Technology
Google brand story; From a small startup to ruling the web world
Published
2 weeks agoon


Proper noun: A search engine that popularized the company of the same name.
Preposition: For each; per.
Noun: A topology name.
Adverb: Beyond all others.
Preposition: For each; per.
Noun: A topology name.
Adverb: Beyond all others.
Preposition: For each; per.
Noun: A topology name.
Proper noun: A particular Internet company.
Proper noun: A search engine that popularized the company of the same name.
Proper noun: A particular Internet company.
Proper noun: A search engine that popularized the company of the same name.
Proper noun: A particular Internet company.
Proper noun: A search engine that popularized the company of the same name.
Proper noun: A particular Internet company.
Proper noun: A search engine that popularized the company of the same name.
Proper noun: A particular Internet company.
Proper noun: A search engine that popularized the company of the same name.
Google brand story; From a small startup to ruling the web world
The general public of the world cannot imagine removing Google services from their lives today. Regardless of the search engine or the Chrome browser, most of us set our programs on Google Calendar, and using Gmail, Google Drive, Google Docs, Google Maps, Google Photos, YouTube, and the like has become a daily habit for us.
Google’s role in shaping our relationship with the Internet world is undeniable. Many of this company’s products have known alternatives, But Google has designed its comprehensive and integrated ecosystem in such a way that we cannot easily abandon the use of all its applications and services.
This article was updated on the occasion of the anniversary of the establishment of Google on 14 September 1403.
But how dangerous will it be for technology companies to gain power at this level? Today’s opponents of Google are divided into several groups: some believe that Google is acting against the direction of freedom of expression by prioritizing certain search results. One group also argues that Google collects user data in a variety of ways that people are unaware of and that this data is not necessarily used in advertising.
For example, some activists of the de-Google movement say: “Spying on people at this level is not acceptable and should not be. “We need to control the technologies we interact with, not the other way around.”
But 26 years ago, before it came under the microscope of US antitrust cases and its empire was in danger of being disintegrated, the initial idea for founding the company was formed with a student project with the aim of facilitating people’s access to web information.
Back then, finding specific content on websites was more like exploring a disorganized library. Even the algorithms of the best search engines, such as Xcite and Altavista, often displayed scattered links in response to user queries that may or may not be related to the user’s search. In fact, finding what you were looking for was more like a game of chance. But Google changed everything.
Join us to review the story of the origin of the Google brand and its evolution.
Getting to know the founders of Google and the BackRub project
Larry Page and Sergey Brin met in the summer of 1995 at Stanford University’s doctoral student induction program, which included a tour around San Francisco. Both of them had just finished their master’s degree in computer science and were about to enter the doctoral degree with brilliant academic records.
Sergi Brin, who had a more social spirit, had volunteered to lead one of the student teams during the event. He had to show the university campus to the students and also lead the said recreational tour. Larry Page happened to be his bandmate and, contrary to expectations, their association during the camp was not pleasant for either of them.
According to Larry Page, Sergey Brin was too proud, while Sergey Brin considered Larry Page to be an unbearable person. They talked about urban infrastructure and social order for almost the entire camp and did not agree at any point.
Page later said in an interview: “We were arguing for a long time, Sergi had strong ideas and I think I was the same.” Sergiy Brin also confirmed his words and continued: “Both of us considered the other party hateful!” But the fact that we took time to discuss with each other showed that we also value thoughts.” They clearly complemented each other.
By the start of the first semester of their Ph.D., Page and Breen were no longer in contact and were working on their own projects and research. Page had learned from his father, a computer science professor at Michigan State, that a doctoral dissertation could determine the ultimate path of one’s academic career. When he approached his advisor, Terry Winograd, to decide on a thesis topic, he put more than 10 interesting ideas on his desk.
Larry Page had more than 10 different topics in mind for his thesis
However, Larry Page’s work did not start with researching the web search engine. Although Stanford graduates were getting rich founding Internet companies, Larry Page found the Web primarily interesting for its mathematical properties: each computer was a node, and each link on a Web page established a connection between nodes, something that a structure It showed classic graphics.
He says:
Computer scientists love graphs, and the World Wide Web could be the largest graph ever created.
Finally, with the consent of his mentor, Terry Winograd, Page began to examine the structure of web links. The point that disturbed his mind in the first stages of research was that although surfing the web from one page to another by following links was a simple and trivial task, few people paid attention to the reverse process, that is, the number of links behind each web page.
Larry Page in the BackRub project was looking for a way to count and determine the importance of each backlink on the web
Page thought that knowing which pages were linking to which pages would have many potential uses. This research led him to BackRub, a project focused on backlinks: perhaps if he could find a way to count and determine the importance of each backlink on the web, the web would become a more valuable place.
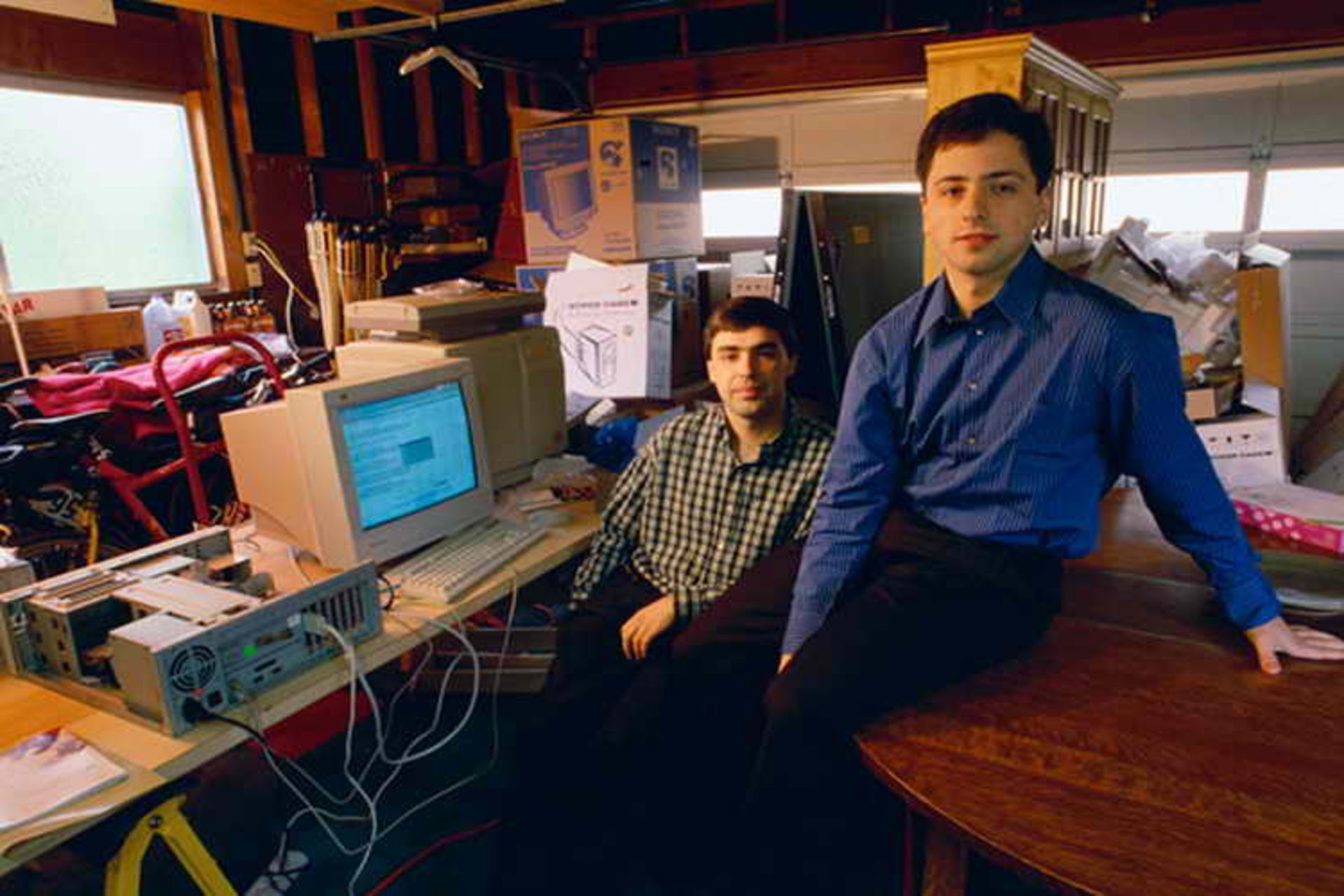

At that time, the web contained about 10 million documents with countless links between them. The computing resources of such a project were estimated far beyond student theses, and the dimensions and complexity of the project attracted the attention of Sergey Brin, who had worked on data mining articles and algorithm analysis during his PhD.
Sergey Brin joined the BackRub project and took over the mathematical side of the research, while Larry Page worked on link weighting and backlinks.
The weight of the links, in simple words, indicated that each link is from which source and with what degree of importance it targets another website. For example, the importance of the link that Intel’s website gave to IBM’s website was very different from the link that a teenager’s diary-blog gave to IBM’s website.
Sergey Brin handled the mathematical part of the research and Larry Page focused on link weighting
On the other hand, each link was placed in a different position and ranked according to the number of links on its home page. In other words, they counted not only the number of links on a page but also the links that were attached to each particular link. As the project progressed, its mathematical dimensions became more surprising and complex.
Sergey Brin says:
I loved data mining, which means analyzing huge amounts of data and finding patterns and trends. At the same time, Larry wanted to download the entire Internet, which contained the most interesting data possible for analysis.
Based on the results of their research, Page and Brin designed an algorithm called PageRank, which sent more popular sites to the top of the list and less important sites to the bottom of the list.
While investigating the work, they realized that the outputs of this model act somewhat similar to the search engine. In fact, BackRab was already a search engine that took a URL and provided a list of backlinks ranked by importance.
In addition, BackRub’s results outperformed those of other existing search engines such as AltaVista and Excite, which often listed irrelevant sites. By focusing on keywords, these search engines only looked at the text of the websites and ignored the most important factor, the ranking of the web pages.
Page and Brin developed the first search tool experimentally. This software only considered the headlines and page titles of the websites and then used the PageRank algorithm to rank and sort the websites. The results were significantly better than popular search engines.
Search engine development
At this point, Sergey Brin and Larry Page realized that they had taken a big step: the backrub engine not only performed well but also scaled as the Internet expanded. In other words, since the algorithm worked by analyzing links, the bigger the web, the more powerful the search engine.

For this reason, Page and Brin chose the name Googol (meaning the number one and 100 zeros in front of it) for their search engine, which was a symbol of processing the endless amount of information on the web. They published the first version of Google in August 1996 on the Stanford website with the domain google.stanford.edu, a year after they first met and got to know each other.
Page and Brin released the first version of Google for Stanford students with the domain google.stanford.edu
Its initial version was a success among a small group of Stanford users, and the two classmates quickly began improving the service to monitor the entire content of websites in addition to titles, while indexing more pages.
After Page’s room was filled, Brain’s room became their programming center and management office. Before long, the former BackRab was a legendary project in Stanford’s computer science department, consuming nearly half of the university’s network bandwidth. By the fall of 1996, it had gotten to the point where the search engine was regularly disconnecting Stanford’s Internet connection.
Larry Page later recalled:
We were lucky that there were so many forward-thinking people at Stanford who didn’t blame us too much for the resources we used.
The founding of Google: A Star rises
Page and Brin registered the google.com domain in September 1997. They knew that they could no longer rely on university resources to continue. In August 1998, one of the university advisors suggested that they meet Andy Bechtolsheim, the founder of Sun Microsystems. The meeting was held on the porch of this consultant’s house with a demonstration of the Google search engine.
Andy Bechtolsheim wrote a check for $100,000 to Google Inc. But the problem was that there was no company called Google yet. Page and Breen kept the check in their dorm room for several weeks while they went through the business registration process and opened new bank accounts for their business.
 Andy Bechtolsheim, Google’s first investor
Andy Bechtolsheim, Google’s first investor
Google was officially registered on September 4, 1998, and according to the previous agreement, Larry Page became the CEO and Sergey Brin became the company’s president. The two defined the company’s mission in one phrase: “Organizing the world’s information and making it accessible and useful to all people.”
Google’s mission: “Organizing the world’s information and making it accessible and useful for everyone.”
Page and Breen moved their tools and equipment to the company’s first office, which was the garage of their friend Susan Wojitsky’s house in Menlo Park, and by the end of the year, they had hired six more software engineers to work with them. By the end of 1999, the number of Google employees reached 21 people, among whom the names of Salar Kamangar, Omid Kurdestani, Suzan Vejitsky, and Marisa Mir stand out.
While Google’s daily searches were growing exponentially, the development of the company’s infrastructure required more capital.
 Google’s first office in the garage of Suzanne Wojitsky’s house
Google’s first office in the garage of Suzanne Wojitsky’s house
At the end of the first year of its establishment, it held its first fundraising round and received a total of one million dollars from three angel investors, Amazon CEO Jeff Bezos, Stanford University computer science professor David Cheriton, and Ram Shriram, one of the entrepreneurs of the technology world.
Andy Bechtolsheim, the founder of Sun Microsystems, was Google’s first investor
Many investors thought that the idea of a search engine startup would go nowhere, because the effort of technology companies was to keep users on their websites longer, and the search engine made people go from one website to another.
 Google page in 1998
Google page in 1998
But the potential and early success of Google in the second round of fundraising attracted the attention of two famous venture capitalists: John Doerr of Kleiner Perkins and Michael Moritz of Sequoia Capital, after carefully examining Google, they decided to invest a total of $50 million in this fledgling startup. .
The interesting point is that before these investments, Larry Page and Sergey Brin had offered Excite to buy their startup for one million dollars, but Excite refused to pay more than 750,000 for Google, and thus the contract was canceled.
 Google team in 1999 Palo Alto office
Google team in 1999 Palo Alto office
After raising capital, Google moved to its second office in Palo Alto, home to many famous Silicon Valley startups. In 2000, the Google team launched Google AdWords with the idea of Susan Wojitsky, which optimally changed the company’s revenue stream.
The AdWords service allowed companies to show their ads precisely to those who were looking for related products or services. This service was a revolutionary example in the world of online advertising and allowed Google to have a powerful money-making machine in addition to the search engine.
While the number of Google searches increased daily, with these changes, Google employees found a better mood and focused strongly on the path of progress.
At this time, John Doerr and Michael Koritz, the main investors of the company, according to their long-term experiences in the technology world, suggested to the founders of Google to hire a more experienced manager to lead their startup. Sergey Brin and Larry Page conducted complex interview sessions with several candidates but found none of them aligned with Google’s vision and long-term horizon.
In 2001, Eric Schmidt went to the interview meeting of the founders of Google with his hands full: he had detailed plans for developing Google internationally, diversifying products, sales, and accounting strategies, and managed to get on the Google board. A few months later, Page and Brin tapped him to become Google’s CEO, seeing Schmidt as the best fit for the company’s IPO event.
CEO Eric Schmidt’s tenure: Google’s explosive growth
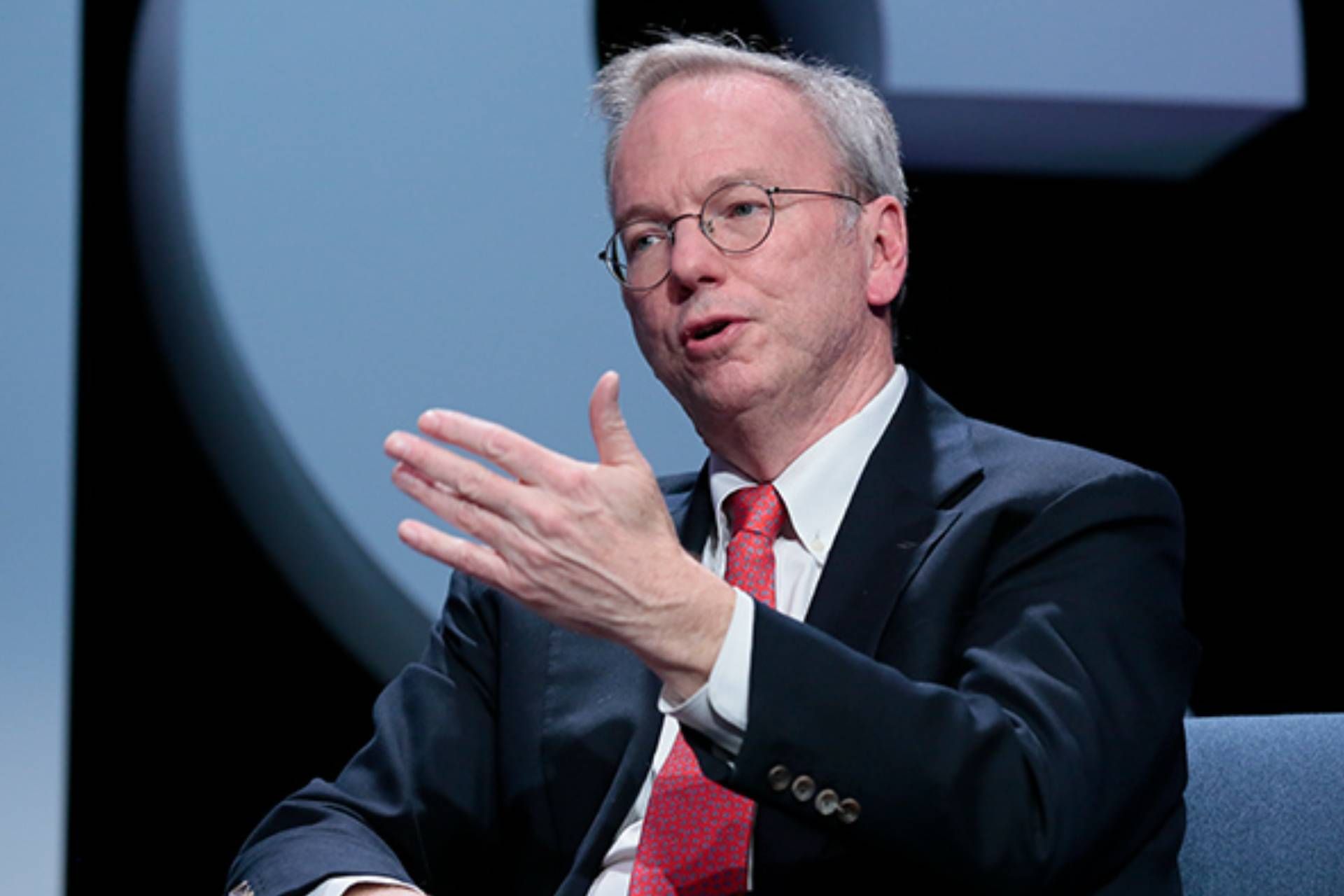

Eric Schmidt was appointed CEO of Google in August 2001 and remained in this position for 10 years. The joint idea of Sergey Brin, Larry Page, and Eric Schmidt was to create a comprehensive ecosystem that would meet all the digital needs of users through Google.
In the product development department, Schmidt had Merissa Meyer by his side, who had previously managed web products with user interface changes and the introduction of Google Doodles. One of the first developments of Google in the search engine side was the addition of the image search section.
In 2002, Yahoo planned to buy Google for $3 billion
In 2002, Yahoo tried to buy Google for $3 billion, but Page and Brin rejected the offer; Because they believed that their startup has more value.
Google executives wanted this company to be a symbol of the endless power of innovation; For this reason, they adopted a policy that allowed Google employees to dedicate 20% of their working time to projects that interest them, even if it is outside the scope of their official duties. This policy led to the emergence of some of Google’s most popular products in the following years.
In 2003, the Google News division was launched, and the board of directors purchased a building complex in Mountain View, California, to provide a suitable space for the company’s operations until they employed a thousand employees.
 Google Camp in Mountain View
Google Camp in Mountain View
This office, known today as “Google Plex”, expanded over time by purchasing the surrounding buildings and became the largest company camp in the world.
From Gmail to Chrome: The products that changed the web market forever
In 2004, the Gmail service created a storm in the world and raised the company’s position among users to a new level.
With 1 gigabyte of storage space, Gmail allowed users to quickly search for any email they had sent or received. In addition, this service provided users with new ways to automatically organize emails by topic. Many people thought that Gmail was Google’s April fool, but luckily it was not.
Gmail’s features far exceeded other free email services
In this era, Google’s revenue-generating strategies worked well, so that a few days before the initial offering of Google shares, stock market experts considered the company’s future to be very profitable.
 Gmail in 2004
Gmail in 2004
Finally, on August 19, 2004, Google’s IPO event took place at a price of $85 per share, bringing a fortune of about $1.7 billion to the company’s founders and early investors. In addition, the value of the company was estimated at 27 billion dollars.
 Google IPO on Nasdaq with Eric Schmidt and Larry Page
Google IPO on Nasdaq with Eric Schmidt and Larry Page
The introduction of the Google Maps service in 2005 marked another success in Google’s career and became a background for the company’s research collaboration with NASA. Google Maps evolved over time and became one of the most valuable features of Google to facilitate people’s daily lives.
Google started working with NASA after the introduction of Google Maps
But no one expected the company’s next revolutionary product to impact the entire tech world.
In September 2008, Google introduced the Chrome browser to the world. Interestingly, Eric Schmidt was against Google’s entry into the web browser market from the beginning, and this product was developed at the insistence of Sundar Pichai, one of the company’s forward-looking executives who was supposed to play a key role in the company’s future.
To create Chrome, Google hired some of the original Firefox engineers and developed the browser first for Windows and then for other operating systems. The first version of Chrome came with a 40-page visual guide to show users how to work with the browser. In just 4 years, the popularity of Google’s browser surpassed Firefox and Internet Explorer.
Schmidt later said in an interview:
I told Larry Page and Sergey Brin that we shouldn’t think about browser or operating system development, we shouldn’t compete with Microsoft. They told me they were hiring people to improve Firefox, and six months later they showed me Chrome. To be honest, I was so excited to see the Chrome demo that I had no choice but to admit I was wrong.
At the same time, Google’s organizational culture was still at the center of attention. This company was known as one of the best working environments in the world by maintaining a creative work environment. In such an environment that was based on the freedom of creativity and innovation, Google could attract the best talents and encourage them to create new and efficient products.
Strategic purchases: Doubleclick, YouTube and Android
At a time when Google was improving the level of user experience by offering various products that often had better performance than competitors, it was also preparing the ground for building an inclusive ecosystem by buying leading startups.
For example, the company took the biggest step toward expanding its pervasive advertising empire across the Internet with its $3.1 billion purchase of DoubleClick, the company’s most expensive acquisition at the time. In 2006, Google also bought YouTube for 1.65 billion dollars to give its plans in the field of video content a more serious color.
Under the leadership of Salar Kamangar and then Susan Wojitsky, YouTube became one of Google’s most valuable assets and one of the best online video content platforms, used by millions of users every day.
One of the other decisive actions of Google is the purchase of the Android operating system for 50 million dollars in 2005, which was released in 2008 for the T-Mobile G1 phone known as the HTC Dream. Open source software and integration with the Google ecosystem and the highest levels of notification capabilities were the most important features of Android that made it the most popular mobile operating system in the world.
So far, there has been no news of Google’s serious presence in the smartphone market.
Founding of Alphabet and CEO Larry Page: Reorganizing the company
Between 2010 and 2014, Google was trying to create a new chapter in its history. Delving into fields beyond the search engine and web browser, the company had become a global innovation laboratory pursuing ideas ranging from driverless cars to projects in healthcare, renewable energy, and artificial intelligence.
In April 2011, Eric Schmidt resigned, saying that Google no longer needed the supervision of veteran executives like him, and Larry Page took his place. Larry Page and Sergey Brin realized a long time ago that they needed structural changes to better manage a company as big as Google and focus more on their ambitious projects. For this reason, in 2015, they made a bold decision.
They established a new holding company called Alphabet and brought Google and their other projects and companies under its umbrella. This move was not only a structural rearrangement but also reflected a profound philosophical change in Page and Breen’s approach. In this way, Google found a different position and at the same time in sync with a set of independent companies, each of which was looking for its specific and sometimes ambitious goals.
For example, the Google X division managed modern projects such as self-driving cars and smart cities. Meanwhile, Calico oversaw research related to increasing human lifespan and improving quality of life, and Verily focused on medical and biotechnology research.
In May 2011, Google reached a record of one billion visitors
Larry Page remained the CEO of Google until 2015, after which he took over the management of Alphabet. During his CEO tenure, Google experienced many ups and downs.
In May 2011, Google reached a record of one billion unique visitors. In the same year, “Chrome OS” was also introduced, which was mainly used in Chromebook laptops. These laptops were manufactured by Acer and Samsung and were first released to the general public in some retail stores, but in later years were made available to students and teachers in schools for educational purposes.
 Google+ circles page
Google+ circles page
This period coincided with the introduction of one of Google’s famous and failed projects, namely Google Plus. The fact was that Google managers wanted to compete with Facebook by launching a social network, and in this regard, they replaced Google Plus with the Google Buzz microblogging service. Despite repeated redesigns, Google Plus never achieved success.
Google wanted to compete with Facebook by launching Google Plus
Another unfinished project of the company was Google Glass, whose experimental hardware was developed in the Google X and ATAP divisions. Despite the good idea and design, Google Glass needed technologies to process information that had not yet been developed at that time. In addition, some companies considered this product to be against their privacy and banned employees from using Google Glass.
July 2013, when Google announced the end of the Google Reader service, fans of this popular feed reader looked at this decision in disbelief. Shutting down Google Reader required courage, as we later saw in removing the headphone jack from iPhones. But this action made many Google users move to Twitter and search for daily news in tweets.
Finally, the purchase of DeepMind, an artificial intelligence laboratory based in London, was one of the most important steps taken by Google in this era, which later played a significant role in gaining the power of Google’s artificial intelligence department.
CEO Sundar Pichai’s era: the season of fighting with rivals
In 2015, together with the founding of Alphabet, Sundar Pichai, the company’s senior vice president under Eric Schmidt, replaced Larry Page as Google’s new CEO. Pichai, who joined Google in 2004, had proven his ability in leading the Google search bar, Google Gears, Google Pack, and Google Drive projects.
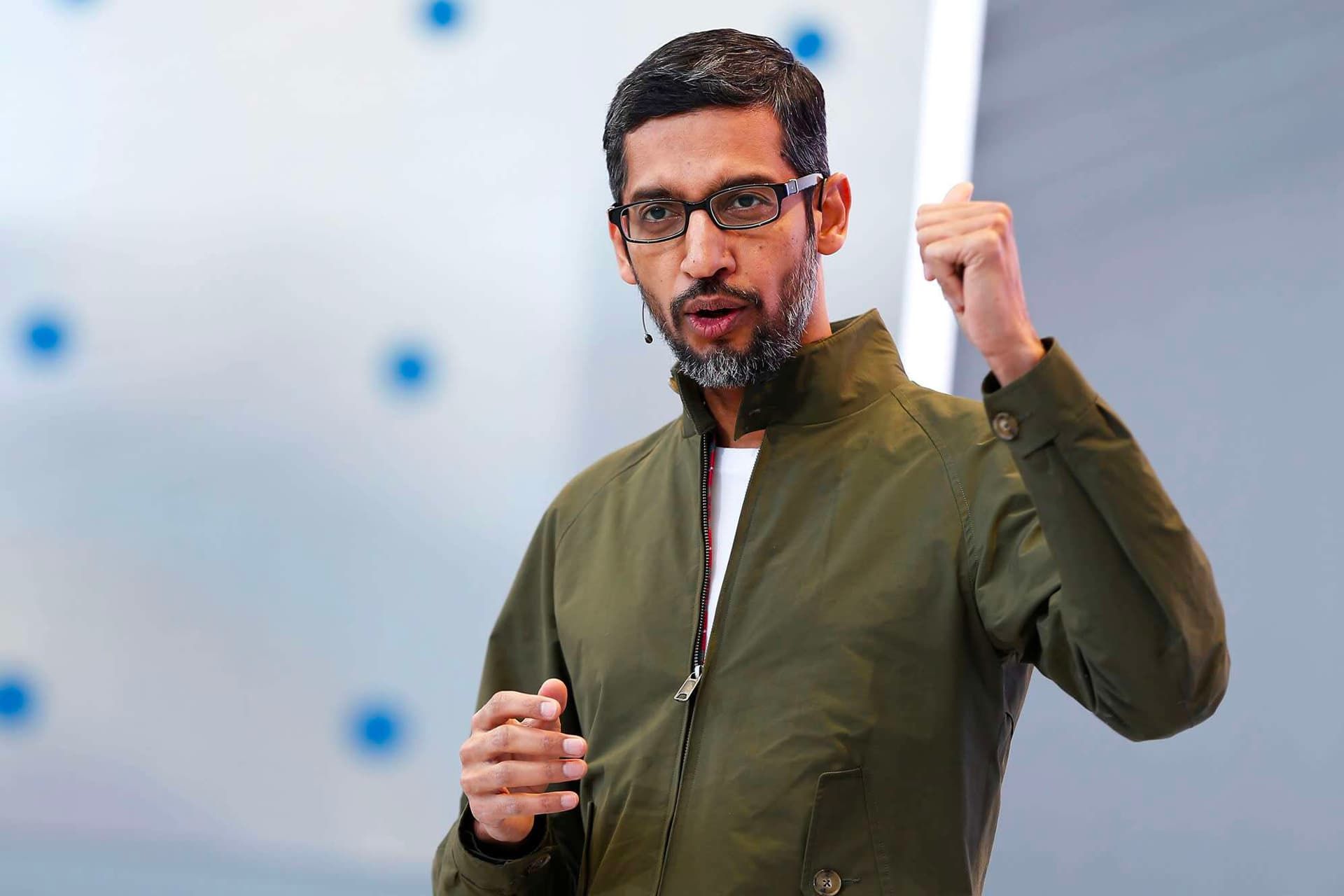

Pichai soon became one of the well-known faces of Google due to the idea of the Chrome browser and the management of the team that was responsible for the development of this software, and he became the deputy CEO of the company. He also played a significant role in the development of Android and the development of Google Apps.
One of the most important products that was introduced in the early days of Pichai’s CEO was Google Assistant. Google Assistant was introduced two years later than Amazon’s Alexa and 5 years after Apple’s Siri, But very soon it found its right place among users.
The wish of the founders of Google for the development of an inclusive and integrated ecosystem was realized during the management of Sundar Pichai
The strength of this virtual assistant was its synchronization with other products of the Google ecosystem, such as Google Home speakers, smart TVs, and most importantly, Android systems. Also, in 2016, Google announced the production of tensor processing units.
In October 2016, Google was at the forefront of the competition of flagship phones in the hardware sector with the introduction of Pixel phones, and two months later, the self-driving car project, which was considered one of the most successful projects of the Google X laboratory, was transferred to Waymo as an independent company after 6 years of testing. Guide the alphabet.
Sundar Pichai, unlike Eric Schmidt, was not afraid of competing with powerful technology companies, although now Google had also found a different face and no one considered it a new Silicon Valley player.
For example, Sundar Pichai had a special focus on the company’s cloud services, and despite long-standing competitors in this field such as Amazon and Microsoft, he invested heavily in building new data centers and developing cloud networks. With his efforts, Google Cloud became one of the top three cloud service providers in the world.
By introducing artificial intelligence tools and platforms in its cloud platform, Google was able to support corporate customers in various fields, including data analysis, machine learning, and process automation. During this period, the development and expansion of Nest smart home products also reached its peak. Although Google bought Nest in 2014, in recent years the integration of these products with the Google ecosystem has provided customers with an unparalleled user experience.
Some Google products, such as Google Translate, Google Lens, and Google Mate, found an undeniable role in people’s daily lives, and some projects, such as Google DeepMind projects, with every development and news, surprise the world beyond the technology world. Also, under the effective leadership of Sundar Pichai, Google has become one of the most powerful companies in the highly competitive market of generative artificial intelligence.
Google’s presence in the mobile market: from Nexus to Pixel
In the early 2010s, Google executives decided that they needed to enter the mobile market to improve the Android user experience and ensure timely updates for users.
At that time, Android was available as an open-source operating system to different manufacturers, and each company released its own version with desired changes and different user interfaces. But by producing Nexus phones, Google intended to provide users with a pure and integrated Android experience.

The first Nexus phone, named Nexus One, was introduced in January 2010 in collaboration with HTC. After that, Google introduced new Nexus models every year in partnership with one of the smartphone manufacturing companies:
- Nexus S: Samsung manufacturer, Android 2.1 Eclair operating system can be updated to Android 2.2 Froyo and Android 2.3 Gingerbread
- Galaxy Nexus: manufactured by Samsung, the operating system Android 4.0 Ice Cream Sandwich can be updated to Android 4.1 Jelly Bean
- Nexus 4: manufactured by LG, the Android 4.2 Jelly Bean operating system can be updated to Android 5.1
- Nexus 5: manufactured by LG, the Android 4.4 KitKat operating system can be updated to Android 6.0.1 Marshmallow
- Nexus 6: Motorola manufacturing company, Android 5 operating system before update to Android 7.1.1 Nougat
- Nexus 5X: manufactured by LG, operating system Android 6.0 Marshmallow updatable to Android 8.1.0 Oreo
- Nexus 6P: Huawei manufacturer, Android 6.0 Marshmallow operating system
The production of Nexus phones continued until 2015, but Google gradually realized that this series of phones, despite the loyal fans, could not compete well with other flagships in the market.

The production of the first series of Pixel phones began in 2016, and Google played the main role in the design and development of this series. The company optimized pure Android for Pixel phones to provide a smoother experience to the audience.
Since Google’s main goal was to compete with the flagships of Google and Samsung, it used better hardware and especially improved cameras in these products, which consequently raised their prices higher than the Nexus series. Also, the peak of Android integration with Google platforms was also seen in these phones.
However, since 2019, Google has tried to gain popularity among mid-range phone users by adding the Pixel series to its product series. Also, in 2023, the first Pixel Fold was introduced to compete with foldable phones of competing brands.
Google and artificial intelligence
Google was aware of the power of algorithms and machine learning from the beginning of its activities, and one of the most important areas in which it continuously invested was artificial intelligence.
As we said, in 2014, Google bought DeepMind Lab, which had advanced research in the field of artificial intelligence. Among the achievements of this laboratory, we can mention Alphago and AlphaFold projects.
 Demis Hessabis, co-founder of Deepmind
Demis Hessabis, co-founder of Deepmind
Researchers at the AlphaGo project developed neural network models specifically for video games and game boards, and in 2016 AlphaGo beat the world champion Go player in a competition. Alphafold also made a significant contribution to the pharmaceutical industry by accurately predicting the three-dimensional structure of proteins using a deep learning system.
On the other hand, Google had opened a special account on the development of neural processing units. TPUs, or tensor processing units, were custom-designed silicon chips developed specifically for machine learning and optimized for TensorFlow. According to Google, TPUs train and run AI models much faster than traditional chips.
In 2019, Google used Bert algorithms in its search engine, which understood the meaning of words in the text instead of understanding words separately. According to Google, Bert greatly improved the responsiveness of the search engine, because users could ask Google their questions naturally instead of listing their desired keywords.

In 2023, Google finally made Bard’s generative artificial intelligence system available to users, which was based on the large conversational language model LaMDA. Google Bard was integrated into many everyday Google services such as Drive, Maps, Docs, Gmail, and YouTube.
With the increasing popularity of ChatGPT, in May 2023, Google introduced the next generation of its artificial intelligence language model called PaLM 2, which had more capabilities in the field of understanding different languages and the power of reasoning and coding. Google Jumnai based on this model was developed and replaced Bard.

Getty Images
Google’s noticeable speed and effort in the field of productive artificial intelligence can be considered one of the most obvious competitive manifestations of this company to obtain a greater share of various technology markets. After Microsoft’s huge investment in the startup OpenAI, Google also invested 500 million dollars in the startup Entropic.
The challenges of Google Jamnai photo production caused Sundar Pichai to invite Sergey Brin and Larry Page to have a closer relationship with this company by declaring an emergency (code red). Following this event, Sergey Brin officially confirmed his return to Google.
Also, in 2024, Google showed its readiness to compete with Apple by completely redesigning Android and took great steps towards local processing of artificial intelligence features in phones, such as Circle to Search.
Google Antitrust Cases: Growing Challenges
The flow of legal cases and complaints related to Google’s monopoly started in 2010; That is when the European Union Commission started a wide-ranging investigation into the anti-competitive behavior of this company. At that time, one of the main accusations was that Google placed its products and services above competitors in the search results, thereby marginalizing other companies.
This investigation became one of the longest and most complex antitrust cases in the history of technology, and finally, in 2017, the European Union sentenced Google to pay a heavy fine of 2.4 billion euros for prioritizing its shopping services (Google Shopping). .
A year later, the European Union condemned Google to pay a fine of 4.34 billion euros; But this time because of the Android operating system. Now Google was accused of encouraging mobile phone manufacturers to install their own apps (such as Google Maps, Gmail, and Play Store) and thus keeping competitors out of the market.
Read more: Amazon brand story; A store for everything
In this case, Microsoft, Nokia, and Oracle were influential in the final verdict and condemnation of Google by participating in the research group called FairSearch. In 2019, Google was fined another 1.5 billion euros by the European Commission. Google Adsense service was the main focus of these accusations.
 Judge Amit Mehta in the Google monopoly case
Judge Amit Mehta in the Google monopoly case
After this case, it was the turn of the US Department of Justice to file a new and detailed complaint regarding Google’s monopolistic actions in the search engine and advertising market. In this lawsuit, more than 30 US states were on the opposite side of Google and sided with the judiciary.
In response to the accusations of the United States Department of Justice, Google announced that the online search and advertising market is a competitive market and different companies operate in this market. According to Google, users choose the company’s products and services because of their high quality, and this does not indicate exclusivity.
But in August 2024, Google finally lost its biggest antitrust case and was convicted by a Colombian court that it illegally monopolized the search market.
The Department of Justice and US prosecutors say that Google pays billions of dollars annually to mobile phone manufacturers such as Apple and Samsung to install the company’s search engine as the default application on their products in order to maintain its 95% share of mobile searches.
The consequences of this ruling can be very heavy for Google, while Google still has several other antitrust cases pending.
On the eve of the 26th year of Google’s establishment, this company with a market value of 2.02 trillion dollars is known as the fourth most valuable company in the world.
However, Google has never faced such serious challenges. Will it break up as US government and judicial officials say? Will the emergence of new artificial intelligence search systems such as SearchGPT diminish the popularity of Google’s search engine? How do you see the future of it?


You may like
-




The biography of Andy Rubin, the creator of Android
-




How to prevent your location from being revealed through photos?
-




The chip battle of flagship phones in 2024; Which is the winner?
-




What is Kali Linux? Everything you need to know about this popular but mysterious distribution
-




Sony Brand Story; From the production of rice cookers to becoming one of the most famous companies in the world
-




How did the people of the past imagine the future?


RobinNoun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
RobinNoun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the, as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the, as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the, as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Adverb: To such an extent or degree; to the same extent or degree.
Adverb: consider to be, in relation to something else; in the relation (specified).
Conjunction: In the (same) way or manner that; to the (same) degree that.
Conjunction: At the time that; during the time when:
Conjunction: Being that, considering that, because, since.
Conjunction: ; specifically.
Conjunction: than.
Preposition: In the role of.
Preposition: by way of
Noun: A libra.
Noun: Any of several coins of Rome, coined in bronze or later copper; or the equivalent value.
Adverb: ; very much; extremely
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
RobinNoun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Adverb: To such an extent or degree; to the same extent or degree.
Adverb: consider to be, in relation to something else; in the relation (specified).
Conjunction: In the (same) way or manner that; to the (same) degree that.
Conjunction: At the time that; during the time when:
Conjunction: Being that, considering that, because, since.
Conjunction: ; specifically.
Conjunction: than.
Preposition: In the role of.
Preposition: by way of
Noun: A libra.
Noun: Any of several coins of Rome, coined in bronze or later copper; or the equivalent value.
Adverb: ; very much; extremely
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
Noun: Someone connected with any number of sports teams known as the , as a fan, player, coach, etc.
The biography of Andy Rubin, the creator of Android
Andy Rubin (Andy Rubin) with the correct pronunciation of Andy Rubin, is a programmer and entrepreneur from the United States, who is best known for his work in founding Android. Before creating the popular mobile operating system, he had worked in many companies for many years and finally, his idea and plan were supported by Google. An idea that has become the most popular mobile operating system in the world today. Rubin left Google after a few years and decided to start his own business and invest in startups. Of course, none of his subsequent activities were as big as Android.
People who have worked with Rubin consider him a genius with technical knowledge. An engineer who understands the subtleties of management and entrepreneurship and has dynamic leadership. Android was Andy Rubin’s nickname during his years at Apple. This term, which was generally used for robots, was given to Rubin because of his strong interest in these human-made creatures. Rubin has always been interested in making, be it coding or building robots. When Rubin was developing his mobile operating system, he was trying to create a competitor to Symbian, Blackberry, and Microsoft Windows Mobile. An effort that came to fruition and finally turned Android into the main competitor of Apple’s iOS. The competition between Google and Apple reached its peak since then, and the late Steve Jobs sent harsh comments to Rubin and his mobile operating system.
In the years of working at Google and managing the Android sub-category, Andy Rubin made the foundations of the operating system he built so strong that the development in the coming years went quickly; The result of an ethical case became the point of Rubin‘s credit at Google. He was forced to leave the company due to the lawsuit and scandal, despite the secrecy of Google managers. Rubin‘s departure from Google was accompanied by a lot of controversy and media hype, and he sent severe criticism to Mountain View executives, who had even rewarded him. However, after leaving Google, Rubin focused on investing in the business ecosystem. He also started a smartphone manufacturing company, Essential, which was announced in the media recently.
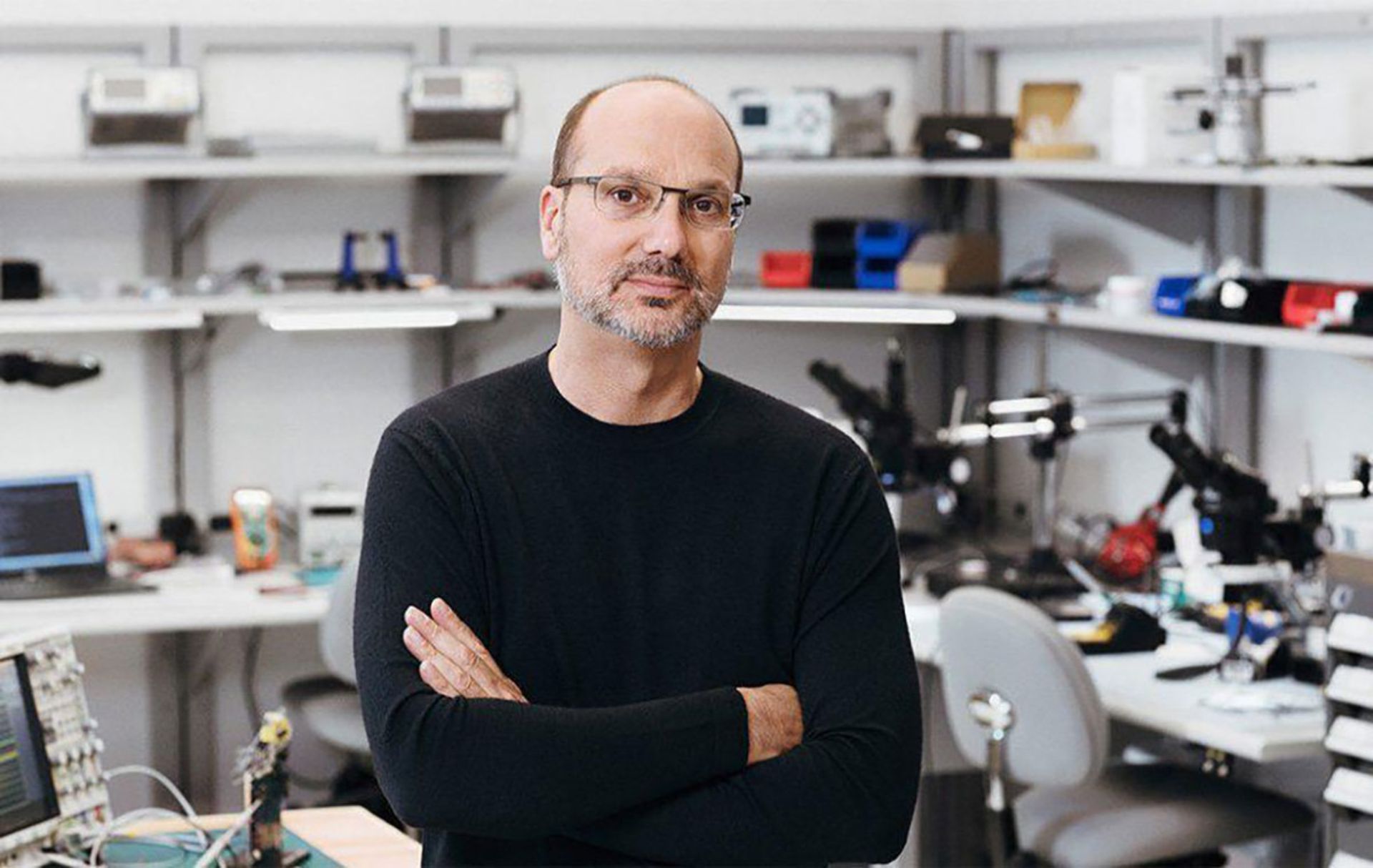

Early years and entering the business world
Andy Rubin (full name Andrew E. Rubin) was born in 1963 in Chappaqua, New York. Since childhood, he lived in a world full of gadgets. His father’s company was active in the field of industrial photography, and Andy was introduced to attractive images of smart industrial products from childhood. He completed his high school education at Horace Greeley School in his hometown, and during high school, he did his first serious robotics activities. Rubin designed a remote control for the Kenner R2-D2 toy and moved it around the house with computer control.
Rubin‘s talent and interest in the computer world were evident from childhood and adolescence. For this reason, he chose the field of computer science at university and completed his higher education in 1986 at Utica College in New York. As we said, robots were an important part of Rubin‘s interests. On the other hand, due to the development of a social network-like survey called Spies at the University (1981), Rubin took pride in creating the concept of a social network 23 years before Facebook. From a young age, he focused on the development of products and technologies in this field and chose his first job related to his interest.
Carl Zeiss was Andy Rubin‘s first workplace. He was employed as a robotics engineer in a German company and worked there for two years. The next destination of the American engineer was again Europe. After Carl Zeiss, Andy went to the SIP Institute in Geneva, Switzerland.
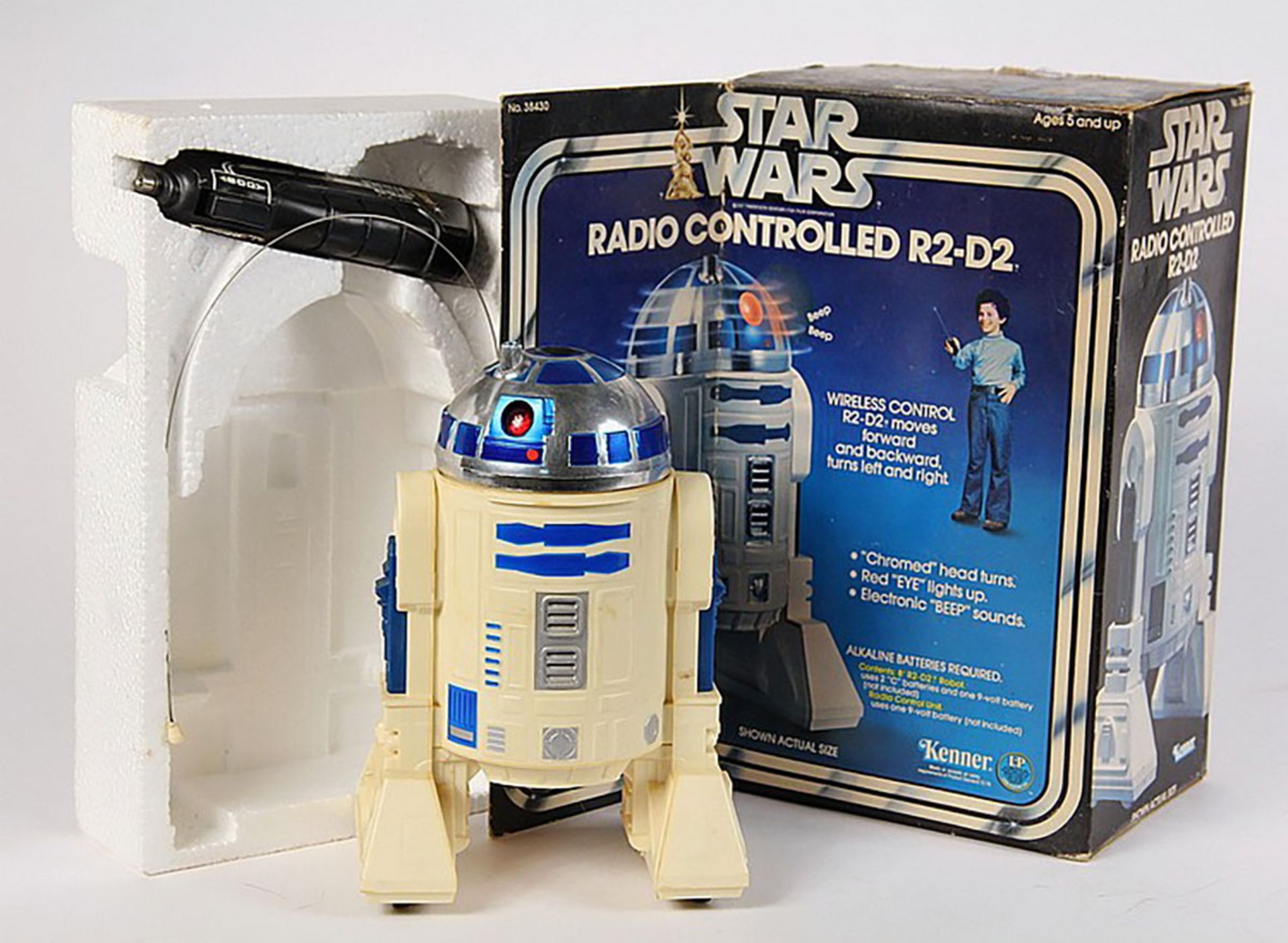

Andy Rubin‘s popular toy that became an Android icon
Andy Rubin‘s serious entry into the world of technology took place with a company that later became his serious competitor. Andy Rubin met Bill Caswell during a summer vacation in the Cayman Islands. Their relationship became more serious and Bey offered Andy a job at Apple. This offer became an excuse for Rubin to pursue his life path more seriously in the world of technology.
By the time Andy Rubin joined Apple, they were in good shape. Mackintosh’s popularity had reached its peak, But Steve Jobs was not present in the company he founded. However, Rubin gained a lot of experience while working at Apple and was one of the most popular employees. The nickname Android was given to him by a colleague in the same years to show that Andy has a great interest in robots.
Andy Rubin‘s love for building and especially developing robots sprouted from childhood
Andy Rubin first worked as a manufacturing engineer at Apple; But after a while, he went to the research and development department. In 1990, they launched a spin-off company called General Magic, where Rubin continued to work. General Magic was launched as a company focused on handheld and mobile devices so that Apple could focus its activities on the same PC ecosystem. General Magic engineers, in collaboration with Andy Rubin, developed a software called Magic Cap, which, of course, was not very successful. Finally, General Magic was closed in 1995.
The closure of General Magic meant the end of Rubin‘s cooperation with Apple. He started a new company called Artemis Research together with some of his colleagues in the mentioned company and some of the former employees of Apple. They developed a product called WebTV, which was designed to combine the worlds of the Internet and television. The Artemis company finally became an excuse for Rubin to continue his work in another giant of the technology world: Microsoft. The Redmondis welcomed the Artemis product and bought the company, and Rubin continued his work at Microsoft. One of Rubin‘s interesting projects at Microsoft was the creation of a robot equipped with a camera, which was done with the sole purpose of attracting the attention of colleagues. Rubin eventually left Microsoft and WebTV in 1999.

After leaving Microsoft, Andy Rubin decided to work independently. He rented space in Palo Alto and continued his research and hardware and software experiments there. His office was full of robots that he designed and produced for research development and testing. The same environment somehow inspired Rubin to do something new.
Danger Inc. was the brainchild of Andy Rubin, who started working with his old friends Matt Hershensen and Joe Britt in 1999. The name of the company was taken from a robot from the movie Lost in Space. Rubin became the CEO of the company; A company that was launched with the aim of designing and developing hardware, software, and services for mobile processing devices. The success of Rubin‘s new company was notable with a device called the Danger Sidekick. This device, which was first developed as Danger Hiptop, was finally marketed as T-Mobile Sidekick. Rubin said about the mentioned device: “We wanted a device that would be the size of a chocolate bar and come to the market at a price of less than 10 dollars. We wanted this device to have the ability to scan objects and receive information about them from the Internet. A device that acted like an intelligent assistant.
Rubin‘s new company was a center of genius engineers and designers who produced a product ahead of its time. However, they could not market their idea well and other companies were not willing to cooperate with Danger. Ultimately, Andy Rubin kept his faith in his new idea and company alive until Microsoft bought the company in 2008.
The ideas and experiences that Andy Rubin had gained from the Danger Company led to the development of a revolutionary idea in his mind. He nurtured his many ideas to create Android. An idea whose name was taken from the same nickname of Andy Rubin‘s distant years. It is interesting to know that the Android.com website was Andy Rubin‘s personal website until 2008.
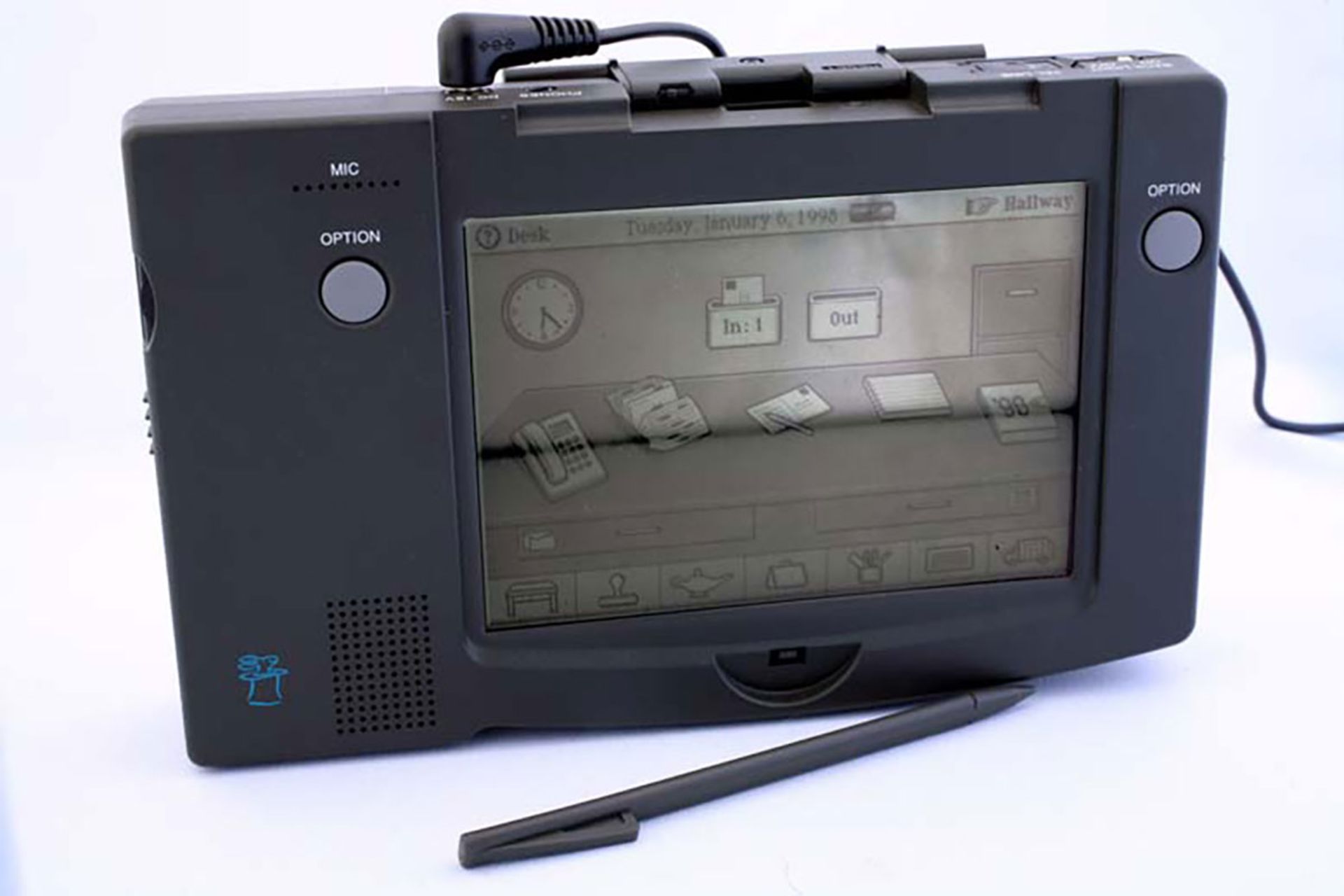 One of the few devices equipped with Magic Cap
One of the few devices equipped with Magic Cap
Creating Android and joining Google
Andy Rubin founded Android, Inc. in October 2003. His early colleagues were Rich Miner (co-founder of Wildfire Communications), Nick Sears (former SVP of T-Mobile), and Chris White (WebTV user interface designer and developer). Andy Rubin needed investors to develop and develop the idea of Android and cooperated with Redpoint Ventures. His initial idea was to create a powerful mobile platform that would be open source and lead to faster innovation and multiple benefits for the customer.
Android company first decided to develop an operating system for cameras. Of course, the digital camera market was not big enough to guarantee the financial return of Andy Rubin‘s idea; That’s why he and his colleagues decided to develop the operating system for smartphones. They wanted to be a competitor to the giants of the market at that time, Symbian, Blackberry OS, and Windows Mobile. In the early stages of Android development, Rubin proposed interesting concepts for its users. For example, he believed that people need smarter mobile phones that are more aware of the owner’s priorities and position.
Android was the nickname of Andy Rubin at Apple and he used the same name for the open-source mobile operating system
In the early years, Android worked quietly and without attracting attention. They only introduced themselves as a company focused on mobile software development. The quiet activity came with financial challenges for Rubin and his company. He could not manage the available resources well and even after some time, he could not afford to pay for the office of the company.
Andy finally called his friend Steve Perlman and explained the startup’s challenges. Although Rubin did not directly ask for investment and funding in his conversation with Perelman; Steve promised to inject new capital into the company. Perlman donated $10,000 from his personal account to the Android company. About his action, he says that he trusted Andy’s idea and decided to help him. Perlman later did not ask for any shares from Android. Andy Rubin, by receiving cash help from his friend, returned the development process of Android to the normal routine. He used the new capital to expand the team and leased a larger office in Palo Alto.
 Andy Rabil at the launch of Android
Andy Rabil at the launch of Android
Google executives’ familiarity with Andy Rubin goes back to a lecture at Stanford University. A university that has been the place of study for many great people in the current world of technology and plays an important role in the development of Silicon Valley. In 2002, Andy Rubin gave a talk about the Sidekick device at Stanford, which was attended by Larry Pitch and Sergey Brin. Later, in a private meeting with Rubin, Page had seen his device up close and admired the idea even more for using the Google search engine in it.
Larry Page’s relationship with Andy Rubin deepened in the following years. Page imagined a bright future for Android from the very beginning, while Sergey Brin and Eric Schmidt (then CEO of Google) distanced themselves from the idea and considered themselves far from the mobile world. However, Page became fascinated with the idea of an open-source mobile operating system and the prospect of global development managed by Google fascinated him more. He believed that Android is one of the most suitable ideas for Google. Page also had the idea of a Google smartphone in mind and tried his best to bring Android to Mountain View. At first, Rubin was hesitant to join Google and did not consider the organizational culture to be a good fit.
Andy Rubin has been instrumental in many of the technology industry’s historic innovations. During the same years of Android development, he also made serious investments and in 2004, he contributed $100,000 to Sebastian Theron’s project to develop a self-driving car. Theron won the Darpa Grand Challenge with Rubin‘s help and later worked as the manager of Google’s self-driving car division.
Page’s efforts to recruit Andy Robin and the Android team finally came to fruition in 2005. They acquired Android by paying about 50 million dollars. The main team members, including Andy Rubin, joined the new company. The interesting thing is that at that time and even until some time later, no one knew why Google should buy a mobile operating system. Even now, much of the narrative surrounding Google’s original intentions is speculation. However, Android is still known as a mobile software development company, and most thought that Google was planning to enter the mobile market.

Andy Rubin started working at Google as the senior vice president of a new team called Android. He managed a team of eight people responsible for the development of a mobile platform based on the Linux kernel. Google was also committed to marketing processes for Android as a platform for mobile devices. They started their cooperation with numerous software and hardware companies and the news of the development of the operating system was also announced to mobile operators.
Andy Rubin‘s tenure at Google was accompanied by the management and development of numerous projects. He helped form the Android Update Alliance, which coordinated the release of updates between carriers. Other positive activities of Rubin at Google include supporting and managing the purchase of Motorola.
Apple and Google war
In 2007, Apple introduced the iPhone, which entered the mobile world as a revolutionary product. At that time, Google was still developing its mobile operating system, Android. When Steve Jobs showed the iPhone on stage with his usual marketing skills, Andy Rubin realized that he had to completely redesign his ideas for the launch of the operating system.
Andy Rubin was watching the iPhone launch event via the Internet while riding in a taxi. When Steve Jobs was showing his company’s new smartphone to the audience, Andy asked the driver to stop the car. Surprised by the introduction of the Apple device, he came to the conclusion that he should not introduce the desired phone. Apple was carrying out the development and design plans for its new phone with appropriate news coverage. In fact, most Google engineers were aware of the plans of Steve Jobs and his team; But none of them imagined that a competitor would introduce and offer a product of this quality.

Rubin‘s smartphone display style looks similar to Steve Jobs
Google decided to introduce the mobile operating system by the end of 2007. After the iPhone was announced, they decided to postpone the launch schedule; Because Android had many similarities with the iPhone operating system. In fact, the introduction of the iPhone gave a strong blow to the entire Android project. In addition to the similarity of the operating system to iOS, Google engineers faced a more serious problem, which is the same high quality as the iPhone. A quality that made their achievement look like old technology. Even one of the Android engineers said that the initial design of the operating system was really inappropriate and weak compared to the iPhone, and in comparison, it looked like a product from the 1990s.
The Android team continued the development of the operating system despite the hard blow it received from Apple. Finally, in cooperation with HTC, they launched the first Android smartphone called HTC G1 or HTC Dream in 2008. The software on that phone was nowhere near as good as iOS on the iPhone, But it seemed so similar to Apple’s achievement that it brought anger and a strong reaction from Steve Jobs. In a sharp comment, he said that all parts of Android are disgusting imitations of their work.
Steve Jobs accused Andy Rubin of copying all parts of the iOS
Before the public release of Android, Steve Jobs had a good relationship with the main managers of Google. He trusted Larry Page Sergey Brin and Eric Schmidt. Even Eric Schmidt, along with the executive management of Google, was also a member of Apple’s board of directors. These three people had informed Jobs about Android development and promised him that the final product would be different from iOS. However, Jobs trusted them until the first Android-equipped smartphone hit the market.
After Jobs saw and experienced Android closely, he seriously asked Google managers to change its design. He arranged an important meeting with the iPhone’s chief software designer, Scott Forstall, in which Larry Page Andy Rubin , and Alan Eustis, Google’s senior vice president of engineering, were also present; A historical meeting that proceeded in a worrying manner. One of Apple’s executives, who was later informed by Jobs about the content of the meeting, said about it: “The meeting went completely towards personal problems. Jobs said that Rubin got very angry and told him that he had an anti-innovation approach. Then Steve had spoken angrily to Andy. He accused Andy of trying to be like him and even imitating his style of dressing and glasses.

The historic meeting between Apple and Google was beneficial for Apple despite all the hatred and animosity it created between Jobs and Rubin. Android engineers were forced to change and even remove parts that were very similar to iOS. For example, the multi-touch function that was present in the iPhone was removed from Android. Meanwhile, Rubin was very angry with Jobs. After the historic meeting, he wrote on a board in his office: “STEVE JOBS STOLE MY LUNCH MONEY”.
Rubin was so angry with Jobs that he even decided to leave Google. Andy believed that many of the capabilities that Apple claims to have invented are not actually theirs. However, Android gradually added more features to the operating system, and Rubin also forgot to the leave Google program. After five years, the number of his team members had increased from eight to 250 people.
The controversial story of leaving Google
Andy Rubin left Google in 2014. The path that led to Rubin ‘s separation from Mountain View was a tortuous one, with many crises for both parties. When Rubin was leaving Google, the executives gave him extended appreciation and presented Rubin as a hero. Larry Page, CEO of Google at the time, said about Andy Rubin: “I wish Andy a bright and great future. He had a really big achievement with Android, which now has more than a billion satisfied and happy users.
The process of Andy Rubin ‘s separation from Google began in 2013. Larry Page announced in a blog post in March that Rubin would be moving from managing the Android team to managing a new project at Google. Rubin was replaced by Sundar Pichai, who is currently serving as the company’s CEO. After Android, Rubin went to Google’s robotics department to continue his work in his main field of interest. He was very happy and excited to manage the robotics department and described the new situation as ideal in various interviews. Finally, Andy Rubin left Google in 2014 and started a hardware startup incubator. We will continue the story of his life after leaving Google in the next section.
What was not initially told to the media in the story of Rubin ‘s separation was the illicit relationship of the Google hero with one of the employees, the consequences of which affected the entire company. The former Google employee even accused Rubin of sexual harassment. Google investigated his claims and confirmed their accuracy. Two Google executives made this story public in interviews with the media and said that Pitch asked Andy to resign after learning about the matter. Google could have fired Rubin without paying any benefits. Instead, they paid him a $90 million bonus. Also, the company committed to pay two million dollars to Rubin every month for four years.
 Along with Vic Gandotra and Sundar Pichai
Along with Vic Gandotra and Sundar Pichai
Google’s action in support of Andy Rubin was a repeated action. They had previously supported two other male managers in a similar process and even paid allowances after they left the company. The same decisions and actions of senior managers later turned into serious challenges for the people of Mountain View, and many employees described the Google environment as suitable and even encouraging for sexually harassing managers.
Many international media analyzed and analyzed the case of his accusation and Google’s support for years after Rubin‘s separation. Numerous reports from the media such as the New York Times focused the attention of people and company employees on a deep-rooted problem at Google. The media pressure was such that Sundar Pichai later sent a message to employees as CEO, claiming 48 managers and employees were fired for sexual allegations. However, current and former Google employees believed that the company’s actions were not enough.
In the media stream that arose after Rubin‘s departure from Google, many of his colleagues and former managers began to talk about the negative parts of his personality. On the other hand, Rubin was the one who brought Google services from the limited environment of the desktop to the devices that were seen in the hands of billions of users. Rubin, with all his problems, was still Google’s hero in the mobile world. On the other hand, managers who worked with him say that Rubin even humiliated his subordinates in various incidents. Naturally, Rubin and his representative deny this claim.
Investment and independent activity again
Regardless of the reasons and consequences of Rubin‘s departure from Google, he returned to his favorite path, namely designing and creating new concepts. Working in Google’s robotics department did not meet Rubin‘s mental needs. He had solved a big problem, the world of smartphones, and he needed a new problem. Two years after Rubin‘s departure, Wired published an interesting article about his new ideas, excerpts from which we quote.

Andy Rubin launched Playground Global a few months after leaving Google; A company that, according to Rubin, was a new type of company; A combination that combined the concepts of incubator and consulting company; But none of them were. At the new company, Andy Rubin supported hardware startups. He did not, of course, limit his support to grants or advice, and provided them with a centralized engineering department. A department consisting of experienced and professional engineers who all worked with Rubin at Google, General Magic, Apple, and other companies. The engineering team worked closely with young and disruptive startup groups to develop hardware and software to power smart machines.
Rubin‘s vision for Polygrand Global was huge. He didn’t want his company to be limited to making a few products or even nurturing a few companies. Rubin and his colleagues envisioned a future focused on artificial intelligence and attempted to build the foundation of technology development through sponsored companies; Foundations that are freely available to others and eventually lead to the development of an ecosystem like Android. His new company was the booster of the idea; A structure that transformed basic concepts and ideas into products with maximum impact on the surrounding world. Playgrand was Rubin‘s first company in which there was no mention of robots (after Danger and Android), But they had a serious development in mind.
Essential was the last serious activity of Andy Rubin, which was closed in 2020
In 2015, Rubin‘s new company was able to receive 300 million in investments from Google, HP, Foxconn, Redpoint, Seagate, and Tencent. The attracted capital was spent on several projects, the most important of which is Owl Labs. Rubin finally left Polygrand in 2019.
Essential Products was Andy Rubin ‘s next entrepreneurial achievement. He decided to try his luck again in the world of mobiles and peripherals and in 2015, he launched the company. The Essential Phone and its accessories such as the 360-degree camera were one of the main products of the company. Rubin claimed that the Essential Phone will offer users a pure Android experience and will have the fastest software updates. Essential Phone was launched in 2017 and was well received by those interested in the Android ecosystem. Andy Rubin‘s lawsuit and scandal in 2017 caused him to leave Essential Management for a few months. Finally, the Palo Alto-based company announced in 2020 that it would no longer be operating.
 Essential Phone
Essential Phone
Personal life of Andy Rubin
In the story of Andy Rubin‘s departure from Google, we mentioned aspects of his personal life. Misbehavior with employees and leaked documents of Rubin ‘s sexual misconduct have tarnished his reputation alarmingly. She was married to Rei Hirabaru, but they divorced after a series of scandals and lawsuits. They had a coffee shop in Los Altos, California that closed in 2018.
Rubin and his ex-wife lived in a house in Woodside, California, which they bought in 2014 for $23 million. That house was also sold in 2018 during the separation, But now Rubin lives in it. Apparently, he is now known only as a Redpoint Ventures company in terms of employment.
In the story of Rubin ‘s life, there is always a trace of robots. In the years he was active at Google, in addition to managing the Android team, he spent his leisure time designing and developing robots. Rubin had designed several robotic arms for tasks such as preparing coffee. He also had a remote-controlled helicopter that he flew around Google’s yard.
Andy Rubin is known today for a legendary achievement called Android; An operating system that was born with the aim of developing the open-source concept in the mobile world and was seen in all smart devices from cars to home assistants and even televisions. Rubin‘s personal life has somewhat eroded his credibility in various tech circles; But it still has a place next to the greats like Jobs, Torvalds, Gates, and others.
Technology
How to prevent your location from being revealed through photos?
Published
18 hours agoon
18/09/2024

Noun: tonne.
Noun: A particular point or place in physical space.
Noun: An act of locate.
Noun: An apartheid-era urban area populated by non-white people; township.
Noun: A lease on rent.
Noun: An Institute of the Law of Scotland</ref>
Noun: An administrative region in Kenya, below county and subcounty, and further divided into sublocations.
Noun: A particular point or place in physical space.
Noun: An act of locate.
Noun: An apartheid-era urban area populated by non-white people; township.
Noun: A lease on rent.
Noun: An Institute of the Law of Scotland</ref>
Noun: An administrative region in Kenya, below county and subcounty, and further divided into sublocations.
Noun: A particular point or place in physical space.
Noun: An act of locate.
Noun: An apartheid-era urban area populated by non-white people; township.
Noun: A lease on rent.
Noun: An Institute of the Law of Scotland</ref>
Noun: An administrative region in Kenya, below county and subcounty, and further divided into sublocations.
Adjective: happen; ; being or due to be put into action.
Adjective: Fitted; covering or being worn.
Adjective: Of a stated part of something, oriented towards the viewer or other specified direction.
Adjective: Acceptable, appropriate.
Adjective: Possible; capable of being successfully carried out.
Adjective: destined; involved, doomed.
Adjective: Having reached a base as a runner and being positioned there, awaiting further action from a subsequent batter.
Adjective: Within the half of the field on the same side as the batsman’s legs; the left side for a right-handed batsman.
Adjective: Of a ball, being the next in sequence to be potted, according to the rules of the game.
Adjective: Acting in character.
Adjective: Performative or funny in a wearying manner.
Adverb: To an operate state.
Adverb: So as to cover or be fitted.
Adverb: Along, forwards (continuing an action).
Adverb: In continuation, at length.
Adverb: later.
Adverb: See also ‘odds-on’.
Preposition: Positioned at the upper surface of, touching from above.
Preposition: Positioned at or resting against the outer surface of; attached to.
Preposition: At or in (a certain region or location).
Preposition: Near; adjacent to; alongside; just off.
Preposition: support by (the specified part of itself).
Preposition: Aboard (a mode of transport, especially public transport, or transport that one sits astride or uses while standing).
Preposition: At the date or day of.
Preposition: At a given time after the start of something; at.
Preposition: deal with the subject of; about; concerning.
Preposition: In the possession of.
Preposition: Because of; due to; upon the basis of (something not yet confirmed as true).
Preposition: At the time of (and often because of).
Preposition: Arrived or coming into the presence of.
Preposition: Toward; for; .
Preposition: Engaged in or occupied with (an action or activity).
Preposition: Regularly taking (a drug).
Preposition: Under the influence of (a drug, or something that is causing drug-like effects).
Preposition: In addition to; besides; indicating multiplication or succession in a series.
Preposition: Serving as a member of.
Preposition: By virtue of; with the pledge of.
Preposition: To the account or detriment of; denoting imprecation or invocation, or coming to, falling, or resting upon.
Preposition: Against; in opposition to.
Preposition: According to, from the standpoint of; expressing what must follow, whether accepted or not, if a given premise or system is assumed true.
Preposition: In a position of being able to pot (a given ball).
Preposition: Having as identical domain and codomain.
Preposition: Having <math>V^n</math> as domain and V as codomain, for the specified set V and some integer n.
Preposition: generate by.
Preposition: of.
Preposition: At the peril of, or for the safety of.
Verb: To switch on.
Noun: In the Japanese language, a pronunciation, or reading, of a kanji character that was originally based on the character’s pronunciation in Chinese, contrasted with kun.
Adjective: In the state of being active, functioning or operate.
Adjective: happen; ; being or due to be put into action.
Adjective: Fitted; covering or being worn.
Adjective: Of a stated part of something, oriented towards the viewer or other specified direction.
Adjective: Acceptable, appropriate.
Adjective: Possible; capable of being successfully carried out.
Adjective: destined; involved, doomed.
Adjective: Having reached a base as a runner and being positioned there, awaiting further action from a subsequent batter.
Adjective: Within the half of the field on the same side as the batsman’s legs; the left side for a right-handed batsman.
Adjective: Of a ball, being the next in sequence to be potted, according to the rules of the game.
Adjective: Acting in character.
Adjective: Performative or funny in a wearying manner.
Adverb: To an operate state.
Adverb: So as to cover or be fitted.
Adverb: Along, forwards (continuing an action).
Adverb: In continuation, at length.
Adverb: later.
Adverb: See also ‘odds-on’.
Preposition: Positioned at the upper surface of, touching from above.
Preposition: Positioned at or resting against the outer surface of; attached to.
Preposition: At or in (a certain region or location).
Preposition: Near; adjacent to; alongside; just off.
Preposition: support by (the specified part of itself).
Preposition: Aboard (a mode of transport, especially public transport, or transport that one sits astride or uses while standing).
Preposition: At the date or day of.
Preposition: At a given time after the start of something; at.
Preposition: deal with the subject of; about; concerning.
Preposition: In the possession of.
Preposition: Because of; due to; upon the basis of (something not yet confirmed as true).
Preposition: At the time of (and often because of).
Preposition: Arrived or coming into the presence of.
Preposition: Toward; for; .
Preposition: Engaged in or occupied with (an action or activity).
Preposition: Regularly taking (a drug).
Preposition: Under the influence of (a drug, or something that is causing drug-like effects).
Preposition: In addition to; besides; indicating multiplication or succession in a series.
Preposition: Serving as a member of.
Preposition: By virtue of; with the pledge of.
Preposition: To the account or detriment of; denoting imprecation or invocation, or coming to, falling, or resting upon.
Preposition: Against; in opposition to.
Preposition: According to, from the standpoint of; expressing what must follow, whether accepted or not, if a given premise or system is assumed true.
Preposition: In a position of being able to pot (a given ball).
Preposition: Having as identical domain and codomain.
Preposition: Having <math>V^n</math> as domain and V as codomain, for the specified set V and some integer n.
Preposition: generate by.
Preposition: of.
Preposition: At the peril of, or for the safety of.
Verb: To switch on.
Noun: In the Japanese language, a pronunciation, or reading, of a kanji character that was originally based on the character’s pronunciation in Chinese, contrasted with kun.
Noun: A collection of interlinked web pages on the World Wide Web that are typically accessible from the same base URL and reside on the same server.
Noun: A collection of interlinked web pages on the World Wide Web that are typically accessible from the same base URL and reside on the same server.
Noun: A collection of interlinked web pages on the World Wide Web that are typically accessible from the same base URL and reside on the same server.
Noun: ton.
Noun: tonne.
Noun: ton.
Noun: tonne.
Noun: A particular point or place in physical space.
Noun: An act of locate.
Noun: An apartheid-era urban area populated by non-white people; township.
Noun: A lease on rent.
Noun: An Institute of the Law of Scotland</ref>
Noun: An administrative region in Kenya, below county and subcounty, and further divided into sublocations.
Noun: A particular point or place in physical space.
Noun: An act of locate.
Noun: An apartheid-era urban area populated by non-white people; township.
Noun: A lease on rent.
Noun: An Institute of the Law of Scotland</ref>
Noun: An administrative region in Kenya, below county and subcounty, and further divided into sublocations.
Noun: A particular point or place in physical space.
Noun: An act of locate.
Noun: An apartheid-era urban area populated by non-white people; township.
Noun: A lease on rent.
Noun: An Institute of the Law of Scotland</ref>
Noun: An administrative region in Kenya, below county and subcounty, and further divided into sublocations.
How to prevent your location from being revealed through photos?
The penetration of the Internet in all ages and strata of society has caused many to share many parts of their lives online without considering the consequences. This makes it easier than ever for malicious individuals, cyber intruders, and even criminals to find complete information about our lives, including what we eat, where we go, and even who we hang out with.
One of the scariest ways criminals can collect information about you is by using location data stored in photos you post online. This hidden data can reveal the exact location of the photo recording and endanger your privacy and even security.
In order for your photos not to reveal your location, in this guide, we discuss how to manually and group delete location information and other data stored in photos on various platforms, including Windows, Android, and iOS, and also introduce some programs to delete metadata in groups.
-
How do the photos you take reveal your location?
-
Manually remove location information from photos
-
Remove location from photo on Android
-
Remove location from photos on iPhone and iPad
-
Remove location from photo in Windows
-
Remove location from photo in Mac OS
-
Batch removal of EXIF and location information from photos
-
Android tools
-
iOS tools
-
Windows, Mac, and Linux tools
-
Online tools
How do the photos you take reveal your location?
Every photo you take contains EXIF (short for Exchangeable Image File Format) data, which includes details such as camera type, exposure level, and color information. Modern GPS-enabled devices (almost all smartphones, tablets, and some cameras) also store the exact location of the photo in EXIF data by default.
There is no harm in recording the location in each photo; Because there is no need to manually record this information. Image management programs like Google Photos and Apple Photos also use this data to show your photos on a map.
The problem arises when you share photos with this embedded location information. Anyone with malicious intent can find the photos you’ve uploaded and get sensitive information like where you live, work, or places you frequent.
Although major platforms such as Meta and, of course, Instagram remove location data from photos, many smaller websites and apps do not; So it’s best to exercise caution and remove location information from anything you post online before sharing.
Manually remove location information from photos
Below are simple steps to clear photo data on different platforms. It should be mentioned that editing and erasing metadata in Photoshop is also possible to some extent, But this program does not allow editing and removing location information from photos, and alternative software should be used.
Remove location from photo on Android
The Google Photos application, as the default gallery of many Android phones, does not allow the user to delete the location information of the images taken with the phone itself; However, in the gallery applications of some manufacturers, including Samsung and Xiaomi, it is possible to remove the location information of the images when they are shared.
- On Samsung phones, when sharing a photo, tap Options and turn off Include location data. You can also swipe up on the photo in the gallery and delete the location by selecting Edit and the delete option in front of the location icon.


- In Xiaomi phones, it is enough to enter the Secure sharing section from the gallery settings and turn off the two options Share without location info by default and Share without metadata by default.


If your Android phone gallery does not have the option to remove location information, use the two applications that are introduced below in the section on batch removal of EXIF and location information from photos.
Remove location from photos on iPhone and iPad
- Open the photo and tap on the three dots (…) icon.
- Select the Adjust Location option.
- Tap Remove Location.

Remove location from photo in Windows
- Right-click on the photo and select Properties.
- Go to the Details tab .
- Click on Remove Properties and Personal Information.
- Select the Latitude and Longitude option under GPS and click OK.

Remove location from photo in Mac OS
- Open the photo in the standard Mac Preview program.
- Go to the menu Tools > Show Inspector.
- On the GPS tab, click Remove Location Info.

Batch removal of EXIF and location information from photos
Manually removing metadata from large numbers of images is tedious; To save time, there are several tools for removing metadata from photos and removing data from photos on Windows, MacOS, Linux, Android, and iOS, here are some of the best options.
Android tools
- Scrambled Exif


Scrambled Exif is a completely free, open-source app that makes it easy to de-decrypt photos taken on Android before sharing them. To remove metadata from photos, simply import them into Scrambled Exif via Android’s share menu. After a few moments, the sharing menu will appear again and you can share the photos whose metadata has been removed with the app of your choice.
- EXIF Image & Video Date Fixer


In addition to removing metadata, this program can correct the date and order of images and videos using EXIF metadata and filenames. It is also possible to modify the date manually and support batch processing. The free version can process up to 50 files simultaneously.
iOS tools
- Metapho


Through Metapho it is possible to manage metadata including viewing, editing, and deleting EXIF data. It includes batch editing, location spoofing, and secure sharing options. Viewing metadata is free; But for advanced features, you need to buy a subscription or a permanent license of the program.
- Exif Metadata


This tool allows you to easily view, edit, or delete metadata including GPS data. For batch processing of images, the paid version of the program must be purchased.
Windows, Mac, and Linux toolsExifCleaner
ExifCleaner for Windows works like the Mac version and allows you to delete batch EXIF files for free. ExifCleaner is also available for Linux with the same features as the Windows and Mac versions.
- EXIF Purge
A simple and lightweight tool to remove EXIF batches from images with one click. EXIF Purge is user-friendly and free; But it doesn’t support videos and PDFs.

Online tools
- Pics.io Metadata Remove

A free online tool that supports all types of files including images, videos, and PDFs, and there’s no limit to the number of files you can process.
- VerExif

Using VerExif, you can view and remove metadata from images. This website has a simple user interface and is free to use, But the images must be less than 20 MB.
By removing location data and other EXIF data from photos before sharing them, you can ensure that these images do not reveal unwanted information.
In addition to the introduced tools, countless options are available for removing and editing metadata from photos and videos; If you know of better tools, share them with us in the comments section
Technology
The chip battle of flagship phones in 2024; Which is the winner?
Published
2 days agoon
17/09/2024

PNoun: on an electrocardiogram.
Noun: An academic grade issued by certain educational institutions to indicate that a student passes a class.
Adjective: (used on a vehicle’s P-plate)
Adjective: (used on a vehicle’s P-plate)
Proper noun: The set of all problems that are solvable in polynomial time by a deterministic Turing machine
Verb: (of a quantity, etc.) To become larger or greater.
Verb: To make (a quantity, etc.) larger.
Verb: To multiply by the production of young; to be fertile, fruitful, or prolific.
Verb: To become more nearly full; to show more of the surface; to wax.
Noun: An amount by which a quantity is increased.
Noun: For a quantity, the act or process of becoming larger
Noun: offspring, progeny
Noun: radiotelephony clear-code word for the letter H.
Proper noun: named after Calvin F. How Jr.
The chip battle of flagship phones in 2024; Which is the winner?
Choosing the best flagship smartphone in today’s market is no longer just about choosing the most expensive option. While price is likely to be considered as a primary indicator, it is very difficult to make the right decision without adequate knowledge of technical specifications and key metrics. Ignoring these criteria can lead to incorrect selection. So what is the best chip for smartphones?
In choosing the best flagship phone in the market, various criteria are considered; From photography experience battery life, and clear display to software and design and price tag. These cases are usually easy to check, and conclusions can be drawn within minutes; But if the criterion is the power of the chip, the comparison will be challenging.
In the discussion of chip power, various criteria are involved; Including processing performance, which is one of the important criteria for choosing the most powerful phone in the market. A smartphone should be able to perform all daily tasks, including opening apps, browsing the web, running games, and managing background apps at high speed and without lag. One of the important features of smartphone chips is the number of cores. Some cores are designed for light tasks with low energy consumption, and others for heavy and graphic processing. Note that the number of cores is not the only factor that increases the speed, but their architecture and optimization also have a great effect.
Graphical capabilities are also of particular importance. Graphics processors (GPU) are responsible for processing games and graphic programs. On the other hand, battery consumption is one of the most important influencing factors in choosing a phone, which is directly related to the optimality of the chip. A smartphone with a high processing power, but a weak battery, cannot meet the daily needs of users well.
The stability of the chip during heavy usage should also be considered. Phones that slow down or increase body temperature under heavy pressure, such as running graphic games or complex programs, usually do not provide a good user experience.
Considering these parameters, it is challenging to choose a smartphone without having detailed information about the chip’s performance; That’s why we decided to put the most powerful chips on the market against each other to see which one matches the user’s needs by carefully examining the technical specifications and benchmark results.
-
Which chips?
-
Qualcomm Snapdragon 8 Generation 3
-
Apple A17 Pro
-
Samsung Exynos 2400
-
Mediatek Dimension 9300
-
Google Tensor G4
-
Comparison of processing performance
-
Comparison of graphics processing similar to the game
-
Comparison of battery life and power consumption
-
Comparison of stability in heavy processing
-
Summary: Which is the winner of the competition?
Which chips?
In the next article, we are going to review and compare the most powerful chips inside the 2024 flagship phones. These chips include Snapdragon 8 generation 3 from Qualcomm, A17 Pro from Apple, Dimension 9300 from MediaTek, Exynos 2400 from Samsung, and Tensor G4 from Google. In the following, we will try to review the strengths and weaknesses of each chip by comparing the Zomit benchmark results in order to reach a suitable conclusion about their performance.
Considering that the A18 Pro chip of the iPhone 16 Pro was released in the last months of 2024, we will compare the performance of this chip with 2025 flagship phones equipped with chips such as Snapdragon 8 generation 4 in another article.
Qualcomm Snapdragon 8 Generation 3
The Snapdragon 8 generation 3 chip (which we call S8G3 for short) was unveiled at Qualcomm’s technology conference in October 2023 (Mehr 1402).
Using Cortex v9 technology, this new processor has been able to operate about 30% faster than its previous generation, and its energy consumption has been optimized by 20%.
Also, by providing facilities such as Snapdragon Elite Gaming and Adreno Frame Motion Engine, the gaming experience has been improved by about 12% compared to the generation.
 Snapdragon 8 generation 3 entered the market with one goal: to conquer the battle between flagships
Snapdragon 8 generation 3 entered the market with one goal: to conquer the battle between flagships
In the field of artificial intelligence, the S8G3 chip can perform complex calculations in a shorter time by improving its performance by 98%. This feature is especially useful in applications such as machine learning and image processing and enables interesting features such as Sketch to Image in Samsung’s new foldables.
Apple A17 Pro
Every year Apple releases a new chip with the introduction of the new iPhone generation. Last year’s chip was called A17 Pro and it was exclusively used in iPhone 15 Pro and 15 Pro Max; The chip is built on TSMC’s 3nm manufacturing process, making it the first member of the 3nm family in the industry.
The A17 Pro chip has a 6-core configuration: two high-performance cores and four high-performance (and low-power) cores. High-performance cores are 10% faster than the previous generation, and low-power cores handle everyday tasks that don’t require high speed but help optimize battery consumption.
The graphics processing unit of the A17 Pro has also undergone major changes. This six-core GPU is up to 20% faster and provides more stable performance in games with less energy consumption. Also, for gamers, it offers MetalFX functionality to increase the graphic details of games while controlling battery consumption.
The A17 Pro chip also uses an advanced neural engine that can perform up to 35 trillion operations per second. The A17 Pro’s AI and machine learning capabilities provide new features such as more accurate auto-correction, background blurring in portrait photos, and personalized voice creation for people with speech impairments.
All in all, Apple’s chip has become one of the most powerful and efficient mobile chips by combining advanced architecture, energy consumption optimizations of up to 15%, and artificial intelligence capabilities, which not only provide great performance but also improve the user experience in various areas. forgives
Samsung Exynos 2400
Rumors about the Exynos 2400 chip were first heard in early 2023. The Exynos 2400 chipset acts as the beating heart of the Galaxy S24 and S24 Plus in some versions, but it is not present in the Ultra model. Recently, Samsung announced that it will launch all 2025 Galaxy flagships (S25 family) with Snapdragon chips only.
In this product, Samsung has used a different configuration of 1+2+3+4, which includes a total of 10 cores: one high-performance Cortex-X4 core with a frequency of 3.2 GHz, two Cortex-A720 cores with a frequency of 2 9 GHz, two A720 cores with a frequency of 2.6 GHz and four low-power Cortex-A520 cores with a frequency of 1.92 GHz. This combination allows the processor to operate optimally in energy consumption while having high processing power.
On the other hand, the Xclipse 920 graphics processor, which was also used in the Exynos 2200, using AMD’s RDNA 2 architecture and ray tracing capabilities, showed a higher potential by showing a 58% improvement in graphics performance in the 3DMark benchmark. is

One of the outstanding strengths of the Exynos 2400 is the 14.7 times increase in AI computing performance compared to the Exynos 2200. The upgrade improves the chip’s ability in areas such as text-to-speech summarization, simultaneous translation of conversations, and image generation.
Mediatek Dimension 9300
For the first time, MediaTek has used only powerful cores in the Dimension 9300 (MT6989) chip, abandoning low-power cores. According to MediaTek CEO Joe Chen, “Dimensity 9300 is MediaTek’s most powerful flagship chip to date, bringing extraordinary computing power with its unique All Big Core design.”
Taking advantage of the concept of “only big cores”, Dimension 9300 consists of eight powerful cores, including four Arm Cortex-X4 cores and four Cortex-A720 cores. This combination provides up to 67% better processing power than Dimension 9200, and It is
In addition, MediaTek has increased the cache memory by 29%, increasing its capacity to 18 MB. This upgrade not only increases the speed and efficiency of the chip in performing complex tasks but also improves the simultaneous management of multiple applications.
Mediatek
The Dimension 9300 also supports hardware ray tracing, which is commonly used in high-end PCs and game consoles. Although this technology is in its early stages in the mobile world, the Dimension 9300 chip allows developers to create games with stunning visual effects.
In addition, Dimension 9300 uses the world’s first hardware-based artificial intelligence engine. This artificial intelligence processing unit can improve the graphics performance of games by up to 25% (for processing graphics floating point data), adjust settings for optimal performance and even predict user behavior, with support for advanced language models such as MetaLlama 2 and Baidu. AI LLM provided the basis for the development of diverse and efficient artificial intelligence programs.
Google Tensor G4
On August 13, 2024, Google introduced the Pixel 9 series, which has a new G4 tensor chip at its heart. According to Google, the new chip makes the device one of the “smartest” phones on the market.
The Tensor G4 has a 7% higher clock speed than the Tensor G3, and its GPU is also 6% faster. In general, the G4 tensor has up to 10% performance improvement compared to the G3 tensor.
Tensor G4 processor is a custom chip designed and produced jointly by Google and Samsung with 4nm architecture. Tensor G4 with eight processing cores and using the Cortex-X4 core allows users to enjoy optimal performance and high processing power. Also, the A720 and A520 cores help maintain efficiency and stable performance.
One of the outstanding features of the Tensor G4 is the Arm Immortalis-G715 GPU, which significantly improves the visual quality of games and graphics-heavy applications with support for hardware ray tracing.
In addition, Tensor G4, thanks to the DeepMind team, can run complex artificial intelligence models such as Jumna Nano at a faster speed, allowing users to benefit from advanced capabilities such as voice recognition, image processing, and environmental awareness, directly on their device. become
Using Samsung’s 4nm LPP+ process, Tensor G4 has been able to provide better efficiency and thermal management than G3. Google claims that Tensor G4 can revolutionize the smartphone user experience by combining high processing power, optimal energy consumption, advanced graphics capabilities, and support for artificial intelligence.
Smartphones equipped with G4 tensor
Comparison of processing performance
In this section, we will examine the processing power of the introduced chips. But before the comparison, it is worth taking a look at the technical specifications of these chips:
|
Specifications |
Snapdragon 8 Generation 3 |
A17 Peru |
Exynos 2400 |
Dimension 9300 |
Tensor G4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The main processor |
8 cores 12 MB of L3 cache memory |
6 cores 256 KB of L1 cache memory 16 MB of L2 cache memory |
10 cores 8 MB of L3 cache memory |
8 cores 10 MB of L3 cache memory |
8 cores No cache information available. |
|
GPU |
Adreno chip Shading noise canceller Operating capacity of 4435.2 gigaflops |
Apple A17 GPU chip 6 processing lines 128 shading units Operating capacity of 2147.2 gigaflops |
Xclipse 940 chip Ray tracing support Operating capacity of 3407 gigaflops |
Arm Mali-G720 Immortalis chip Ray tracing Operating capacity of 5990.4 gigaflops |
Chip Mali-G715 MC7 Operating capacity of 2625.7 gigaflops |
|
Artificial intelligence processor |
Vector processing engine Hexagon DSP accelerator Scalar Accelerator Accuracy INT4 |
Powered by Apple’s Neural Processing Engine (NPU). |
2 low-consumption neural processors 2 powerful neural processors |
APU 790 chip Support for INT4 Hardware compression |
Google’s custom tensor processor |
|
memory |
LPDDR5X 4 bands of 16-bit Support up to 24 GB |
LPDDR5 4 bands of 16-bit Support up to 8 GB |
LPDDR5X 16-bit bus width Support up to 24 GB |
LPDDR5T 4 16-bit bass Support up to 24 GB |
LPDDR5X 4 16-bit bass Support up to 16 GB |
|
manufacturing process |
4 nm TSMC |
3 nm TSMC |
Samsung 4 nm |
4 nm TSMC |
Samsung 4 nm |
In the table below, you can see the CPU score of the chips in single-core and multi-core processing based on the official GeekBench 6 benchmark. The results of all chips except Dimension 9300 are obtained from Zomit tests.
|
product/chip |
GeekBench 6 |
|
|---|---|---|
|
single core |
multi-core |
|
|
Snapdragon 8 Generation 3 (Galaxy S24 Ultra) |
2262 |
7005 |
|
Apple A17 Pro (iPhone 15 Pro Max) |
2960 |
7339 |
|
Dimension 9300 (Vivo X100 Pro) |
*2007 |
*7408 |
|
Exynos 2400 (Galaxy S24) |
2148 |
6618 |
|
Tensor G4 (pixels) |
1710 |
3799 |
Snapdragon 8 generation 3 and A17 Pro both use powerful processing cores, but A17 Pro has better processing performance using Apple’s proprietary architecture and detailed optimizations. This difference is felt especially in single-core tasks, where Apple has been able to provide much higher efficiency.
On the other hand, Dimensity 9300 has a very powerful performance in multitasking and running heavy programs and even surpasses A17 Pro by five percent. This issue is especially evident in situations where multiple processes are running at the same time.
Dimension 9300 showed a very powerful performance in processing benchmarks. This chip was able to challenge S8G3 and A17 Pro chips in multi-core tests. It can be said that Dimension 9300 has a higher position than its competitors in the field of multi-core processing, by sacrificing energy efficiency; But it still can’t reach the level of the A17 Pro in single-core tasks (two percent weaker) and is almost at the same level as the S8G3. Due to the good performance and relatively lower cost of phones equipped with Dimension 9300 compared to competitors, this chip offers users an efficient option.
The Exynos 2400 performs well in multitasking and heavy computing overall, but compared to the A17 Pro and Snapdragon 8 Gen 3, it still lacks in some areas such as single-core performance (5% weaker than the S8G3 and 27% lower than the A17 Pro). . Due to Samsung’s optimizations, this chip has an acceptable performance in Samsung devices, but it falls short in the competition with Qualcomm and Apple.
Although Tensor G4 is more focused on artificial intelligence processing, compared to other chips in the field of general processing, it shows weaker performance. With this chip, Google has tried to provide improvements in certain areas such as camera-related processing and machine learning, but it is still far from competing with the A17 Pro and Snapdragon 8 Gen 3. Pixels equipped with G4 tensor will be a good option for users who are looking for a different experience, but it won’t work for people who care about powerful performance in most areas.
Comparison of graphics processing similar to the game
In this section, we compare the graphics capabilities of the chips in-game rendering based on the GFXBench benchmark. Each of these chips uses an advanced graphics processor that provides a satisfying experience in running games and programs.
|
product/chip |
GFXBench (with reference display resolution) |
|---|---|
|
Snapdragon 8 Generation 3 (Galaxy S24 Ultra) |
81 |
|
Apple A17 Pro (iPhone 15 Pro Max) |
46.8 |
|
Dimension 9300 (Vivo X100) |
83 |
|
Exynos 2400 (Galaxy S24) |
68 |
|
Tensor G4 (pixel 9) |
44 |
These numbers are based on Aztec Ruins High Tier Offscreen. A higher number indicates better performance.
Snapdragon 8 Gen 3 with its advanced GPU that supports ray tracing technology is one of the best options for gamers. Compared to Apple’s A17 Pro, which uses Apple’s own GPU, this chip offers better performance in some graphics-heavy games. The benchmark results show a very close competition between S8G3 and Dimension 9300 chips. That being said, it would be fair to consider the top ranking for both chips jointly.

A17 Pro does not perform satisfactorily in graphics processing, because Apple focuses more on optimizing energy consumption, and as a result, it may not appear as powerful as Dimension 9300 and S8G3 in some graphics tests. In any case, getting the fourth place in this table is not far from the expectation; If you go back to the processor details comparison table, the A17 Pro’s GPU performance is 2.8 times lower than the Dimension 9300 chips, about half of the S8G3, and even 1.5 times lower than the Exynos 2400.
According to the results of both benchmarks, Dimension 9300 has close competition with Snapdragon 8 generation 3 and according to the numbers, it is placed beyond it. Using Immortalis-G720, Dimension 9300 has provided an impressive performance and has an absolute and significant advantage over A17 Pro in playing heavy games and advanced graphics programs, and has been able to provide a smooth and satisfying experience to users.
Exynos 2400 uses the Xclipse 940 GPU, which is based on AMD’s RDNA 3 architecture. Using this chip, Samsung has been able to provide satisfactory performance in graphics games, but it is 16% behind Qualcomm’s flagship and 19% behind MediaTek. The interesting thing about this chip is its 45% advantage over Apple A17 Pro.
In some heavy games, the Samsung chip may have lower performance due to less thermal management. Despite the Exynos’ impressive improvements, Qualcomm’s graphics unit still has a significant edge in rendering.
Although Tensor G4 focuses more on software optimizations and processing related to cameras and artificial intelligence, compared to competitors, it shows weaker performance in the field of graphics. This chip may face challenges in heavy games like Call of Duty or Genshin Impact. Therefore, Tensor G4 is a suitable processor for light games.
Comparison of battery life and power consumption
Optimizing energy consumption is one of the other factors affected by the chip, which has an impact on choosing the best phone. This issue is especially important during long-term use of the device and when running heavy programs.
Because each chip may have been released in a smartphone with a different battery capacity, we have used a new benchmark in the table below for equal comparison. To obtain this new benchmark, we perform several different activities (calls, games, web browsing, video playback) with each phone in order to drain the battery. Then we divide the weighted average of the device’s activity time (in minutes) by the battery capacity (in amp hours). You may be asking yourself:
Why division?
Because of the direct relationship between the charging time and battery capacity. Longer charge-discharge time should be a positive factor in the calculation of the criterion; While increasing the battery capacity is a factor unrelated to the chip.
The resulting number indicates that the operation of the chip consumes 1000 mAh of energy in a few minutes. We use the GSMArena benchmark to make the charge drain times fair.
|
product/chip |
Battery capacity (ampere-hours) |
Activity time (minutes) |
Reduction comparison criteria Charging (minutes/amp hours) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Snapdragon 8 Generation 3 (Galaxy S24 Ultra) |
5 |
829 |
165.8 |
|
Apple A17 Pro (iPhone 15 Pro) |
3.29 |
961 |
292.1 |
|
Dimension 9300 (Vivo X100 Pro) |
5.5 |
833 |
151.4 |
|
Exynos 2400 (Galaxy S24) |
4 |
726 |
181.5 |
|
Tensor G4 (Pixel 9 Pro XL) |
5.06 |
752 |
148.6 |
Benchmark for fair comparison of power consumption of flagship chips
A17 Pro has been able to achieve the best performance in this field with its special focus on energy efficiency. Due to its high energy efficiency, this chip can significantly increase the battery life of iPhone devices (at least two hours more than competitors) and at the same time have stable performance in heavy applications.

Snapdragon 8 generation 3 also minimizes energy consumption by using optimal architecture and advanced technologies, and while it has high processing power, in the field of energy consumption optimization, it offers 14 minutes more energy per amp hour than Dimensity 9300; But it still doesn’t reach the peak of A17 Pro (130 minutes more hours per amp hour). Meanwhile, Qualcomm’s chip is 10% behind Samsung’s Exynos 2400 in terms of energy efficiency.
Dimension 9300 also minimizes energy consumption and has high energy efficiency by using new technologies and optimizations. The chip outperforms the competition in the device battery life benchmark, but it still lags behind the A17 Pro when it comes to battery life. Don’t forget that MediaTek only used high-power cores in the Dimension chip and it is not far from the expectation that it does not provide optimal consumption. This fact makes most phones with this chip need to use a battery with a high nominal capacity to provide proper charging for users.
The Exynos 2400 is surprisingly energy efficient and consumes less power compared to MediaTek and Qualcomm chips. Let’s not forget that this chip with 10 cores holds the record for the highest number of cores in this comparison. With this chip, Samsung has tried to create a balance between performance and energy consumption, and it seems to have succeeded in this; But this success has a heavier bottom in favor of energy consumption.
The Tensor G4 optimized power consumption in these areas by focusing on AI and special processing but is more power-hungry compared to other chips, especially in general graphics and gaming (using 1 amp hour per 148.6 minutes). The chip is suitable for users looking for an AI-based experience, but it still needs improvement in terms of general energy efficiency.
Comparison of stability in heavy processing
In the world of smartphone technology, the stability of chips under challenging conditions is very important. We used the 3D Mark Wildlife Stress Test to check the stability of the investigated chips. This test provides the final score and percentage of stability by checking the performance of the device in heavy processing. This percentage shows how well the device can maintain its performance over time; The higher the percentage, the more stable the chip.
|
product/chip |
Percent stability |
|---|---|
|
Snapdragon 8 Generation 3 (Galaxy S24 Ultra) |
52 |
|
Apple A17 Pro (iPhone 15 Pro Max) |
78.9 |
|
Dimension 9300 (Vivo X100 Pro) |
55.5 |
|
Exynos 2400 (Galaxy S24) |
63.4 |
|
Tensor G4 (Pixel 9 Pro XL) |
68.3 |
Snapdragon 8 generation 3, despite the significant improvement in processing power and graphics, does not show very good stability and is placed at the bottom of the ranking list. This generation shows even less stability than the previous generation (with 64%).
Apple’s A17 Pro has been very successful in this field due to the use of advanced technologies. By using a proprietary architecture and focusing on software optimizations, Apple produced a chip that has stable and fast performance even under the most challenging conditions, but in some situations, its performance may drop slightly due to the focus on optimizing energy consumption (see the graphic comparison table). see).

Dimensity 9300 despite its high ability to manage heavy tasks, in some cases due to higher temperature, may suffer a slight decrease in performance stability. The difference of 3% in the reported numbers shows the close rank of stability of this chip to Snapdragon.
The Tensor G4 lags behind the competition in areas such as processing and graphics but ranks well in terms of performance stability.
Samsung’s Exynos 2400, with 10 processing cores and a 70% improvement in CPU performance compared to Exynos 2200, has managed to gain a good place among flagship chips.
Summary: Which is the winner of the competition?
Finally, after considering all aspects, we can rank the current flagship chips based on overall performance, power efficiency, and cost:
- Snapdragon 8 generation 3: This chip is a good choice for Android users with its extraordinary graphics power and excellent performance in multitasking processes. With this chip, Qualcomm was able to compete shoulder-to-shoulder with Apple and even surpass it in some areas. The Achilles heel of this chip is the performance stability during heavy processing and the single-core performance is weaker than A17 Pro.
- Dimension 9300: By providing a powerful and optimal chip, MediaTek has been able to prove its superior position at the top of the comparison table. Due to the higher power consumption of this phone with powerful cores, the said chip is used in phones that have larger batteries than others. Small chip stability and thermal problems are unavoidable considering the target market.
- A17 Pro: Despite its high processing power and unparalleled energy efficiency, this chip ranks in the middle of this comparison due to its average graphics performance in-game rendering. With detailed optimizations and a focus on very stable performance, Apple introduced the A17 Pro as a powerful chip against competitors; However, this chip has given the user a longer battery life by sacrificing graphics processing power.
- Exynos 2400: Samsung has provided good performance with this chip, but it still needs improvement in some areas. This chip has moderate performance stability and lags behind in terms of graphics processing compared to Apple and Qualcomm chips.
- Tensor G4: Google has introduced this chip with a focus on artificial intelligence and specific user experiences; But compared to other chips, especially in the field of general and graphic processing, it has much weaker performance.
Finally, we can conclude that Snapdragon 8 generation 3 and Dimension 9300 are jointly known as flagships of almost everything in the world of smartphone chips and can handle all the processing and graphics needs of users; However, the performance stability is weaker than Apple chip. Along with them, the A17 Pro chip is a very good choice for those who ignore high graphics power and expect great processing power and longer battery life than other flagships. Finally, in the bottom ranks of the table, we can comment on the superiority of Exynos 2400 over Tensor G4. The G4 chip is clearly inferior to its competitors in CPU processing, game rendering, and energy efficiency. Google has a difficult road ahead to compensate for this gap.


The biography of Andy Rubin, the creator of Android


How to prevent your location from being revealed through photos?


The chip battle of flagship phones in 2024; Which is the winner?


Do animals have an understanding of the concept of death?


What is Kali Linux? Everything you need to know about this popular but mysterious distribution


How to use iMessage on Android?


Xiaomi Glorimi M2 Max watch review; Alternative economic option for iPhone owners

Can humans endure the psychological torment of living on Mars?


Why do we humans sleep?

What is the difference between the brain of athletes and the brain of normal people?
Popular
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoWho has checked our Whatsapp profile viewed my Whatsapp August 2023
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoSecond WhatsApp , how to install and download dual WhatsApp August 2023
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoHow to use ChatGPT on Android and iOS
-



 AI2 years ago
AI2 years agoUber replaces human drivers with robots
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoThe best Android tablets 2023, buying guide
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoThe best photography cameras 2023, buying guide and price
-


 Humans2 years ago
Humans2 years agoCell Rover analyzes the inside of cells without destroying them
-


 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoHow to prevent automatic download of applications on Samsung phones


















