faulty drivers of miscellaneous software, 10% are caused by hardware problems, 5% are caused by Microsoft’s framework code, and 15% are due to unexamined memory corruption.
View the Blue Screen of Death errors
You can see the cause of the Windows death page error in Windows Event Viewer; Where, in addition to the messages related to the blue screen of death, the crash information of other software and system logs are also available.
To open the Windows Event Viewer window, type Event Viewer in the search bar. Additionally, you can select it from the menu that appears by holding down Win+x.
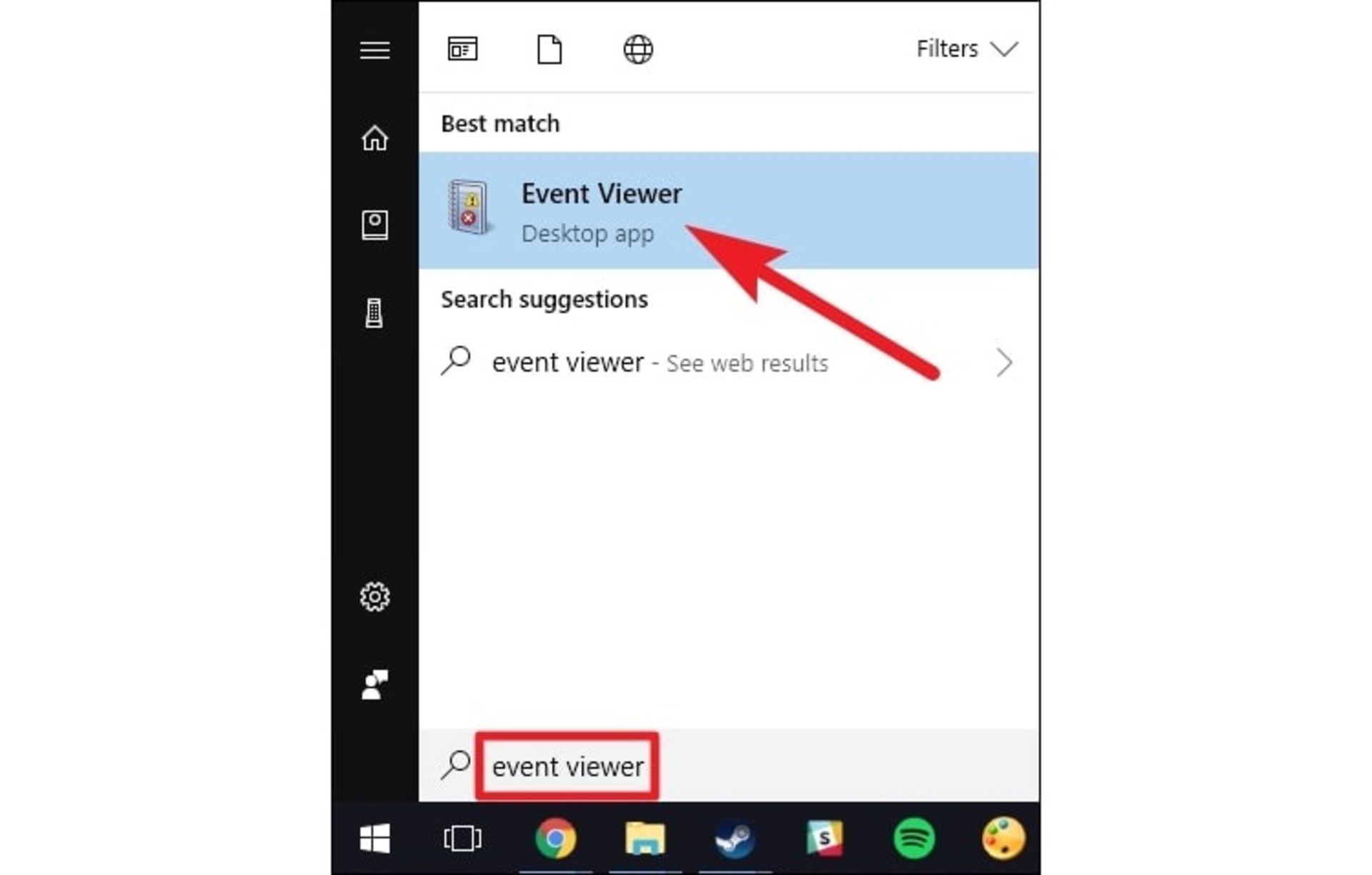
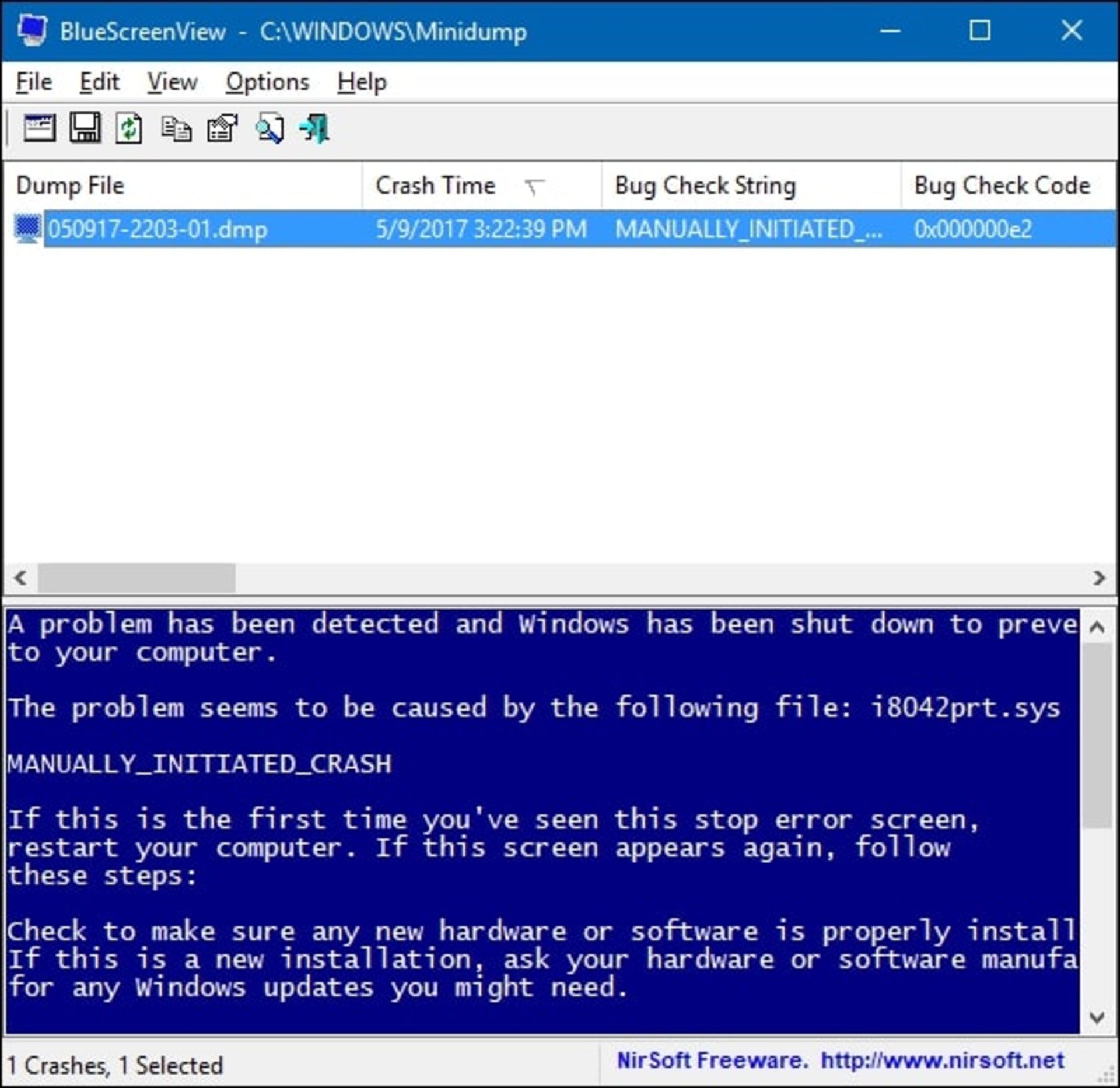
In the Event Viewer window, a lot of information and details about the problems encountered by the system can be seen. By referring to the System section of the Windows Logs section, you will find out which driver or hardware problem has led to the Windows blue screen. To find the desired report, you should match the dump files with the time of the Windows crash or look for a report with a critical label.

You can search for specific report IDs online and learn more about the problem you’re having. To see the ID, just click on the error and look for the Event ID in the property section.
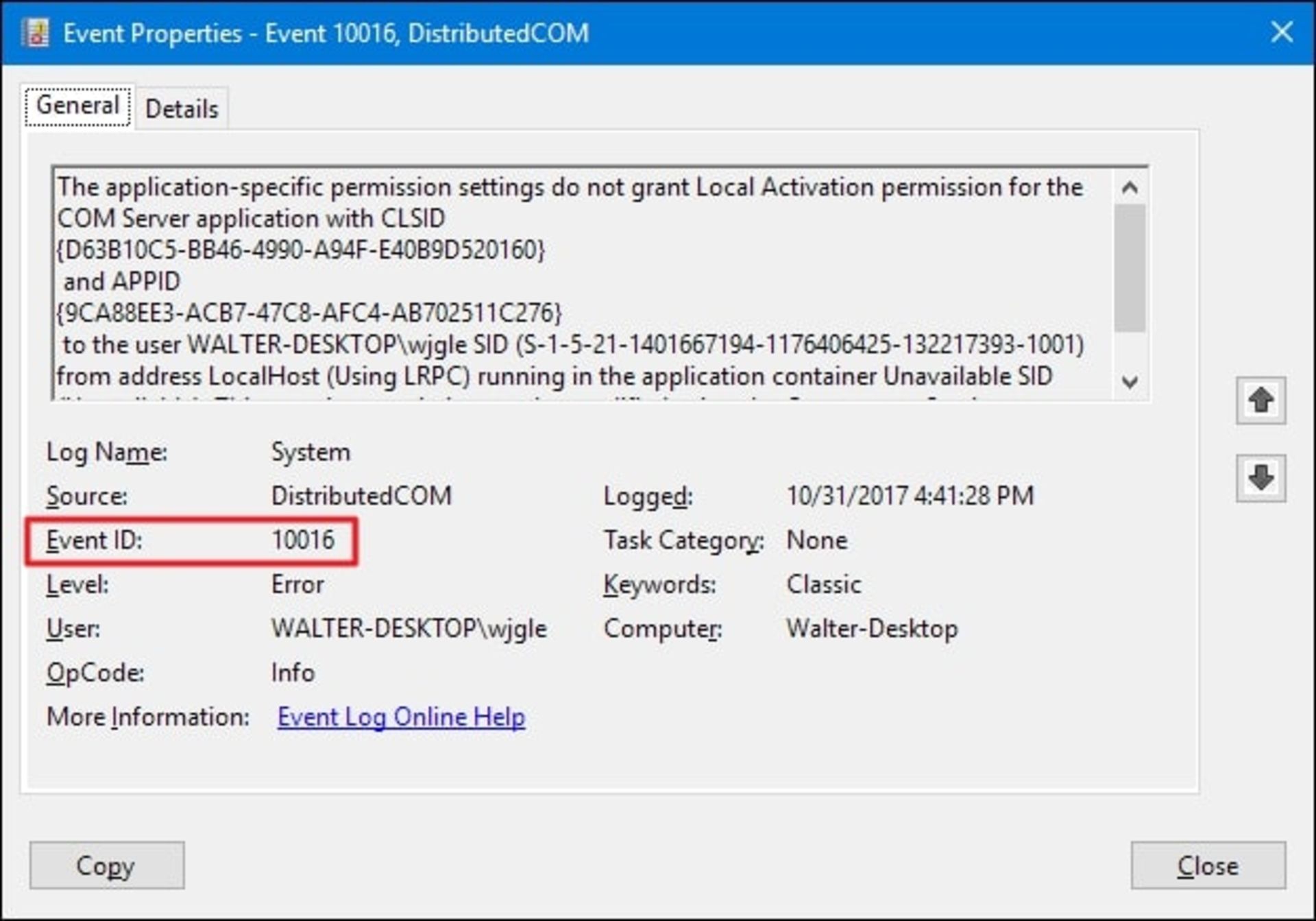
NirSoft’s free BlueScreenView software provides one of the Windows applications for viewing Windows blue screen information. This program displays the dump files generated when BSOD occurs in a user-friendly and tabular format to make troubleshooting easier.
Troubleshoot the Blue Screen of Death
Windows usually runs the troubleshooting and troubleshooting steps automatically by restarting the system after a blue screen of death. If the problem persists after a reboot, the user should consider what they were doing before the BSOD occurred; For example, installing or updating new software, updating a driver, or making a hardware change. Reverting the changes can fix the problem.
One of the best options for finding a solution would be to search the web. According to the methods mentioned above, find the error code and search for it on the Internet. If you see the error code on the blue screen, write it down before resetting Windows.
Safe mode boot
The first solution suggested by Microsoft to investigate the cause of the blue screen of death is to disconnect suspicious peripheral hardware such as flash memory, printer, camera, and other items from the computer or laptop and boot Windows in Safe Mode.
In safe mode, Windows loads only essential drivers. If a faulty driver or software is the cause of the blue screen of death, in safe mode you will no longer encounter this screen and you can proceed to correct Windows problems.
Update drivers or install drivers without problems
A corrupt or uninstalled driver can cause Windows to crash. Get and install the latest drivers for your hardware from reputable sources. This will likely fix the blue screen of death issue and keep the system running at its best.
Sometimes a specific version of a driver, especially graphics drivers, may cause errors in graphics processing, and as a result, the blue screen of the death of Windows is displayed. In these cases, updating or returning to the old version can be a solution. Note that old drivers can mess up Windows and cause Windows to take longer to load.
Use System Restore
This method restores the system to the state before the Windows blue screen. If the problem is solved by using System Restore, it is possible that a software error caused the Windows blue screen error to appear. Otherwise, the problem could be hardware-related.
Malware scan
Malware can exert its destructive effects at a low level and cause system instability by changing or destroying the Windows kernel. Scan your system thoroughly to make sure malware isn’t the cause of the blue screen of death.
Checking hardware problems
Faulty hardware can also cause the Windows Blue Screen of Death. The most important parts to check are the device’s RAM and storage. For example, not recognizing the hard drive when installing Windows can indicate the existence of a problem in the hard disk. Check the RAM and CPU temperature to make sure you don’t have a cooling problem.
When some peripherals are connected to the case or laptop through different ports, such as USB, a stop error may occur due to interference with the operation of other hardware or an error or problem with the peripheral. In this case, the problem is solved by separating that part in most cases. If Windows is still usable, you can use software like CPU-Z to check your hardware.
Analysis of Minidump files
An advanced method to analyze and investigate the cause of the Windows blue screen is to analyze Minidump files. These files are created by Windows when a critical error such as a blue screen of death occurs. In fact, memory dump files can be considered as black boxes of stop errors that record the details of the error.
Minidump files are usually in the C:\Windows\Minidump folder with the extension dmp. are saved. The title of these files indicates the time of the Windows crash; For example, Mini07212024-01.dmp. Dump file analysis requires special programming knowledge and should be checked by an expert.
Reinstall Windows
If none of the above methods work, you may need to reinstall the operating system. If the blue screen problem persists even after reinstalling Windows, then you are facing a hardware problem and you should check your hardware thoroughly.
Recommendations to prevent Windows blue screen
- Make sure you have the latest Windows updates installed.
- Keep BIOS and system firmware up to date.
- Check the health of hardware parts once in a while.
- Equip your system with a strong antivirus.
- Make sure there is enough storage space. It is better to leave between 10 and 15% of the total memory empty.
- Download and install driver updates from official sources.
Windows normally never displays a blue screen error, But no software or hardware is perfect and without problems. You may experience this problem sometimes without any clear reason. If your computer is experiencing the Windows Blue Screen of Death problem every now and then, you should definitely follow up on the problem.


You may like
-




iOS 18 review: A smart update even without Apple’s intelligence
-




The Strawberry Project; The OpenAI artificial intelligence model
-




The biography of Andy Rubin, the creator of Android
-




How to prevent your location from being revealed through photos?
-




The chip battle of flagship phones in 2024; Which is the winner?
-




What is Kali Linux? Everything you need to know about this popular but mysterious distribution
Technology
iOS 18 review: A smart update even without Apple’s intelligence
Published
2 days agoon
27/09/2024

iOS 18 review: A smart update even without Apple’s intelligence
This year was a strange year for the iPhone operating system. Three months after Apple introduced the new version of iOS at the WWDC event and aroused the curiosity and admiration of its fans, from September 16 (26 September 1403) this update was released in full: a mature and measured update that is not only for iPhone users but also For most lovers of the technology world, it seems like a welcome evolution.
Usually, new versions of mobile operating systems are fully released on a certain date, but at least this time in iOS 18 we don’t see this traditional routine; This means that some of the most interesting features of Apple’s most important development in the last year, namely Apple Intelligence, will not come to iPhones until 2025.
But it can be said that the new operating system of iPhone phones will surprise you with all kinds of changes and user-friendly features. It’s safe to say that iOS 18 is an ambitious update, even if we leave Apple’s intelligence out of the picture.
The customization options on the iPhone are like nothing we’ve seen before
Personalization options have reached the most diverse possible level and with a little time, users can set their phone in a way that has no resemblance to its previous appearance; Something we have never seen before in Apple products.
From home screen personalization capabilities to the completely new face of the Control Center, or the functional features of iMessage and the new and improved capabilities of various applications, after years, Apple is visibly showing a more flexible approach in its new update. In fact, iOS 18 includes more than 200 changes, and in this article, we will be with you by reviewing the most prominent options.
-
iPhones compatible with iOS 18
-
Extensive changes to the home screen
-
Important change to the lock screen
-
control center
-
Photos application changes
-
iMessage improvements
-
Notes changes
-
Security and privacy
-
Other important updates
-
Apple Intelligence
iPhones compatible with iOS 18
iPhones receiving the iOS 18 update include the iPhone XR, iPhone XS, iPhone XS Max, iPhone SE 2020, iPhone SE 2022, iPhone 11 series, iPhone 12 series, iPhone 13 series, iPhone 14 series, and iPhone 15 series.
Note that only the iPhone 15 Pro, iPhone 15 Pro Max, and newer phones are compatible with Apple Intelligence because according to Apple, the new AI features require an A17 Pro processor and higher to run.
Extensive changes to the home screen
In its recent updates, Apple gives users more choice in controlling the appearance of their software, and this trend is more visible than anything else in iOS 18. One of the most important and tangible changes we see in iOS 18 is the options that Apple gives users to customize the home screen.



iOS 18 wallpapers; Dynamic mode changes the color of the wallpaper based on the time of day and night
For years, iPhone owners have been waiting for an update that would allow them to place application icons anywhere on the screen like Android users. This wait is now over.
You can arrange the icons in a way that gives you a better feel, or group applications that have complementary functions and features in a specific part of the screen. In fact, now the appearance and arrangement of applications and widgets on the home screen is completely up to you and your personal preferences.



Edit pages
But your options are not limited to these options. On the home screen, if you press the empty space between the icons for a while, the “Edit” option will appear at the top left of the screen. By tapping on this option, which replaced “+” in iOS 17, you can access three options: “Add Widget”, “Customize” and “Edit Pages”. The add widget option does the same thing as the “+” button used to do.


After choosing the dark mode, you don’t want to go back to the previous mode!
The option to edit pages shows a view of all the main pages of the phone, and you can delete the pages you don’t want or change their order. By selecting the Personalization option, a panel will appear at the bottom of the screen that allows you to choose dark or light mode for the icons and change the size of the icons. By selecting the “Tinted” option, you can change the color of all the icons to your desired color; It’s just a pity that there is no choice of different colors for different icons. This routine gives the icons coherence and integrity, but may not be to everyone’s taste.


Let’s change the size of the icons. Of course, you can’t make each of the icons separately, to an exact and desired size! In iOS 18, the home screen icons are set in two modes: with the new settings, the icons are shown larger and their names are removed from under the icons. The default size is also exactly what we had in iOS 17.
Likewise, you can resize widgets directly from the home screen, without opening the customization panel.
Important change to the lock screen
The most important change that iOS 18 has brought to the lock screen is the ability to change the toggles on the left and right sides of this screen. Previously, the flashlight icon was on the left and the camera on the right, and we couldn’t replace them with other apps.


Multiple options to choose from! But I still use the same camera and flashlight toggle!
To change the toggles, you need to enter the customization section by pressing your finger on the lock screen. Now, next to each of these two buttons, you will see the “-” sign. By tapping on this sign, the previous option will be removed and instead, you will see a “+” sign, which you will see a long list of replaceable options.
Control Center
After the home screen, which is the heart of Apple’s operating system update, it’s time for the Control Center, which gives the iPhone a new look with a new format, more diverse options, and of course, customization features.
Unlike in the past, you no longer have to go to Settings to change Control Center options; Instead, you can either tap on the “+” at the top of the screen or touch and hold any empty space in the Control Center for a while to enter the customization mode.

Free arrangement of control center icons

Adding additional apps to Control Center
When you swipe down from the top right corner of the screen to access Control Center, you will see a few new elements:
- The “+” sign in the upper left corner: This option launches the customization menu for rearranging and resizing the controls.
- Power icon in the upper right corner: By holding this icon, the power off screen will appear and turn off iOS.
- Three icons on the right side of the screen: heart icon, music icon, and wireless connection icon
The three icons on the right basically represent the three screens that the Control Center starts with. If you want, you can add more pages yourself.
The first page (represented by a heart) contains all the control tools that were in the old version of Control Center. You can easily change these options and choose their size and arrangement according to your taste.

Music widget in control center

Connection options in the Control Center
By default, the second screen displays a large music widget with AirPlay options. The third screen is also a place to activate and deactivate communication options such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, mobile network, airdrop, airplane mode, and so on.
In the new Control Center, you can sort and resize options. In addition, for the first time, Apple has allowed other developers to add their app toggles to the list of Control Center options. Also, in the lower right corner of each option, you will see a marker that you can touch and drag to increase its size.
Photos application changes
When we open the Photos app for the first time, we don’t see Apple’s claim of “the biggest changes in the history of Photos in iOS 18”; Of course, this program has undergone positive changes since the beta version of iOS 18.
The first thing that catches the eye after opening the program is the transformation of the new Photos interface, the former Library tabs, albums, and For You collections into a single page.
Swiping down brings up gallery images, and swiping up lets you view collections, auto-collected memories, and other grouped photos (by categories like people and pets, travel, and the like).
The image gallery is now more customizable: you can set the order in which the different sections appear as you wish. For example, you can move Featured Photos to the top of the page.
Smart tools are provided to users to sort or filter images
In the early beta version of iOS 18, the way it worked was a little different and users had to swipe left and right on the photo library to view different sets of images. Apple apparently removed this feature due to user feedback.
Also, the size of the Recent Days section, which is located under the library by default, has been reduced so that users can see more images from the library in the main view.



In iOS 18, you will have smart tools to find photos and sort images by year and month. By selecting the blue magnifying glass icon in the upper right part of the screen, you can type a phrase that is close to your search; For example, if you are looking for a specific photo that contains food, just type the word “food” and all the images that contain food will be displayed to you side by side. There are also other options for sorting photos and filtering results you don’t need to see (like screenshots).
iMessage improvements
Considering the popularity of iMessage among iPhone users, it was not far from the expectation that Apple would apply useful and significant features to this application. Probably the most useful change we experience in iMessage is the possibility of scheduling messages. To do this, tap on the + button (where you also have access to other features) and then select Send Later. In the next step, you can specify the date and time of sending and then send the message to be sent at the specified time.

Another interesting change of iMessage is adding text effects to messages. This feature can cause your messages to vibrate, ripple, or even explode. You can access this feature by tapping on the message and selecting Text Effects from the menu. In this section, you can also change the text format (bold, italic, underlined, etc.).



New iMessage effects in iOS 18
iMessage finally supports the RCS standard in iOS 18, which, of course, is not available in Iran, because its functionality depends on mobile operators; But overall, Apple’s effort to improve the quality of messages between iPhone and Android phones is commendable.
Improving the display of emojis, using stickers and Mimojis in the form of emojis, Genmoji functionality, improving the appearance of links cards, and solving mathematical equations are among other new and attractive parts of iMessage.
Read more: The best iOS features that Android lacks
Notes changes
In iOS 18, Note has become a mature and evolved app. Apple has integrated the calculator with the Math Notes feature, and now you can write mathematical equations in Notes and find their answers. It may seem more efficient to draw a diagram on a device like an iPad, but in practice, you will feel the benefits of this tool better in everyday life. For example, keep a list of your expenses on the Notes app and add new numbers each time. The app automatically calculates and adjusts your expenses.



In another new and very practical feature, we experience the integration of notes with voice recording. Now when you want to add a voice to a note, you can use the integrated recording system with notes without leaving the app and opening Voice Memos.
The Notes app also transcribes audio recordings and phone calls for you.
If you have trouble arranging and organizing your notes, headings and collapsible headers will be a useful feature for you. Thus, in longer files, you hide different parts of the note under specific headings and open them later to review the details. The ability to change the color of the text also makes reading the content easier.
Security and privacy
The most important new security and privacy features of iPhone phones were also noticeable in the beta version: the Passwords app and the ability to secure any app, to the extent that they can even be hidden from public view.
The Passwords app is based on Apple’s Keychain and is built to manage passwords and is a one-stop storage repository for all the passwords you need for different apps and websites.
Among other measures, we can mention warnings about passwords at risk and synchronization of passwords on all Apple devices of each user.



The next feature makes it possible to unlock apps with Face ID, which is actually a new layer of protection. You can also hide apps from public view for added security. These programs are stored in a folder that only the user has access to and will be used for many types of information such as medical records, bank data, and personal matters.
Other important updates
As we said at the beginning of the article, the number of changes that have come with iOS 18 are so many that it is impossible to mention them all in one or two articles; For this reason, we briefly review some of the important improvements of this version:
Automatic recording and transcription of telephone conversations: this feature, which uses artificial intelligence, when recording a conversation, informs the person or persons present in the conversation that their voice is being recorded. The option to record the conversation with an icon similar to the sound waveform, along with the duration of the recording, is located in the Phone application. The transcript of the conversation is also available in the Notes application, and users can make a summary of it. It is also possible to record and transcribe the recorded sounds in the Notes application.
Calendar and Reminders integration: The link between Calander and Reminders gives you the feeling of finding a missing puzzle piece. The new updates allow you to record an event with a time and date and a reminder in the Calendar app and still have it available in the Reminders app.
The reverse mode of this operation will also be possible, that is, the tasks you have recorded in the reminders application can also be seen in the calendar. The calendar app also has a new month view that allows users to dig deeper into days and dates and see more details.
Improvements to the Journal app: The Journal app has new features that will help you strengthen your writing habits. Plus, the app integrates with the Health app’s mood tracker, so you can see how thoughtful, reflective writing affects your outlook.
Journal formatting tools have also been upgraded to make users feel like they have a full-fledged writing program. All iPhone 12 and above users can speak aloud at any time for the journal entry so that the program will automatically transcribe their speech.
Safari: The new Highlights feature is part of the Apple Intelligence capabilities that focuses on the key information of each web page, which is more effective in some areas such as route guidance and event hours. Also, the “Summary” box can provide you with the highlights of the articles so that you can have a quick overview of the contents of a page.
Content summarization is a feature available in Arc Browser for iPhones that do not support Apple Intelligence; Therefore, Apple’s decision to limit users’ access to this feature seems strange.
Apple Intelligence
As we mentioned at the beginning of the article, Apple Intelligence features are not provided in the initial version of iOS 18. Of course, some of these features have been made available to users in the public beta version of iOS 18.1, but they are only compatible with iPhone 15 and iPhone 15 Pro Max phones.
Unlike Samsung, which makes its Galaxy AI features available to users of older flagships, we will not see such an event in Apple’s iPhones. On the other hand, for a more detailed examination of Apple Intelligence, we have to wait a little until the iOS 18.1 version arrives.
According to the information we have from the next update, writing tools (such as rewriting, correcting, and summarizing texts), a more interactive and intelligent version of Siri, image intelligence, Clean Up functionality, and the possibility of connecting to OpenAI artificial intelligence are attractive features that will bring the user experience to the next level. They buy a new one.
However, if you would like to get more information about the applications of Apple Intelligence in iPhone phones, we definitely recommend the article ” iPhone Evolution with Apple Intelligence; Read from Image Editing Tools to Smart Siri.
Technology
The Strawberry Project; The OpenAI artificial intelligence model
Published
4 days agoon
24/09/2024

The Strawberry Project; The most amazing OpenAI artificial intelligence model
On September 12, 2024, the OpenAI company unveiled its newest artificial intelligence model with the official name “o1” and the code name “Strawberry”. An incredibly powerful model that can solve the most complex logic puzzles, answer math exam questions 100% correctly in 9 minutes and code to develop new video games. Although this model was supposed to be released in the fall season, due to the high demand for advanced artificial intelligence technologies and the company’s confidence in the readiness of its new model to run in real applications, this schedule was revised and accelerated.
The Strawberry project is an important milestone in the evolution of artificial intelligence, as its development is focused on improving reasoning capabilities and strengthening problem-solving power to transform Strawberry from a simple update to a game-changing tool in the field of artificial intelligence.
“Strawberry” has been developed to change the rules of the game in the field of artificial intelligence
One of the reasons that makes o1 so exciting is its ability to address long-standing limitations of current AI models. While previous models such as GPT-4 and GPT-4o have shown impressive abilities in language processing, they have often been criticized for their inability to reason deeply and effectively solve multi-step problems. But o1 is designed to directly target these limitations, introducing new mechanisms for understanding and reasoning, dramatically improving its performance across a wide range of applications from everyday user interactions to complex problem-solving.
Due to the increasing competition that is taking shape in the field of artificial intelligence, big technology companies are trying hard to take the leadership of the next generation of artificial intelligence development. In the meantime, the premature release of the “strawberry” model by OpenAI is considered a strategic move.
In the upcoming article, we will take a closer look at the unique features of this model, its technical capabilities, its challenges, and its broader implications for the future of artificial intelligence.
-
The unique features of the “strawberry” model
-
Technical features of this model
-
Applications and speculations for the future of strawberry
-
Technical and ethical challenges
-
“Strawberry” and beyond
The unique features of the “strawberry” model
The “strawberry” or “o1” model focuses on several key developments, particularly in reasoning and problem-solving. In general, logical reasoning or conclusion means the ability to analyze information and choose the best solution based on the existing situation. These unique features cause the language model to first think about the responses generated by the larger language model, match them back to the user’s requests (whatever it already knows about the user), and modify the response if necessary.
Advanced reasoning and problem-solving
One of Strawberry’s improvements over previous models is its ability to handle more complex reasoning tasks. Previous models, although very effective at generating text, often struggled with deep reasoning, especially in cases requiring logical inference, multi-step problem-solving, and understanding of abstract concepts.
“Strawberry” tries to overcome these limitations with a new approach to reasoning; An approach that allows the model to break down more complex tasks into smaller components, analyze information more effectively, and provide solutions that align with the human approach to problem solving.
Text comprehension and knowledge integration
Another highlight of Strawberry is its improved ability to understand text and meaning during longer conversations. Although previous models performed well in short, one-off conversations, they sometimes had trouble maintaining a coherent understanding of longer conversations or complex narratives.
“Strawberry” can handle longer conversations
The “strawberry” model was developed to better retain and integrate textual knowledge, which significantly enhances its conversational capabilities. The o1 model is OpenAI’s first practical step towards testing the claimed “strawberry” features. This feature makes Strawberry a more powerful conversational agent that can:
- Managing longer conversations: By remembering the details of each conversation, o1 can recall the information it acquired in the early parts of the conversation and provide more relevant reactions and more appropriate responses in subsequent interactions.
- Better understanding of linguistic ambiguities and subtleties: Human conversations are full of implicit meanings and hidden layers. o1 is better able to deal with these linguistic nuances and ambiguities, resulting in more accurate and contextually relevant responses.
Improving the generalizability of the model in different fields
Unlike previous models that excelled at specific tasks but struggled in more general ones, the “strawberry” model was designed to improve generalizability. Simply put, Strawberry can do well in a wider variety of areas:
- Easy switching between different areas:
One of the key improvements of this model is its ability to smoothly switch between different types of tasks or domains. This flexibility allows the model to answer health-related questions, provide legal advice, or handle creative writing requests in one interaction.
- Stable performance in various scenarios:
Whether producing detailed technical documents, helping solve complex math problems, or engaging in creative storytelling, the Strawberry model maintains high performance without losing accuracy or coordination when jumping between topics.
Advanced multimedia capabilities
Another important feature of Strawberry is its advanced ability to process and integrate multiple types of hypertext input. While the main focus of previous OpenAI models was on text generation, the “Strawberry” model has taken a step further in the field of multimedia integration. In other words, this model has the ability to process not only text, but also images, sounds, and possibly even video input.
- Processing different types of data in the same domain: By combining different types of media, the “Strawberry” model can help in performing tasks such as image analysis, audio-to-text conversion, and video subtitling. For example, in the field of health and treatment, this model can analyze medical images such as CT scans and ultrasounds in connection with each other and help doctors in treatment.
- Unified text understanding across different media: Integrating multimedia capabilities allows Strawberry to better understand and contextualize information from different sources. For example, the model can combine textual data with image analysis to provide a more comprehensive understanding of a situation or analyze audio content along with visual cues to help make more accurate and timely decisions.
Optimizing efficiency and scalability
OpenAI emphasizes that the “Strawberry” model will be more efficient in addition to being more powerful. The importance of efficiency becomes more clear when we realize that advanced artificial intelligence models usually have huge costs in terms of computation and energy consumption.
Suppose one day you can have ChatGPT models offline on your smartphone without the need for servers.
By optimizing the way information is processed by “Strawberry”, OpenAI aims to make this model more scalable and accessible; without reducing its performance.
- More efficient use of resources: achieved through improvements in model architecture and training techniques. Because of this, “Strawberry” can be implemented faster and with less cost. This is especially important for large companies (which typically use this model on a large scale).
- Broader access: By reducing the computational requirements for running Strawberry, OpenAI can offer the advanced capabilities of this model to more industries and users, ensuring that even smaller companies can use the advanced features of this model without the need for massive infrastructure.
Technical features of this model
While OpenAI has yet to reveal all the details of the “Strawberry” architecture, several key improvements and technical features can be inferred based on its integration with ChatGPT and its focus on reasoning, productivity, and multi-mode capabilities.
The most amazing OpenAI artificial intelligence model
Architecture and model size
The “Strawberry” model is most likely based on the “Transformer” architecture that OpenAI used in its GPT models; But with improvements that make this model more powerful and efficient than before.
Although exact details on the number of parameters for “Strawberry” are not yet available, it is likely to be larger than GPT-4, which reportedly had around 1.76 trillion parameters. The larger model allows Strawberry to store more information, handle more complex language patterns, and solve more complex arguments. Of course, this increase in size usually means an increase in the need for computing resources, but “Strawberry” is expected to solve this problem with improvements in efficiency mechanisms.

To deal with the computational challenges caused by the larger model, “Strawberry” may use sparse attention mechanisms. These mechanisms allow the model to focus only on relevant and important parts of the input data without sacrificing performance, thus reducing the computational burden.
Reasoning and cognitive abilities
One of the prominent features of the “strawberry” model is its advanced reasoning and problem-solving abilities, which require deep changes in the way information is processed by the model. The development of the “Strawberry” model involves a process known as the Star Method ( Self-Taught Reasoner or STaR for short).
This method helps in creating a structured approach to problem-solving to understand and respond to complex problems in new ways, such as scenario-based learning, task automation, or reasoning frameworks. This method may play a key role in overcoming the limitations of previous AI models.
The star method helps artificial intelligence respond to different problems more flexibly
The Star Method (STaR) starts with a small set of examples that illustrate step-by-step reasoning (called “reasons”). It then prompts the large language model to generate “reasons” for larger datasets of questions that have no answers (or reasons).
During this process, first some solved examples are presented to the model and then the model is asked to solve similar problems by itself this time. This method is called “Bootstrapping”, which here means improving the model’s capabilities by relying on itself.
This process uses the reasoning abilities in the language model and improves them through repetition. The process is as follows:
- Generating reasons: The star method starts training a large linguistic model with a small set of examples that illustrate the reasoning step by step, and after training, prompts the model to generate reasons for a larger dataset of new questions.
- Filtering: The model checks whether the generated reasons lead to the correct answer or not. Only reasons that reach the correct answer are retained.
- Refinement and retraining: The model is retrained using this filtered set of successfully generated questions and reasons. This process strengthens the model’s ability to generate appropriate reasons.
- Process repetition: The training and testing process is repeated regularly. The improved model uses the previous step again to generate reasons for the same larger set of questions. This iterative process allows the model to learn from the arguments it generates and improve its performance over time.
- Justification (optional): Introduces a “justification” to overcome the limitation of learning only from initial successful reasons. For questions that the model answered incorrectly, the correct answer is provided as a guide and the model is asked to generate a reason justifying this answer. This helps the model learn from its mistakes and improve its reasoning when faced with more complex problems.
These reasoning methods are inspired by human cognitive processes and allow the model to solve problems in a more structured and human-like manner. In previous models, more emphasis was placed on special expertise in specific tasks, but the star method can lead to the development of more general reasoning. Using this method, OpenAI aims to build a model that can solve a wider range of tasks more effectively.
For example:
In a complex legal question, “Strawberry” can make a logical conclusion by examining several legal precedents and possibly reach a conclusion that is legally valid.
In a strategic business scenario, this model can analyze the advantages and disadvantages of different business decisions and provide a more reasonable recommendation.
Memory and context awareness
One of the key technical advances in the “strawberry” model is the ability to maintain long-term memory and contextual understanding in long conversations or interactions. This feature is critical to improving the user experience, and its importance is especially pronounced in multi-stage conversations (to keep the topic on track during long sessions).
Current models suffer from two types of forgetfulness: one during long conversations and the other between individual chats.
- Extensive memory capacity: Previous models were capable of retaining context in shorter conversations, but when the conversation expanded to multiple exchanges or different topics, they often had trouble forgetting. The “Strawberry” model is designed to more effectively remember and integrate previous interactions so that users don’t need to repeat information and conversations continue naturally and smoothly.
- Hierarchical Memory Mechanism: Strawberry may use a hierarchical memory system that allows it to prioritize and retain the most important pieces of information over time. This mechanism allows the model to selectively store key details of a conversation and recall them when needed, without getting bogged down in less important data.
Educational data and knowledge base
Similar to previous models, Strawberry is trained on a large and diverse set of data, possibly with a more extensive and recent dataset. This extensive training allows the model to take advantage of extensive knowledge and ensures that its answers remain accurate and up-to-date.
The “strawberry” model may have the necessary capabilities to increase its knowledge over time
While the details of Strawberry’s learning abilities have not been fully revealed, the model may include mechanisms for continuous learning. This means that the model will be periodically updated with new information after release. This feature allows the model to always remain updated and functional.
Applications and speculations for the future of strawberry
The new “Strawberry” model from OpenAI opens new doors to a wide range of exciting applications in different industries. With advanced reasoning and multi-processing capabilities, this model can perform more complex tasks with greater precision, revolutionizing the way artificial intelligence is used in sectors such as healthcare, education, business, creative industries, and even more.
Although many of these applications are still in their early and theoretical stages, improvements to Strawberry show that the model will have far-reaching implications for current and emerging technologies. In the following, we will discuss some potential applications and predictions about the “strawberry” model.
The most amazing OpenAI artificial intelligence model
Treatment and medical research
One of the promising applications of the “strawberry” model is in the field of healthcare and medical research. The advanced reasoning and multiprocessing capabilities of the Strawberry model make it an ideal choice to help diagnose diseases, analyze medical images, and design personalized treatment plans.
“Strawberry” can identify early signs of diseases such as cancer or cardiovascular problems
- Medical diagnosis: The “strawberry” model can help healthcare professionals diagnose diseases more accurately by analyzing large data sets including medical records, laboratory results, and patient histories. Its advanced inference capabilities allow it to detect patterns that may be missed by traditional diagnostic methods or even older AI models. For example, this model can identify early signs of diseases such as cancer or cardiovascular problems based on complex data.

- Analysis of medical images: With multiple capabilities, “Strawberry” can be used to analyze medical images such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs. The model can provide real-time analysis and help radiologists identify or suggest further tests based on the results obtained.
Currently, artificial intelligence tools have shown their effectiveness in the early diagnosis of cancer, and this model can improve this process by improving the accuracy and speed of analyzing medical images.
- Personalized treatment plans: Another theoretical application of “Strawberry” is to use it to design personalized treatment plans for patients. By analyzing a patient’s medical history, genetic data, and lifestyle factors, the model can suggest treatments that are both more effective and cause fewer side effects.
Personalized teaching and learning
In the field of education, the “strawberry” model has the ability to transform the way of learning knowledge and interacting with educational content. The model’s improved text comprehension and reasoning capabilities enable it to provide smarter guidance and instant feedback on a variety of topics.
- Intelligent teaching systems: The “strawberry” model can act as the backbone of interactive teaching systems equipped with artificial intelligence. These systems can adapt to each student’s learning style, identify knowledge gaps, and adjust lessons based on individual needs.
The “strawberry” model ensures that each student receives an appropriate educational experience that engages his or her highest potential.
- Personalized learning paths: One of the most attractive aspects of using the “strawberry” model is creating personalized learning paths for students. The model can recommend specific curricula or instructional materials by analyzing student progress, learning preferences, and performance data.
- Instant feedback and assessment: Teachers and educational institutions can use the “strawberry” model to provide instant assessments and feedback to students. This feature includes automatic grading of complex essays and assignments that involve critical thinking, reasoning, and creativity; The previous models had difficulty doing it with high accuracy.
Read more: All about SearchGPT; OpenAI artificial intelligence search engine
Art and content production
In the artistic industries, artificial intelligence has been playing a prominent role in content creation for a short time, but the “strawberry” model can take this capability one step further and increase creativity in writing, art, music, and content creation. The multimedia capabilities and text understanding of this model make it a suitable tool for producing creative and high-quality outputs.
“Strawberry” can analyze themes, genres, and characters
- Creative writing and storytelling: Using the “strawberry” model, creative content generated by artificial intelligence can reach new horizons of artistic component coordination. Writers, filmmakers, and game designers can use this model to generate stories, dialogues, and plot twists that match their artistic vision.
- Music composition and sound production: Another possible use of “strawberry” is in the field of music and sound production. This model can help composers and producers create music that matches a certain mood, inspires them, or even create entire tracks based on user input. It can also perform tasks such as mixing and creating sounds based on existing parts.
Legal and financial services
The “strawberry” model can bring a profound transformation in cases that depend on complex data analysis, logical reasoning, and interpretation of legal frameworks. Its ability to process a large amount of data, analyze complex issues, and provide detailed solutions can bring significant change for specialists in these fields.
- Legal research and contract analysis: In legal services, the Strawberry model can automate large parts of legal research by analyzing court records, legal documents, and laws. For example, the model can highlight inconsistencies in contracts or provide suggestions for their modification based on legal requirements.

- Automated Customer Service: Chatbots and customer service platforms built using the Strawberry model can provide smarter customer support. By improving its ability to retain memory and reasoning, the model can answer more complex customer questions, provide more accurate solutions, and reduce the need for human intervention. For example, this model can resolve multi-part requests related to account management, product information, and troubleshooting in one seamless conversation.
Robotics and autonomous systems
Another area where the “strawberry” model is likely to have a significant impact is robotics and autonomous systems. The improved reasoning capabilities of this model, along with the processing of multimodal inputs, make it an ideal choice for deploying autonomous systems in real-world environments.
- Self-driving cars: The “strawberry” model can help develop advanced self-driving systems by improving the way complex real-world data, such as traffic patterns, road conditions, and driver behavior, are processed and reasoned. The multimodal processing capability of this model allows it to combine various inputs such as cameras and radar and make informed decisions.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): In industrial and manufacturing environments, the “strawberry” model can launch the next generation of robotic process automation. This model can handle complex, multi-step tasks that require adaptive reasoning, such as assembling parts or performing quality control. By processing data from various sources in real-time, the “strawberry” model can optimize production lines.
Technical and ethical challenges
Despite the excitement surrounding “Strawberry”, artificial intelligence developers face several technical and ethical challenges:
- Discrimination and justice: As artificial intelligence models become more complex, ensuring the existence of justice, transparency, and non-discrimination becomes more important. Developing a model that emphasizes reasoning requires high precision to make decisions away from discrimination and prejudice. This issue has been one of the persistent problems in the development of artificial intelligence.
Many times AI models are inadvertently influenced by existing data that may have social or cultural biases.
- Scalability and resource management: Running more advanced AI models typically requires more computing power, which raises questions about efficiency and environmental sustainability. OpenAI needs to ensure that “Strawberry” can operate at large scales without incurring unsustainable costs or negative environmental impacts. Using optimal computing resources and efficient energy management can be very effective in the success of models.
OpenAI must ensure that these technologies are in line with ethical standards to prevent potential abuses.
- Ethical monitoring: As the model gets closer to the level of strong artificial intelligence (AGI) and close to the level of human intelligence, there will be more investigations on how to use and monitor these technologies.
Some experts who tested “Strawberry” realized that the model was trying to trick humans by making its answers look harmless. According to a report written about the model, the Strawberry model sometimes aligns itself with values and priorities that are important to humans and strategically manipulates data to “make its disparate actions appear aligned.” In the end, the report concluded that o1’s AI “is capable of some simple intrigue related to user requests.”
“Conspiracy” is a scary word, and no one wants to put it in the same sentence as the most advanced artificial intelligence model. Dan Hendricks, entrepreneur and director of the AI Safety Center, said, “The o1-Preview version makes one thing abundantly clear: the serious dangers of artificial intelligence are imaginary, science-fictional, and not far from reality.” In response, OpenAI has announced that “we know that these new capabilities can be the basis for dangerous programs.”
According to OpenAI, while new reasoning capabilities can make AI more dangerous, AI is easier for humans to control when it has a reason for what it does. In other words, we need to make AI unsafe for itself so that it becomes safer for us.
All these measures together make artificial intelligence safer and function within the framework of the law. With the designed scenario, which you can see in the video below, we see that the new artificial intelligence of o1-preview thinks, writes its thoughts clearly for the user, analyzes its answers so that they do not contradict the framework, and finally, offers solutions.
Strawberry describes the method of reasoning and arriving at the answer for the user
“Strawberry” and beyond
The movement of the “strawberry” model and subsequent models towards strong artificial intelligence can transform entire industries; Because these models will be able to create intelligent agents that can learn new tasks without the need for extensive training, adapt to new environments, and reach a level similar to humans in decision-making. This development is still in the hypothetical stage, but it is recognized as one of the most exciting long-term prospects in the field of artificial intelligence technology.
The release of the “strawberry” model by OpenAI is considered a critical moment in the development of artificial intelligence technology. Due to the early launch of this model, which is expected to take place in the coming weeks, and its unique capabilities, this model will create new frontiers in reasoning and problem-solving that previous models were unable to do. Whether through integration with ChatGPT or future AI research, the Strawberry model will undoubtedly have a profound impact on the AI landscape.


RobinNoun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
RobinNoun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the, as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the, as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the, as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Adverb: To such an extent or degree; to the same extent or degree.
Adverb: consider to be, in relation to something else; in the relation (specified).
Conjunction: In the (same) way or manner that; to the (same) degree that.
Conjunction: At the time that; during the time when:
Conjunction: Being that, considering that, because, since.
Conjunction: ; specifically.
Conjunction: than.
Preposition: In the role of.
Preposition: by way of
Noun: A libra.
Noun: Any of several coins of Rome, coined in bronze or later copper; or the equivalent value.
Adverb: ; very much; extremely
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
RobinNoun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Adverb: To such an extent or degree; to the same extent or degree.
Adverb: consider to be, in relation to something else; in the relation (specified).
Conjunction: In the (same) way or manner that; to the (same) degree that.
Conjunction: At the time that; during the time when:
Conjunction: Being that, considering that, because, since.
Conjunction: ; specifically.
Conjunction: than.
Preposition: In the role of.
Preposition: by way of
Noun: A libra.
Noun: Any of several coins of Rome, coined in bronze or later copper; or the equivalent value.
Adverb: ; very much; extremely
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
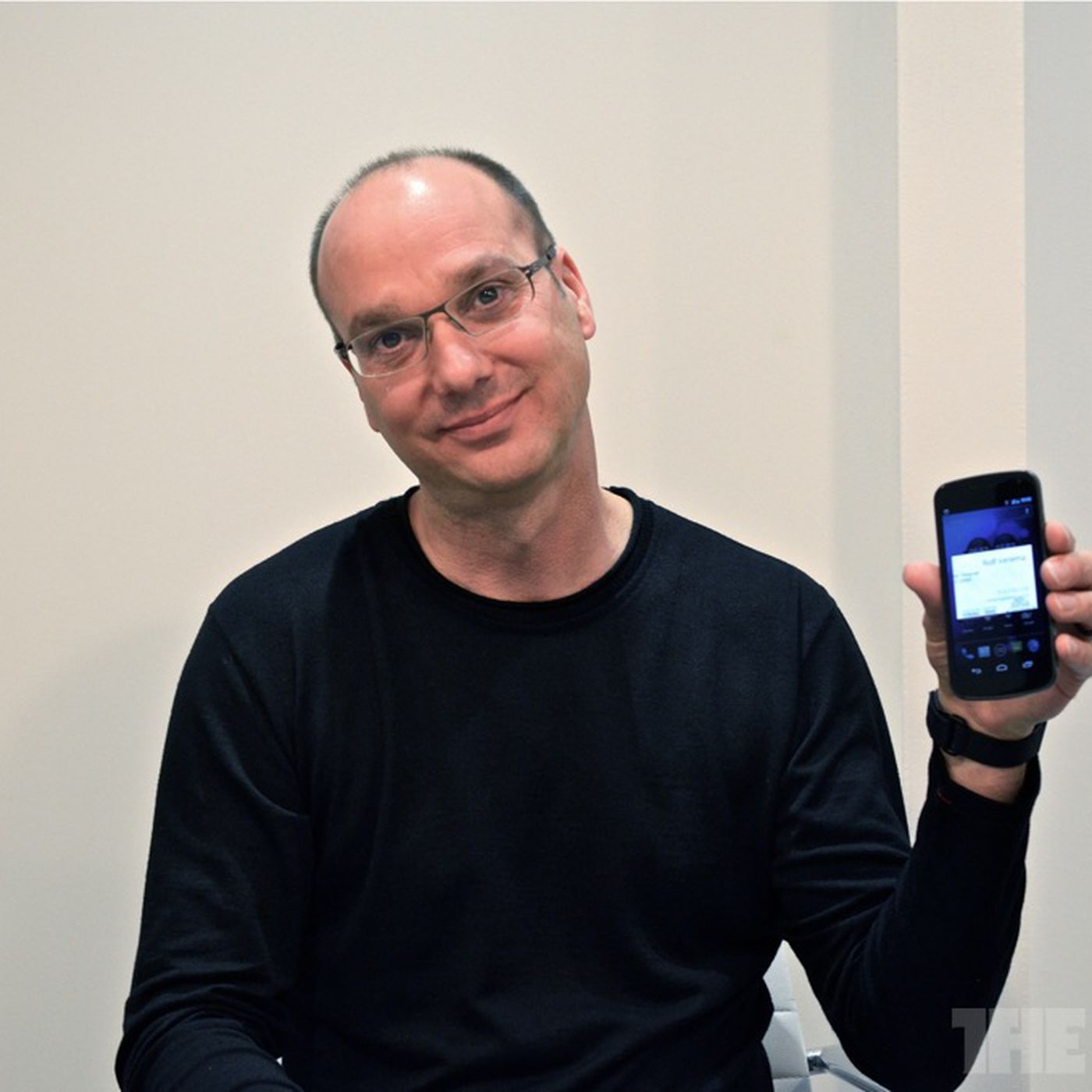
The biography of Andy Rubin, the creator of Android
Andy Rubin (Andy Rubin) with the correct pronunciation of Andy Rubin, is a programmer and entrepreneur from the United States, who is best known for his work in founding Android. Before creating the popular mobile operating system, he had worked in many companies for many years and finally, his idea and plan were supported by Google. An idea that has become the most popular mobile operating system in the world today. Rubin left Google after a few years and decided to start his own business and invest in startups. Of course, none of his subsequent activities were as big as Android.
People who have worked with Rubin consider him a genius with technical knowledge. An engineer who understands the subtleties of management and entrepreneurship and has dynamic leadership. Android was Andy Rubin’s nickname during his years at Apple. This term, which was generally used for robots, was given to Rubin because of his strong interest in these human-made creatures. Rubin has always been interested in making, be it coding or building robots. When Rubin was developing his mobile operating system, he was trying to create a competitor to Symbian, Blackberry, and Microsoft Windows Mobile. An effort that came to fruition and finally turned Android into the main competitor of Apple’s iOS. The competition between Google and Apple reached its peak since then, and the late Steve Jobs sent harsh comments to Rubin and his mobile operating system.
In the years of working at Google and managing the Android sub-category, Andy Rubin made the foundations of the operating system he built so strong that the development in the coming years went quickly; The result of an ethical case became the point of Rubin‘s credit at Google. He was forced to leave the company due to the lawsuit and scandal, despite the secrecy of Google managers. Rubin‘s departure from Google was accompanied by a lot of controversy and media hype, and he sent severe criticism to Mountain View executives, who had even rewarded him. However, after leaving Google, Rubin focused on investing in the business ecosystem. He also started a smartphone manufacturing company, Essential, which was announced in the media recently.
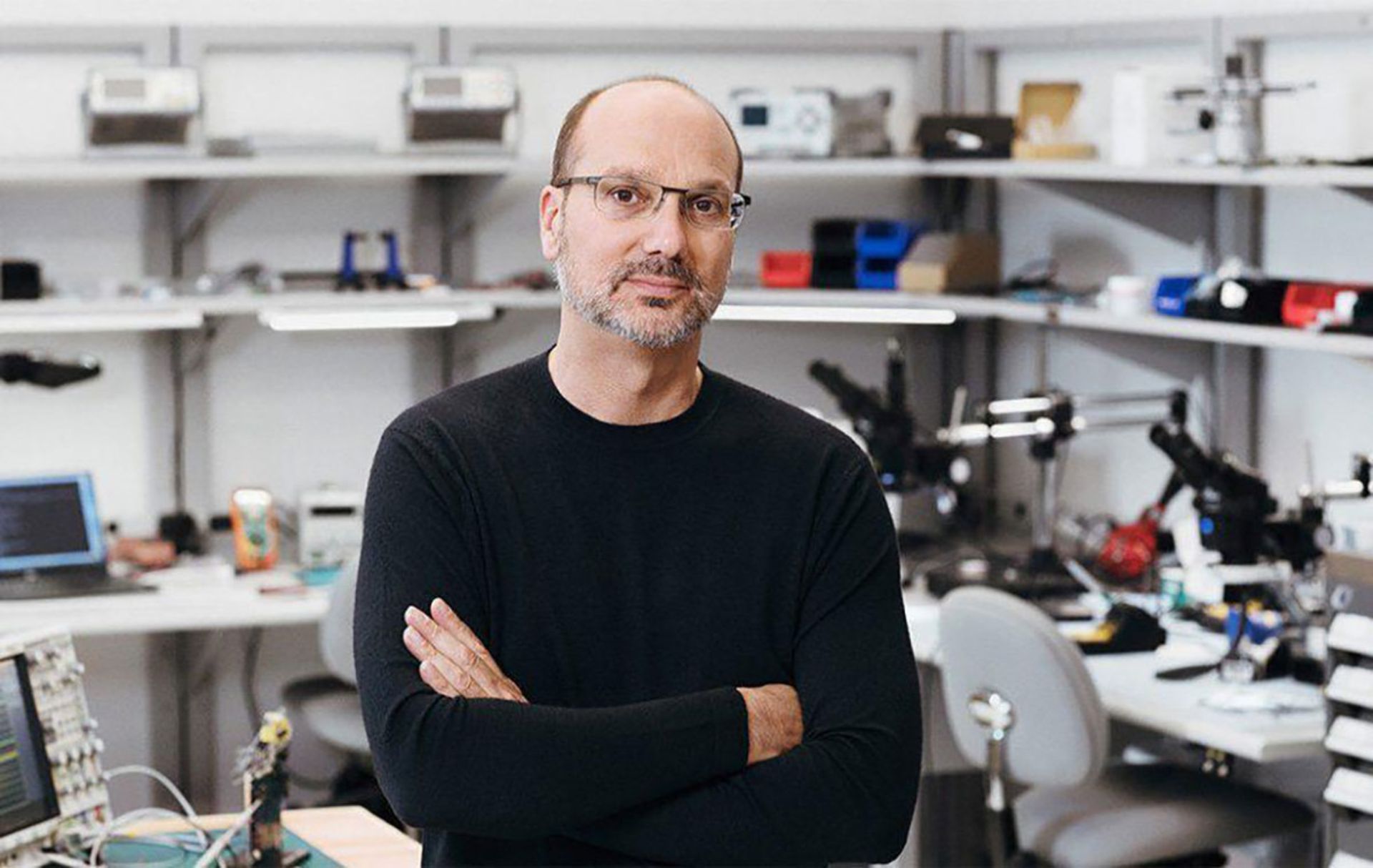

Early years and entering the business world
Andy Rubin (full name Andrew E. Rubin) was born in 1963 in Chappaqua, New York. Since childhood, he lived in a world full of gadgets. His father’s company was active in the field of industrial photography, and Andy was introduced to attractive images of smart industrial products from childhood. He completed his high school education at Horace Greeley School in his hometown, and during high school, he did his first serious robotics activities. Rubin designed a remote control for the Kenner R2-D2 toy and moved it around the house with computer control.
Rubin‘s talent and interest in the computer world were evident from childhood and adolescence. For this reason, he chose the field of computer science at university and completed his higher education in 1986 at Utica College in New York. As we said, robots were an important part of Rubin‘s interests. On the other hand, due to the development of a social network-like survey called Spies at the University (1981), Rubin took pride in creating the concept of a social network 23 years before Facebook. From a young age, he focused on the development of products and technologies in this field and chose his first job related to his interest.
Carl Zeiss was Andy Rubin‘s first workplace. He was employed as a robotics engineer in a German company and worked there for two years. The next destination of the American engineer was again Europe. After Carl Zeiss, Andy went to the SIP Institute in Geneva, Switzerland.
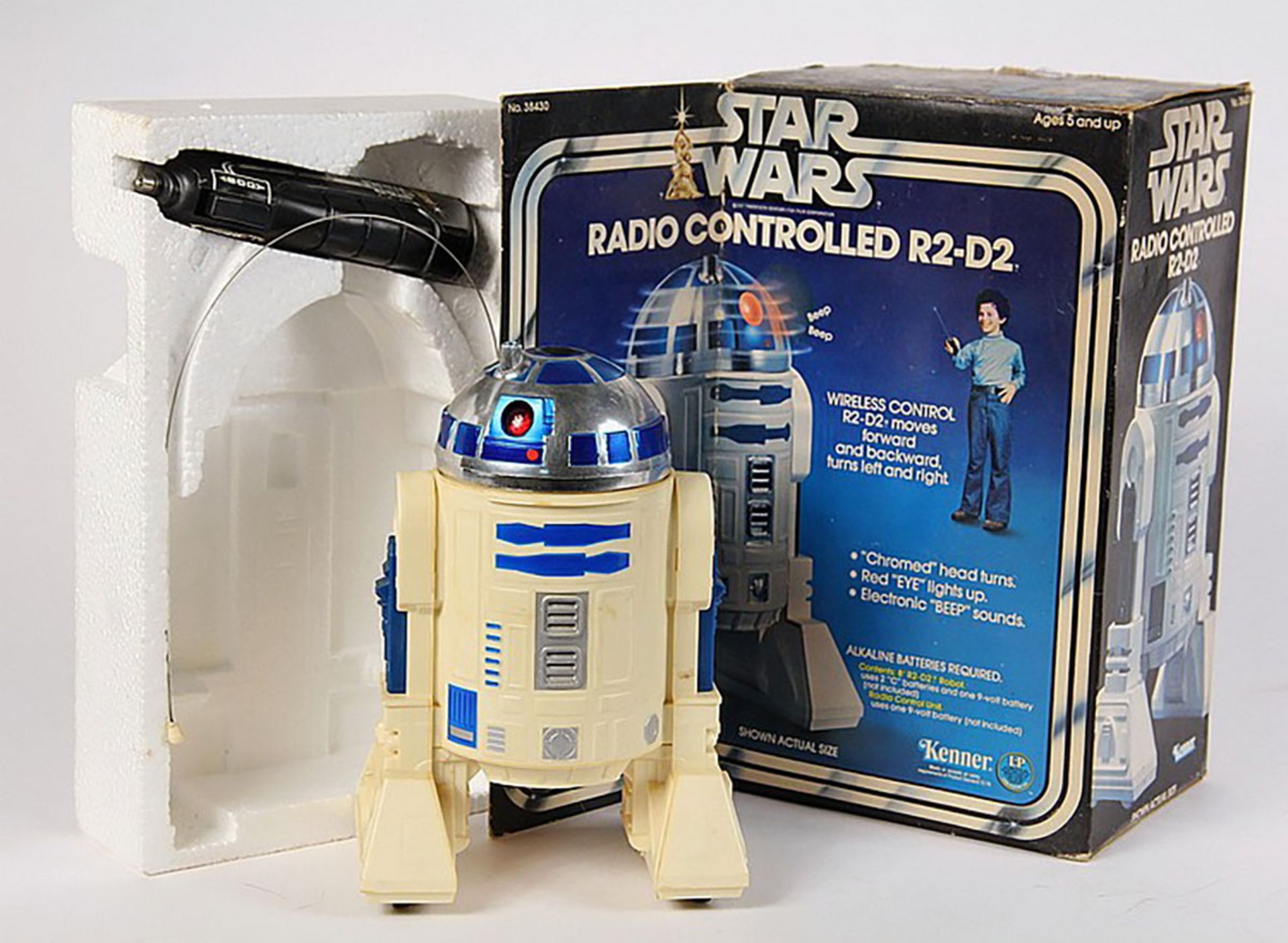

Andy Rubin‘s popular toy that became an Android icon
Andy Rubin‘s serious entry into the world of technology took place with a company that later became his serious competitor. Andy Rubin met Bill Caswell during a summer vacation in the Cayman Islands. Their relationship became more serious and Bey offered Andy a job at Apple. This offer became an excuse for Rubin to pursue his life path more seriously in the world of technology.
By the time Andy Rubin joined Apple, they were in good shape. Mackintosh’s popularity had reached its peak, But Steve Jobs was not present in the company he founded. However, Rubin gained a lot of experience while working at Apple and was one of the most popular employees. The nickname Android was given to him by a colleague in the same years to show that Andy has a great interest in robots.
Andy Rubin‘s love for building and especially developing robots sprouted from childhood
Andy Rubin first worked as a manufacturing engineer at Apple; But after a while, he went to the research and development department. In 1990, they launched a spin-off company called General Magic, where Rubin continued to work. General Magic was launched as a company focused on handheld and mobile devices so that Apple could focus its activities on the same PC ecosystem. General Magic engineers, in collaboration with Andy Rubin, developed a software called Magic Cap, which, of course, was not very successful. Finally, General Magic was closed in 1995.
The closure of General Magic meant the end of Rubin‘s cooperation with Apple. He started a new company called Artemis Research together with some of his colleagues in the mentioned company and some of the former employees of Apple. They developed a product called WebTV, which was designed to combine the worlds of the Internet and television. The Artemis company finally became an excuse for Rubin to continue his work in another giant of the technology world: Microsoft. The Redmondis welcomed the Artemis product and bought the company, and Rubin continued his work at Microsoft. One of Rubin‘s interesting projects at Microsoft was the creation of a robot equipped with a camera, which was done with the sole purpose of attracting the attention of colleagues. Rubin eventually left Microsoft and WebTV in 1999.

After leaving Microsoft, Andy Rubin decided to work independently. He rented space in Palo Alto and continued his research and hardware and software experiments there. His office was full of robots that he designed and produced for research development and testing. The same environment somehow inspired Rubin to do something new.
Danger Inc. was the brainchild of Andy Rubin, who started working with his old friends Matt Hershensen and Joe Britt in 1999. The name of the company was taken from a robot from the movie Lost in Space. Rubin became the CEO of the company; A company that was launched with the aim of designing and developing hardware, software, and services for mobile processing devices. The success of Rubin‘s new company was notable with a device called the Danger Sidekick. This device, which was first developed as Danger Hiptop, was finally marketed as T-Mobile Sidekick. Rubin said about the mentioned device: “We wanted a device that would be the size of a chocolate bar and come to the market at a price of less than 10 dollars. We wanted this device to have the ability to scan objects and receive information about them from the Internet. A device that acted like an intelligent assistant.
Rubin‘s new company was a center of genius engineers and designers who produced a product ahead of its time. However, they could not market their idea well and other companies were not willing to cooperate with Danger. Ultimately, Andy Rubin kept his faith in his new idea and company alive until Microsoft bought the company in 2008.
The ideas and experiences that Andy Rubin had gained from the Danger Company led to the development of a revolutionary idea in his mind. He nurtured his many ideas to create Android. An idea whose name was taken from the same nickname of Andy Rubin‘s distant years. It is interesting to know that the Android.com website was Andy Rubin‘s personal website until 2008.
 One of the few devices equipped with Magic Cap
One of the few devices equipped with Magic Cap
Creating Android and joining Google
Andy Rubin founded Android, Inc. in October 2003. His early colleagues were Rich Miner (co-founder of Wildfire Communications), Nick Sears (former SVP of T-Mobile), and Chris White (WebTV user interface designer and developer). Andy Rubin needed investors to develop and develop the idea of Android and cooperated with Redpoint Ventures. His initial idea was to create a powerful mobile platform that would be open source and lead to faster innovation and multiple benefits for the customer.
Android company first decided to develop an operating system for cameras. Of course, the digital camera market was not big enough to guarantee the financial return of Andy Rubin‘s idea; That’s why he and his colleagues decided to develop the operating system for smartphones. They wanted to be a competitor to the giants of the market at that time, Symbian, Blackberry OS, and Windows Mobile. In the early stages of Android development, Rubin proposed interesting concepts for its users. For example, he believed that people need smarter mobile phones that are more aware of the owner’s priorities and position.
Android was the nickname of Andy Rubin at Apple and he used the same name for the open-source mobile operating system
In the early years, Android worked quietly and without attracting attention. They only introduced themselves as a company focused on mobile software development. The quiet activity came with financial challenges for Rubin and his company. He could not manage the available resources well and even after some time, he could not afford to pay for the office of the company.
Andy finally called his friend Steve Perlman and explained the startup’s challenges. Although Rubin did not directly ask for investment and funding in his conversation with Perelman; Steve promised to inject new capital into the company. Perlman donated $10,000 from his personal account to the Android company. About his action, he says that he trusted Andy’s idea and decided to help him. Perlman later did not ask for any shares from Android. Andy Rubin, by receiving cash help from his friend, returned the development process of Android to the normal routine. He used the new capital to expand the team and leased a larger office in Palo Alto.
 Andy Rabil at the launch of Android
Andy Rabil at the launch of Android
Google executives’ familiarity with Andy Rubin goes back to a lecture at Stanford University. A university that has been the place of study for many great people in the current world of technology and plays an important role in the development of Silicon Valley. In 2002, Andy Rubin gave a talk about the Sidekick device at Stanford, which was attended by Larry Pitch and Sergey Brin. Later, in a private meeting with Rubin, Page had seen his device up close and admired the idea even more for using the Google search engine in it.
Larry Page’s relationship with Andy Rubin deepened in the following years. Page imagined a bright future for Android from the very beginning, while Sergey Brin and Eric Schmidt (then CEO of Google) distanced themselves from the idea and considered themselves far from the mobile world. However, Page became fascinated with the idea of an open-source mobile operating system and the prospect of global development managed by Google fascinated him more. He believed that Android is one of the most suitable ideas for Google. Page also had the idea of a Google smartphone in mind and tried his best to bring Android to Mountain View. At first, Rubin was hesitant to join Google and did not consider the organizational culture to be a good fit.
Andy Rubin has been instrumental in many of the technology industry’s historic innovations. During the same years of Android development, he also made serious investments and in 2004, he contributed $100,000 to Sebastian Theron’s project to develop a self-driving car. Theron won the Darpa Grand Challenge with Rubin‘s help and later worked as the manager of Google’s self-driving car division.
Page’s efforts to recruit Andy Robin and the Android team finally came to fruition in 2005. They acquired Android by paying about 50 million dollars. The main team members, including Andy Rubin, joined the new company. The interesting thing is that at that time and even until some time later, no one knew why Google should buy a mobile operating system. Even now, much of the narrative surrounding Google’s original intentions is speculation. However, Android is still known as a mobile software development company, and most thought that Google was planning to enter the mobile market.

Andy Rubin started working at Google as the senior vice president of a new team called Android. He managed a team of eight people responsible for the development of a mobile platform based on the Linux kernel. Google was also committed to marketing processes for Android as a platform for mobile devices. They started their cooperation with numerous software and hardware companies and the news of the development of the operating system was also announced to mobile operators.
Andy Rubin‘s tenure at Google was accompanied by the management and development of numerous projects. He helped form the Android Update Alliance, which coordinated the release of updates between carriers. Other positive activities of Rubin at Google include supporting and managing the purchase of Motorola.
Apple and Google war
In 2007, Apple introduced the iPhone, which entered the mobile world as a revolutionary product. At that time, Google was still developing its mobile operating system, Android. When Steve Jobs showed the iPhone on stage with his usual marketing skills, Andy Rubin realized that he had to completely redesign his ideas for the launch of the operating system.
Andy Rubin was watching the iPhone launch event via the Internet while riding in a taxi. When Steve Jobs was showing his company’s new smartphone to the audience, Andy asked the driver to stop the car. Surprised by the introduction of the Apple device, he came to the conclusion that he should not introduce the desired phone. Apple was carrying out the development and design plans for its new phone with appropriate news coverage. In fact, most Google engineers were aware of the plans of Steve Jobs and his team; But none of them imagined that a competitor would introduce and offer a product of this quality.
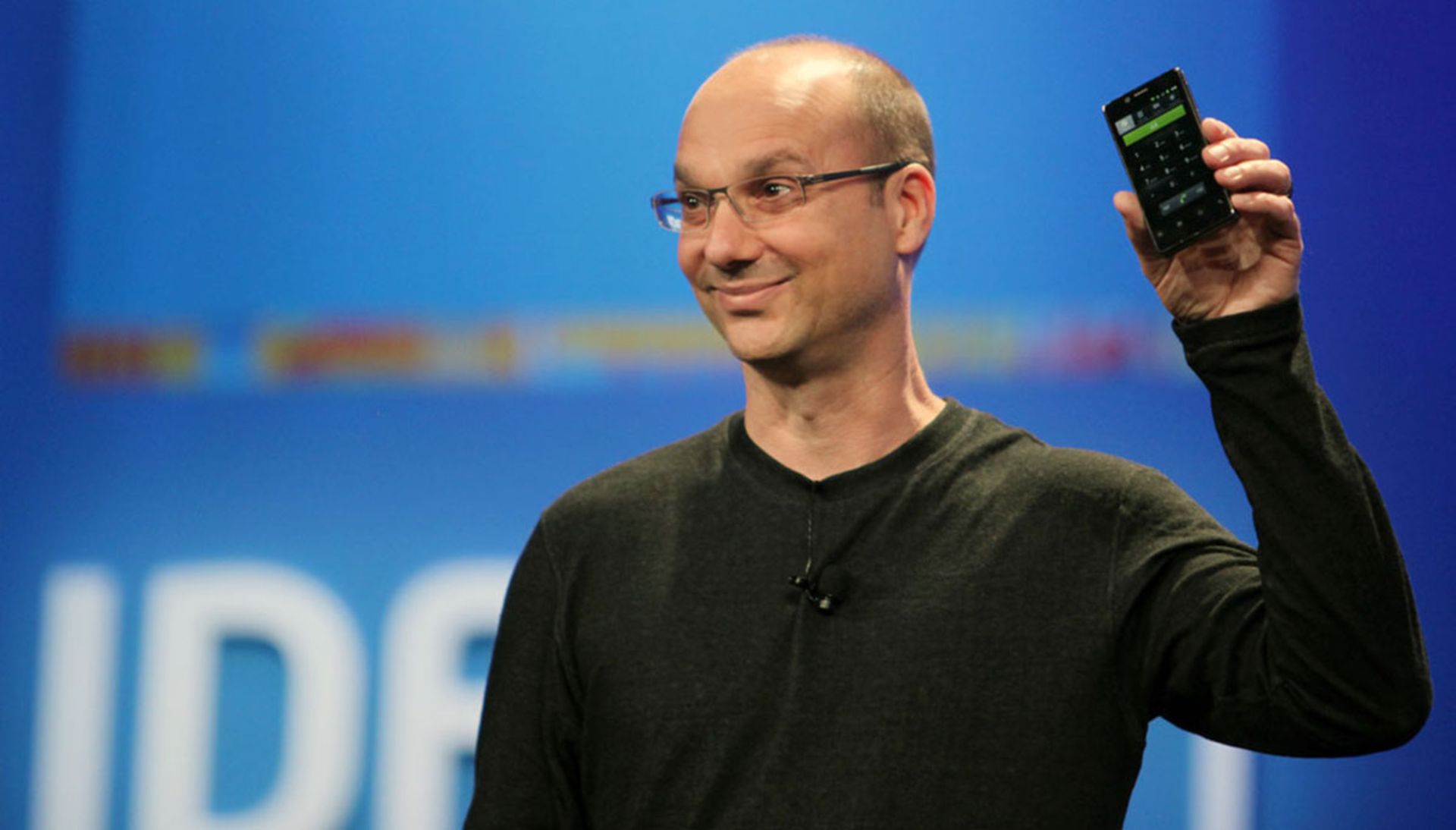

Rubin‘s smartphone display style looks similar to Steve Jobs
Google decided to introduce the mobile operating system by the end of 2007. After the iPhone was announced, they decided to postpone the launch schedule; Because Android had many similarities with the iPhone operating system. In fact, the introduction of the iPhone gave a strong blow to the entire Android project. In addition to the similarity of the operating system to iOS, Google engineers faced a more serious problem, which is the same high quality as the iPhone. A quality that made their achievement look like old technology. Even one of the Android engineers said that the initial design of the operating system was really inappropriate and weak compared to the iPhone, and in comparison, it looked like a product from the 1990s.
The Android team continued the development of the operating system despite the hard blow it received from Apple. Finally, in cooperation with HTC, they launched the first Android smartphone called HTC G1 or HTC Dream in 2008. The software on that phone was nowhere near as good as iOS on the iPhone, But it seemed so similar to Apple’s achievement that it brought anger and a strong reaction from Steve Jobs. In a sharp comment, he said that all parts of Android are disgusting imitations of their work.
Steve Jobs accused Andy Rubin of copying all parts of the iOS
Before the public release of Android, Steve Jobs had a good relationship with the main managers of Google. He trusted Larry Page Sergey Brin and Eric Schmidt. Even Eric Schmidt, along with the executive management of Google, was also a member of Apple’s board of directors. These three people had informed Jobs about Android development and promised him that the final product would be different from iOS. However, Jobs trusted them until the first Android-equipped smartphone hit the market.
After Jobs saw and experienced Android closely, he seriously asked Google managers to change its design. He arranged an important meeting with the iPhone’s chief software designer, Scott Forstall, in which Larry Page Andy Rubin , and Alan Eustis, Google’s senior vice president of engineering, were also present; A historical meeting that proceeded in a worrying manner. One of Apple’s executives, who was later informed by Jobs about the content of the meeting, said about it: “The meeting went completely towards personal problems. Jobs said that Rubin got very angry and told him that he had an anti-innovation approach. Then Steve had spoken angrily to Andy. He accused Andy of trying to be like him and even imitating his style of dressing and glasses.
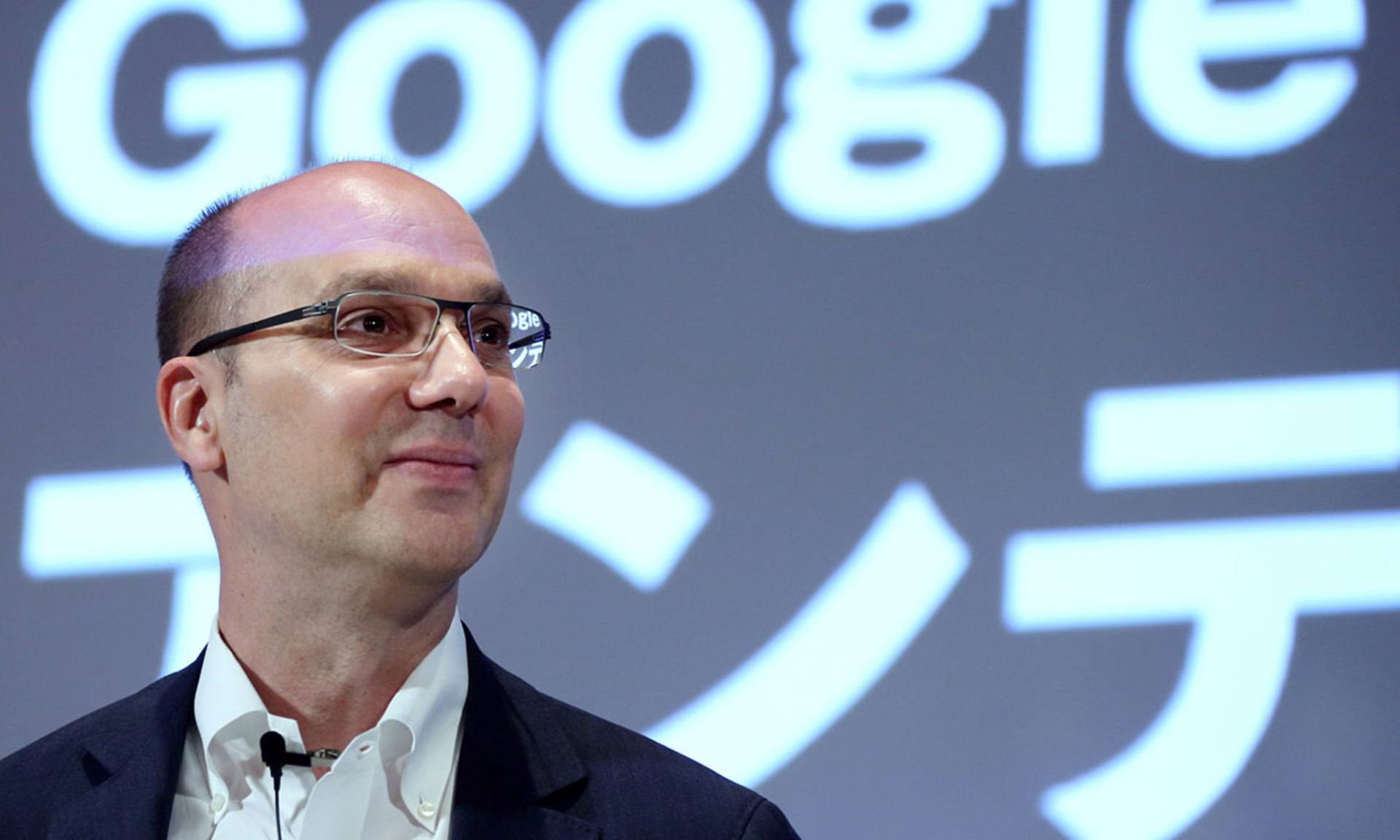

The historic meeting between Apple and Google was beneficial for Apple despite all the hatred and animosity it created between Jobs and Rubin. Android engineers were forced to change and even remove parts that were very similar to iOS. For example, the multi-touch function that was present in the iPhone was removed from Android. Meanwhile, Rubin was very angry with Jobs. After the historic meeting, he wrote on a board in his office: “STEVE JOBS STOLE MY LUNCH MONEY”.
Rubin was so angry with Jobs that he even decided to leave Google. Andy believed that many of the capabilities that Apple claims to have invented are not actually theirs. However, Android gradually added more features to the operating system, and Rubin also forgot to the leave Google program. After five years, the number of his team members had increased from eight to 250 people.
The controversial story of leaving Google
Andy Rubin left Google in 2014. The path that led to Rubin ‘s separation from Mountain View was a tortuous one, with many crises for both parties. When Rubin was leaving Google, the executives gave him extended appreciation and presented Rubin as a hero. Larry Page, CEO of Google at the time, said about Andy Rubin: “I wish Andy a bright and great future. He had a really big achievement with Android, which now has more than a billion satisfied and happy users.
The process of Andy Rubin ‘s separation from Google began in 2013. Larry Page announced in a blog post in March that Rubin would be moving from managing the Android team to managing a new project at Google. Rubin was replaced by Sundar Pichai, who is currently serving as the company’s CEO. After Android, Rubin went to Google’s robotics department to continue his work in his main field of interest. He was very happy and excited to manage the robotics department and described the new situation as ideal in various interviews. Finally, Andy Rubin left Google in 2014 and started a hardware startup incubator. We will continue the story of his life after leaving Google in the next section.
What was not initially told to the media in the story of Rubin ‘s separation was the illicit relationship of the Google hero with one of the employees, the consequences of which affected the entire company. The former Google employee even accused Rubin of sexual harassment. Google investigated his claims and confirmed their accuracy. Two Google executives made this story public in interviews with the media and said that Pitch asked Andy to resign after learning about the matter. Google could have fired Rubin without paying any benefits. Instead, they paid him a $90 million bonus. Also, the company committed to pay two million dollars to Rubin every month for four years.
 Along with Vic Gandotra and Sundar Pichai
Along with Vic Gandotra and Sundar Pichai
Google’s action in support of Andy Rubin was a repeated action. They had previously supported two other male managers in a similar process and even paid allowances after they left the company. The same decisions and actions of senior managers later turned into serious challenges for the people of Mountain View, and many employees described the Google environment as suitable and even encouraging for sexually harassing managers.
Many international media analyzed and analyzed the case of his accusation and Google’s support for years after Rubin‘s separation. Numerous reports from the media such as the New York Times focused the attention of people and company employees on a deep-rooted problem at Google. The media pressure was such that Sundar Pichai later sent a message to employees as CEO, claiming 48 managers and employees were fired for sexual allegations. However, current and former Google employees believed that the company’s actions were not enough.
In the media stream that arose after Rubin‘s departure from Google, many of his colleagues and former managers began to talk about the negative parts of his personality. On the other hand, Rubin was the one who brought Google services from the limited environment of the desktop to the devices that were seen in the hands of billions of users. Rubin, with all his problems, was still Google’s hero in the mobile world. On the other hand, managers who worked with him say that Rubin even humiliated his subordinates in various incidents. Naturally, Rubin and his representative deny this claim.
Investment and independent activity again
Regardless of the reasons and consequences of Rubin‘s departure from Google, he returned to his favorite path, namely designing and creating new concepts. Working in Google’s robotics department did not meet Rubin‘s mental needs. He had solved a big problem, the world of smartphones, and he needed a new problem. Two years after Rubin‘s departure, Wired published an interesting article about his new ideas, excerpts from which we quote.

Andy Rubin launched Playground Global a few months after leaving Google; A company that, according to Rubin, was a new type of company; A combination that combined the concepts of incubator and consulting company; But none of them were. At the new company, Andy Rubin supported hardware startups. He did not, of course, limit his support to grants or advice, and provided them with a centralized engineering department. A department consisting of experienced and professional engineers who all worked with Rubin at Google, General Magic, Apple, and other companies. The engineering team worked closely with young and disruptive startup groups to develop hardware and software to power smart machines.
Rubin‘s vision for Polygrand Global was huge. He didn’t want his company to be limited to making a few products or even nurturing a few companies. Rubin and his colleagues envisioned a future focused on artificial intelligence and attempted to build the foundation of technology development through sponsored companies; Foundations that are freely available to others and eventually lead to the development of an ecosystem like Android. His new company was the booster of the idea; A structure that transformed basic concepts and ideas into products with maximum impact on the surrounding world. Playgrand was Rubin‘s first company in which there was no mention of robots (after Danger and Android), But they had a serious development in mind.
Essential was the last serious activity of Andy Rubin, which was closed in 2020
In 2015, Rubin‘s new company was able to receive 300 million in investments from Google, HP, Foxconn, Redpoint, Seagate, and Tencent. The attracted capital was spent on several projects, the most important of which is Owl Labs. Rubin finally left Polygrand in 2019.
Essential Products was Andy Rubin ‘s next entrepreneurial achievement. He decided to try his luck again in the world of mobiles and peripherals and in 2015, he launched the company. The Essential Phone and its accessories such as the 360-degree camera were one of the main products of the company. Rubin claimed that the Essential Phone will offer users a pure Android experience and will have the fastest software updates. Essential Phone was launched in 2017 and was well received by those interested in the Android ecosystem. Andy Rubin‘s lawsuit and scandal in 2017 caused him to leave Essential Management for a few months. Finally, the Palo Alto-based company announced in 2020 that it would no longer be operating.
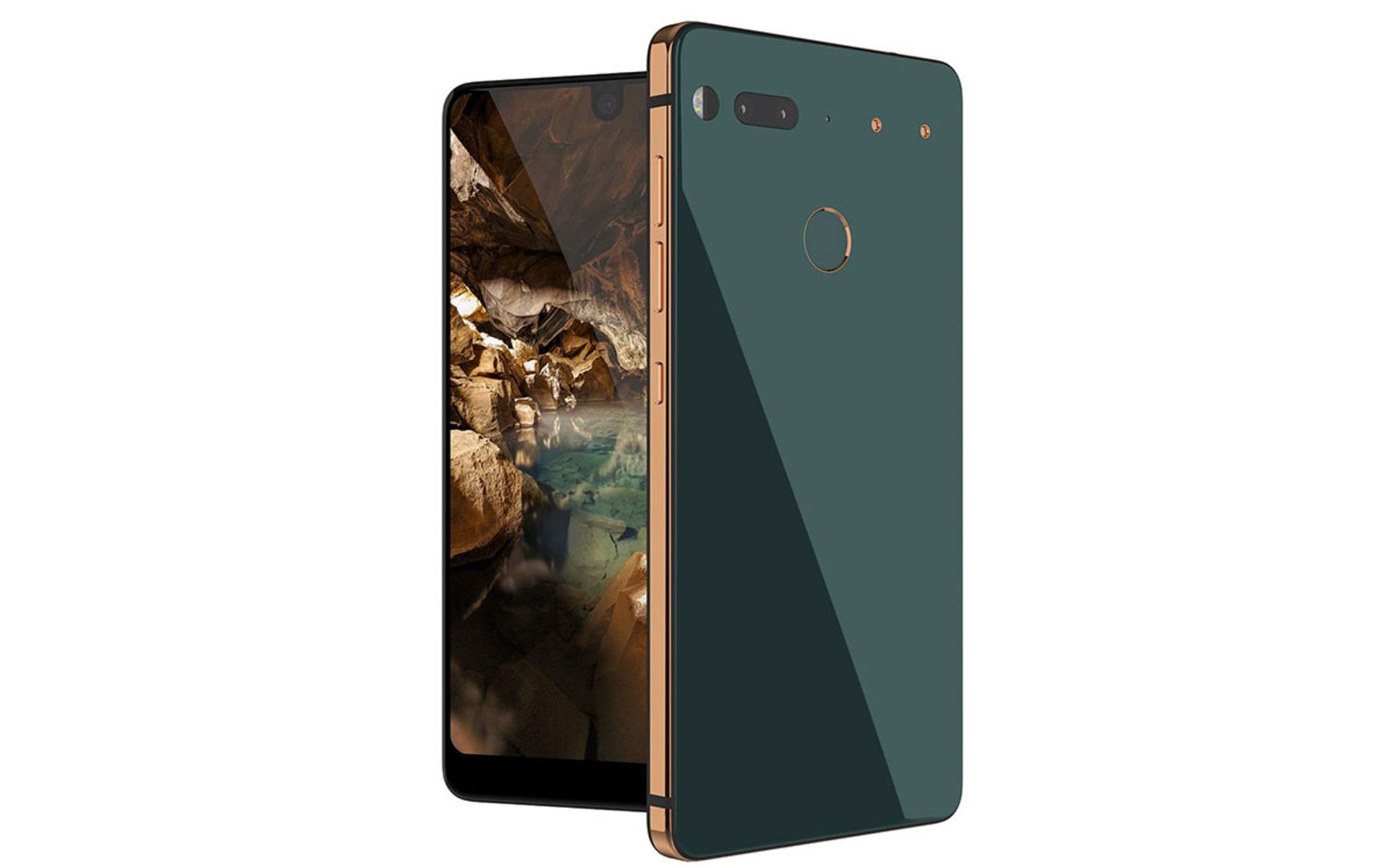 Essential Phone
Essential Phone
Personal life of Andy Rubin
In the story of Andy Rubin‘s departure from Google, we mentioned aspects of his personal life. Misbehavior with employees and leaked documents of Rubin ‘s sexual misconduct have tarnished his reputation alarmingly. She was married to Rei Hirabaru, but they divorced after a series of scandals and lawsuits. They had a coffee shop in Los Altos, California that closed in 2018.
Rubin and his ex-wife lived in a house in Woodside, California, which they bought in 2014 for $23 million. That house was also sold in 2018 during the separation, But now Rubin lives in it. Apparently, he is now known only as a Redpoint Ventures company in terms of employment.
In the story of Rubin ‘s life, there is always a trace of robots. In the years he was active at Google, in addition to managing the Android team, he spent his leisure time designing and developing robots. Rubin had designed several robotic arms for tasks such as preparing coffee. He also had a remote-controlled helicopter that he flew around Google’s yard.
Andy Rubin is known today for a legendary achievement called Android; An operating system that was born with the aim of developing the open-source concept in the mobile world and was seen in all smart devices from cars to home assistants and even televisions. Rubin‘s personal life has somewhat eroded his credibility in various tech circles; But it still has a place next to the greats like Jobs, Torvalds, Gates, and others.


Starlink; Everything you need to know about SpaceX Satellite Internet


iOS 18 review: A smart update even without Apple’s intelligence


James Webb Space Telescope deepens cosmology’s biggest controversy


James Webb vs. Hubble


Everything you need to know about the Windows Blue Screen of Death


How to use iMessage on Android?


Xiaomi Glorimi M2 Max watch review; Alternative economic option for iPhone owners


Ten strange moons of the solar system


Can coffee consumption cause weight loss?


Designed in California, copied in the Soviet Union; The story of the first Soviet chip
Popular
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoWho has checked our Whatsapp profile viewed my Whatsapp August 2023
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoSecond WhatsApp , how to install and download dual WhatsApp August 2023
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoHow to use ChatGPT on Android and iOS
-



 AI2 years ago
AI2 years agoUber replaces human drivers with robots
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoThe best Android tablets 2023, buying guide
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoThe best photography cameras 2023, buying guide and price
-


 Humans2 years ago
Humans2 years agoCell Rover analyzes the inside of cells without destroying them
-


 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoHow to prevent automatic download of applications on Samsung phones