Space
Do the stars move in the sky and change their position?
Published
7 months agoon


Do the stars move in the sky and change their position?
The night sky is very dark, But it has its own beauty and those bright points that we call stars adorn the night sky. These stars are eternal stars and are located in fixed constellations, and their location does not change during a person’s life; Even humans who lived in the past saw constellations in the same way we see them and of course used other names to identify them. We now see what ancient humans saw as if the stars were always fixed and did not move, unlike the planets.
Have you ever seen animations made from the movements of galaxies? If you pay close attention, you will see that when these galaxies merge with each other or are affected by each other’s gravity, the stars move like bees to and fro. We all know that the stars also move; But can we never see them move? How fast are these stars moving? Can we ever notice their movement?
Of course, the stars move; But their distance from us is so great that we cannot notice their movement. For thousands of years, astronomers have studied the motion of the stars, calling it astrometry. They observe the stars closely and study how the stars move over many years. Astrometry has a long history and has been done since 190 BC. In 190 BC, Hipparchus, one of the famous astronomers, geographers and mathematicians from ancient Greece, prepared and arranged a long list of 850 bright stars in the sky along with their positions. One of the students of Hipparchus, named Ptolemy, made more observations of the sky and continued in the footsteps of his master. After many observations, he compiled a precious work called al-Majsti (Majsti).
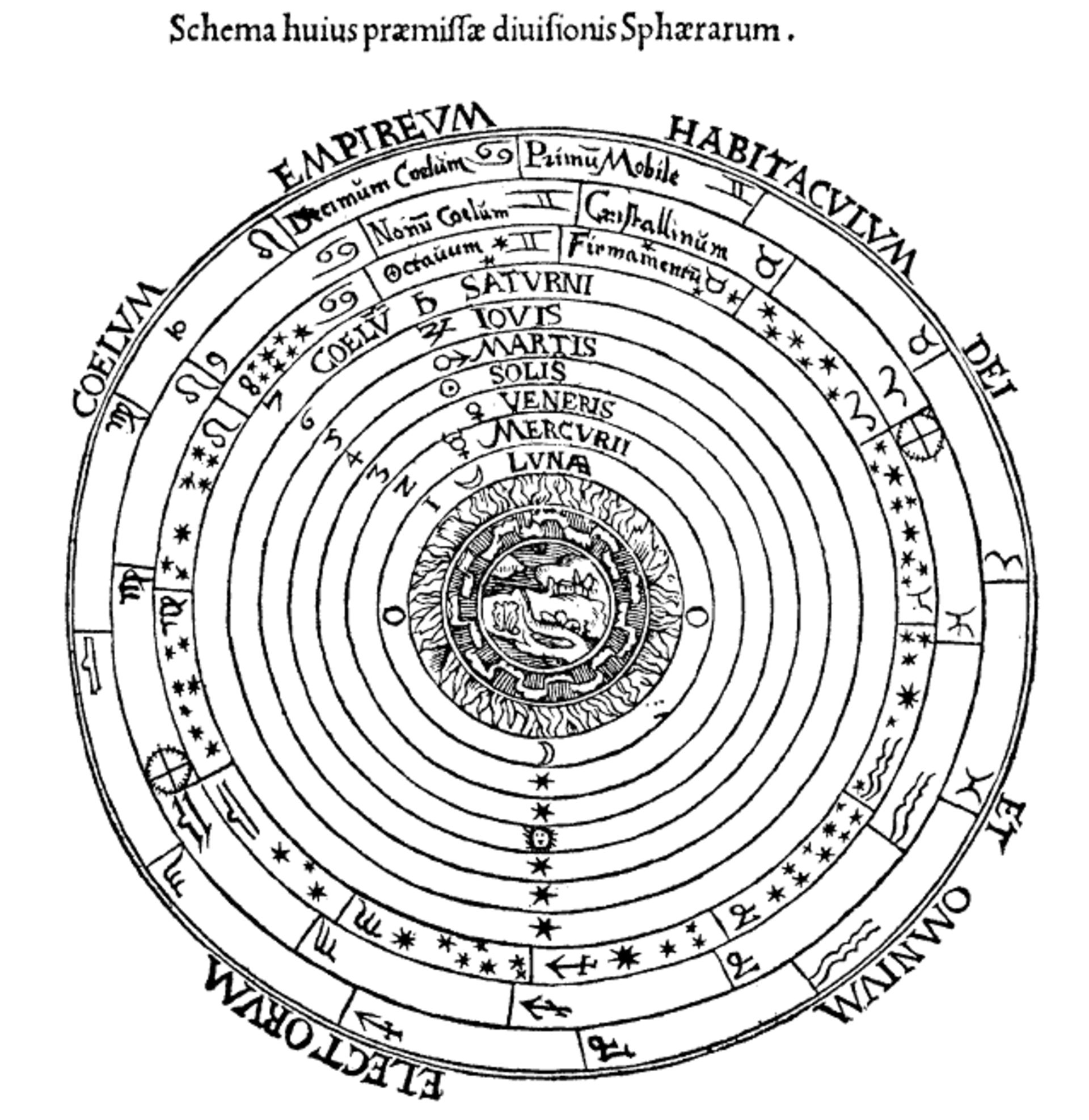
Ptolemy called the earth the center of the universe and stated that the stars, the sun, the moon, and other planets revolve around the earth concentrically. Of course, Ptolemy’s view of the world was wrong; But what is important is his precious writings in Kitab al-Majasti. Ptolemy was able to calculate and record the brightness and position of more than 1000 stars in the sky with extraordinary accuracy. A thousand years after Ptolemy, Abdulrahman Sufi, a prominent Iranian mathematician and astronomer, managed to make much more accurate measurements of the sky by means of an astrolabe.
Undoubtedly, one of the most famous astronomers in history is Tycho Brahe. An astronomer from Denmark, he was known by the people for his extraordinary ability to measure the position of the stars. At that time, Tyco Brahe succeeded in designing very precise instruments for tracking stars so that he could track many more stars. He was able to measure the position of the stars with an accuracy of 15 to 35 seconds of arc. In order to make a comparison with the accuracy of Tyco Brahe’s measurement, it is enough to know that a strand of human hair seen at a distance of 10 meters is equal to one second of arc. One interesting thing to know about Brahe is that he had no nose; In fact, Brahe lost his nose in a duel and designed a brass alloy artificial nose to replace it.
In 1807, Friedrich Bessel, a famous German astronomer, managed to calculate the distance of a nearby star called 61 Cygni or 61 chickens from the Earth for the first time. He used the parallax or parallax method to determine the distance between this star and the Earth. He acted in such a way that he considered the radius of the earth’s orbit around the sun as the base of a triangle and then observed the star. 6 months later, that is, when the earth was on the other side of its orbit with respect to the sun, he again observed the star he wanted. He knew that the stars move in the sky, after measuring this amount of displacement, he measured the distance between the two points of the earth’s orbit where the earth was located during the observation of the star, and then he was able to calculate the distance from the earth to that star. slow
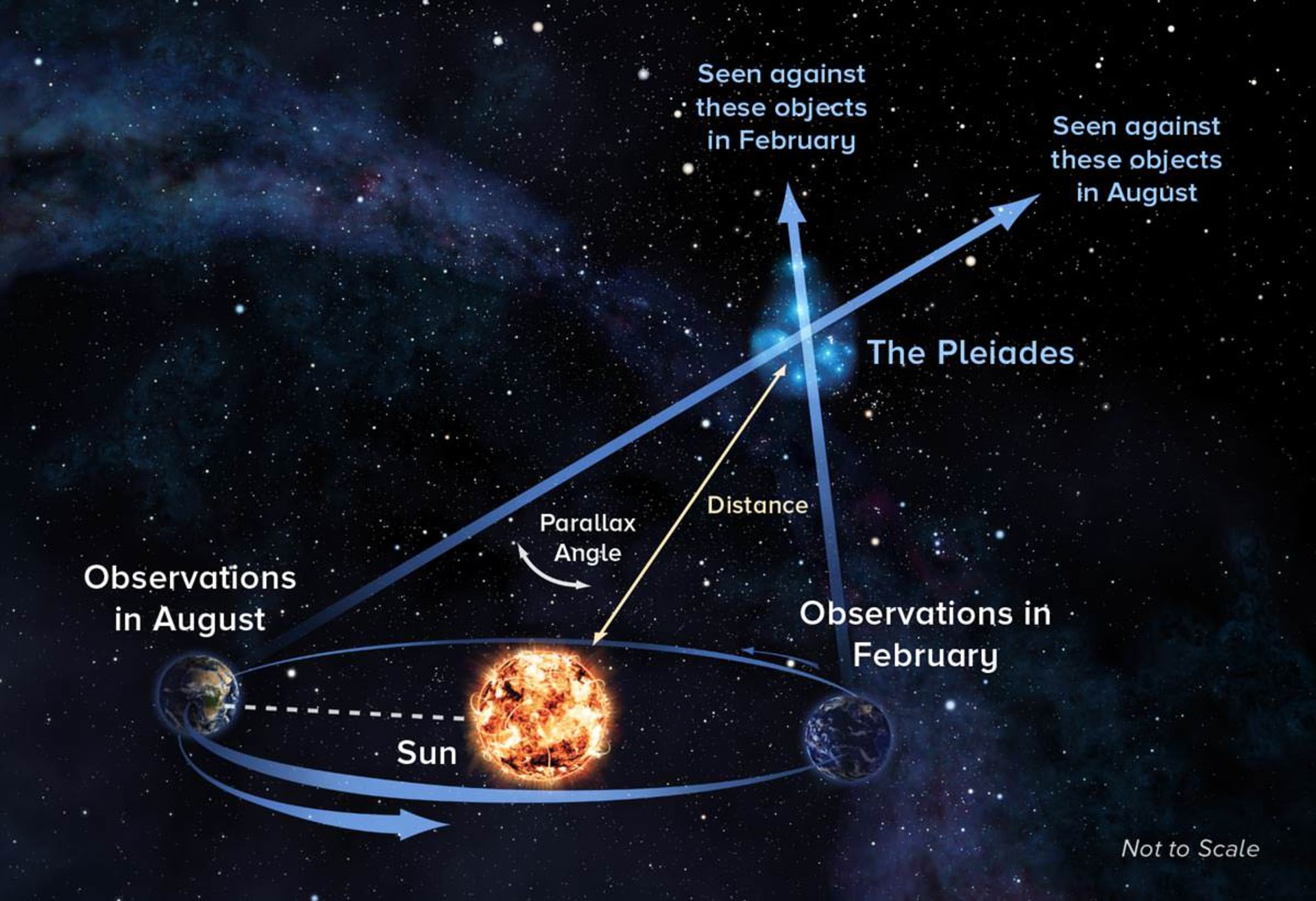
Two centuries after Friedrich Bessel, astronomers managed to develop this method and accurately calculate the distance of the stars from the Earth and the amount of their displacement; But in order to be able to accurately measure the displacement of the stars and observe them, we need to travel to space. In 1989, the European Space Agency launched a mission called Hipparchus, named after the Greek astronomer. The purpose of the mission was to measure the positions as well as the motions of nearby stars in the Milky Way. During this mission, Hipparchus was able to measure the positions and motions of 118,000 stars with high precision, paving the way for the calculation of another 2 million stars.
Hipparchus was an efficient mission and many astronomers used it; But this mission was not the best because shortly after the end of the mission, a new phenomenon named Gaia arrived.
In December 2013, the European Space Agency launched a new mission called Gaia (named after an ancient legend) to make such calculations for the billion stars in the Milky Way. Although one billion is a very big number, this only accounts for one percent of the stars in the Milky Way. Gaia will soon complete the calculations for 150 million stars and tell us everything that has happened over time. This is a huge achievement and one that Hipparchus would probably be proud of.
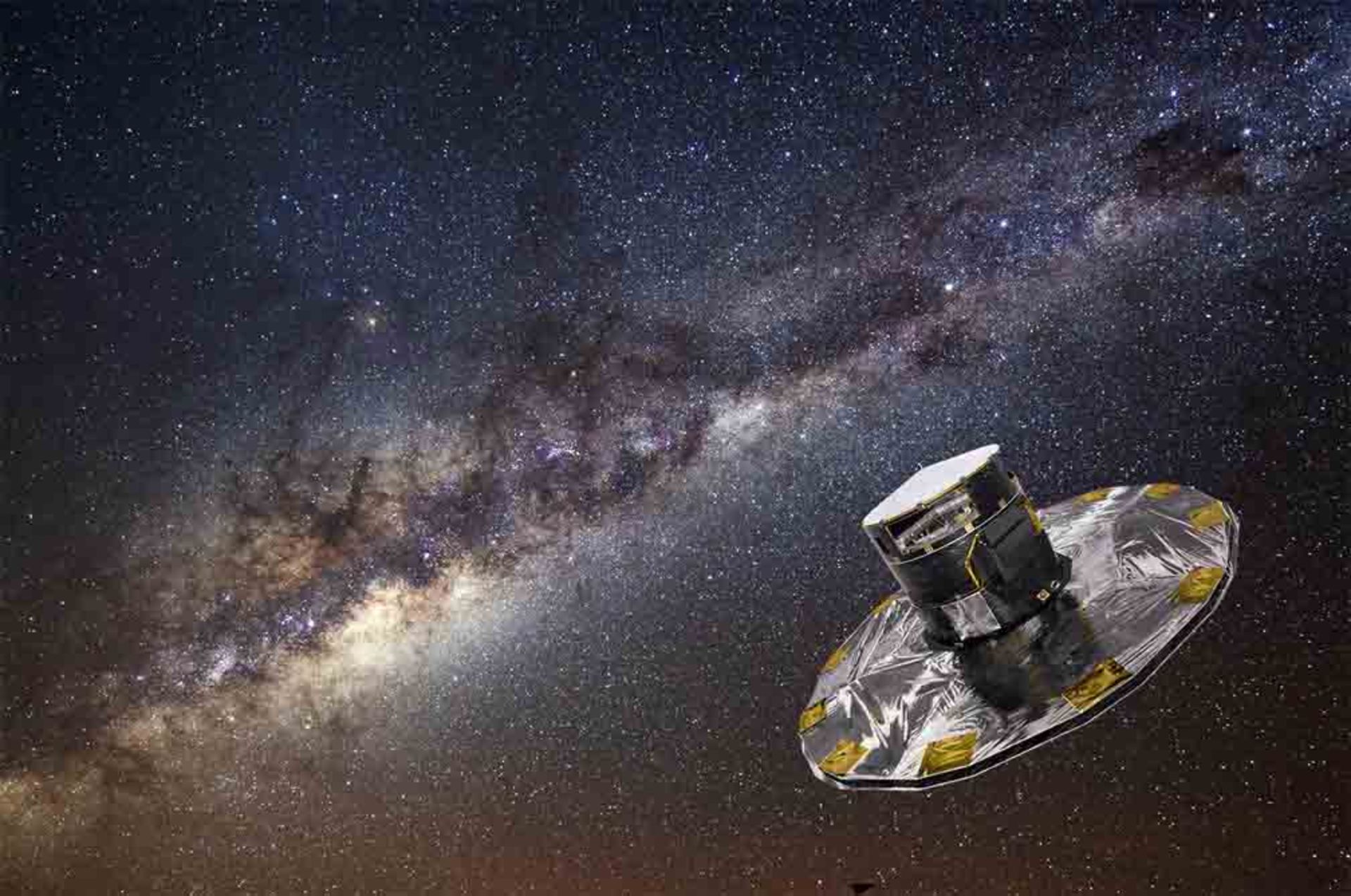

These precise measurements, which took several years, show us how the stars move in the sky. Of course, the movement of the stars cannot be detected with the naked eye, and it may take thousands or tens of thousands of years for a star to slightly change its position in the sky. For example, consider the constellation Ursa Major (the Great Bear); If you could travel back in time or into the future, you would see the stars in this constellation change position, or you might not even be able to recognize this constellation.
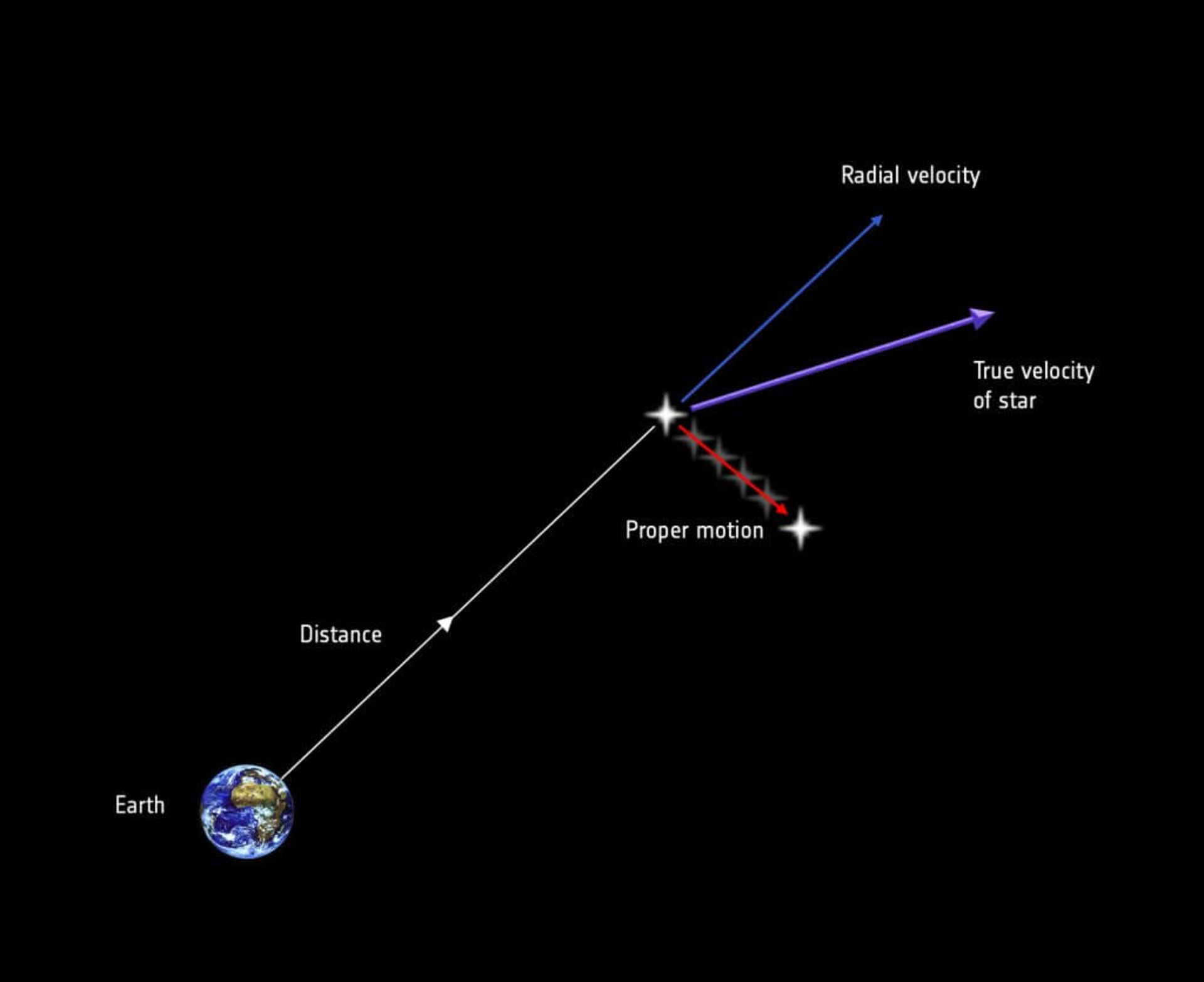
When a star moves in one direction in the sky, astronomers call this type of motion ” relative displacement “. The speed of movement of a star in the sky is usually 0.1 seconds of arc per year. This amount is not visible at all; But over the course of 2,000 years, the star can move about half a degree across the sky, or in other words, it can move across the sky as wide as the Moon. The fastest relative displacement is that of Bernard’s Star, which moves across the sky at a speed of 10.25 arcseconds per year, and after 2000 years, it can move as much as 5.5 degrees or 11 times the width of your hand.

When a star moves closer or farther away from us, astronomers say that the star has accelerated radially. They calculate the star’s radial velocity using the Doppler effect . When a star approaches us, the light that reaches us from that star tends towards the blue wavelength, and if that star moves away from us, we see that its light tends towards the red wavelength at the end of the spectrum. This phenomenon is called redshift, which has many uses in astronomy. By taking into account the redshift as well as the relative displacement of a star, we can calculate the path a star has taken in the sky with very high precision. In fact, this is one of the applications of the Doppler effect in astronomy, and another application of the Doppler effect is that it shows us that the universe we live in is expanding.
Read More: Why was Pluto removed from the list of planets in the solar system?
We know that the dwarf star Hipparchus 85605 is moving towards us at a very high speed. This star is currently 16 light years away from us; But by the next 100,000 years, this distance will reach 13 light years (8,200 times the distance of Earth from the Sun). The approach of the star does not directly affect us, But its gravitational effect can take some of the comets that are in the Oort cloud region out of orbit and send them toward the solar system.
The movement of the stars is relatively gentle; But as they move in their orbit around the center of the Milky Way galaxy, they interact gravitationally with each other and may collide. Most stars move slowly, But there are phenomena in the universe that make the stars move at a very high speed.
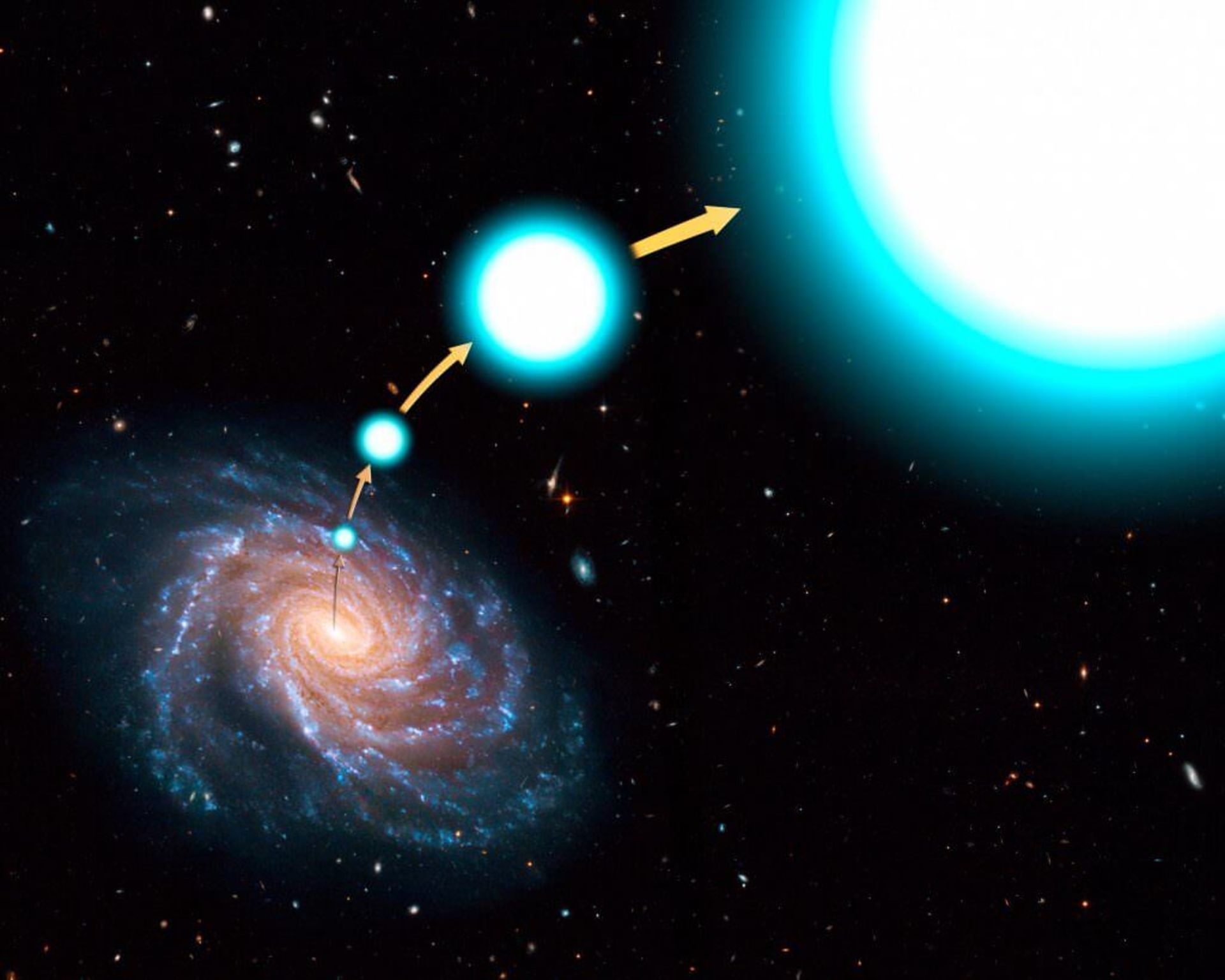
When a pair of stars get very close to the supermassive black hole cloud at the center of the Milky Way galaxy, one of them gets caught in the black hole’s gravity; But the other star is accelerated and thrown without causing the slightest change in the mass of the other. Once every 100,000 years, a star is ejected from the center of the Milky Way due to being in such a situation.
A similar thing happens when a small star orbits a larger star. Over time, the big star becomes ever bigger and becomes a red giant, and a supernova explosion occurs. It is at this point that the smaller star, like a stone thrown from a rock hook, will no longer be affected by gravity and will be thrown towards the boundless space at an extraordinary speed. Astronomers have found that these stars are moving at a speed of 1.1 million kilometers per hour towards the center of the Milky Way galaxy.
All the movements we have talked about had a natural origin; But imagine that in the future, human civilization or other civilizations will be advanced enough to move a star in different directions at will. In 1987, a Russian astrophysicist named Leonid Shkadov presented a very advanced method by which scientists could move a star at a slow speed. Of course, this was a very imaginative hypothesis; But it is not impossible to do. The method presented by Shkadov was such that a very large mirror was placed on one side of the star and the star itself could act as an accelerator. Photons hitting the mirror from the star were reflected, creating a momentum similar to a solar sail.
The mirror that is made must be big enough to have a gravitational interaction with the star and overcome it, But the light can create enough pressure to prevent the star from moving toward the mirror. This can create a very weak but steady push on the other side of the star, moving it in any direction our civilization wants. It may take billions of years for the star to settle in the desired position, But it is possible to do this in the future.
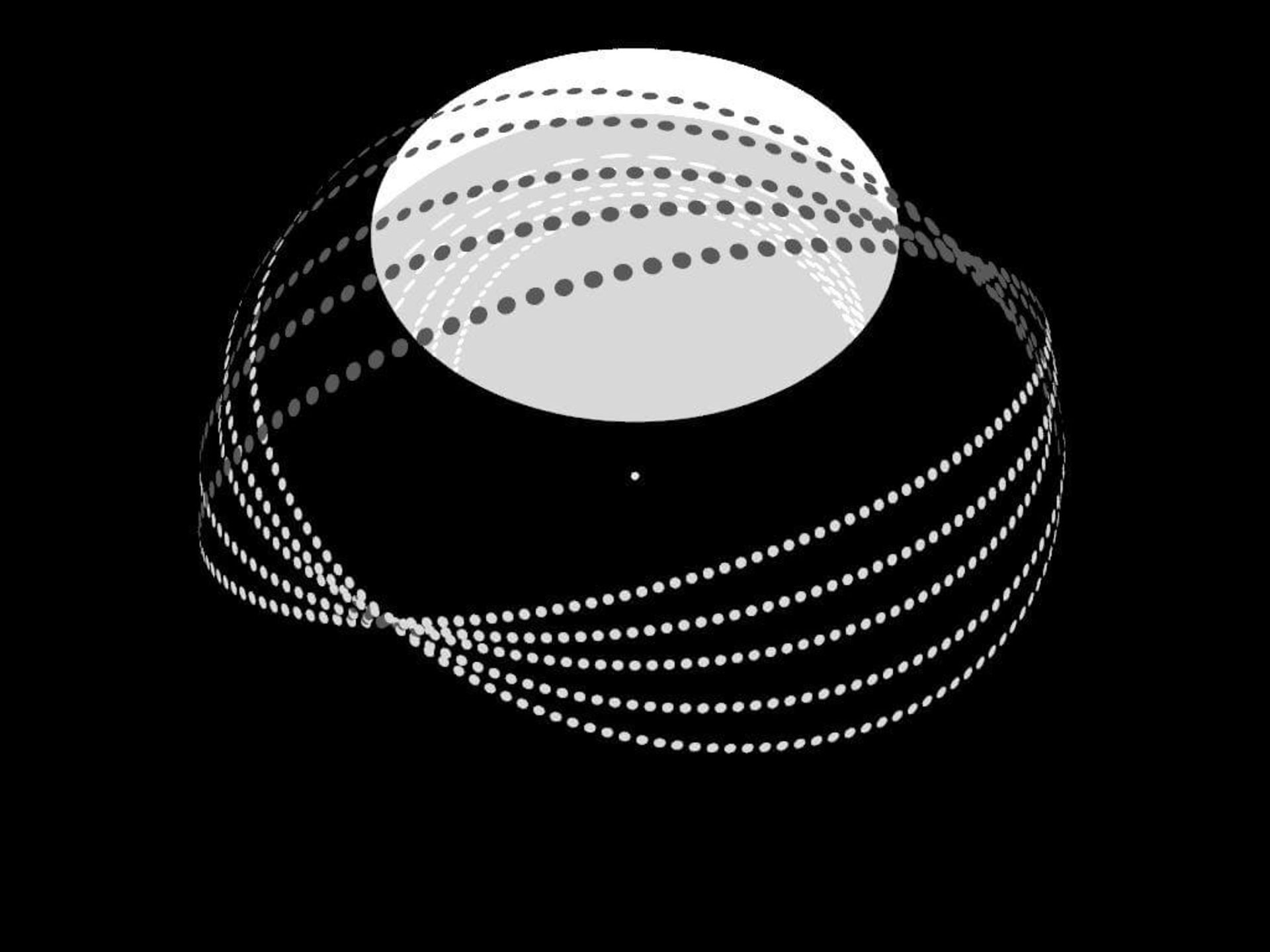
Those who are able to do such a thing will be a type 3 civilization. A Type 3 civilization could control vast swaths of the Milky Way galaxy, harness and control the energy of billions of stars, and continue to expand its empire. It is possible that this civilization could gather all the stars together in a sphere or place them in a flat disk to minimize communication time. Astronomers are now looking for galaxies that are under the control of a Type 3 civilization. Such galaxies can be seen at visible wavelengths; But unfortunately, we have not managed to observe one of them, which of course is normal; Because the galaxies that are in this world are very far from us and we cannot observe some of them.
Our lifespan as humans is limited and that is why we think that the stars are fixed in the sky and do not move; But if you can speed up time, you will see that everything in the sky is moving and the stars are moving back and forth like airplanes. Unfortunately, limited life does not allow us to enjoy this beautiful view.


You may like


Why is it still difficult to land on the moon?
This year, the private company Spacel and the Indian Space Organization both met tragic ends when they tried to land their spacecraft on the surface of the moon. Despite the astonishing leaps made in recent decades in computing, artificial intelligence and other technologies, it seems that landing on the moon should be easier now; But recent setbacks show that we still have a long way to go with safe and trouble-free landings on the surface of Earth’s only moon.
50 years after sending the first man to the surface of the moon, the question arises as to why safely landing a spacecraft on Earth’s nearest cosmic neighbor is still a difficult task for space agencies and private space companies. Stay with Zoomit to check the answer to this question.
Why is the lunar landing associated with 15 minutes of fear?
Despite the complexities of any space mission, sending an object from Earth into orbit around the moon today is easy. Christopher Riley, the director of the documentary film In the Shadow of the Moon produced in 2007 and the author of the book Where We Stood (2019), both of which are about the history of the Apollo 11 mission, explained the reasons for the difficulty of landing on the moon in an interview with Digital Trends. is According to him: “Today, the paths between the Earth and the Moon are well known, and it is easy to predict them and fly inside them.”

Chandrayaan 2 mission launch
However, the real challenge is getting the spacecraft out of orbit and landing it on the lunar surface; Because there is a delay in the communication between the Earth and the Moon, and the people in the control room who are present on the Earth cannot manually control the spacecraft in order to land it safely on the Moon. As a result, the spacecraft must descend automatically, and to do so, it will fire its descent engines to slow its speed from thousands of kilometers per hour to about one meter per second, in order to make a safe landing on the lunar surface.
For this reason, the director of the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO), who was trying to land the Vikram lander last month, described the final descent of the spacecraft as “frightening 15 minutes”; Because as soon as the spacecraft enters the landing stage, the control of its status is out of the hands of the mission control members. They can only watch the spacecraft land and hope that everything goes according to plan, that hundreds of commands are executed correctly, and that the automatic landing systems gently bring the spacecraft closer to the surface of the moon.
The Great Unknown: The Landing Surface
One of the biggest challenges in the final descent phase is identifying the type of landing site. Despite the availability of instruments such as the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) that can capture amazing views of the lunar surface, it is still difficult to know what kind of surface the spacecraft will encounter when it lands on the moon.
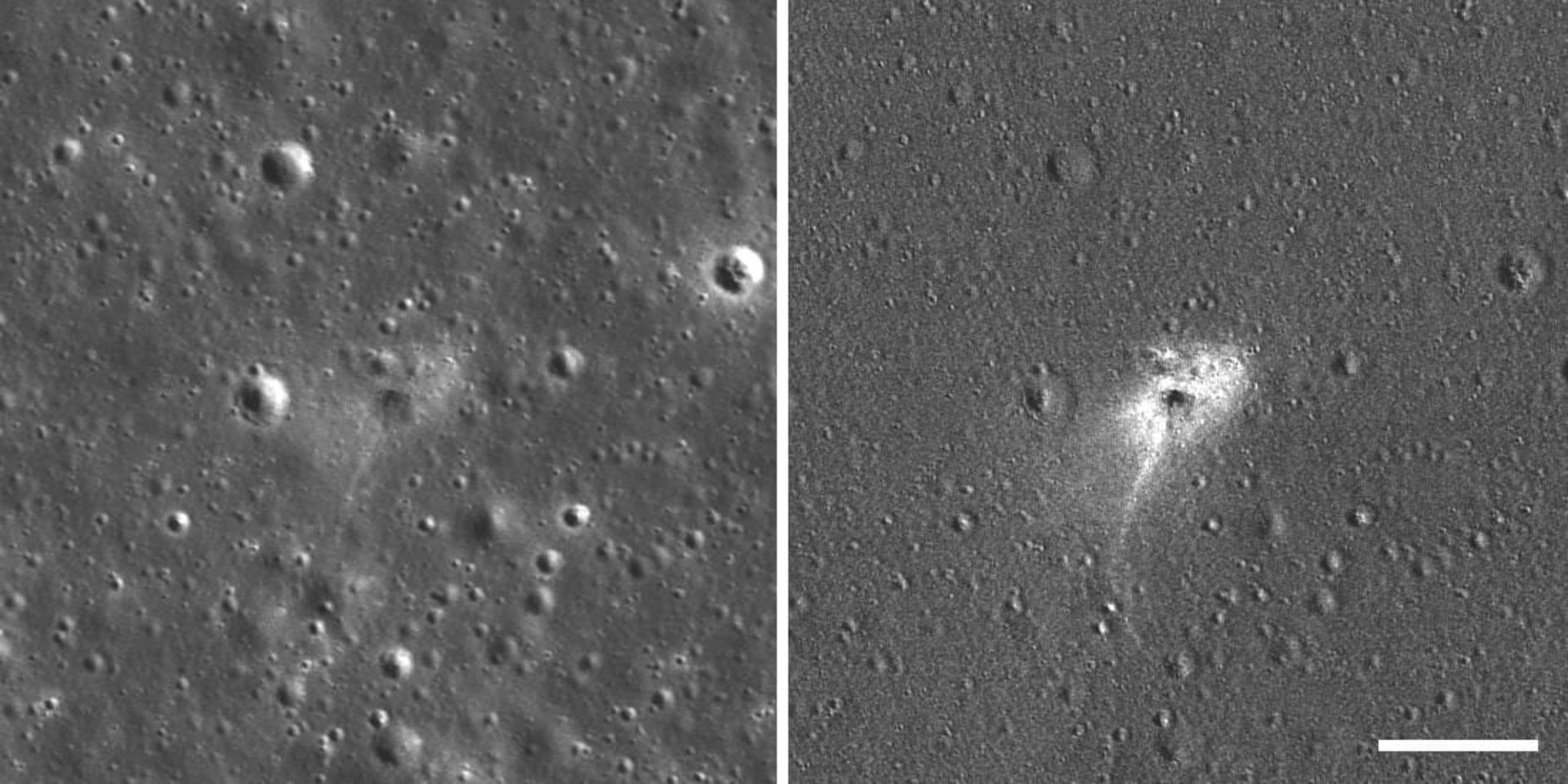

Left: Breshit crash site. Right: The ratio of the before and after images highlights the occurrence of minor changes in surface brightness.
Leonard David, author of Moon Fever: The New Space Race (2019) and veteran space reporter, says:
The Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter is a very valuable asset that has performed really well over the years; But when you get a few meters above the surface of the moon, complications appear that cannot be seen even with the very powerful LRO camera.
Even today, despite the imaging data available, “some landing sites still have unknown remains,” Riley says. He notes that the Apollo 11 mission included an advantage that today’s unmanned landers lack, which is the presence of an astronaut’s observer’s eyes that can closely observe the surface of the spacecraft’s landing site. As you probably know, in the mission that led to the landing of the first man on the surface of the moon, the Eagle computer was guiding the spacecraft to a place full of boulders; But to avoid hitting the rocky surface of the moon, Armstrong took control of the spacecraft himself and landed it on a flat surface.
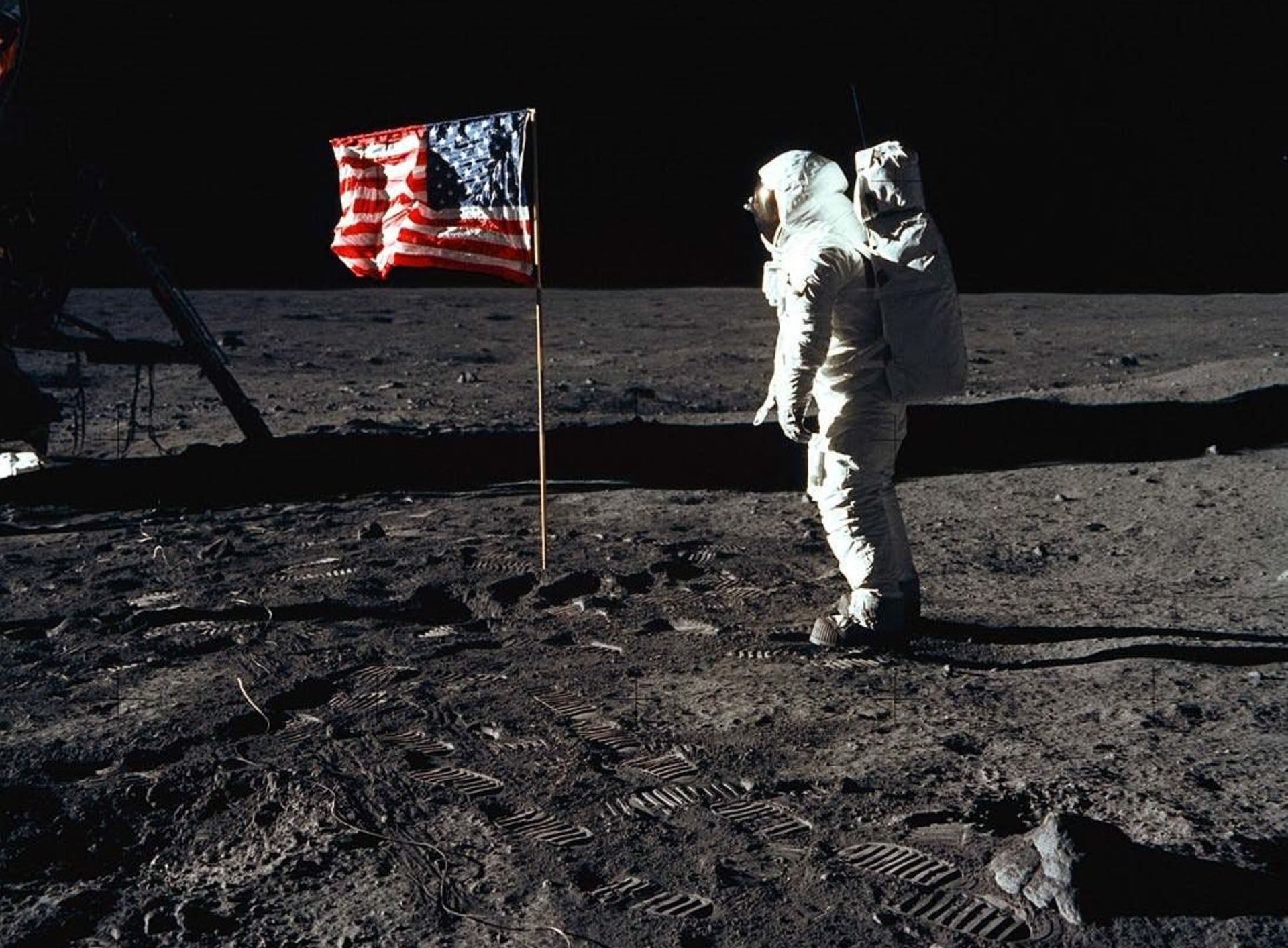

The uneven surface of the landing site had caused many problems in previous lunar missions such as Apollo 15. In this mission, the astronauts were told that as soon as the spacecraft touched the surface of the moon, they should turn off the engines to prevent dust from being sucked in and the risk of a return explosion. But the Apollo 15 spacecraft landed in a crater, and because of this, one of its legs came into contact with the surface earlier than the others. When the crew shut down the engines, the spacecraft, moving at a speed of 1.2 meters per second, experienced a hard landing. The lander landed at an oblique angle, and although it eventually landed safely, it nearly overturned, causing a fatal disaster.
- Half a century after Apollo 11; How did the great human leap happen?
- dust storms; The nightmare of space missions to the moon
The difficult landing of Apollo 15 introduced another complicating factor in lunar landings: lunar dust. The Earth’s moon is covered with dust that is thrown into the air by any movement and sticks to everything it comes in contact with. As the spacecraft approaches the surface of the moon, huge plumes of dust are kicked up that limit the field of view and endanger the spacecraft’s electronics and other systems. We still do not have a solution to deal with the dust problem.
An achievement that has been achieved before
Another reason why the moon landing remains a challenge is that gaining public support for lunar projects seems difficult. Referring to Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin, the two astronauts who walked on the moon during the Apollo 11 mission, David says, “We convinced ourselves that we had sent Neil and Buzz [to the surface of the moon]; “As a result, when it comes to lunar missions, people may say we’ve been there before and we’ve had this success.”

But in reality, our understanding of the moon is still very little, especially in relation to long-term missions. Now, with a 50-year gap between the Apollo missions and NASA’s upcoming Artemis project, the knowledge gained has been lost as engineers and specialists retire. David says:
We need to recover our ability to travel into deep space. We haven’t gone beyond near-Earth orbit since Apollo 17 and since 1972. NASA is no longer the same organization that put men on the moon, and there is a whole new generation of mission operators.
The importance of redundancy
As the first private spacecraft entered into orbit around the moon, the Space project was of considerable importance; But its failure to land smoothly on the surface of the moon made the achievement of landing on the surface of the moon still remain in the hands of governments. However, we can expect more private companies, such as Jeff Bezos ‘ Blue Origin, which is developing its lunar lander, to target the moon in the future. According to Elon Musk, even the giant SpaceX Starship spacecraft, which is being built with the ultimate goal of sending a human mission to Mars , can also land on the moon.
According to David, private companies’ participation in lunar landings has advantages such as increased innovation. However, companies are under pressure to save money, and this can lead to a lack of redundancy and support systems that are essential in the event of errors and malfunctions. Lunar rovers typically include two or even three layers of support systems. David is concerned that private companies will be encouraged to eliminate these redundancies in order to cut costs and save money.
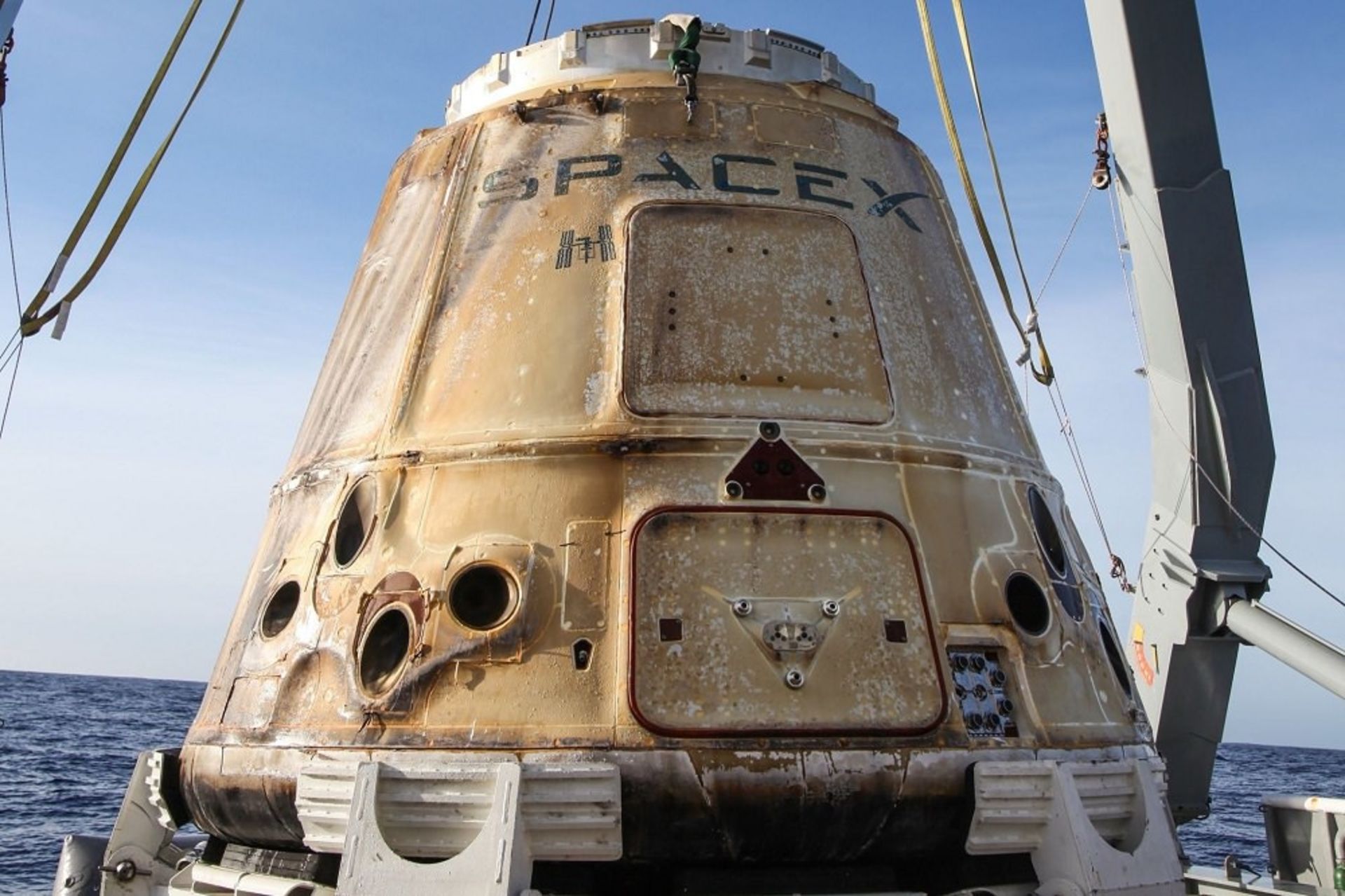

Crew Dragon SpaceX passenger capsule
“We saw Elon Musk’s Dragon capsule catch fire after a failed test on the stand,” says David, referring to the explosion of the SpaceX spacecraft in April, which had no crew on board. “This accident was kind of a wake-up call about how unpredictable the performance of spacecraft can be.” David compared the Crew Dragon incident to the Apollo 1 disaster, which killed three NASA astronauts during a test launch in 1967.
Another problem related to the lack of redundancy systems is the lack of information needed when an error occurs. As for the recent landings, it seems that the SpaceX crash was caused by human error; however, it is not clear what caused the failure of Chandrayaan 2 in the calm landing, and it is possible that without the necessary systems to record and send information to the lander, we will never find out the main reason for the failure of this mission. Without the required data, it becomes much more difficult to prevent problems from reoccurring in the future.
The future of lunar landings
Currently, many projects are underway to facilitate future moon landings. Ultimately, we need to be able to build the necessary infrastructure for a long-term stay on the moon.
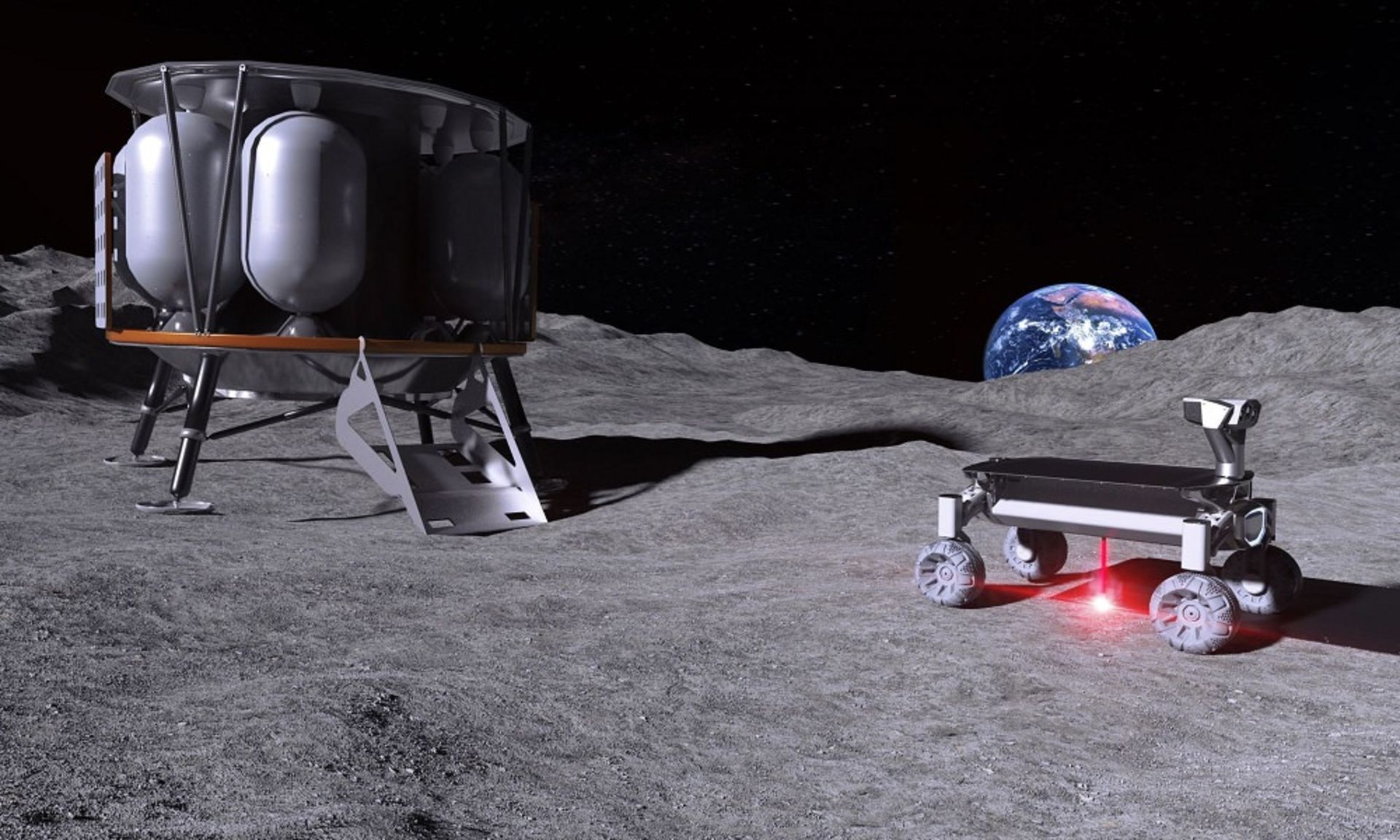

Conceptual design of Moonrise technology on the moon. On the left side is the Alina lunar module, and on the right side, the lunar rover equipped with Moonrise technology melts the lunar soil with the help of a laser.
If we can make long-term stays on the moon possible, or even build a permanent base there, landing spacecraft on the lunar surface will be much easier. By constructing the landing sites, a flat, safe, and free surface of unknown debris can be created for the landing of surface occupants. For example, researchers are currently conducting research at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center to investigate the feasibility of using microwaves to melt the lunar soil (regolith) and turn it into a hard foundation so that it can be used as a landing and launch site. The European Space Agency is also investigating how to use 3D printing to create landing sites and other infrastructure on the moon.
Read more: Europa Clipper, NASA’s flagship probe was launched
Other ideas include the use of lidar remote sensing systems, which are similar to radar systems; But instead of radio waves, it uses lasers to land the spacecraft. Lidar technology provides more accurate readings and uses a network of GPS satellites to help guide the spacecraft during landing.
The problem of public support
As important as technology is, public interest and support are essential to the success of the lunar landing program. “Apollo had enormous resources that are perhaps only comparable today to China’s space program,” says Riley. “Remember that Apollo carried the best computer imaginable, the human brain.” It goes without saying that there is an element of luck involved in every landing.

US Vice President Mike Pence speaking at the 50th anniversary of the Apollo 11 mission
Finally, there is the question of what kind of failure is acceptable for people. David says:
I think we have to be serious about the fact that we’re probably going to lose people. There is a serious possibility that the manned lunar lander will crash and kill the astronauts inside. The American people continued to support NASA despite the failures and bad luck of the Apollo program, But at that time there was a lot of pressure to compete with the Soviet Union. Without the bipolar atmosphere of the Cold War and the space race, would people still support missions with human lives in between?
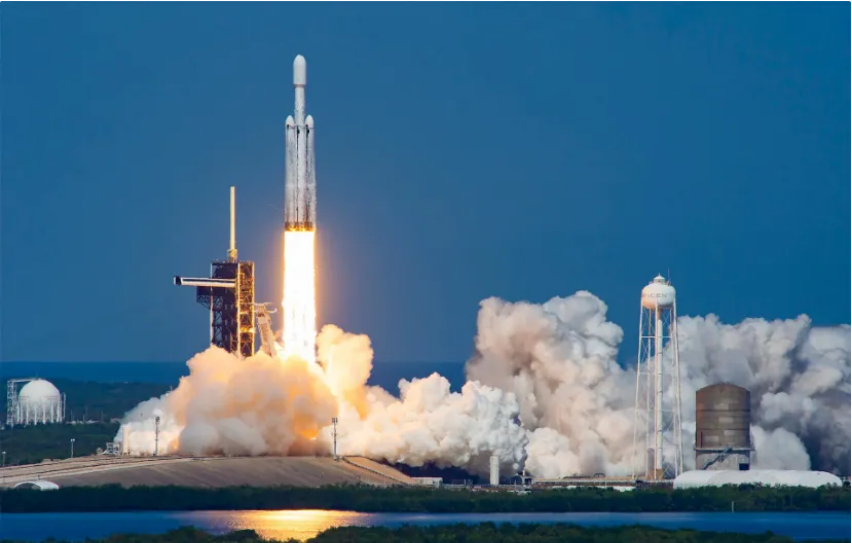


Europa Clipper, NASA’s flagship probe was launched
After years of waiting, NASA’s Europa Clipper probe was finally launched on Monday at 7:36 p.m. Iran time from the Kennedy Space Center on top of SpaceX’s Falcon Heavy rocket and began a major astrobiology mission to Europa, the potentially habitable moon of Jupiter.
As SpaceX’s massive rocket powered by 27 powerful Merlin engines lifted off from pad 39A, NASA live broadcast reporter Dron Neal said, “The launch of Falcon Heavy with Europa Clipper will reveal the secrets of the vast ocean beneath the icy crust of Europa, Jupiter’s moon. It has been hidden, it will reveal.”
The engines of the two side boosters of the Falcon Heavy were shut down and separated from the central booster approximately three minutes after the flight. The central booster continued to fly for another minute, and then in the fourth minute of the launch, the separation of the upper stage from the first stage was confirmed. Finally, 58 minutes later, Europa Clipper was injected into interplanetary orbit as scheduled. A few minutes later, the mission team made contact with the probe, and people in the control room cheered and applauded.
Falcon Heavy’s unique launch
The launch of NASA’s new probe was delayed due to some mishaps. NASA and SpaceX initially planned to launch the Europa Clipper mission on Thursday, October 10; But with powerful Hurricane Milton hitting Florida’s Gulf Coast on Wednesday evening, a delay in the launch became inevitable. NASA shut down Kennedy Space Center to deal with the storm, and Europa Clipper was placed inside SpaceX’s hangar near Launch Pad 39A.
The recent launch was Falcon Heavy’s 11th flight overall and its second interplanetary mission. Also, this was the first flight of the Falcon Heavy, when all three boosters of the first stage of the rocket were deployed.
Typically, the Falcon Heavy and Falcon 9 first-stage boosters store enough fuel to perform landing maneuvers for recovery and reuse in the future; But Europa Clipper needed all the power that Falcon Heavy could provide in order to make it on its way to the Jupiter system.
A long way to the launch pad
In late 2015, the US Congress directed NASA to launch Europa Clipper using the Space Launch System (SLS), NASA’s massive rocket. SLS was still under construction at the time and was several years away from reaching the launch pad. The delay in completing the construction of this powerful rocket and NASA’s need to assign at least the first three versions of SLS to the Artemis lunar mission caused the Europa Clipper launch date to be in an aura of uncertainty.
In the 2021 House budget draft for NASA, the agency was directed to launch Europa Clipper by 2025 and, if possible, with SLS. However, due to the unavailability of the Space Launch System, NASA had to go to SpaceX’s Falcon Heavy. This decision was not without cost. As the most powerful rocket ever used in an operational mission, SLS can send Europa Clipper directly to the Jupiter system in less than three years.
Europa Clipper will use the gravitational assistance of Mars and Earth on its way to the Jupiter system
Now, even in Falcon Heavy’s fully disposable mode, the Clipper’s trip to Europe takes almost twice as long. The probe should make a flyby of Mars in February 2025 and a flyby of Earth in December 2026 to gain enough speed to reach its destination in April 2030.
Missile problems were not the only obstacles facing Europa Clipper on its way to the launch pad. For example, the rising costs of this five billion dollar probe forced NASA to cancel the construction of one of the probe’s science instruments. This instrument, named “Identification of Europa’s internal features using a magnetometer” (ICEMAG), was designed to measure Europa’s magnetic field.
Then in May 2024, NASA found that transistors similar to those used in Europa Clipper, which are responsible for regulating the probe’s electricity, were “failing at lower-than-expected radiation doses.” Following this discovery, NASA conducted more tests on the transistors and finally concluded in late August that these components could support the initial mission in the radiation-rich environment around Jupiter.
Ambitious mission to a fascinating moon

NASA/Jet Propulsion Laboratory-Caltech
Europa Clipper is one of NASA’s most exciting and ambitious flagship missions, and it has impressive features. For example, the mission probe is the largest spacecraft NASA has ever built for a planetary mission. Europa Clipper weighed almost 6,000 kg at the time of launch and will be more than 30 meters long (bigger than a basketball court) by opening its huge solar panels in space.
Clipper’s Europa destination is also a prominent location: Europa, one of Jupiter’s four Galilean moons. The moon is covered with an icy outer shell, which scientists believe hides a vast ocean of salty liquid water. For this reason, Europa is considered one of the best places in the solar system to support alien life.
In early 2012, studies began to look for potential plumes of water rising from Europa’s surface. Some researchers theorize that those water columns and vents from which the columns protrude may contain evidence of life living beneath the moon’s icy crust. However, NASA scientists have made it clear that Europa Clipper is not looking for extraterrestrial life in Europa; Rather, this probe will only investigate the potential of the submoon water environment to support life.
“If there’s life on Europa, it’s going to be under the ocean,” Bonnie Buratti, senior Europa Clipper scientist at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, said in September. As a result, we cannot see it.” “We will be looking for organic chemicals that are prerequisites for life on the surface of the moon,” Borrati added. There are things we can observe; such as DNA or RNA; But we don’t expect to see them. As a result, [the probe] is only looking for habitable environments and evidence for the ingredients of life, rather than life itself.”
NASA scientists have made it clear that Europa Clipper is not looking for extraterrestrial life in Europa
Europa Clipper will collect data using a suite of nine scientific instruments, including visible and thermal cameras, several spectrometers, and special equipment to identify Europa’s magnetic environment. As stated on NASA’s Europa Clipper page, the probe will help scientists achieve three main goals:
- Determining the thickness of Europa’s ice sheet and understanding how Europa’s ocean interacts with the lunar surface.
- Investigating the composition of Europa’s ocean to determine whether it has the materials necessary to form and sustain life.
- Studying the formation of Europe’s surface features and discovering signs of recent geological activities; such as the sliding of crustal plates or the discharge of water columns in space.
Europa Clipper also transports Earth’s culture to the Solar System. A piece called “In Praise of Mystery: A Poem for Europe” by Edda Lemon, a famous American poet, is engraved in the artist’s own handwriting on a metal plate. In addition, the probe carries a coin-sized chip that contains the names of 2.6 million inhabitants of planet Earth.
6-year journey

Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics
If all goes according to plan, Europa Clipper will enter Jupiter’s orbit in April 2030. When the probe gets there, it will use up 50-60% of its 2,722 kg of fuel by performing an injection maneuver for 6-8 hours.
The injection maneuver puts Europa Clipper in an elliptical orbit around the gas giant. A series of long maneuvers will then be performed to align the trajectory so that the probe can fly by Europa more than 45 times and study it closely. In fact, Europa Clipper will remain around Jupiter throughout its mission; Because according to the launch environment of Europa, it will be very dangerous for the spacecraft to go around the moon.
If all goes according to plan, Europa Clipper will enter Jupiter’s orbit in April 2030
The first flight over Europe will not take place before the spring of 2031. NASA will use the first pass to make further corrections to Europa Clipper’s trajectory in preparation for the probe’s first science mission. With the start of scientific flybys in May 2031, Europa Clipper will aim its array of sensors towards the far hemisphere from Jupiter and will approach the surface of the moon up to 25 km. The second science campaign will begin two years later, in May 2033, in the Jupiter-facing hemisphere of Europa.
The end of the Europa Clipper mission is set for September 2034. At that time, NASA will crash the spacecraft into Ganymede, another Galilean moon of Jupiter. This disposal strategy was chosen because Ganymede is considered a relatively poor candidate to host life, and the mission team wanted to make sure they did not contaminate potentially life-hosting Europa with terrestrial microbes.
Space
Dark matter and ordinary matter can interact without gravity!
Published
3 weeks agoon
01/10/2024

Preposition: For each; per.
Noun: A topology name.
Noun: which has mass but which does not readily interact with normal matter except through gravitational effects.
Adverb: Beyond all others.
Preposition: For each; per.
Noun: A topology name.
Dark matter and ordinary matter can interact without gravity!
Why is dark matter associated with the adjective “dark”? Is it because it harbors some evil forces of the universe or hidden secrets that scientists don’t want us to know? No, it is not. Such fanciful assumptions may sound appealing to a conspiracy theorist, but they are far from the truth.
Dark matter is called dark because it does not interact with light. So when dark matter and light collide, they pass each other. This is also why scientists have not been able to detect dark matter until now; it does not react to light.
Although it has mass and mass creates gravity, this means that dark matter can interact with normal matter and vice versa. Such interactions are rare, and gravity is the only known force that causes these two forms of matter to interact.
However, a new study suggests that dark matter and ordinary matter interact in ways other than gravity.
If this theory is correct, it shows that our existing models of dark matter are somewhat wrong. In addition, it can lead to the development of new and better tools for the detection of dark matter.
Read more: There is more than one way for planets to be born
A new missing link between dark and ordinary matter
Dark matter is believed to have about five times the mass of normal matter in our universe, which helps hold galaxies together and explains some of the motions of stars that don’t make sense based on the presence of visible matter alone.
For example, one of the strongest lines of evidence for the existence of dark matter is the observation of rotation curves in galaxies, which show that stars at the outer edges of spiral galaxies rotate at rates similar to those near the center. These observations indicate the presence of an invisible mass.
Also, for their study, the researchers studied six ultra-dim dwarf (UFD) galaxies located near the Milky Way. However, in terms of their mass, these galaxies have fewer stars than they should. This means they are mostly made up of dark matter.
According to the researchers, if dark matter and normal matter interact only through gravity, the stars in these UFDs should be denser in the centers and more spread out toward the edges of the galaxies. However, if they interact in other ways, the star distribution looks different.
The authors of the study ran computer simulations to investigate both possibilities. When they tested this for all six ultra-dim dwarf (UFD) galaxies, they found that the distribution of stars was uniform, meaning that the stars were spread evenly across the galaxies.
This was in contrast to what is generally observed for gravitational interactions between dark matter and normal matter.
What causes this interaction?
The results of the simulations showed that gravity is not the only force that can make dark matter and normal matter interact. Such an interaction has never been observed before, and it could change our understanding of dark matter and dark energy.
However, this study has a major limitation. What caused the interaction between the two forms of matter is still a mystery. While the current study provides tantalizing hints of a novel interaction, its exact nature and underlying causes remain unknown. Hopefully, further research will clarify the details of such interactions.
This study was published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.


Ancient humans survived the last ice age just fine


iPhone 16 Pro Review

Why is the colon cancer increasing in people younger than 50?

Why is it still difficult to land on the moon?


Biography of Geoffrey Hinton; The godfather of artificial intelligence


The Strawberry Project; The OpenAI artificial intelligence model


Everything you need to know about the Windows Blue Screen of Death


Starlink; Everything you need to know about SpaceX Satellite Internet


iOS 18 review: A smart update even without Apple’s intelligence


James Webb vs. Hubble
Popular
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoWho has checked our Whatsapp profile viewed my Whatsapp August 2023
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoSecond WhatsApp , how to install and download dual WhatsApp August 2023
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoHow to use ChatGPT on Android and iOS
-



 AI2 years ago
AI2 years agoUber replaces human drivers with robots
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoThe best Android tablets 2023, buying guide
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoThe best photography cameras 2023, buying guide and price
-


 Humans2 years ago
Humans2 years agoCell Rover analyzes the inside of cells without destroying them
-


 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoHow to prevent automatic download of applications on Samsung phones