Space
The planet Venus; Everything you need to know
Published
3 months agoon


The planet Venus; Everything you need to know
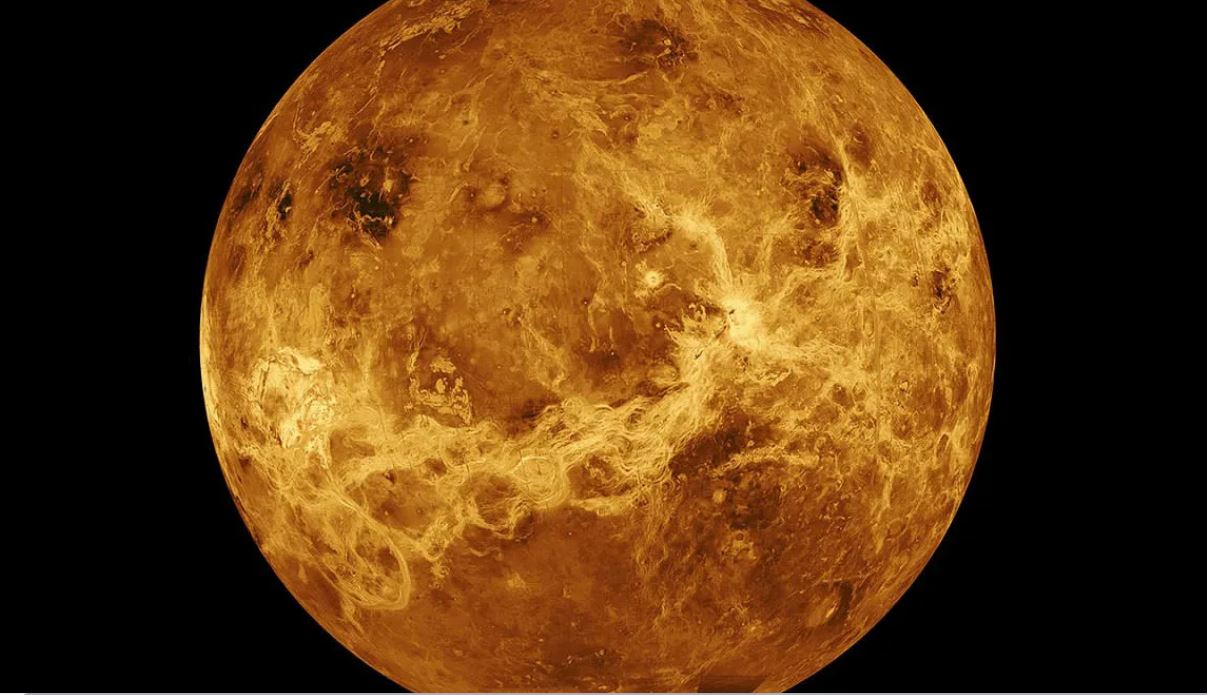
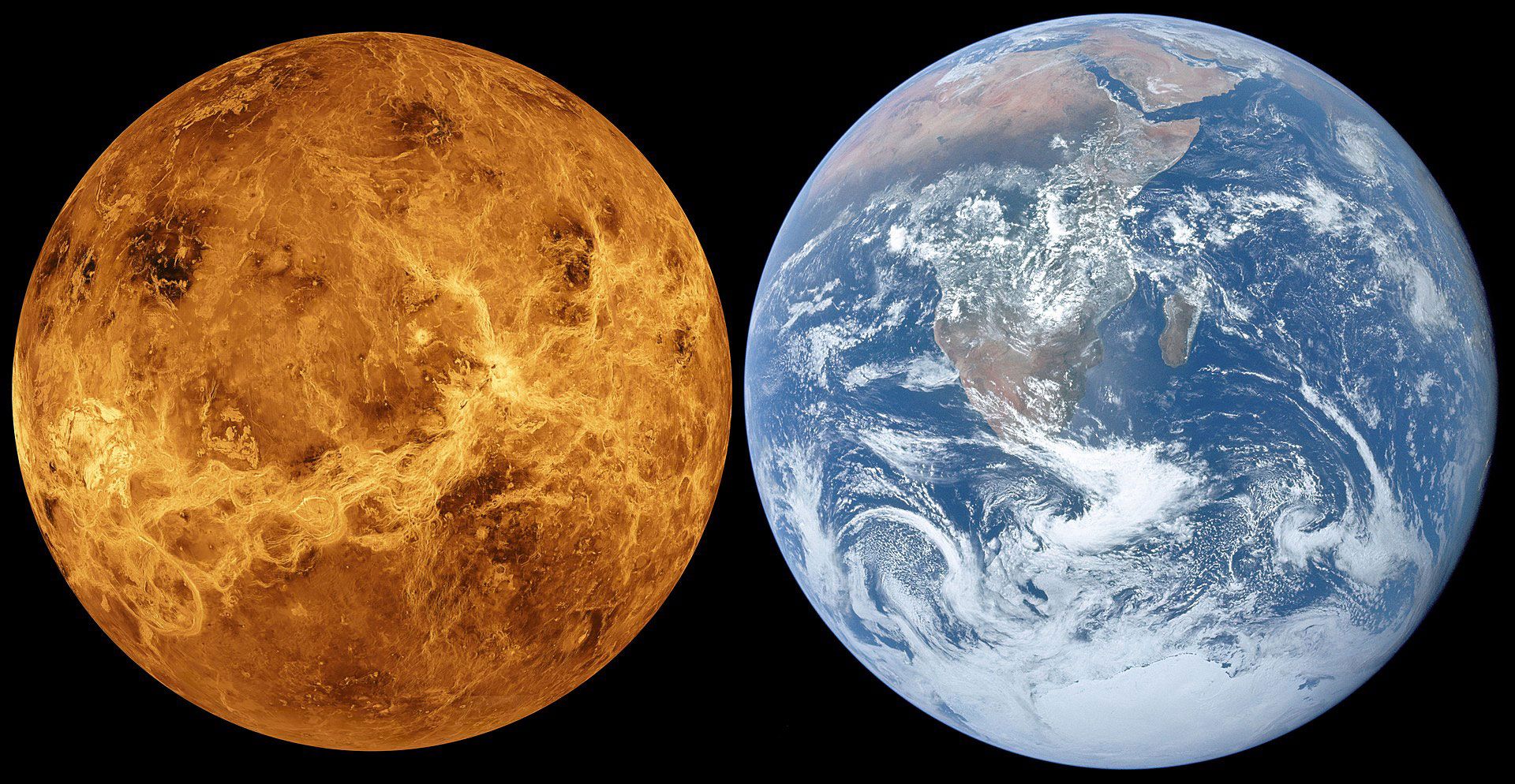
Venus, Venus, or Venus is the second planet of the solar system. This planet has many features in common with the Earth, and for this reason, it has earned the title of Earth’s sister. For example, both planets are in the habitable zone of the solar system. In addition, both are rocky bodies and a large part of them is composed of metal and silicate.
Table of Contents
-
What does the planet Venus symbolize?
-
The planet Venus in popular culture
-
How was the planet Venus formed?
-
Nucleus accumulation theory
-
Physical characteristics and composition of the planet Venus
-
The internal structure of the planet Venus
-
Geographical conditions, mountains, and volcanoes
-
The atmosphere of Venus: composition, climate and clouds
-
The climate of the planet Venus
-
Greenhouse escape effect and distant pasts of the planet Venus
-
The possibility of life on the planet Venus
-
The magnetic field of the planet Venus
-
Rotation and orbit of the planet Venus
-
Experience a real hell!
-
Observations and explorations of the planet Venus
-
Phases of Venus
-
transitions
-
Telescopic observations of the planet Venus
-
Space discoveries of the planet Venus
-
Venus Express, an unprecedented mission
-
Future missions to Venus
But the planet Venus, contrary to its calm appearance, is very turbulent and restless. 96% of Venus’s atmosphere is made up of carbon. The pressure on the surface of the planet Venus is more than 90 times the pressure on the surface of the Earth. Such pressure exists only at a depth of 900 meters in the Earth’s seas. Despite the closer distance of Mercury to the Sun, Venus is the hottest known planet in the solar system, and the average temperature of its surface reaches 471 degrees Celsius. Venus is covered with a thick layer of sulfuric acid reflective clouds. Clouds prevent sunlight from reaching the surface of this planet and reflect the light. The strong reflection of sunlight is the main reason why Venus shines above the night sky and is visible to the naked eye. The surface of Venus is dry and full of slate-like rocks and volcanic activity.
A year on Venus is equal to 224.7 Earth days, But the movement of Venus is slow, and for this reason, the longest day among the planets of the solar system belongs to this planet. One Venus day is equal to 243 Earth days. Unlike other planets, Venus rotates clockwise around its axis. This means that the sun rises in the west of Venus and sets in the east. Venus also has no moons.
As the brightest object in the night sky, Venus has played a prominent role in human culture since ancient times. This planet is the holy god of many cultures and has inspired many writers and poets with nicknames such as Morning Star or Evening Star. The other name of this planet, Venus, is derived from the Roman goddess of love and beauty. In the second millennium BC, the movements of Venus in the night sky were mapped for the first time. Because of its small distance from the Sun, Venus has been the target of interplanetary probes many times.
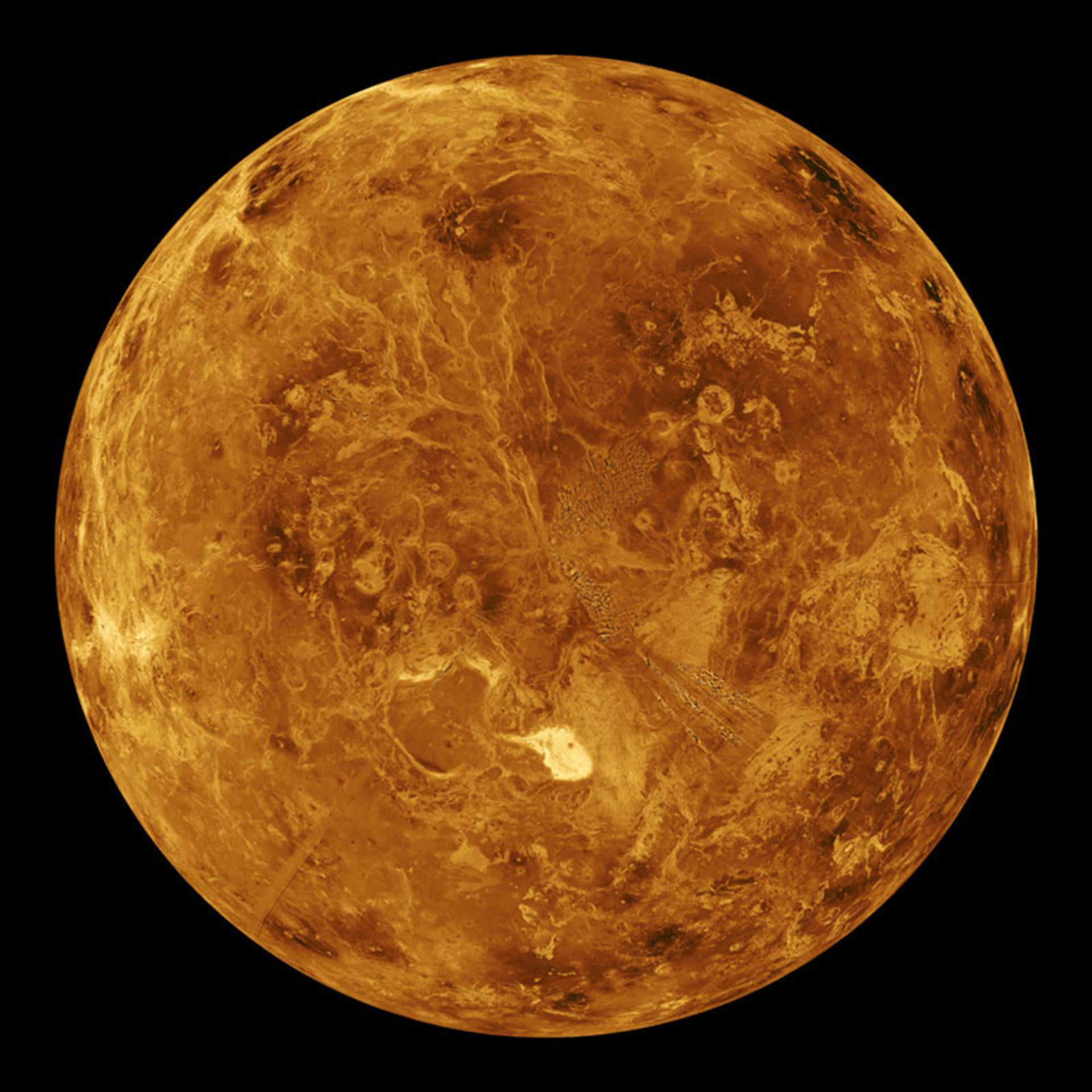
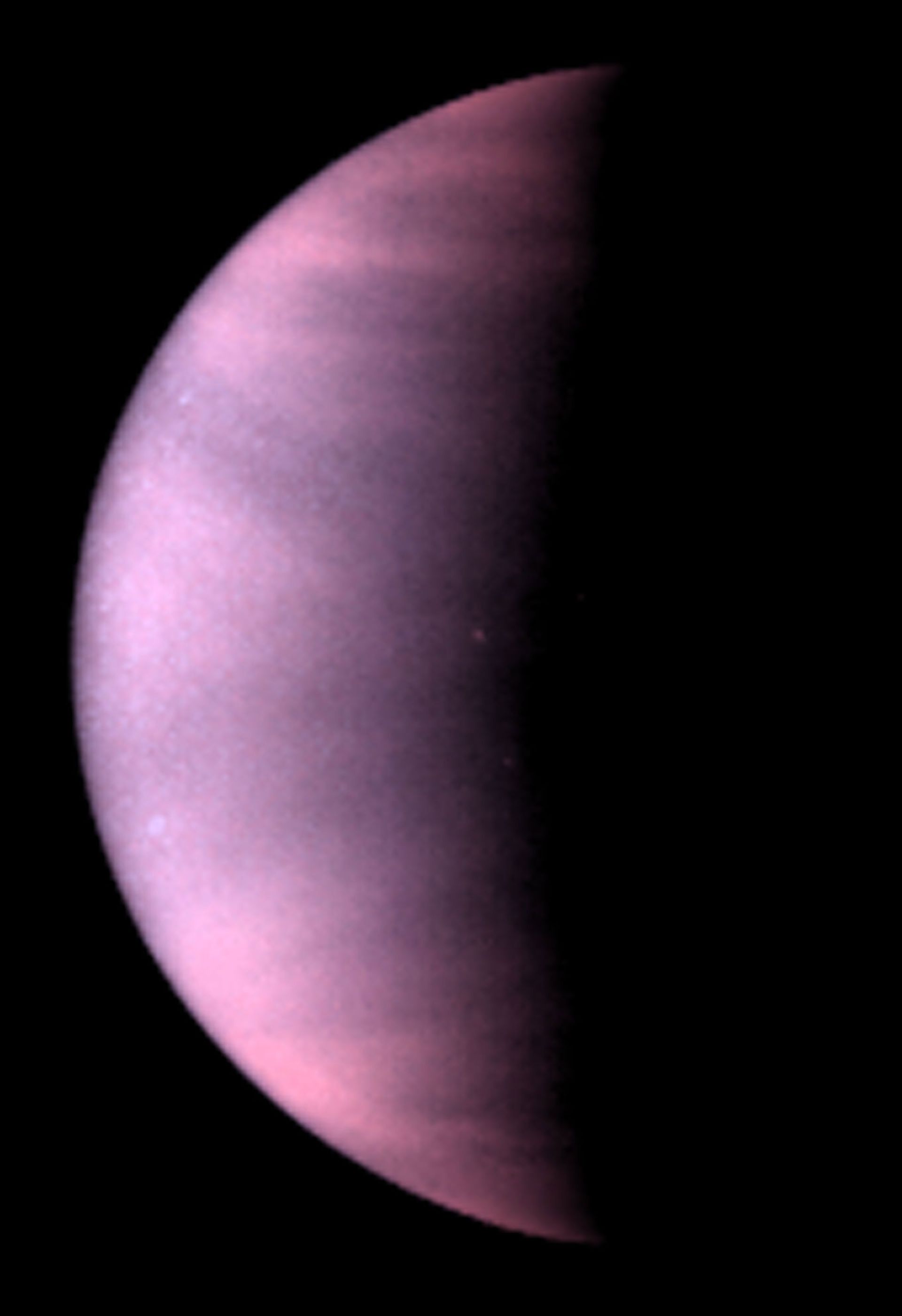
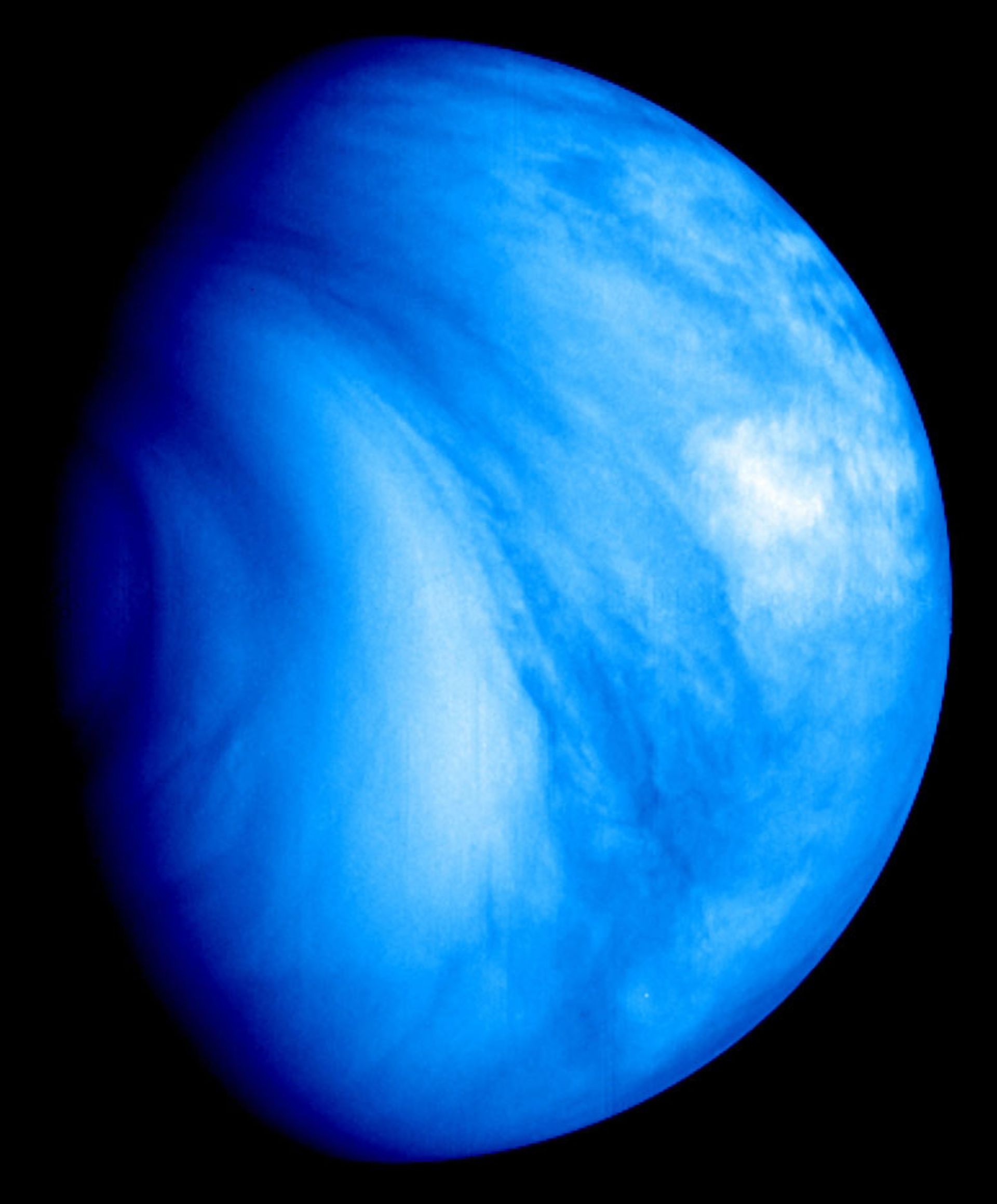
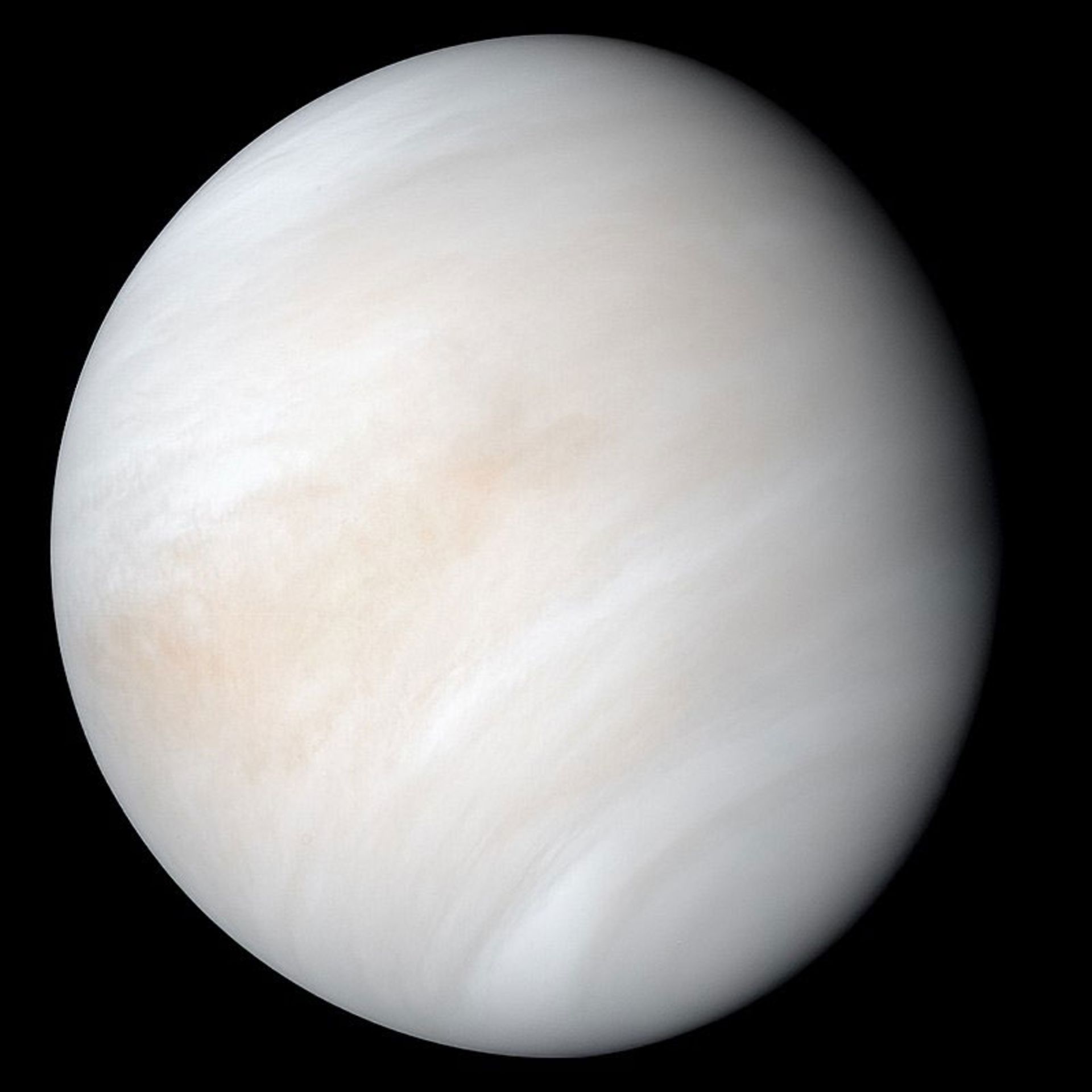 False color image of Venus in visible and ultraviolet wavelengths captured by the Mariner 10 probe. Clouds completely cover the surface of this planet.
False color image of Venus in visible and ultraviolet wavelengths captured by the Mariner 10 probe. Clouds completely cover the surface of this planet.
What does the planet Venus symbolize?
The astrological symbol of the planet Venus is the same symbol used in biology for the female gender. A circle with a cross below it. The symbol of Venus also means femininity and in Western alchemy, it represents the metal copper.

The planet Venus is one of the prominent indicators of the night sky, as a result, it has had a high importance in mythology, astrology, and science fiction texts of different cultures. In Sumerian religion, Inanna is associated with the planet Venus. Classical poets such as Homer, Sappho, and Vigil also spoke about the star of Venus and its light. Poets such as William Blake, Robert Frost, Elizabeth Landen, Alfred Lord Tennyson, and William Wordsworth have also written odes about it.
In Chinese culture, the planet Venus is called Zinxing, the golden god of the metal element. In India, Shukra Graha (Shukra planet) is derived from the powerful holy Shukra, which in Sanskrit means pure, pure, or shine and purity. Mayan civilization considered Venus to be the most important astronomical object after the Sun and the Moon. Ancient Egyptians and Greeks considered Venus to be two separate bodies, one of which was the morning star and the other the evening star.

The planet Venus to the right of the tree in Vincent Van Gogh’s 1889 painting of the starry night sky
How was the planet Venus formed?
From the collection of articles on the introduction of planets: Jupiter Characteristics, number of moons and wonders of the planet Saturn Features, number of moons, rings, and wonders
Despite a lot of information that has been obtained about the planets of the solar system in recent years, there are still doubts about how they formed. Currently, there are two main theories for how planets form. The first and most acceptable theory is the core accretion theory, which is compatible with rocky planets like Venus; But it is not so suitable for gas giants. The second theory is the disc instability theory, which is more suitable for gas giants.
Nucleus accumulation theory
According to the core accretion model, initially, the rocky cores of the planets were formed; Then the lighter elements formed the mantle and crust of the planets. On rocky worlds, other lighter elements made up the atmosphere. By examining the outer planets (outside the solar system), the core accumulation theory can be considered as the dominant theory of formation. Stars with more metal in their cores (a term astronomers use for elements other than hydrogen and helium) have larger planets in their systems than stars made only of metal.

Physical characteristics and composition of the planet Venus
Since the size, mass, density, and composition of Venus and Earth are almost equal, the title of twins or sister has been given to these two planets. The diameter of Venus is 12103.6 km and only 638.4 km less than Earth. However, the similarities end there. Venus is not the closest planet to the Sun, but it is the hottest planet in the solar system due to its dense atmosphere and ability to trap heat and the greenhouse effect (a situation in which, due to positive feedback between the surface temperature and the atmosphere, the greenhouse effect is intensified and the oceans evaporate). Is. As a result, the temperature on the surface of Venus even reaches 471 degrees Celsius, which easily melts lead. For this reason, probes that have already landed on the surface of Venus lasted only a few hours.
The internal structure of the planet Venus
The internal structure of Venus is probably similar to that of Earth. Like Earth, Venus is a rocky planet composed of rock and metal and probably has a molten metal core, a rocky mantle, and a crust. Since Venus is slightly smaller than the Earth, the pressure in its depths is 24% lower than the pressure in the depths of the Earth. The main difference between the two planets is the absence of tectonic plates on the surface of Venus. The reason for this problem can be the high strength of the crust of Venus.
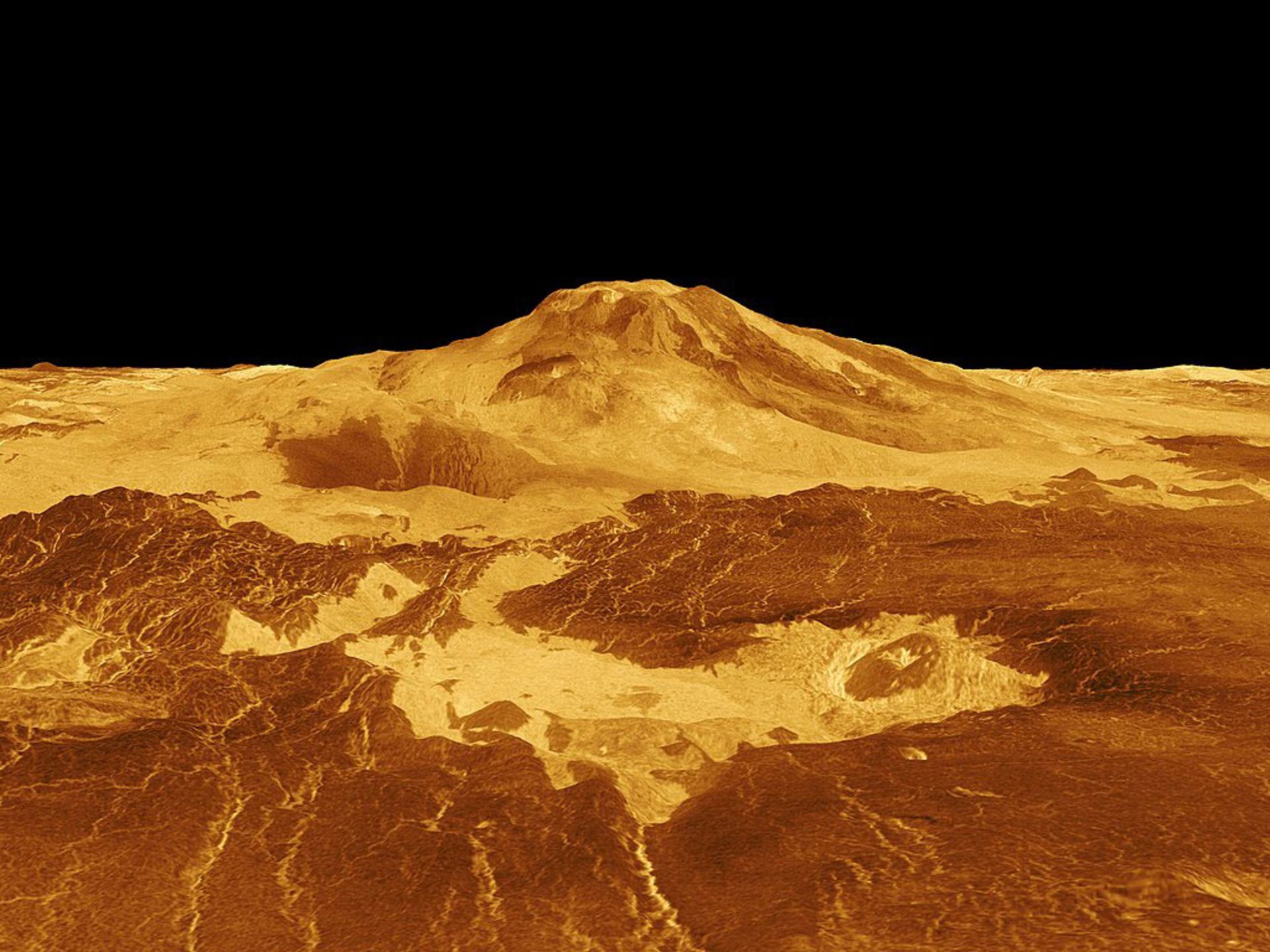
Geographical conditions, mountains, and volcanoes
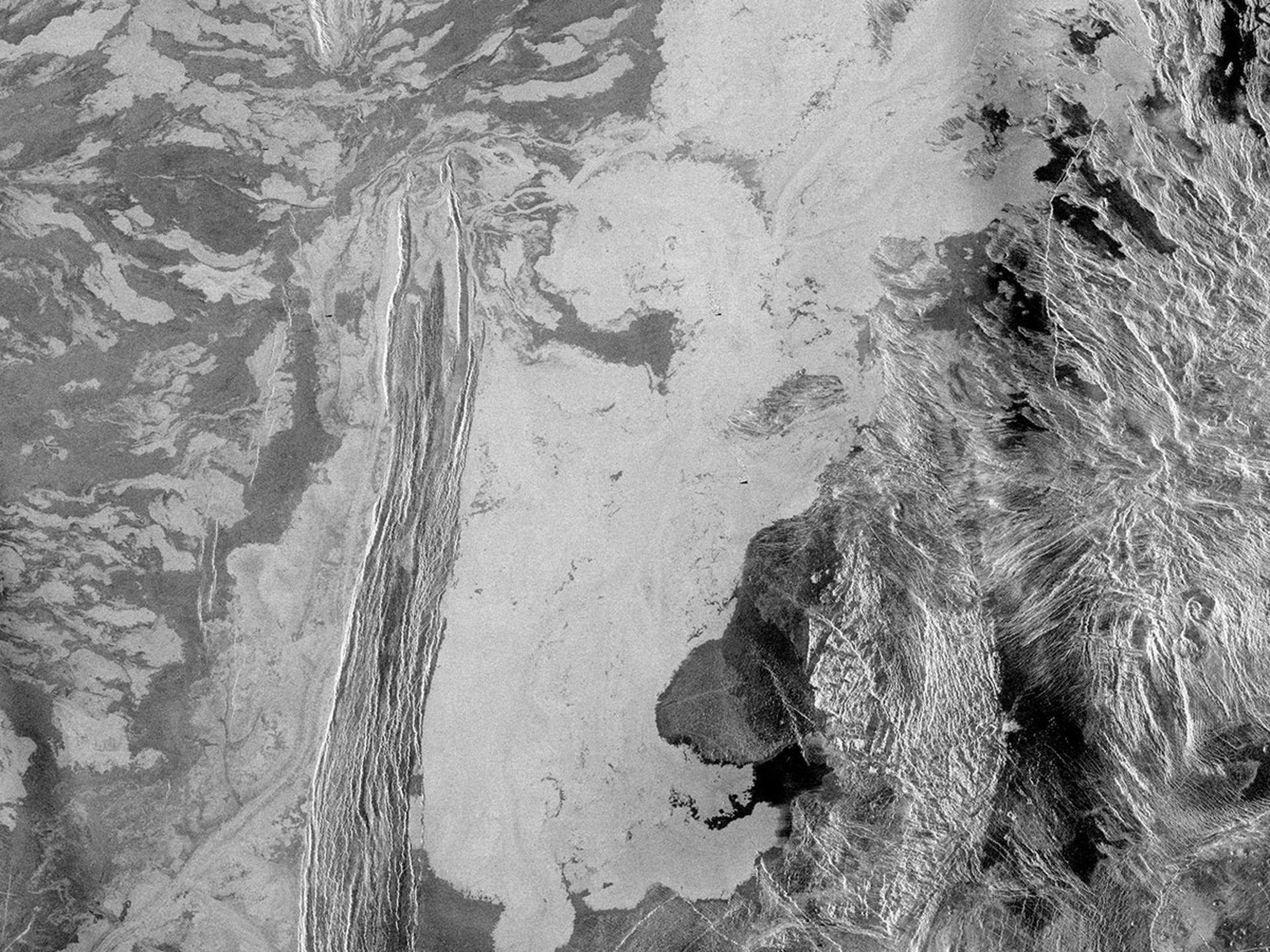
The surface of Venus has been the subject of many investigations by planetary scientists in the 20th century. Venus rovers in 1975 and 1982 sent images of angular rocks and surface sediments on Venus. The mapping of the surface of Venus was done by the Magellan probe in 1990 and 1991. The surface of Venus shows evidence of volcanic activity, and sulfur in the atmosphere may also be a product of this activity. Six mountainous regions make up one-third of the surface of Venus. One of the areas known as Maxwell is approximately 870 km wide and its mountains are 11.3 km high, which are the highest mountains on this planet.
Most of the surface of Venus was formed by volcanic activity. The number of volcanoes on Venus is seven times that of Earth. Although there are a total of 1,600 volcanoes on the surface of Venus, they do not seem to be active. Venus has a total of 167 large volcanoes that are more than a hundred kilometers wide.
However, the radars of the Magellan probe found evidence of volcanic activity in the Moat Mons region of Venus, which was seen in the form of gray streams near the summit and southern slope of the mountain. This probe also managed to discover impact holes on the surface of Venus, although their number was very small; Because volcanic lava covered them.
 False color map by Matt Moons
False color map by Matt Moons
Almost a thousand impact craters have been discovered on Venus, which are evenly distributed. In other planets such as Earth and Moon, the cavities undergo erosion and collapse. For example, the craters of the moon collapsed due to subsequent collisions, while the erosion factors of the impact craters of the earth are water and wind. Approximately 85% of Venus impact craters are new. Although the Earth’s crust is constantly moving, such a process does not exist on Venus. The diameter of Venus impact craters varies from 3 to 280 km.
The crust of Venus is older due to the accumulation of lava on it; But the Earth’s oceanic crust has been replaced by tectonic plates and its average age is 100 million years; While the average age of the crust of Venus is 300 to 600 million years. Now the question is raised that considering the conditions and harsh weather, why are the volcanic activities of Venus small compared to Earth?
According to Dr. Mikhail from the Faculty of Environmental Sciences (a geologist at St. Andrews University), due to the extreme heat, the integrity of the crust of Venus is less than that of Earth, and magmas (lavas) cannot enter the crevices of the crust and lead to renewed volcanic activity. The soft, plastic-like crust of Venus prevents the formation of tectonic plates (plate tectonics are a geological phenomenon that plays a very important role in the Earth’s carbon cycle and is essential for climate).
Investigating the environmental and geological differences of these two twin planets is the key to discovering extrasolar planets and the reason they are habitable (like Earth) or uninhabitable (like Venus). The Venus Express orbiter from the European Space Agency also managed to discover new evidence of volcanic activity on the surface of Venus; So that the volcanic eruptions in some places caused the temperature to rise up to 800 degrees Celsius.
The atmosphere of Venus: composition, climate and clouds
The atmosphere of Venus is almost completely composed of carbon dioxide. The atmosphere of this planet also has small amounts of nitrogen and clouds of sulfuric acid. This combination results in a greenhouse effect that makes the planet’s surface even hotter than Mercury. In addition to the intense heat, the planet is surrounded by heavy clouds that act like a reflective shield, protecting it from meteorite bombardments. However, numerous craters and craters can be seen on the surface of this planet.
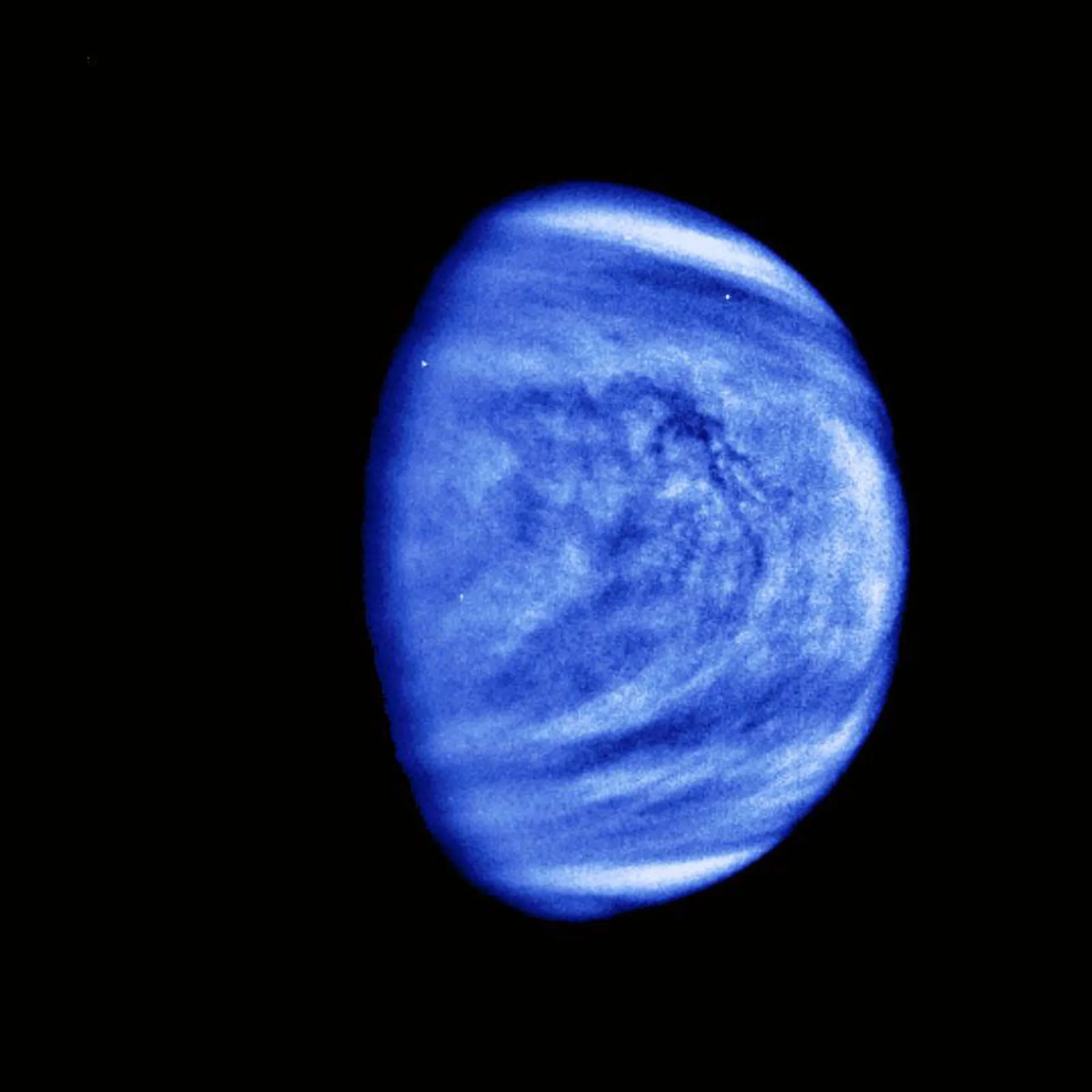
 Ultraviolet image of Venus captured by Akatosky spacecraft
Ultraviolet image of Venus captured by Akatosky spacecraft
The climate of the planet Venus
The constant speed of Venus’s winds reaches 360 km/h. Wind speed decreases near the surface and reaches several kilometers per hour. On Earth, seasons change based on Earth’s axis; When one of the hemispheres is closer to the sun, the temperature in that hemisphere increases; But on Venus, much of the sun’s heat cannot pass through its thick atmosphere. As a result, the temperature difference during a year and the difference between day and night temperature of this planet is not much.
Research shows that the atmosphere of Venus was like the Earth’s atmosphere billions of years ago, But 600 million years of greenhouse effect resulting from water evaporation brought the level of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere of this planet to a critical limit. Even before this happened, the surface of Venus was not habitable like Earth, but there was a possibility of life in the upper layers of Venus’ atmosphere.
The clouds of Venus are mainly composed of sulfuric acid. In addition, one percent of Venus’ atmosphere consists of ferric chloride. Other possible substances in clouds include ferric sulfate, aluminum chloride, and phosphoric anhydride. Clouds at different levels have different compositions and the way they are distributed is different. The clouds of Venus reflect almost 90% of sunlight and prevent sunlight from reaching Earth.
Greenhouse escape effect and distant pasts of the planet Venus
According to a hypothesis, the planet Venus had a different face in the distant past. According to studies, Venus was probably a habitable world like Earth billions of years ago. One of the parameters influencing the harsh environment of this planet is its slow axial rotation (rotation around itself). So one day on Venus is equal to 243 Earth days or two-thirds of an Earth year; Therefore, in any part of this planet, sunlight lasts for months. According to the simulations, Venus probably had oceans early in its life, but tidal forces from the oceans slowed the planet’s rotation and eventually evaporated the oceans.
But based on NASA’s clues and past missions, Venus probably wasn’t as hellish in the past, it had blue oceans, a thinner atmosphere, and a faster rotation. All these criteria could make Venus a true paradise. According to new research by scientists at NASA, the University of Bangor and the University of Washington, the ancient oceans of Venus have been the main cause of its climate changes.
The greenhouse effect has made the planet Venus uninhabitable
According to this hypothesis, ocean tides have led to a reduction in the speed of the planet’s axial rotation by creating friction between water currents and the sea floor. For example, this process on Earth causes the days to get 20 seconds longer every 1 million years. Assuming the presence of oceans on ancient Venus, such a process probably occurred, and since Venus has no moons, the Sun was the main cause of tides.
But according to another research, the above hypothesis is not true. According to more recent studies, there was no liquid ocean on the surface of Venus from the beginning. Although past researches have pointed to its humid and hot environment based on the chemical characteristics of the atmosphere and high areas of Venus, more recent researches have shown that the high points were formed by molten materials and not water. In general, there is still little information about the formation and past of the planet Venus. As future missions launch more probes to the planet, more secrets about its formation and past will be revealed.
The possibility of life on the planet Venus
About two years ago in 2020, scientists reported the presence of a gas called phosphine among the acidic clouds of Venus . This gas could be a sign of life on this hellish planet. Because of how phosphine forms on Earth, it was surprising to find even a small amount of this gas on Venus.
Some scientists believed that this gas is probably the result of the activity of small living organisms that live in the clouds of Venus, and another group considered it the result of the volcanic activities of Venus. On the other hand, even the idea of life on the hellish planet Venus seemed funny because the surface temperatures of this planet can even melt lead or the clouds of Venus are full of toxic and acidic gases and life cannot be imagined in them.
However, phosphine gas could upset all the equations. A group of scientists also believed that waiting for the discovery of life on Venus was futile. According to an analysis by John Hallsworth, a microbiologist at Queen’s University in Belfast, the lack of water in Venus’ clouds prevents life from growing in the planet’s atmosphere. At least there is no possibility of the growth of life similar to Earth in the atmosphere of this planet; Because living things need water to grow.
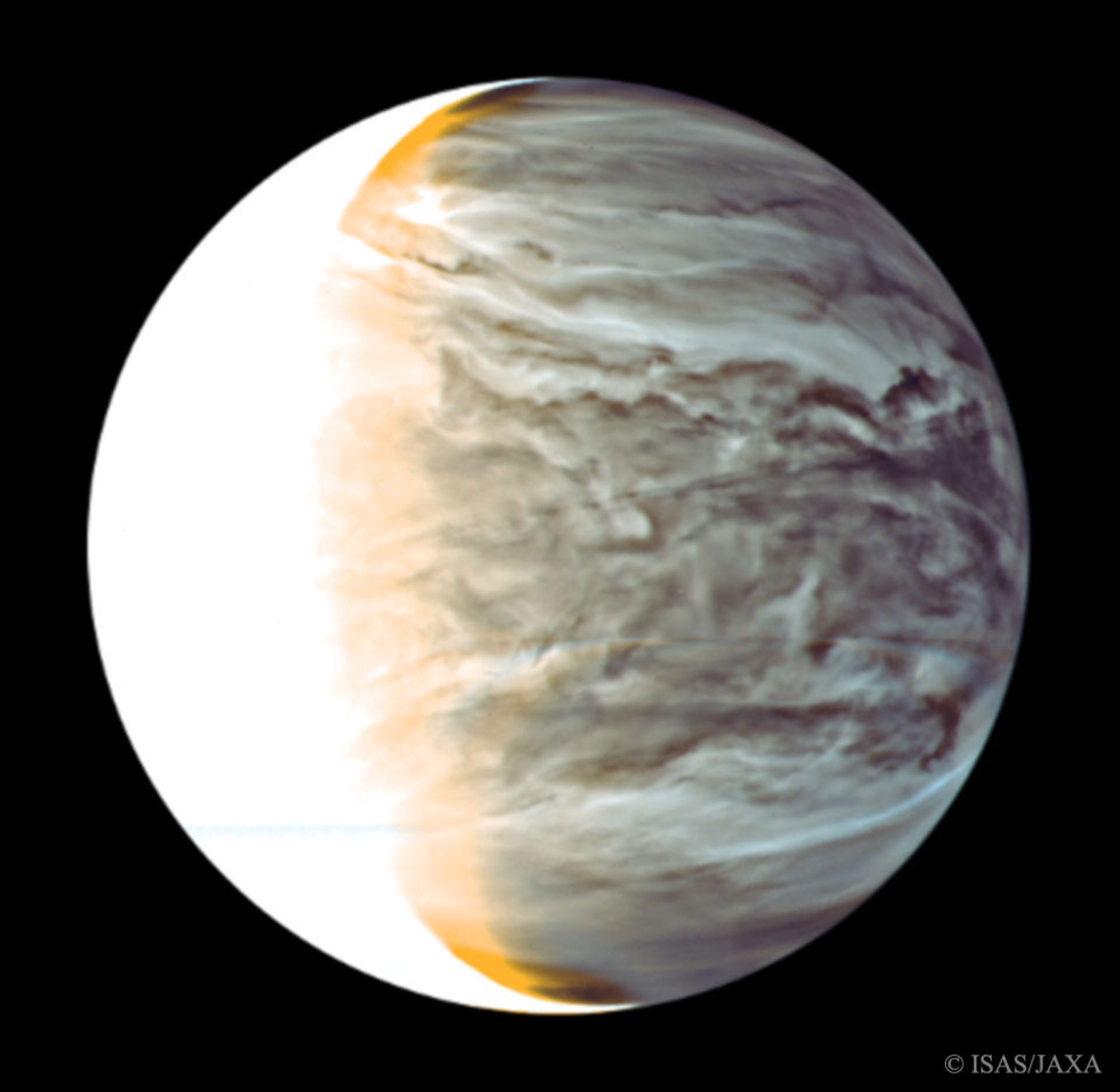
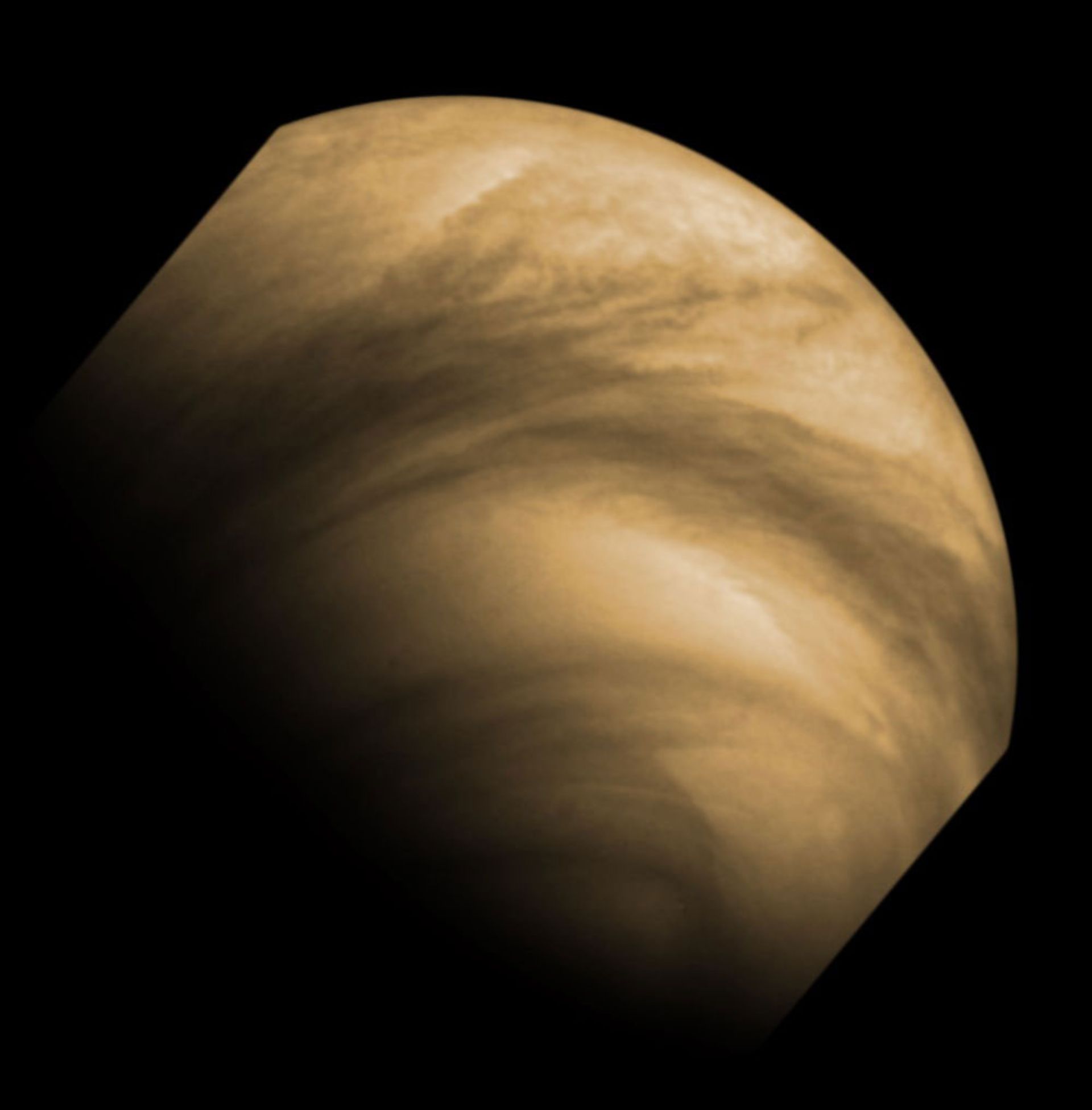
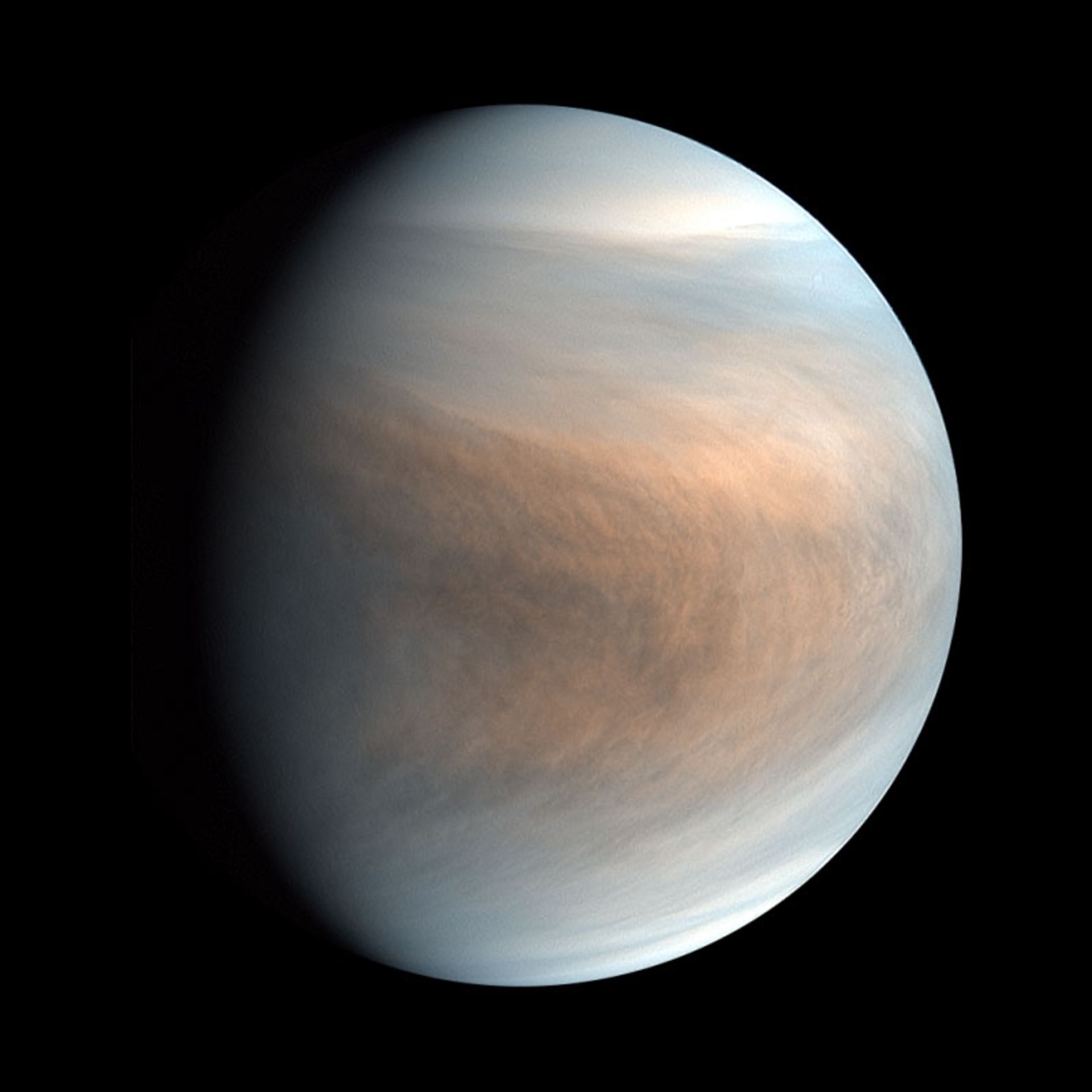 A false color view of Venus captured by Japan’s Akatosky Orbiter. According to new vital research, what we know cannot describe the sulfur dioxide anomalies in the atmosphere of this planet; Therefore, the existence of life on this planet is unlikely.
A false color view of Venus captured by Japan’s Akatosky Orbiter. According to new vital research, what we know cannot describe the sulfur dioxide anomalies in the atmosphere of this planet; Therefore, the existence of life on this planet is unlikely.
However, a detailed and new analysis of the chemical state of the clouds of Venus shows that none of the biological indicators of aerobic life with sulfur metabolism exist in it; As a result, the mystery of discoverable life in the clouds of Venus is largely solved, and at least until we get new information, this conclusion will remain valid. The complex chemical properties of Venus’ upper atmosphere cannot be easily described based on life as we know it. Finally, future discoveries and missions will reveal more about the above results. The definitive conclusion so far is that there is no trace of life in the clouds of the planet Venus.
The magnetic field of the planet Venus
According to the observations of Venus 4 probe in 1967, the magnetic field of Venus is much weaker than the magnetic field of Earth. The magnetic field is created by the interaction between the ionosphere and the solar wind. The small magnetosphere of Venus is not strong enough to protect its atmosphere from cosmic rays. The weak magnetosphere around Venus means that the solar wind interacts directly with the outer atmosphere. Here, hydrogen and oxygen ions are produced by the decomposition of neutral molecules from ultraviolet rays.
Rotation and orbit of the planet Venus
Due to the slow rotation of Venus around its axis, one Venus day is equal to 243 Earth days; And in this way, it has won the record of the longest day in the solar system. Venus is located at a distance of 0.72 AU (108 million kilometers) from the Sun, and its orbit around the Sun is equal to 224.65 Earth days. When Venus is between the Earth and the Sun, inferior conjunction occurs; This means that this planet is at the closest distance to Earth (41 million km). This happens every 584 days.
Venus is on the border of tidal lock. According to the tidal lock, one side of the smaller mass is permanently facing the larger mass. For example, the Moon is tidally locked relative to the Earth, and Earth residents always see one side of the Moon. Unlike other planets, Venus orbits the Sun in the opposite direction. The thick atmosphere of Venus prevents this planet from being completely locked to the Sun.
Venus does not have a natural moon, But instead, it has several asteroids: the asteroid 2002 VE68 and two other transient asteroids, 2001 CK32 and 2012 XE133.
Experience a real hell!
Considering the physical characteristics and atmospheric conditions, suppose you want to travel to Venus. Although such a situation is impossible in reality and Venus is a planet you may never want to see! But you can better understand its conditions with an imaginary trip to Venus. On an imaginary trip to Venus, finding a landing position is almost impossible. Even if you manage to land on its surface, Venus’s atmosphere is full of toxic clouds of sulfur dioxide.
At the beginning of the descent, you will face strong winds (approximately 360 km/h), at a distance of 48 km in the atmosphere, the winds will subside and you will enter a toxic fog. The rains of Venus are composed of sulfuric acid, but the rain never reaches the surface of Venus; Because the atmosphere is so hot that they evaporates in the middle of the road. After leaving the fog, you will experience a temperature of 315 degrees Celsius and the pressure is ten times that of the seas on the surface of the earth.
The approximate speed of winds on the surface of Venus reaches 360 km/h
You experience such heavy pressure only at a distance of 800 meters from the earth’s oceans; But after landing on the surface, the temperature will reach 471 degrees Celsius; A temperature that easily melts lead. Contrary to popular belief, the temperature is not lower at the poles of Venus. Venus spins hard on its axis and the temperature is almost the same across its entire surface. Now suppose you can get out of your spaceship.
Walking on Venus is a very difficult task. The clouds of Venus reflect 90% of the sunlight, so the light hardly reaches the surface and you can hardly see anything up to a few kilometers away. In such conditions, the rate of oxygen consumption will increase. 96% of Venus’ atmosphere is carbon dioxide, 3.5% is nitrogen, and less than 1% of the rest is carbon monoxide, argon, sulfur dioxide, and water vapor.
In such conditions, the risk of damage to cells and cancer will increase. Given that Venus has no known magnetic field, then you will be bombarded with energetic cosmic rays. On the other hand, your weight will be less on the surface of Venus because the mass of Venus is 91% of the mass of Earth. In the past, it was thought that there was a tropical paradise under the clouds of Venus, until in the 20th century, spacecraft revealed the hellish face of Venus.
Observations and explorations of the planet Venus
After the Moon, Venus is the brightest object in the night sky that can be seen with the naked eye. The reason why Venus shines above is its thick cloud layer that reflects more than 90% of sunlight. For this reason, the characteristics of the surface of Venus remained a mystery for a long time.
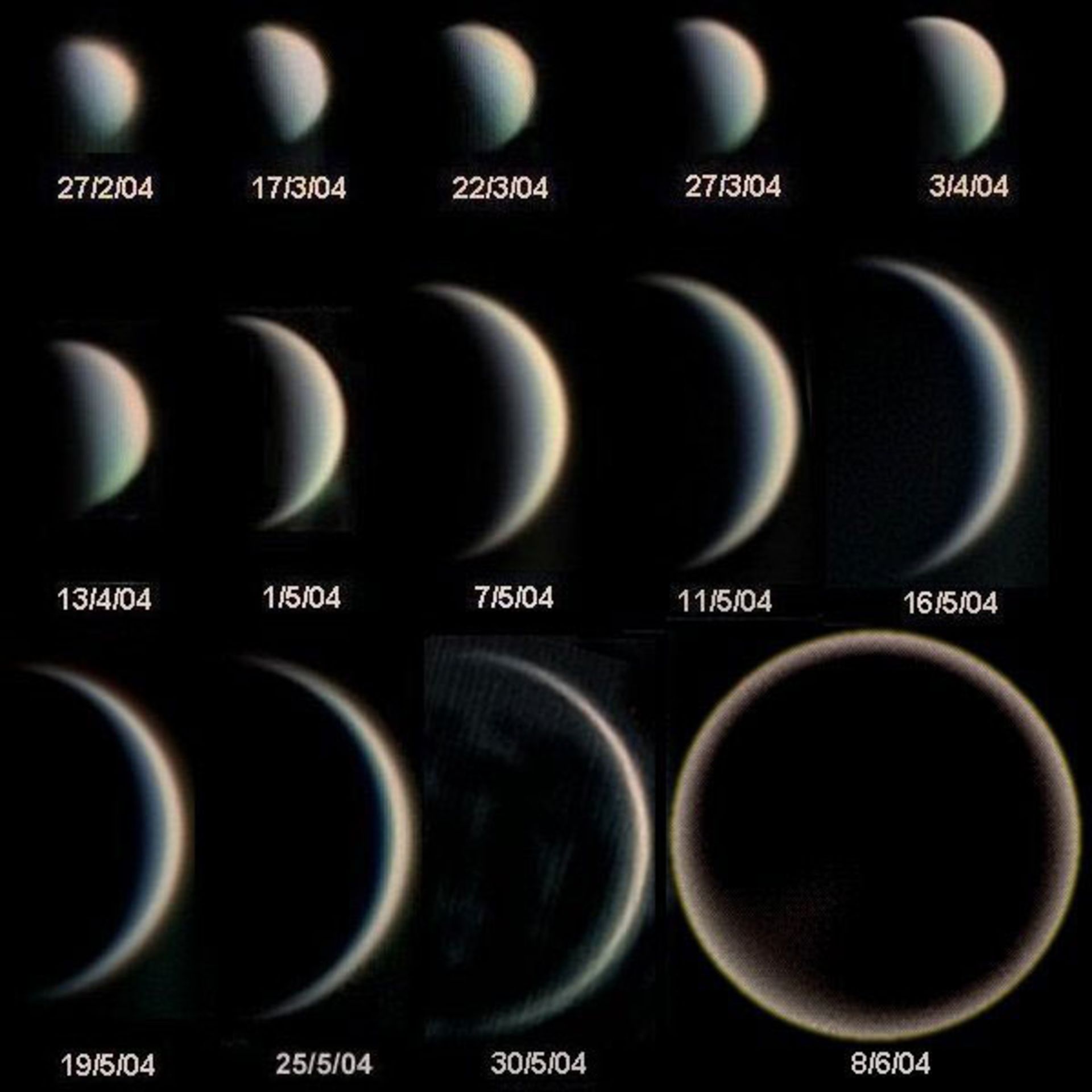
Phases of Venus
Like the moon, Venus appears in a complete cycle of phases. The changes of Venus can be observed in monthly intervals. When Venus is at its maximum distance from the Sun, it appears as a large, bright disk.
Phases of Venus and evolution of its apparent diameter
Transitions
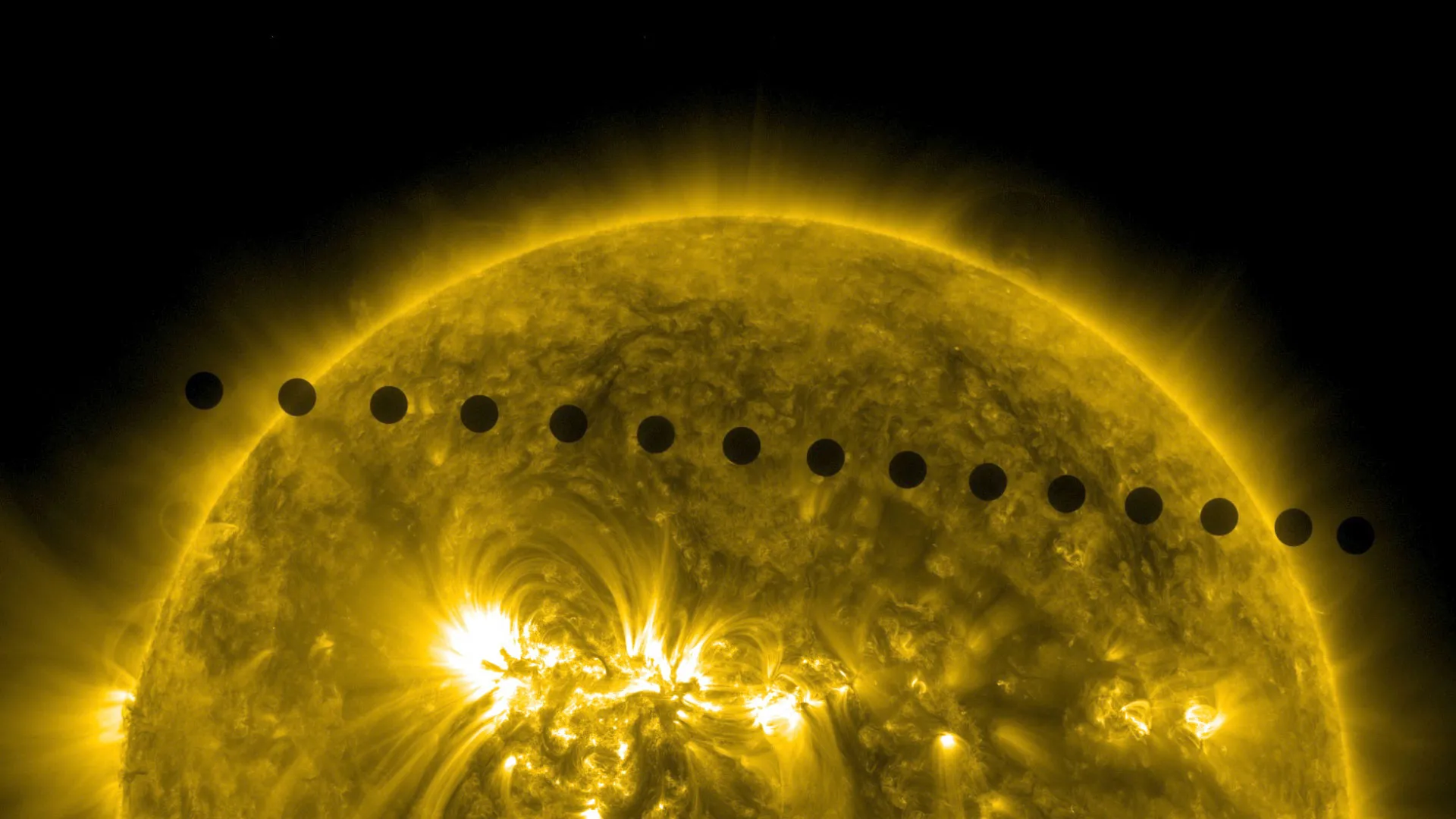
A transit of Venus occurs when the planet passes directly between the Sun and a larger planet. During the transit, Venus can be seen from Earth as a small black dot that passes in front of the Sun. Transits of Venus usually occur in 243-year cycles with a pattern of two pairs of transits at an interval of eight years and at intervals of 105.5 years or 121.5 years. This pattern was discovered in 1639 by the English astronomer, Jeremy Horrocks. The last pair of transitions occurred on June 8, 2004, and June 2012. The previous transit couple occurred in December 1874 and December 1882; The next transit couple will occur in December 2117 and December 2125.
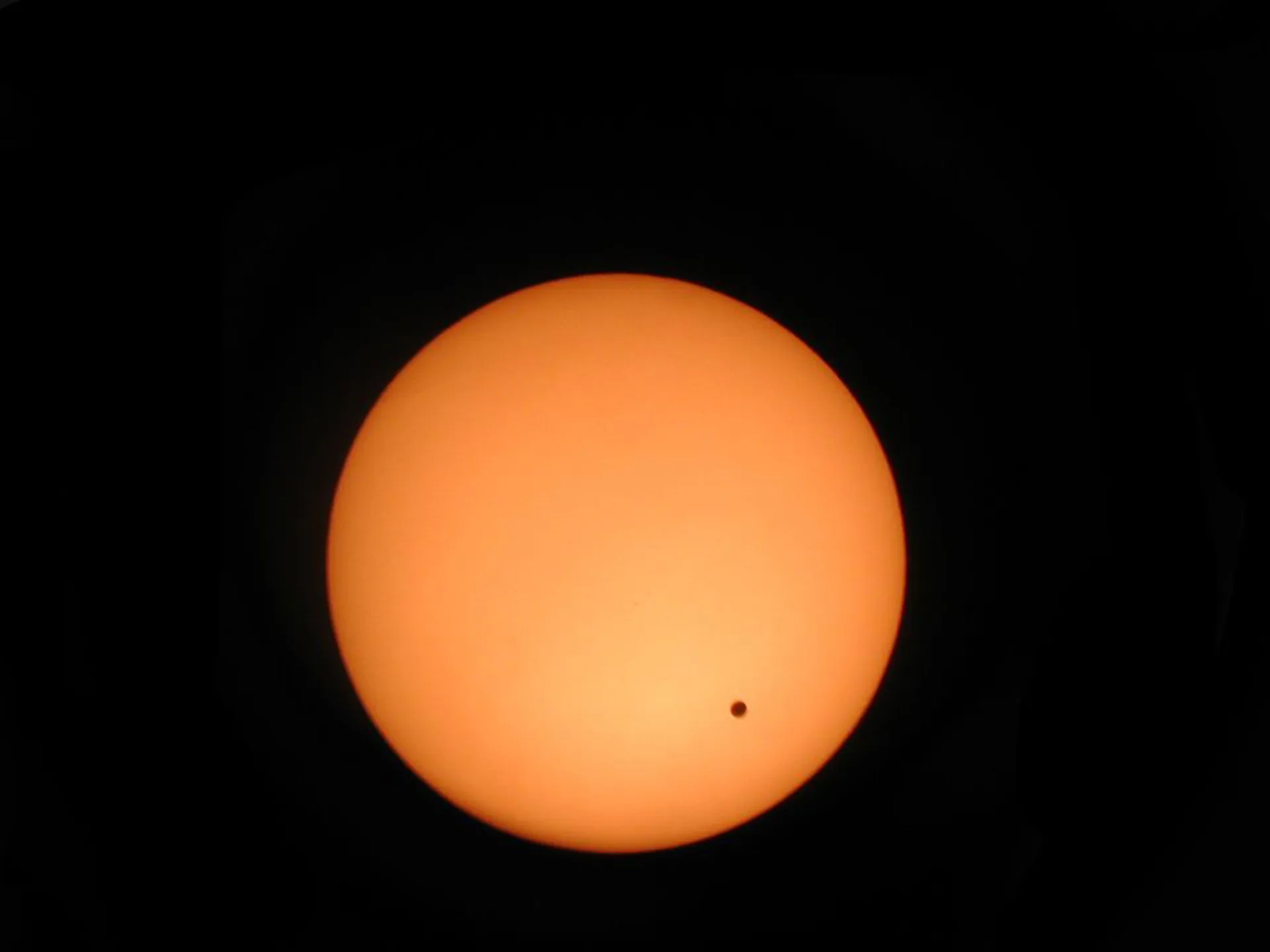 Transit of Venus in front of the Sun, 2004
Transit of Venus in front of the Sun, 2004
Telescopic observations of the planet Venus
Until the 20th century, little was known about Venus. With the discovery of spectrometers, radars, and ultraviolet observations, more information about this planet was obtained. The first ultraviolet observation of Venus was made in the 1920s. The ultraviolet images showed remarkable details that were not visible in infrared and visible images. The yellow and dense atmosphere of Venus along with cirrus clouds were discovered in this research. The first clues to the orbit of Venus came from spectroscopic observations in the 1900s. Radar observations in the 1970s reveal more details of Venus’ surface for the first time. In these observations, the existence of Maxwell’s mountains was proved.
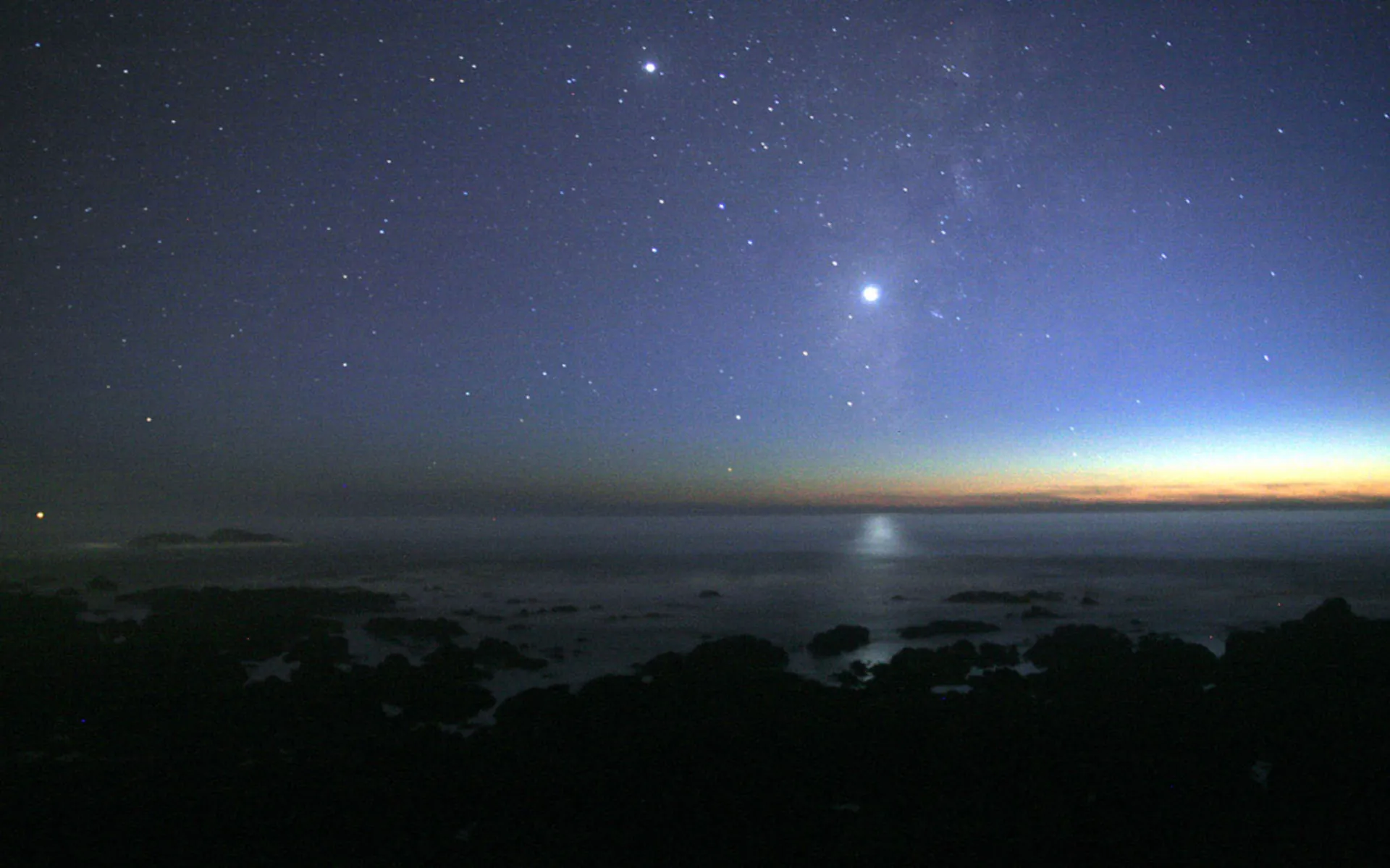 The planet Venus can be seen to the right of the center of the image, brighter than all other planets or stars. Jupiter is at the top of the image.
The planet Venus can be seen to the right of the center of the image, brighter than all other planets or stars. Jupiter is at the top of the image.
Space discoveries of the planet Venus
The first robotic interplanetary probe to visit Venus was the Soviet Union’s Venera probe, launched in 1961. On the other hand, the United States achieved its first success in exploring Venus with the Mariner 2 mission on December 14, 1962. This mission was the first interplanetary mission to collect data from the planet’s atmosphere.
On October 18, 1967, the Soviet Union’s Venera 4 successfully entered Venus’ atmosphere and developed science programs. Venera 4 showed that the surface temperature of Venus is hotter than that calculated by Mariner 2 (approximately 500 degrees Celsius); It also showed that 95% of the atmosphere of Venus consists of carbon dioxide and proved that the density of the atmosphere of this planet is beyond imagination. A Soviet-American science team analyzed data from the Venera and Mariner missions in the years after the mission.
In 1974, Mariner 10 visited Venus on its way to Mercury and recorded some ultraviolet images of it that showed the high speed of Venus’ atmospheric winds. In 1975, the Venus rovers 9 and 10 sent back the first black-and-white images of the surface of Venus. In 1982, Venera 13 and 14 sent back the first color images.
NASA obtained more information about Venus in the form of two separate Pioneer missions, the Pioneer orbiter and the Pioneer probe. The successful Soviet Venera program ended in 1983 with Venera 15 and 16. Other spacecraft, which had a purpose other than Venus, passed by Venus several times in the 1980s and 1990s, including Vega 1 (1985), Vega 2 (1985), Galileo (1990), Magellan (1994), Cassini, Huygens (1998). ) and Messenger (2006) pointed out.
 NASA’s Messenger probe captured this image of Venus in 2007
NASA’s Messenger probe captured this image of Venus in 2007
But Venus Express was another unprecedented mission launched by the European Space Agency for a long-term study of Venus’ atmosphere and entered Venus’ orbit in April 2006. The probe was equipped with seven scientific instruments and sent unprecedented data. Japan’s Akatsuki orbiter was launched on May 20, 2010. At first, this probe could not be placed in the orbit of Venus; But after five years, scientists regained control and were able to place it in the orbit of Venus. This orbiter investigates the atmosphere of Venus.



Gallery of images of Venus missions and explorations
Venus Express, an unprecedented mission
Venus Express was the first mission of the European Space Agency to Venus and the second mission of this organization to the Sun. This 1.2-ton spacecraft orbited Venus for eight years and monitored the long-term atmospheric patterns of the planet and used several instruments to study the conditions of the clouds and surface of Venus. The Venus Express mission ended in December 2014 after the spacecraft ran out of fuel.
This spacecraft found important information such as the existence of auroras; Meanwhile, Venus lacks the magnetic field necessary to maintain auroras. Venus Express reached its destination on April 11, 2006, after traveling 400 million kilometers. The mission duration of this spacecraft was 486 days. The conditions of Venus are very unfavorable for the probe landing due to the high temperature of the surface of this planet. On the other hand, the dense clouds of Venus do not allow surface observation.
Venus Express used ultraviolet to infrared imaging instruments to photograph the surface of Venus. This probe was also equipped with a plasma analyzer, magnetometer, and a radar depth gauge to measure the atmosphere and environment around the planet. In the continuation of this mission, evidence of a vortex around the planet’s south pole was reported, which was similar to another vortex at its north pole. In June, the European Space Agency announced the discovery of an atmospheric vortex called a double eye around the south pole of Venus.
 The southern hemisphere of Venus was recorded in the ultraviolet spectrum by the Venus Express probe.
The southern hemisphere of Venus was recorded in the ultraviolet spectrum by the Venus Express probe.
In 2011, changes were observed in this vortex. The shape of this vortex was sometimes in the shape of the English number 8 and sometimes in the shape of the letter S. According to scientists, the reason for the formation of these eddies is the currents in the meridian orbit and the poles of this planet. Since Venus’ clouds are very thick and difficult to penetrate, Venus Express used another method to probe the surface of the planet. In 2006, researchers were able to detect heat emitted from the planet’s molten crust. Infrared heat can pass through certain holes in the planet’s atmosphere and enter space, and the spacecraft feels this heat. Therefore, scientists were able to make the first temperature map of the southern hemisphere of Venus.
 False color image of the clouds of Venus captured by the VMC Venus Express camera. This image was recorded from a distance of 30 thousand kilometers on December 8, 2011.
False color image of the clouds of Venus captured by the VMC Venus Express camera. This image was recorded from a distance of 30 thousand kilometers on December 8, 2011.
By September 2007, Venus Express had been in orbit for 500 days and its mission was extended. Despite the harsh environment and radiation around the planet, the spacecraft was in good condition and sent back new information about the planet’s changing atmosphere. The new observations showed daily changes in the air currents of Venus. In addition, scientists discovered a new isotope of carbon dioxide that plays an important role in the planet’s greenhouse effect.
In the following years, Venus Express discovered evidence of volcanoes on Venus by examining sulfuric acid (one of the common products of volcanoes) and investigating strange phenomena such as storms. In March 2012, Venus Express was temporarily blinded by a massive solar storm. Star tracking cameras helped the spacecraft stay on track, But the spacecraft had lost its sight.
Exactly one month later, researchers discovered that Venus produces auroras without having a magnetic field. In this way, they were able to explain the strange lights of Venus that the spacecraft had sent during the previous years. Venus has a magnetic tail that is seen when particles from the sun hit the ionosphere. The ionosphere is the part of the planet’s upper atmosphere that contains electrically charged ions.
According to Venus Express observations, the magnetic coupling with the tail resulted in a 3,400 km wide magnetic plasma bubble that lasted only 94 seconds. Between June and July 2014, Venus Express explored the upper atmosphere of Venus. The aim of this study was to obtain more information about the characteristics of the atmosphere of Venus. In the same year, the operation of this spacecraft ended forever due to running out of fuel.
Future missions to Venus
Venus is hellishly beautiful: its clouds are made of sulfuric acid, and its surface is hot enough to melt lead. Its winds are strong and stormy; For this reason, none of the probe robots have been able to survive more than two hours on the rough surface of this planet, but scientists are looking for a better understanding of the events on the surface of this planet, and accordingly, their future plan is to land strong surfacers on the planet.
During several weeks of negotiations with their European counterparts, NASA scientists prepared three new missions to Venus in 2021, which will be launched in the early 2030s. In a few short weeks in June 2021, NASA committed to planning two missions to Venus, VERITAS and DAVINCI, while the European Space Agency launched the EnVision mission. All three missions will begin their observations in the early 2030s and revolutionize scientific research on the planet Venus.
VERITAS, scheduled for launch in 2027, will survey Venus’ thick clouds and provide the first view of Venus’ surface since the Magellan mission in 1994. The spacecraft’s instruments will provide data on the planet’s rock composition, geological activity, and interior.
Another NASA mission called DAVINCI will be launched in the late 2020s. After surveying Venus’ atmosphere, the spacecraft will drop a probe to the planet’s surface, and it will take about an hour for the probe to reach the surface. The probe will take thousands of measurements and send back detailed images of Venus’ surface. Another mission, the European Space Agency’s EnVision, will make detailed observations of Venus. NASA, as one of the key partners of this mission, will install a hybrid radar instrument on this probe, which will make high-quality measurements of the planet’s surface features.


You may like
-




Most alien planets probably do not have day or night
-




The biography of Edwin Hubble
-




Can telescopes see astronaut footprints on the moon?
-




Can you really see the Great Wall of China from space?
-




The James Webb Space Telescope; A look at the vastness of the universe
-



Hubble Space Telescope; A portal to the mysterious depths of the universe


Most alien planets probably do not have day or night
Do aliens sleep? You may take sleep for granted, but research suggests that many possible life-hosting planets may not have a day-night cycle. It is difficult to imagine the absence of day and night, but right now on Earth there are creatures living in lightless habitats in the depths or on the seabed, and they offer a vision of alien life without the existence of a circadian rhythm.
There are billions of potentially habitable planets in our galaxy; But how do we get to this number? The Milky Way has between 100 billion and 400 billion stars, seventy percent of which are cold and small red dwarf stars or M dwarfs.
According to a detailed survey of exoplanets in 2013, approximately 41% of red dwarf stars have a planet in their life belt. At this distance, the planet has the right temperature to support liquid water; Therefore, these planets have the potential to host liquid water.
We still do not know which of the discovered exoplanets have liquid water. However, 28.7 billion planets are only in the red dwarf life belt. We have not even considered the statistics of other types of stars like our sun.
 Planets close to red dwarfs are fatally locked to their star
Planets close to red dwarfs are fatally locked to their star
Rocky planets in the habitable belt of an M dwarf are called M Earths. M-Earths are fundamentally different from our Earth. One difference is that M dwarf stars are much cooler than our Sun. Also, M Earths are located at a close distance from their star, and for this reason, the gravitational influence of the star on them is strong.
The star’s gravity exerts a stronger force on the near side of the planet than on the far side. By creating friction, the planet’s rotation slows down until its orbital and translational rotations become synchronized over millions of years. Thus, M fields are likely to be deadlocked; So that one hemisphere of them is always facing the star and the other hemisphere is always behind it.
The year of a mortally locked planet is as long as its day. Earth’s moon also has a deadly lock on us. For this reason, we always see one side of it and cannot observe its hidden side.
A planet in mortal lock looks strange, But most possible habitable planets are of this type. Our nearest planetary neighbor, Proxima Centauri b, located in the Alpha Centauri system four light-years from Earth, is likely a fatally locked M-Earth.
As a result, unlike our Earth, M Earths have no day or night and even seasons; But terrestrial life, from bacteria to humans, has circadian rhythms corresponding to the day and night cycle. Sleep is one of the most obvious consequences of circadian rhythm.
On Earth, some creatures live in absolute darkness
The circadian cycle affects biochemistry, body temperature, cell regeneration, behavior, and much more. For example, people who are vaccinated in the morning produce more antibodies than people who are vaccinated in the afternoon; Because the response of the immune system is different during the day.
We cannot yet say with certainty how much periods of inactivity and regeneration affect life. Perhaps organisms that evolved without cyclical time never needed to rest.
If you doubt it, you can look at terrestrial organisms such as cave dwellers, deep sea life, and microscopic organisms in dark environments such as the earth’s crust and the human body that thrive in space away from daylight.
Many life forms have biological rhythms that are synchronized to stimuli other than light. Naked burrowing mice spend their entire lives underground and never see the sun, But their day and night hours are proportional to the daily and seasonal cycles of temperature and rainfall. Also, deep-sea bivalves and thermal well shrimps coordinate with ocean tides.
Bacteria that live in the human gut synchronize with melatonin fluctuations in the host’s body. Melatonin is a hormone in the body that is produced in response to darkness. Temperature changes that occur in thermal wells, humidity fluctuations chemical changes, and environmental currents can all cause biological fluctuations in the body of living organisms.
According to new research, M-Earths can have alternate cycles for days and seasons. To evaluate days and seasons on exoplanets, scientists have adapted climate models to simulate the environment of M-Earths and planets such as Proxima Centauri b.
According to the simulations, the contrast between the night and day sides of the planets produces gusts and atmospheric currents similar to Earth’s gust currents. If a planet has water, its dayside is likely to have thick thunderclouds.
The interaction between winds, atmospheric waves, and clouds can change the climate and produce regular cycles of temperature, humidity, and rainfall. The length of these cycles varies from hundreds to thousands of Earth days depending on the state of the planet, But it has nothing to do with the rotation period of the planet. Although the stars in the sky of these planets remain constant, the environment changes.
Perhaps life on M-Earths evolved to match biological rhythms and climatic cycles, or perhaps evolution arrived at a more exotic solution. One can imagine species that live on the day side of the planet going to the night side to rest and regenerate themselves.
These descriptions remind us that if life is out there, it can challenge assumptions we don’t know exist. The only certainty is that it will surprise us.


nameNoun: Any nounal word or phrase which indicates a particular person, place, class, or thing.
Noun: reputation.
Noun: An abusive or insulting epithet.
Noun: A person (or legal person).
Noun: Those of a certain name; a race; a family.
Noun: authority; behalf.
Noun: A unique identifier, generally a string of characters.
Noun: An investor in Lloyd’s of London bearing unlimited liability.
Verb: To give a name to.
Verb: To mention, specify.
Verb: To identify as relevant or important
Verb: To publicly implicate by name.
Verb: To disclose the name of.
Verb: To designate for a role.
Verb: To initiate a process to temporarily remove a member of parliament who is breaking the rules of conduct.
Noun: Any of several types of true yam () used in Caribbean Spanish cooking.
SProper noun: in which several of the axioms of ZF are derivable as theorems.
Noun: Any nounal word or phrase which indicates a particular person, place, class, or thing.
Noun: reputation.
Noun: An abusive or insulting epithet.
Noun: A person (or legal person).
Noun: Those of a certain name; a race; a family.
Noun: authority; behalf.
Noun: A unique identifier, generally a string of characters.
Noun: An investor in Lloyd’s of London bearing unlimited liability.
Verb: To give a name to.
Verb: To mention, specify.
Verb: To identify as relevant or important
Verb: To publicly implicate by name.
Verb: To disclose the name of.
Verb: To designate for a role.
Verb: To initiate a process to temporarily remove a member of parliament who is breaking the rules of conduct.
Noun: Any of several types of true yam () used in Caribbean Spanish cooking.
The biography of Edwin Hubble, the legendary astronomer who discovered the extragalactic space
Edwin Powell Hubble known as Edwin Hubble was a famous American astronomer who played an important role in formulating the basic principles of extragalactic and observational astronomy. Historians and astronomy experts consider him one of the most important astronomers in history. Hubble placed the space clouds, which before her time were known as gas and dust particles and were in the category of nebula or nebula, in the category of galaxies.. Historians consider Hubble’s discovery of other galaxies equal to Copernicus’ theory in terms of scientific value. Copernicus proved that the Earth is not at the center of the solar system, and Hubble proved that the Milky Way is not the center of the universe.
One of the important scientific relics of this astronomer is Hubble’s law in space. In short, this law states that the universe is expanding at a constant rate. In addition, in this law, the distance of each galaxy from the edge of the universe is directly proportional to its speed. Of course, this law was discovered two years before Hubble’s presentation by Georges Lemaitre, but its fame came to Hubble. The Hubble telescope is one of the most famous monuments built in the name of this legendary astronomer. An example of this telescope is installed in his hometown of Marshfield, Missouri. This telescope was sent into Earth orbit in 1990 to capture more detailed images of space outside the Milky Way.
Edwin Hubble has another great achievement in the field of cosmology and that is the classification of galaxies. This classification has been used by astronomers for many years. Hubble played a significant role in adding the astronomy category to the Nobel Prize. Of course, the sudden death of this scientist in 1953 prevented him from receiving this award.

Birth and education
Edwin Hubbell was born on November 20, 1889, in Marshfield, Missouri. His mother was Virginia Lee James and his father was John Powell Hubble. His father was a lawyer and insurance businessman. Edwin was the third child out of 8 children in this family. Of course, like many children of those years, some of Edwin’s siblings died in childhood.
Hubbell lived in a rich family that had to migrate many times because of his father’s work style. During these trips, which were generally in cities around Chicago and Illinois, they lived in luxurious houses with many servants. The children of the Hubble family were all brought up with work and responsibility; Because their parents believed that this style of upbringing would increase their sense of responsibility.
Edwin Hubble was very interested in sports as a child and teenager
As a child, Edwin struggled to keep up with his older siblings and students, so he learned to read before school. He was very fond of adventure books by Jules Verne and H. Rider Haggard. Edwin’s grandfather was an amateur but enthusiastic astronomer. At the age of 7, he got acquainted with one of his grandfather’s telescopes and had his first experience of space exploration. The interesting thing is that instead of participating in the celebration, he observed the space with this telescope on his 8th birthday.
Hubble completed his high school education at Wheaton High School near Chicago. He finished high school easily and with excellent grades in English, mathematics, biology, chemistry, physics, Latin, and German languages. Of course, in high school, Edwin was more into sports than studying, and he owed his high grades to his innate intelligence. On his father’s advice, he was busy delivering goods on holidays. Finally, Edwin Hubbell graduated from high school in 1906 at the age of 16 and received a scholarship to the University of Chicago. He worked at this university as a laboratory assistant of the famous physicist Robert Millikan (Nobel Prize winner).

Edwin Hubble (left), with friends after returning from Oxford
After entering the university, sports still occupied a large part of Hubble’s time. He was fond of sports such as basketball and boxing. He was a tall and strong person and he left several records during his university days. Edwin Hubble graduated from the university in 1910 with a bachelor’s degree in general science and honors in physics and astronomy.
After graduating from the University of Chicago, Hubbell entered Oxford University with a Rhodes scholarship and studied there for three years. Hubble was quickly influenced by English culture and changed many of his past behaviors and habits and adopted an English appearance. Contrary to his strong interest in experimental sciences and especially astronomy, he chose the field of law theory out of respect for his father and graduated from Oxford in 1912. He stayed at this university for another year and studied Spanish. While studying at Oxford, Hubble had another achievement including traveling around Europe. In these trips, in addition to having fun, he paid special attention to planning and thinking about his future. In those years, Edwin wrote in a letter to his mother:
Work is pleasant when it is for a great purpose and end. A goal so great that the thought of it and the anticipation of its achievements, will remove all the fatigue of the difficult task. When I find the purpose and principles I want, I leave everything for it and dedicate my life to it.
Edwin’s father died in the fall of 1912. He asked his father for permission to leave Oxford to visit him but was refused. Young Edwin remained in Oxford and his father died in January 1913.

Hubble exploring the cave
His Career
Hubble’s first job was teaching high school Spanish and physics.
Edwin Hubble returned to America in the summer of 1913. He was employed as a Spanish and Physics teacher at New Albany High School in Indiana. In addition, he coached the school’s basketball team and had a part-time job as a German translator. Although Hubble was a popular teacher, he did not enjoy his job. For this reason, he corresponded with Forrest Ray Moulton, professor of astronomy at the University of Chicago, and asked him for advice on collaborating on astronomy projects and higher education in this field. Moulton also introduced Hubble to Edwin Frost, director of the Yerkes Observatory in Wisconsin. In his letter, he introduced Hubble as a hardworking person, enthusiastic about science, and useful to Frost.
Finally, at the age of 24, Edwin entered the field of science, which he had become interested in nearly two decades ago by observing space through the lens of his grandfather’s telescope. Upon entering the observatory, he began his doctoral course in astronomy and received his degree in 1917 with a thesis entitled Photographic Investigations of Faint Nebulae. With the outbreak of World War I, Hubble served in the army for a year and rose to the rank of colonel despite not being actively involved in combat. He then went to Cambridge University to study astronomy.
Edwin Hubble started working at the Mount Wilson Observatory in California in 1919 at the age of 30. This observatory is famous for its excellent weather and excellent observation conditions. These factors made Hubble research in this place until the end of his life.

Hubble membership card in the army
Scientific achievements
As mentioned, Hubble wrote his doctoral dissertation on nebulae. He continued his research at Mount Wilson using the world’s largest telescope, the Hooker telescope. Hubble’s great discoveries, including galaxies beyond the Milky Way and the phenomenon of redshift, were the results of this astronomer’s research using the Hooker telescope.
In 1912, the American astronomer Henrietta Leavitt published an important discovery related to stars called the Cepheid variable. Beginning in the 1930s, Hubble was able to discover similar stars in nebulae using the Hooker telescope. While studying the Andromeda Nebula, he realized that these stars are very far from Earth and much farther than the stars of the Milky Way.
The discovery of other galaxies and the greatness of the universe was the greatest achievement of this scientist
Eventually, Hubble discovered that the Andromeda Nebula is actually a galaxy. Until then, most astronomers believed that the Milky Way and the Universe were a single entity. Hubble discovered that the universe is much larger than the Milky Way and consists of “island universes”. His findings in this historical discovery are summarized as follows:
- His high-quality images of Andromeda and the Triangulum Nebula showed a massive cluster of stars.
- Many of the stars were of the Cephasian type.
- The studied nebula is one million light years away from Earth. 4 times more than all the objects that had been discovered until that time. (Of course, this distance is proven to be equal to 2.5 million light-years today.)
- The diameter of the Andromeda Nebula is 30 thousand light years. (Today, these dimensions have been proven to be 220,000 light years.)
- Andromeda galaxy emits light equal to one billion suns of our system.
Hubble published his findings three days after his 35th birthday. Of course, his discoveries were not published in a scientific journal, but in the New York Times. The results of his research were debated among astronomers for some time, and finally, his paper was reviewed at the meeting of the American Astronomical Society on January 1, 1925. Hubble changed everyone’s view of the universe with his discoveries. He proved that our vast galaxy, host to the Sun and hundreds of billions of similar stars, is only one of the billions of galaxies in the universe.
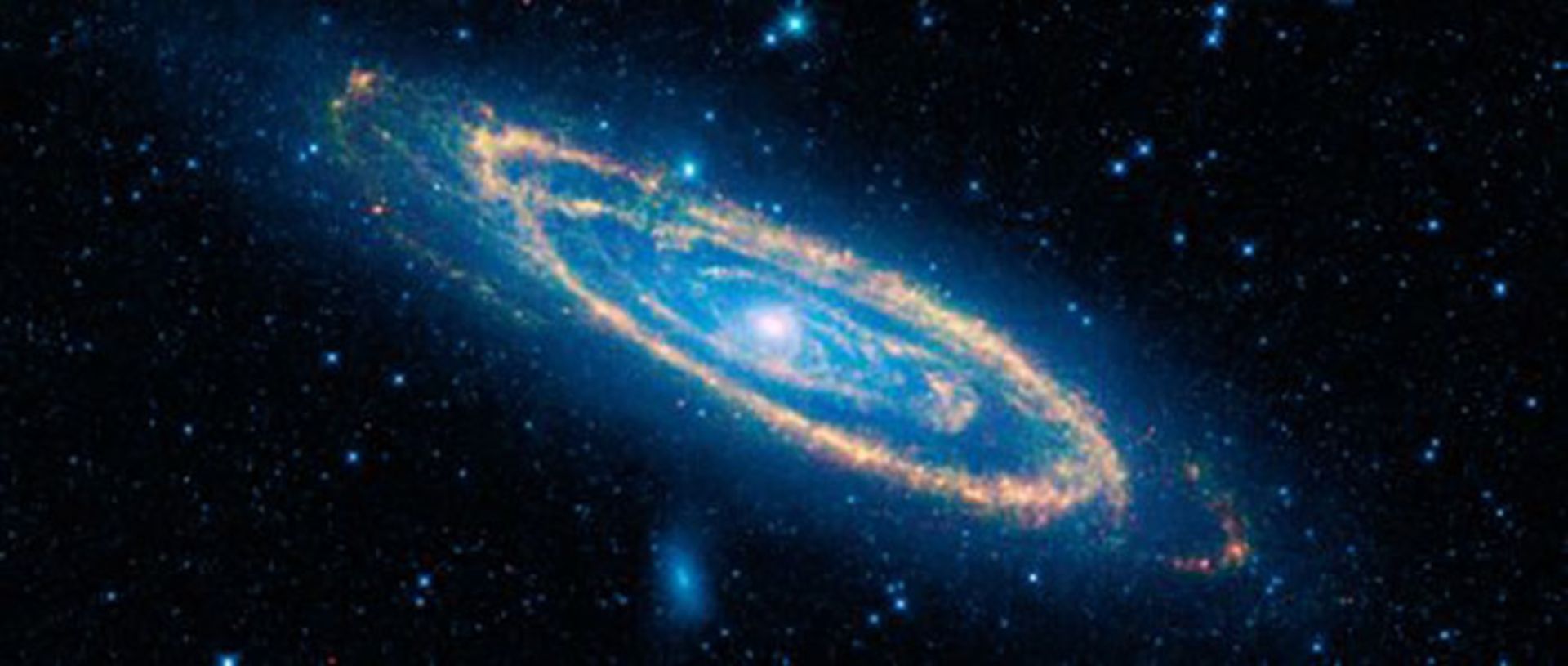

Andromeda Galaxy
In addition to this discovery, Hubble provided a standard for classifying galaxies that was used by astronomers for years.
Redshift phenomenon
Prominent astronomer Veslu Slifer has also researched nebulae. He stated in his report in 1913 that the light of the nebula tends towards the red color of the color spectrum. He explained his discovery as a form of the Doppler effect. According to the same explanation, the light tends to the red side of the color spectrum as the emission source moves away, similar to the Doppler effect. To test his discovery, Slifer studied many nebulae. He came to the conclusion that the light of many of these nebulae has a fast transition towards red color and as a result, they are moving away from Earth at a high speed.
Hubble stated that galaxies are moving away from each other at high speed
In 1929, using Slifer’s findings and combining them with his own discoveries and his assistant Milton Humson’s, Hubble was able to find an explicable relationship between galaxy distance and redshift state. He recorded his findings in a formula known today as Hubble’s law. This formula is displayed as v = Hr, where v is the velocity, r is the distance, and H is Hubble’s constant. This constant was first named as 530 by Hubble, but today, using advanced research and tools, the exact number is 70.
The world is expanding
One of the main interpretations of Hubble’s law is that we live in an expanding universe. Of course, Hubble himself believed that there is not enough credible evidence to prove this interpretation of the redshift effect. The remarkable point is that although Hubble drew the attention of the scientific community to this law, the law was discovered two years earlier by Georges Lemaitre. In fact, Lemaitre’s interpretation of this law is more accepted by new cosmologists; Because he used Einstein’s law of relativity for his interpretation.
However, Hubble’s point of view was quite logical. He believed that the theory of red shift can only be accepted as a proof of the expansion of the universe when the density of matter in the universe is much higher than the amount discovered up to that time. These statements have been the basic foundations for the proof of dark matter in the universe. Hubble said about the density of materials needed to prove the effect of redshift:
The required density of matter is several times higher than the estimated maximum density of matter concentrated in the nebula. Furthermore, we have no evidence of significant interstellar matter increasing the density.
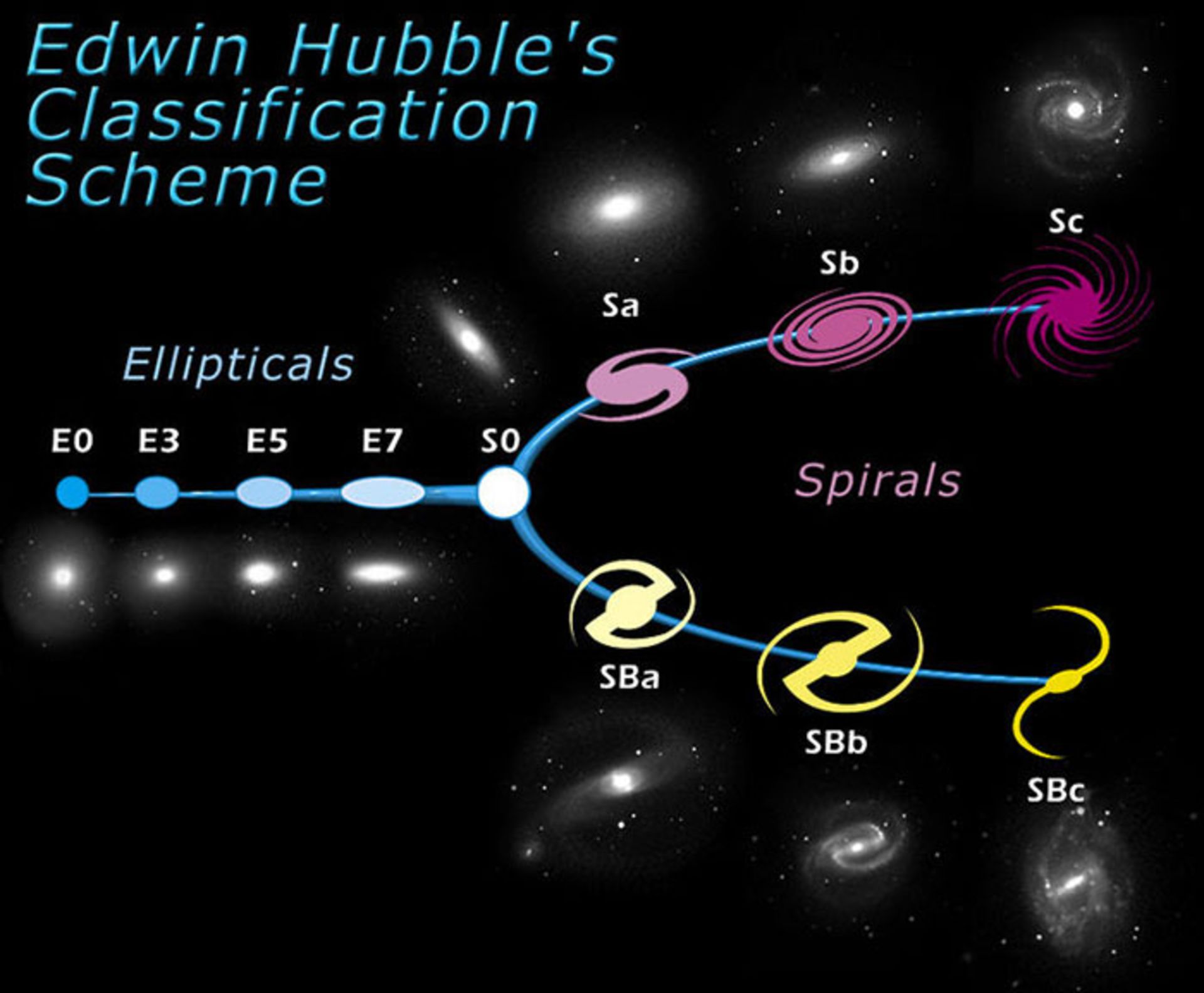
Classification of galaxies by Hubble
However, although Hubble had a lot of resistance to accept the effect of redshift, in his research he found that the speed of this expansion is slowing down. However, these findings and research on the speed of galaxy expansion are still ongoing and astronomers discover new issues every day.
One of the historical events regarding the theory of the expanding universe is Albert Einstein’s meeting with Edward Hubble in 1931. The two met at Mount Wilson Observatory. In 1917, in his theory of relativity, Einstein considered the universe to be constant and without change in size. He did not see any end or end to the universe. Although his research showed signs of the expansion of the universe, this scientist tried to deny it by determining a constant called the cosmic constant.
However, the January 1931 meeting earned Hubble the nickname of the man who forced the world’s smartest man to change his mind. This meeting caused Einstein to call his previous calculations the biggest mistake of his scientific life, and as a result, Hubble’s findings became the center of attention in scientific circles.
The Big Bang theory is influenced by the findings of this scientist about the expansion of the universe
In 1935, Hubble discovered the 1373 asteroid named Cincinnati. A year later he published the book ” The Realm of the Nebulae “. This book is a historical interpretation of his experiences and research on intergalactic astronomy. With the outbreak of World War II, Hubble once again served in the US Army at the Aberdeen Proving Ground. He was in charge of the ballistics research department in this area. His extensive research resulted in several improvements in the power of ballistic bombs and projectiles. One of his major practical achievements in this research was the improvement of ballistic projectile components, which resulted in a high-speed camera to study the characteristics of the bomb after launch. After the war, Hubble returned to Mount Wilson and spent some time at the Palomar Observatory in California.
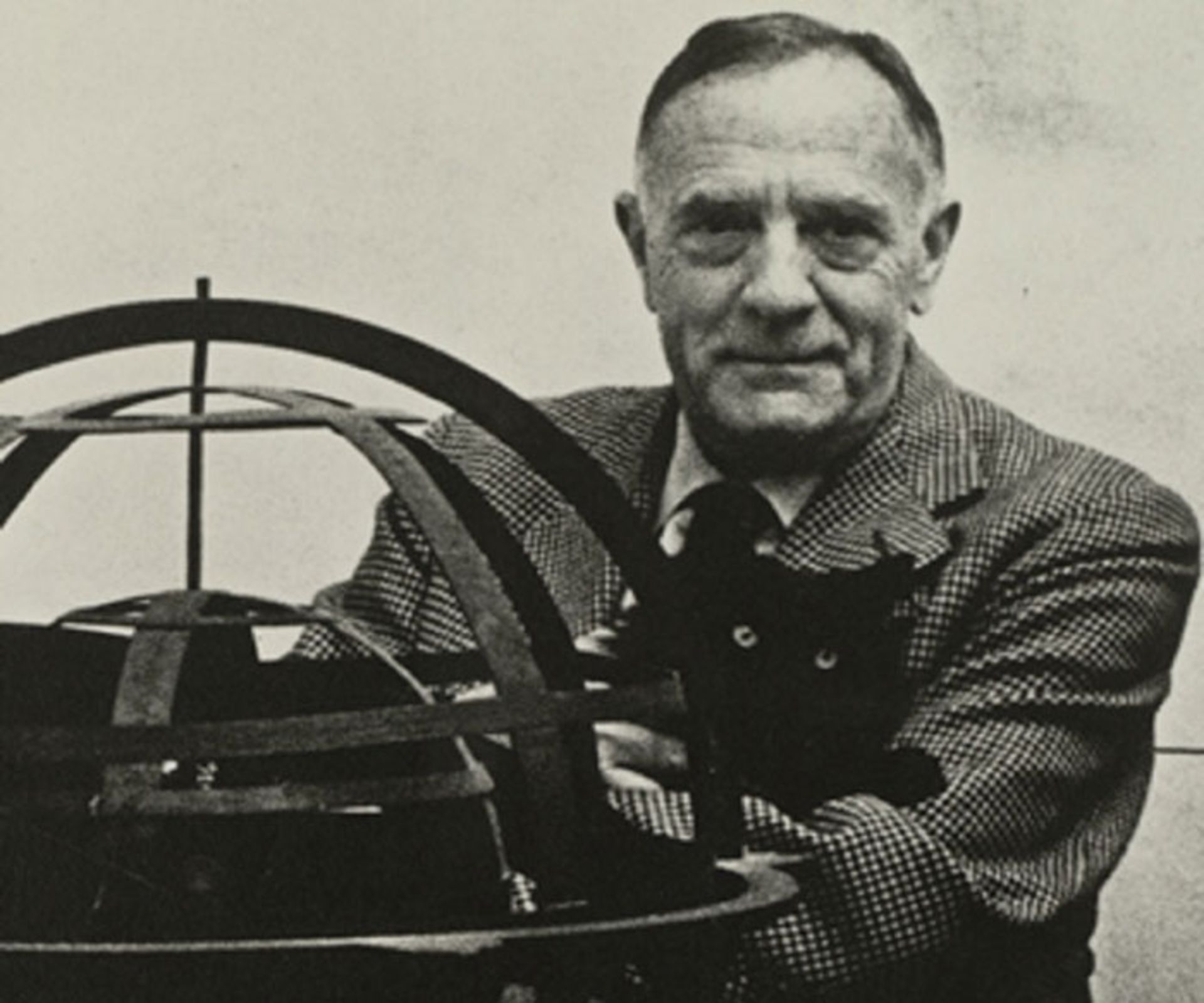

Edwin Hubble in old age
In addition to scientific research, Edwin Hubble worked hard to convince the Nobel Prize Society to add astronomy to the award’s branches. He intended to add this science to this event as an independent subsection of physics. He believed that the efforts of astronomers in stellar physics should be appreciated. Unfortunately, after Hubble’s death, this society decided to appreciate this science as a branch of physics.
Personal life and death
Edwin Hubbell married Grace Burke Leib in 1924 at the age of 34 . They had no children. One of Hubble’s pastimes was collecting books. He was generally interested in books related to the history of science. In addition to scientific research, Hubble was also a member of the Board of Trustees of the Huntington Library in San Marino. The discovery of distant galaxies made him so famous that in 1948 his picture appeared on Time magazine. He and his wife had a close relationship with Hollywood stars and artists such as Aldous Huxley.
In 1949, at the age of 59, Edwin Hubbell suffered a heart attack while on vacation in Colorado and was nursed back to health by his wife. Of course, after this incident, the intensity of his research activities decreased until he died on September 28, 1953, due to a blood clot in the brain. He had willed that his burial place should not be known and personal notes were also destroyed by his wife. Grace also died in 1980 and was buried in a secret place next to her husband.
Awards and honors
The Cleveland Newcomb Prize was awarded to Edwin Hubble in 1924. In 1938, he was awarded the Bruce Medal, and a year later, he was awarded the Franklin Medal Science and Engineering Award by the Franklin Institute in Philadelphia. The Gold Medal of the British Royal Astronomical Society was awarded to this legendary astronomer in 1940. The Legion of Honor, which is a military award from the US Armed Forces, was awarded to him in 1946 for his research in the field of ballistics.
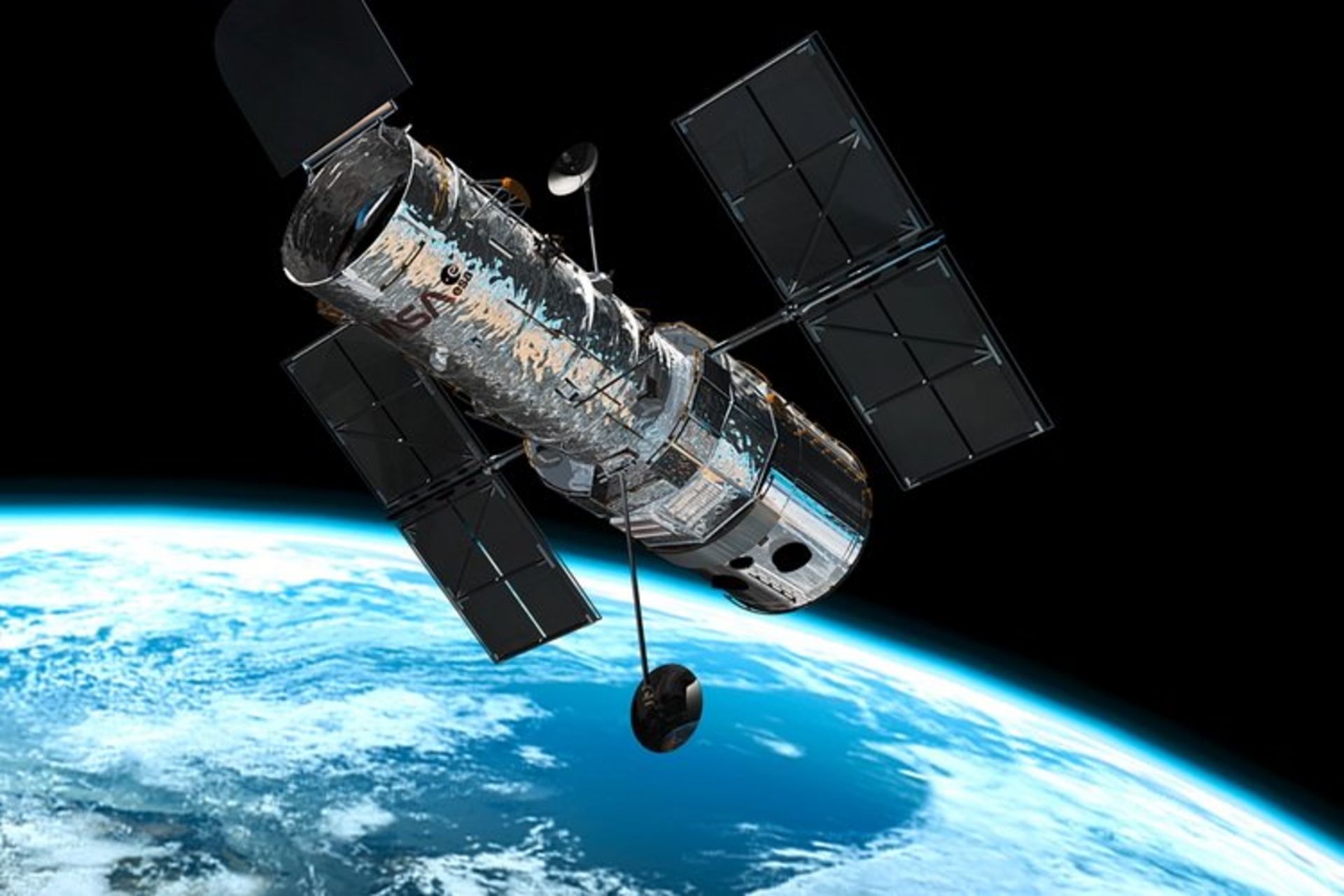

Hubble Space Telescope
After the death of Edwin Hubble, in addition to the aforementioned awards, other honors were also registered to pay tribute to this American scientist. The Missouri City Hall of Fame inducted Edwin Hubbell in 2003. In 2008, a commemorative stamp was printed in the name of this scientist, and in 2017, the Indiana Basketball Hall of Fame registered Hubble’s name.
Asteroid number 2069 and a hole in the moon are among the celestial objects that are registered in the name of this scientist. A planetarium at Edward R. Morrow High School in Brooklyn was also named after this scientist, and a street in Missouri was named after Edwin Hubble.
Certainly, the most famous monument of Edwin Hubble is the Hubble Space Telescope, which was launched in 1990. The main purpose of launching this telescope was to accurately calculate Hubble’s constant in his famous formula. Anyway, astronomers with this telescope first considered the number 72 as a constant in 2001, and then in 2006, by studying the microwave background of the galaxy, they reached the exact number 70. In addition, the Hubble telescope made it possible to observe not only the expansion of the universe but also the acceleration of this expansion. Today, the force that caused this expansion is called dark energy in scientific documents.
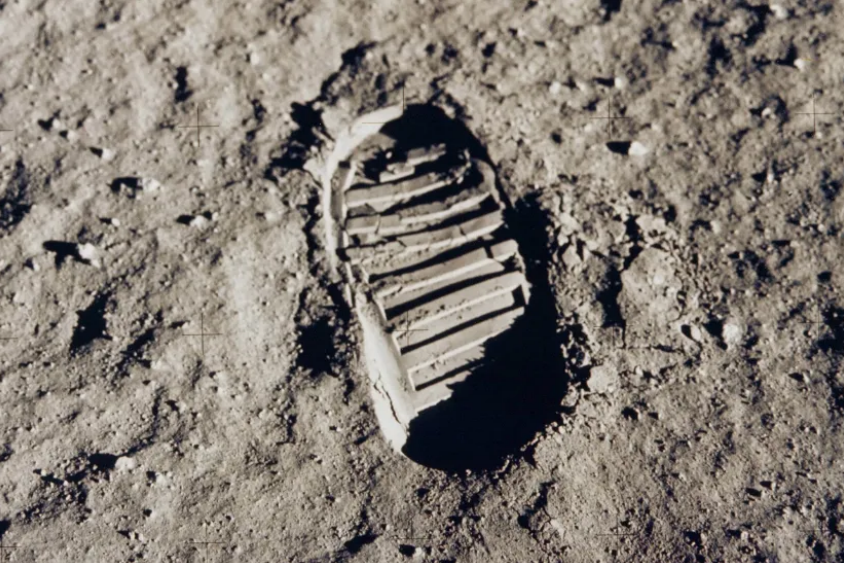


Can telescopes see astronaut footprints on the moon?
In the early 2000s, when there were occasional people who believed that the moon landing was a hoax, the argument was made that if NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope was powerful enough to see the tiny details of distant galaxies, why couldn’t it take the shoes of the Apollo astronauts on the moon?
The aforementioned argument, like many conspiracy theories, seems convincing on the surface; But with the slightest scrutiny, it loses its value. Those who are fooled by this claim are wrong about two things: how telescopes work and how big space is.
Astronomer Phil Platt explains on the Scientific American website that many people think a telescope’s job is to magnify images. Of course, manufacturers of cheap telescopes like to advertise them this way, printing statements like “150x magnification power” in big letters on the box of the telescopes, along with very misleading pictures of much larger telescopes. Although magnification is important, the true power of a telescope is in its resolution. This difference is subtle but very important.
Magnification is how much you can focus on an object and make it appear larger. This is important because while astronomical objects are physically very large, they are very far away and thus appear small in the sky. Magnifying them makes them easier to see.
Magnification is important, but the true power of a telescope is in its resolution
On the other hand, clarity or resolving power is the ability to differentiate between two objects that are very close together. For example, you might think of two stars orbiting each other (a binary star) as one star; Because their distance is very small and the naked eye cannot distinguish them. But if you look at them with a higher-resolution telescope, you may be able to see that they are two separate stars.
Isn’t that the Zoom? No; Because zooming in only makes everything bigger. This can be easily illustrated with the following image: zoom in as much as you want on the image, but once you pass a certain limit, you only enlarge the pixels and get no new information. To overcome this obstacle, you need to have high resolution rather than zoom.
 Hubble Space Telescope image of the Apollo 17 landing area in the Taurus-Lytro Valley of the Moon. This image lacks the necessary resolution to show the traces of the moon landing or the movement of astronauts on the moon.
Hubble Space Telescope image of the Apollo 17 landing area in the Taurus-Lytro Valley of the Moon. This image lacks the necessary resolution to show the traces of the moon landing or the movement of astronauts on the moon.
The problem is that resolution depends on the telescope itself, meaning that a dramatic increase in resolution usually requires a much larger telescope; But no matter how big your telescope gets, it will still have limited resolution.
When light from an infinitesimal point, such as distant stars, passes through a telescope, the light is slightly scattered within the telescope’s optical instruments (mirrors or lenses). This fundamental property is called light diffraction and is unavoidable. The resolution of telescope images depends partly on the size of its mirror or lens. The larger the telescope’s light-gathering instrument, the higher its image resolution.
The way light propagates in optical equipment depends on wavelength, with shorter wavelengths producing higher resolution. So two nearby blue stars may be distinguishable in a telescope, while two red stars at the same distance may not be distinguishable.
When deciding on the size of a telescope’s camera pixels, astronomers must consider the wavelength they want to observe. Otherwise, they just magnify the noise; Like the previous example about zooming too much on the photo.
All these lead to an amazing result. The Hubble Space Telescope has a mirror with a diameter of 2.4 meters and the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has a mirror with a diameter of 6.5 meters. Therefore, the resolution of the James Webb telescope images can be expected to be much higher. At some wavelengths, it is: the shortest wavelength that the James Webb Space Telescope can see is about 0.6 microns (what our eyes perceive as orange light), and the resolution is technically much better than that of the Hubble image.
However, the James Webb Space Telescope was designed as an infrared telescope. At those wavelengths, say around two microns, the resolution is comparable to what Hubble can see at visible light wavelengths. In the mid-infrared, i.e. wavelengths of 10 to 20 microns, the resolution of the James Webb Space Telescope images is even lower. However, because the James Webb is the largest infrared telescope ever sent into space, it can provide the sharpest images we’ve ever had at these wavelengths.
 No telescope on Earth or in low Earth orbit can capture an image like this, a high-resolution view of a boot on the moon’s surface.
No telescope on Earth or in low Earth orbit can capture an image like this, a high-resolution view of a boot on the moon’s surface.
Astronomers measure resolving power as an angle on the sky. From the horizon to the highest point of the sky is 90 degrees and each degree is divided into 60 arc minutes and each arc minute into 60 arc seconds. For example, the angular diameter of the moon from our point of view in the sky is about half a degree. That is, if we look at the moon from the Earth, the moon in the sky occupies a space equal to half a degree of the full circle of the sky, which is equivalent to 30 minutes of arc or 1800 seconds of arc.
The maximum resolution of a telescope refers to the smallest angular distance between two objects that the telescope is able to distinguish as two separate objects. This resolution is expressed as an angle.
At its best, the resolution of the Hubble telescope is about 0.05 of an arc, which is considered a very small angle. But the amount of detail Hubble is able to see depends on the distance and physical size of the target. For example, 0.05 seconds of arc is equivalent to the apparent size of a small coin that can be seen from about 140 km.
In this way, we return to the discussion of conspiracy theorists and their claims regarding the observation of astronaut footprints on the moon. Galaxies are usually tens of millions or even billions of light years away from Earth. At those distances, the Hubble telescope can distinguish objects with dimensions of several light years (i.e. tens of trillions of kilometers) with its best resolution. So even though it looks like we’re seeing galaxies in great detail in those amazing Hubble images, the smallest we can see is still pretty big.
At the same time, the moon is only about 380 thousand kilometers away from us and from the Hubble telescope. At this distance, the resolution of the Hubble telescope is surprisingly limited, unable to resolve objects smaller than about 90 meters. As a result, not only can we not see the astronauts’ footprints in the Hubble images, but we can’t even see the Apollo moon landings, which are about four meters across. Hubble’s resolution at this distance is so limited that it cannot distinguish details smaller than about 90 meters, so it is not possible to see objects smaller than this on the Moon.
 An image of the Apollo 11 landing site captured by NASA’s Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO). Although the LRO telescope uses much smaller lenses than the Hubble Space Telescope, its proximity to the lunar surface has made it possible to see details such as the Apollo 11 lunar lander and astronauts’ footprints.
An image of the Apollo 11 landing site captured by NASA’s Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO). Although the LRO telescope uses much smaller lenses than the Hubble Space Telescope, its proximity to the lunar surface has made it possible to see details such as the Apollo 11 lunar lander and astronauts’ footprints.
In the images taken by the Nass Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO), we can see the moon landings and the footprints of the astronauts. Although the camera of this orbiter has a mirror with a diameter of only about 20 cm, the spacecraft is in lunar orbit and passes the Apollo landing sites at an altitude of 50 km.
The reason NASA’s Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter can see more detail on the surface of the moon is because it is so close to the surface of the moon. This is why we send probes to planets: it allows us to get much better pictures of them. Sometimes, there’s no substitute for being there.
The lesson we learn from this topic is that the way tools actually work is often more complex and different than we expect. Furthermore, claims that may seem reasonable fall apart with a little scientific scrutiny. If a telescope is only advertised based on magnification, it’s best not to buy it and look for other options. It may seem difficult, but with a little determination, you will succeed.


Do animals have an understanding of the concept of death?


What is Kali Linux? Everything you need to know about this popular but mysterious distribution


Sony Brand Story; From the production of rice cookers to becoming one of the most famous companies in the world


How did the people of the past imagine the future?


Mammoth and dodo return to nature


Canopus; What do we know about the second brightest star in the sky?


How to use iMessage on Android?

Can humans endure the psychological torment of living on Mars?


Xiaomi Glorimi M2 Max watch review; Alternative economic option for iPhone owners


Artificial intelligence problems; Frauds based on artificial intelligence and methods to deal with them
Popular
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoWho has checked our Whatsapp profile viewed my Whatsapp August 2023
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoSecond WhatsApp , how to install and download dual WhatsApp August 2023
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoHow to use ChatGPT on Android and iOS
-



 AI2 years ago
AI2 years agoUber replaces human drivers with robots
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoThe best Android tablets 2023, buying guide
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoThe best photography cameras 2023, buying guide and price
-


 Humans2 years ago
Humans2 years agoCell Rover analyzes the inside of cells without destroying them
-


 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoHow to prevent automatic download of applications on Samsung phones

