Technology
Everything you need to know about GPU
Published
3 days agoon


What is a graphics processor? Everything you need to know about GPU
The graphics processing unit (GPU) is a specialized electronic circuit for managing and changing memory to accelerate the creation and display of output images on the monitor . The graphic processor consists of a number of basic graphics operators, which in their most basic state are used to draw rectangles, triangles, circles, and arcs, and are much faster than processors in creating images.
-
What is a graphics processor (GPU)?
-
3D image
-
Bitmapped graphics (BMP.)
-
Vector graphics
-
rendering
-
Graphics API
-
What is GDDR?
-
History of 3D graphics
-
How to produce 3D graphics
-
3D modeling
-
Layout and animation
-
rendering
-
Shading technique
-
Pixel shaders
-
Vertex shaders
-
Difference between GPU and CPU
-
Familiarity with GPU architecture
-
Tensor kernels
-
Ray tracing engine
-
What is GPGPU?
-
What is CUDA?
-
Advantages of CUDA kernels
-
Disadvantages of CUDA kernels
-
OpenCL; CUDA replacement
-
CUDA and OpenCL vs. OpenGL
-
OpenCL or CUDA
-
The most prominent brands
-
Intel
-
Nvidia
-
AMD
-
The difference between graphics processor and graphics card
-
Graphics card components
-
Video memory
-
printed circuit board
-
Display connectors
-
bridge
-
Graphic interface
-
Voltage regulator circuit
-
Cooling system
-
Types of graphics processor
-
iGPU
-
dGPU
-
Cloud GPU
-
eGPU
-
Mobile GPU
-
Types of mobile GPUs
-
Other applications of graphics processors
-
Video editing
-
3D graphics rendering
-
Learning the machine
-
Blockchain and digital currency mining
In fact, what we see on the screens is the output of the graphics processors that are used in many systems such as phones, computers, workstations, and game consoles.
What is a graphics processor (GPU)?
If we consider the central processing unit or processor (CPU) as the brain of the computer that manages all calculations and logical instructions, the graphics processing unit or graphics processor (GPU) can be considered as a unit for managing the visual and graphical output of calculations, instructions and information. Related to images, it is known that their parallel structure works more optimally than central processing units or processors for processing large blocks of data; In fact, GPU is considered a graphic interface for converting the calculations made by the processor into a form that is understandable for the user, and it can be safely said that any device that somehow displays graphic output is equipped with some kind of graphics processor.
The graphics processing unit in a computer can be embedded on the graphics card or on the motherboard, or come with the processor on an integrated chip (for example, AMD APUs). It is also possible to identify the graphics card model in Windows with the fastest method, just refer to the linked article and read it.
Integrated chips cannot produce such impressive graphics output, and their output will definitely not satisfy any gamer; To benefit from higher quality visual effects, a separate graphics card (we will learn more about the differences between graphics processor and graphics card) with capabilities beyond a simple graphics processor should be prepared. In the following, we will briefly familiarize ourselves with some basic concepts used in the discussion of graphics.
3D image
An image that has depth in addition to length and width is called a three-dimensional image, which conveys more concepts to the audience and has more information compared to two-dimensional images. For example, if you look at a triangle, you will only see three lines and three angles, but if you have a pyramid-shaped object, you will see a three-dimensional structure consisting of four triangles, five lines, and six angles.
Bitmapped graphics (BMP.)
Bitmapped graphics, or rasterized graphics, is a digital image in which each pixel is represented by a number of bits; This graphic is made by dividing the image into small squares or pixels, each of which contains information such as transparency and color control; Therefore, in raster graphics, each pixel corresponds to a calculated and predetermined value that can be specified with great precision.

The image resolution of raster graphics is dependent on the resolution of the image , which means that the scale of the images produced with this graphic cannot be increased without losing the appearance quality.
Vector graphics
A vector graphic (ai. or eps. or pdf. or svg. formats) is also an image that creates paths with start and endpoints. These routes are all based on mathematical expressions and consist of basic geometric shapes such as lines, polygons, and curves. The main advantage of using vector graphics instead of bitmapped graphics is their ability to scale without losing quality. The scale of the images produced with vector graphics can be easily increased, without loss of quality and as much as the capability of the device that renders them.
As mentioned, unlike vector graphics that are scaled to any size with the help of mathematical formulas, bitmapped graphics lose their quality by scaling . The pixels of a bitmapped graphic must be interpolated when upscaling, which blurs the image and must be resampled when downscaling, which causes loss of image data.
In general, vector graphics are best for creating works of art consisting of geometric shapes, such as logos or digital maps, typefaces, or graphic designs, while raster graphics deal more with real photos and images and are suitable for photographic images.
Vector graphics can be used to make banners or logos; Because with this method, images are displayed in both small and large dimensions with the same quality. One of the most popular programs used to view and create vector images is Adobe Illustrator.
Rendering
The process of producing 3D images from software based on computational models and displaying it as an output on a 2D screen is called rendering.
Graphics API
Software programming interface (Application Programming Interface) or API is a protocol for communication between different parts of computer programs and is considered an important tool for software interaction with graphic hardware; This protocol may be based on the web, operating system, data center, hardware or software libraries. Today, many tools and software have been developed for imaging and rendering of 3D models, and one of the important uses of graphic APIs is to make the process of imaging and rendering easier for developers. In fact, graphics APIs provide virtual access to some platforms for the developers of their graphics applications and their testing. In the following, we introduce some of the most well-known graphic APIs:
OpenGL (short for Open Graphics Library) is a library of various functions for drawing 3D images, which is a cross-platform standard and application programming interface (API) for 2D and 3D graphics and rendering, and a graphics accelerator in video games, design, virtual reality, and other applications. is considered This library has more than 250 different calling functions for drawing 3D images and is designed in two types: Microsoft (often in Windows or graphics card installation software) and Cosmo (for systems that do not have a graphics accelerator).

The OpenGL graphic interface was first designed by Silicon Graphics in 1991 and was released in 1992; The latest version of this API, OpenGL 4.6, was also introduced in July 2017.
A set of application programming interfaces (APIs) developed by Microsoft to enable the communication of instructions with audio and video hardware. Games equipped with DirectX have the ability to use multimedia features and graphics accelerators more efficiently and have improved overall performance.
When Microsoft was preparing to release Windows 95 in late 1994, Alex St. John, a Microsoft employee, researched the development of games compatible with MS-DOS. The programmers of these games often rejected the possibility of porting them to Windows 95 and considered it difficult to develop games for the Windows environment. For this purpose, a three-person team was formed and within four months, this team was able to develop the first set of application programming interfaces (API) called DirectX to solve this problem.
The first version of DirectX was released in September 1995 as the Windows Games SDK, replacing the Win32 DCI and WinG APIs for Windows 3.1. DirectX for Windows 95 and all subsequent versions of Microsoft Windows allowed them to host high-performance multimedia content.

Microsoft offered to John Carmack, the developer of Doom and Doom 2 games, to transfer these two games from MS-DOS to Windows 95 for free with DirectX, in order to increase the acceptance of DirectX by developers. also save the game. Carmack agreed, and the first version of the game, Doom 95, was released in August 1996 as the first game developed on DirectX. DirectX 2.0 became a part of Windows itself with the release of the next version of Windows 95 and Windows NT 4.0 in mid-1996.
Since at that time, Windows 95 was still in its infancy and there were few published games for it, Microsoft began to promote this programming interface extensively and during an event for the first time, Direct3D and DirectPlay were introduced in the online demo of the MechWarrior 2 multiplayer game. Did the DirectX development team face the challenge of testing each version of this programming interface for each set of computer hardware and software, as well as different graphics cards, sound cards, motherboards, processors, inputs, games, and other multimedia applications with each beta version? The final ones were tested and even tests were produced and distributed so that the hardware industry could check the compatibility of their new designs and driver versions with DirectX.
The latest version of DirectX, namely DirectX 12, was unveiled in 2014, and a year later, it was officially released along with Windows 10. This graphics API supports a special multiple adapter and allows the simultaneous use of multiple graphics on a system.
Before DirectX, Microsoft included OpenGL in its Windows NT platform, and now Direct3D was supposed to be an alternative to Microsoft-controlled OpenGL, which was initially focused on gaming. During this time, OpenGL was also developed and it better supported programming techniques for interactive multimedia programs such as games, but since OpenGL was supported by Microsoft’s DirectX team, it gradually withdrew from the competition.
Vulkan
Vulkan is a low-cost, cross-platform graphics API for graphics applications such as gaming and content creation. The distinguishing feature of this graphic API with DirectX and OpenGL is its ability to render 2D graphics and consume less power.
At first, many thought that Vulkan could be the next improved OpenGL and the continuation of its path, but the passage of time has shown that this prediction was not correct. The following table shows the performance differences of these two graphics APIs.
|
OpenGL |
Vulkan |
|---|---|
|
It has only one global state machine |
It is object-based and lacks a global state |
|
state is limited to only one content |
The concept of all states is placed in the command buffer |
|
Functions are only performed sequentially |
It has multi-threaded programming capability |
|
Memory and GPU synchronization are usually hidden |
It is possible to control and manage synchronization and memory |
|
Error checking is done continuously |
Drivers do not perform error checking at runtime. Instead, there is a validation layer for developers. |
Mantle
The Mantle Graphics API is a low-cost interface for rendering 3D video games. It was first developed by AMD and video game developer DICE in 2013. The partnership was intended to compete with Direct3D and OpenGL on home computers, however, Mantle was officially discontinued in 2019 and replaced by the Vulkan graphics API. Mantle could optimally reduce the workload of the processor and eliminate the nodes created in the processing process.
Metal
Metal is Apple’s proprietary graphical interface written in C++ language and first used in iOS 8. Metal can be seen as a combination of OpenGL graphic interface and OpenCL framework, which was designed to simulate the graphic APIs of other platforms such as Vulkan and DirectX 12 for iOS, Mac and tvOS. In 2017, the second version of the Metal graphics API was released with support for macOS High Sierra, iOS 11 and tvOS 11 operating systems. Compared to the previous version, this version was more efficient and optimized.
What is GDDR?
The DDR memory in the graphics processing unit is called GDDR or GPU RAM . DDR (short for Double Data Rate) is an advanced version of Dynamic Simultaneous RAM (SDRAM) and uses the same frequencies as it. The difference between DDR and SDRAM is the number of times data is sent per cycle; DDR transfers data twice per cycle, doubling the memory speed, while SDRAM transfers signals only once per cycle. DDRs quickly became popular because, in addition to twice the transfer speed, they are cheaper than SDRAM and also consume less power than older SDRAM modules.
-
What is DDR5? Everything you need to know about the latest RAM standard [with video]
GDDR was introduced in 2006 for fast rendering on the graphics processor, compared to normal DDR, this memory has a higher frequency and less heat, and it is considered a replacement for VRAM and WRAM, which has been released for 6 generations and each generation is faster and more advanced than the generation is previous
GDDR5 is known as the previous generation of video RAM, and ten years have passed since the introduction of the last current GDDR standard (i.e. GDDR6); GDDR6 with a transfer speed of 16 GB/s (double GDDR5) and a read/write access of 32 bytes (equal to GDDR5) is used in Nvidia’s RTX30 series and AMD’s latest 6000 series graphics cards; GDDR versions do not numerically correspond to DDR, and GDDR5, like GDDR3 and GDDR4, are based on DDR3 technology, and GDDR6 is also based on DDR4 technology; In fact, it can be said that GDDR takes a relatively more independent path than DDR in terms of performance differences.
The main task of the graphics processor is to render images, however, to do this, it needs space to store the information needed to create the completed image, this graphics unit uses RAM (or random access memory) to store data; Data that includes information about each pixel associated with the image, as well as its color and location on the screen. A pixel can be defined as a physical point in a raster image that represents a dot matrix data structure of a rectangular grid of pixels. RAM can also hold completed images until it’s time to display them, which is called a frame buffer.
Before the development of graphics processors, the CPU was responsible for processing images to create output and render them; This would put a lot of pressure on the processors and slow down the system. In fact, the sparks of today’s 3D graphics were lit up with the further development of arcade games, gaming consoles, military, robotics, and space simulators, as well as medical imaging. Rendering and their applications as well as the way of naming were discussed.
In the following and before examining the history of the graphic processing unit, we will introduce the concepts that are relevant in this industry:
History of 3D graphics
The term GPU was first introduced in the 1970s as an abbreviation for Graphic Processor Unit and described a programmable processing unit that had an independent function from the central processing unit or the same processor and was responsible for setting and outputting graphics. ; Of course, at that time this term was not defined as it is today.
In 1981, IBM developed its two graphics cards for the first time, MDA (Monochrome Display Adapter) and CGA (Color Graphics Adapter). The MDA had four kilobytes of video memory and only supported text display; This graphic is no longer used today but may be found on some older systems.


CGA was also considered the first graphics for computers, which was equipped with only sixteen kilobytes of video memory and was capable of producing 16 colors with a resolution of 160 x 200 pixels. A year after this, Hercules Graphics developed the HGC graphics (Hercules Graphics Card) with 64 kilobytes of video memory, which was a combination of MDA with bitmapped graphics, to respond to IBM’s graphics cards.
In 1983, Intel entered the graphics card market with the introduction of the iSBX 275 Video Graphics Multimodule. This card could display eight colors with a resolution of 256 x 256. A year after this, IBM introduced PGC or Professional Graphic Controller and EGA or Enhanced Graphic Adapter graphics that displayed 16 colors with a resolution of 640 x 350 pixels.
The VGA or Video Graphics Array standard was introduced in 1987, this standard offered a resolution of 640 x 480 with 16 colors and up to 256 kilobytes of video memory. In the same year, ATI introduced its first VGA graphics card called ATI VGA Wonder; Some models of this graphics card were even equipped with a port for connecting a mouse. Until now, video cards had few memories, and processors transferred graphics processing to these video memories and after performing calculations and signal conversion, displayed them on the output device.
After the first 3D video games were released, it was no longer possible to process graphics inputs quickly on processors; In this situation, the basic concept of a graphic processing unit was formed. This concept was initially developed with the introduction of the graphics accelerator; The graphics accelerator was used to boost system performance, perform calculations and graphic processing, and lighten the workload of the processor, and had a significant impact on computer performance, especially intensive graphics processing. In 1992, Silicon Graphics released OpenGL, the first library of various functions for drawing 3D images.
The GPU evolved from the beginning as a complement to the CPU and to lighten the workload of the unit
4 years later, Voodoo introduced its first graphics card by a company called 3dfx. This graphics was called Voodoo1 and it required the installation of a 2D graphics card to render 3D graphics, and it quickly became popular among gamers.
In 1997, in response to Voodoo, Nvidia released the RIVA 128 graphics accelerator. Like the Voodoo1, the RIVA 128 allowed video card manufacturers to use graphics accelerators along with 2D graphics, but compared to the Voodoo1, it had weaker graphics rendering.
After the RIVA 128, 3dfx released the Voodoo2 graphics as a replacement for the Voodoo1. It was the first graphics card to support SLI, allowing two or more graphics to be connected to produce a single output. SLI or Scalable Link Interface is a brand name for an obsolete technology developed by Nvidia for parallel processing and to increase graphics processing power.
The term GPU was popularized in 1999 with the worldwide launch of the GeForce 256 as the world’s first graphics processor by Nvidia. Nvidia introduced this GPU as a single-chip processor with integrated conversion of a 2D view from a 3D scene, lighting and changing the color of surfaces, and the ability to draw parts of the image after rendering. ATI Technologies also released Radeon 9700 graphics in 2002 to compete with Nvidia with the term Visual Processing Unit or VPU.
With the passage of time and the advancement of technology, GPUs were equipped with programmable capabilities, which made Nvidia and ATI enter the competition scene and introduce their first graphics processors (GeForce for Nvidia and Radeon for ATI).
Nvidia officially entered the graphics card market in 1999 with the release of GeForce 256 graphics. This graphics card is known to be the world’s first true GPU that had 32 MB of DDR (same as GDDR) memory and fully supported DirectX 7.
Along with the efforts to speed up the calculations and graphics processing of computers and improve their quality, the companies that produce video games and gaming consoles also tried in some way (Sega with Dreamcast, Sony with PS1, and Nintendo with Nintendo 64) in this field.
How to produce 3D graphics
The process of producing 3D graphics is divided into three main stages:
3D modeling
The process of developing an array based on mathematical coordinates of a physical surface or surface (inanimate or animate) in 3D form is done through specialized software by manipulating sides, vertices, and polygons that are simulated in 3D space.
Physical objects are represented using a set of points in three-dimensional space, which are connected by various geometric elements such as triangles, lines, curved surfaces, etc. Basically, 3D models are first created by connecting points and forming polygons. A polygon is an area that consists of at least three vertices (triangles) and the overall integrity of the model and its suitability for use in animation depends on the structure of these polygons.
Three-dimensional models (3D) are made from two methods of polygon modeling (Vertex) and by connecting grid lines of vectors or curve modeling (Pixel) by weighting each point; Today, due to greater flexibility and the possibility of faster rendering of the 3D modeling process in the first method, the vast majority of 3D models are produced in a polygonal and textured way. One of the main tasks of graphics cards is texture mapping (Texture Mapping), which adds texture to an image or 3D model. For example, adding a stone texture to a model makes it look like a real stone image, or adding a texture that resembles a human face to design a face for a scanned 3D model.
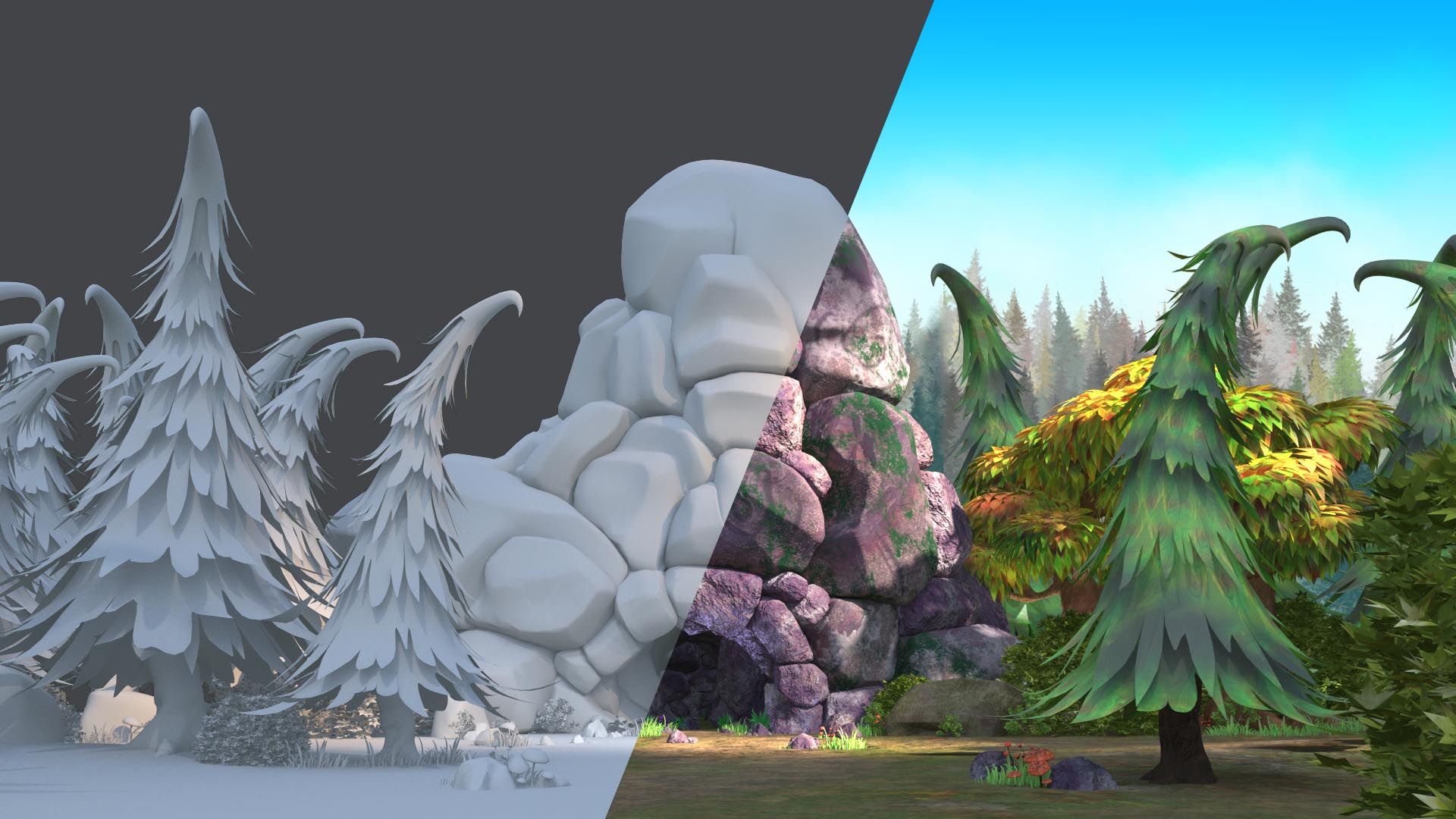

In the second method, modeling with weighted control of curved points is obtained, of course, the points are not interpolated, but only curved surfaces can be created using the relative increase of polygons. In this method, increasing the weight for a point brings the curve closer to that point.
Layout and animation
After modeling, it should be determined how to place and determine the movement of objects (models, lights, etc.) in a scene before rendering the objects and creating the image; This means that before the images are rendered, the objects must be designed and arranged in the scene. In fact, by defining the location and size of each object, the spatial relationship between the objects is formed. Motion or animation also refers to the temporal description of an object ( how it moves and changes shape over time ). Common layout and animation methods include keyframing, reverse kinematics, and motion capture. Of course, these techniques are often used in combination.
Rendering
In the last stage, based on the way the light is placed, the types of surfaces, and other specified factors, computer calculations are performed to produce and pay for the image. In this section, materials and textures are the data used for rendering.
The amount of light transmission from one surface to another and the amount of its distribution and interaction on surfaces are two basic actions in rendering that are often implemented using 3D graphics software. In fact, rendering is the final process of creating a 2D image or animation from a 3D model and a ready-made scene with the help of several different and often specialized methods that may take only a fraction of a second or sometimes up to several days for a single image/frame.
Shading technique
After the development of graphics processors to reduce the workload of processors and provide a platform for producing images with much more impressive quality than before, Nvidia and ATI gradually became the main players in the world of computer graphics. These two competitors worked hard to outdo each other and each tried to compete by increasing the number of levels in modeling and rendering and improving techniques. The shading technique can be seen as the birth of their competition.
In the computer graphics industry, shading refers to the process of changing the color of an object/surface/polygon in a 3D scene based on things like its distance from the light, its angle to the light, or the surface’s angle to the light.
Shaders calculate the appropriate levels of light, dark, and color while rendering a 3D scene.
Shading during the rendering process is done by a program called Shader, which calculates the appropriate levels of light, dark, and color during the rendering of a 3D scene. In fact, shaders have evolved to perform a variety of specialized functions in graphic effects, video post-processing, as well as general-purpose computing on GPUs.
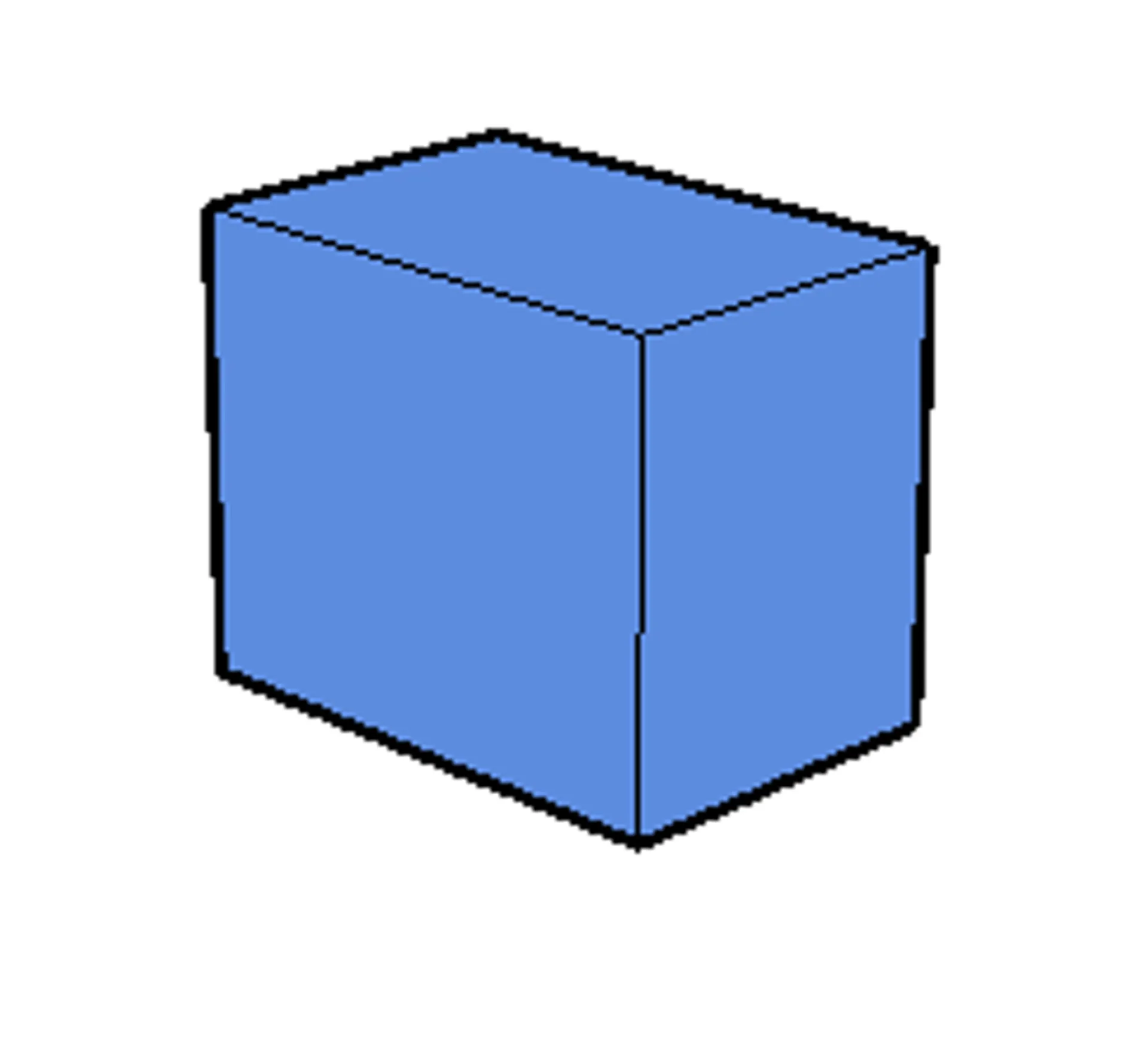
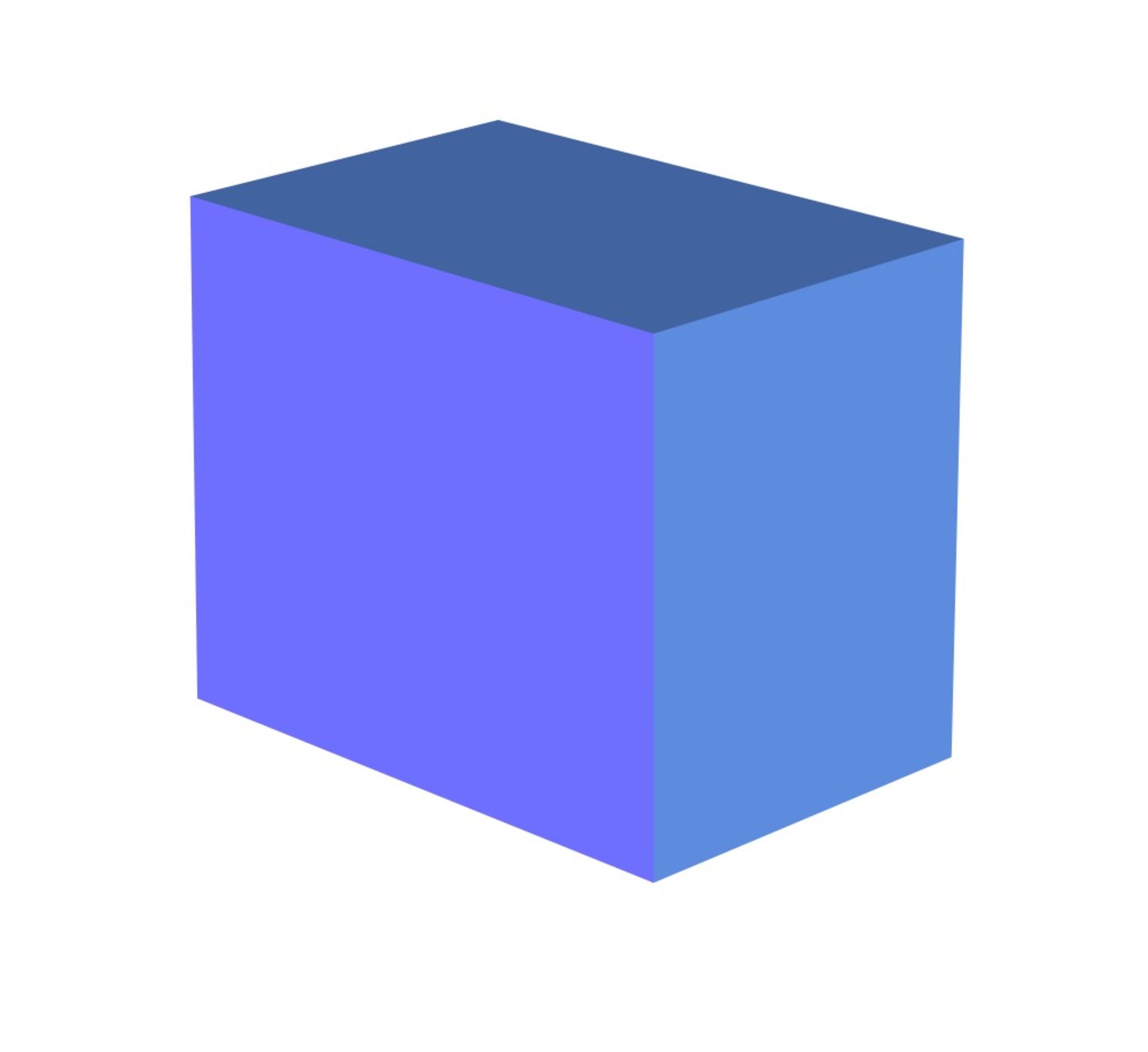
Shader changes the color of surfaces in a 3D model based on the angle of the surface to the light source or light sources.
- In the first image that you can see below, all the surfaces of the box are rendered with one color and only the edge lines are marked to make the image better visible.
- The second image shows the same model without the edge lines; In this case, it is a bit difficult to recognize where one face of the box ends and then starts again.
- In the third image, the shading technique has been applied; The final image looks more realistic and the surfaces are easier to recognize.

Shaders are widely used in cinema processing, computer graphics, and video games to produce a wide range of effects. Shaders are simple programs that describe a vertex or pixel. Vertex shaders describe properties such as position, texture coordinates, colors, etc. of each vertex, while pixel shaders describe the color, z-depth, and alpha value properties of each pixel.
There are three types of shaders in common use (pixel, vertex, and geometric shaders). Older graphics cards use separate processing units for each shader, but newer cards are equipped with integrated shaders that can run any technique and provide more optimized processing.
Pixel shaders
Pixel shaders calculate and render the color and other properties of each pixel region. The simplest types of pixel shaders produce only one screen pixel as the output color. In addition to simple lighting models, pixel shaders provide more complex outputs such as color space change, color saturation, brightness (HSL/HSV) or image contrast, blur generation, light bloom, volumetric lighting, normal mapping (for depth effect), bokeh, cell shading, They may also include posterization, bump mapping, distortion, blue screen or green screen effects, edge highlighting and motion, and simulating psychedelic effects.
Of course, in 3D graphics, the pixel shader alone cannot create complex effects, because it only works on one area and does not have access to the information about the vertices, but if the contents of the entire screen are passed to the shader as a texture, these shaders can use the screen and pixels Sample around and enable a wide range of 2D post-processing effects such as blur or edge detection/enhancement for shaders.
Vertex shaders
Vertex shaders are the most common type of 3D shaders and run once on each vertex given to the GPU. The purpose of using these shaders is to convert the three-dimensional position of each vertex in the virtual space into two-dimensional coordinates for display on the monitor. Vertex shaders can manipulate properties such as position coordinates, color, and texture, but cannot create new vertices.
Shaders needed parallelization to perform calculations and render quickly; The concept of crisp or thread was born from here
In 2000, ATI introduced the Radeon R100 series of graphics cards and with this work launched a lasting legacy of the Radeon series of graphics cards. The first Radeon graphics cards were fully compatible with DirectX 7 and used ATI’s HyperZ technology, which actually uses three technologies: Z compression, Z fast cleanup, and Z hierarchical buffering to conserve more bandwidth and improve rendering efficiency.
In 2001, Nvidia released the GeForce 3 graphics card series; This series was the first graphics card in the world to have programmable pixel shaders. Five years after this incident, ATI was bought by AMD, and since then the Radeon series of graphics cards has been sold under the AMD brand. Shader programs needed parallelization for fast calculations and renderings. To solve this problem, Nvidia proposed the concept of crisp or the same thread for graphics processors, which we will explain more about in the following.
Difference between GPU and CPU
The GPU evolved from the beginning as a complement to the CPU and to lighten the workload of the unit. Today, the performance of processors is becoming more powerful with new achievements in their architecture, increasing the frequency and number of cores, while GPUs are specifically developed to speed up graphics processing.
Processors are programmed in such a way that they can switch between operations very quickly in addition to doing one task with the lowest delay and highest speed. In fact, the processing method in CPUs is serial.
On the other hand, the graphics processor has been specifically developed to optimize the performance of graphics processing and provides the possibility of doing things simultaneously and in parallel. In the image below, you can see the number of cores of a processor and the number of cores of a graphics processor; This image shows that the main difference between CPU and GPU is the number of cores they have to process a task.
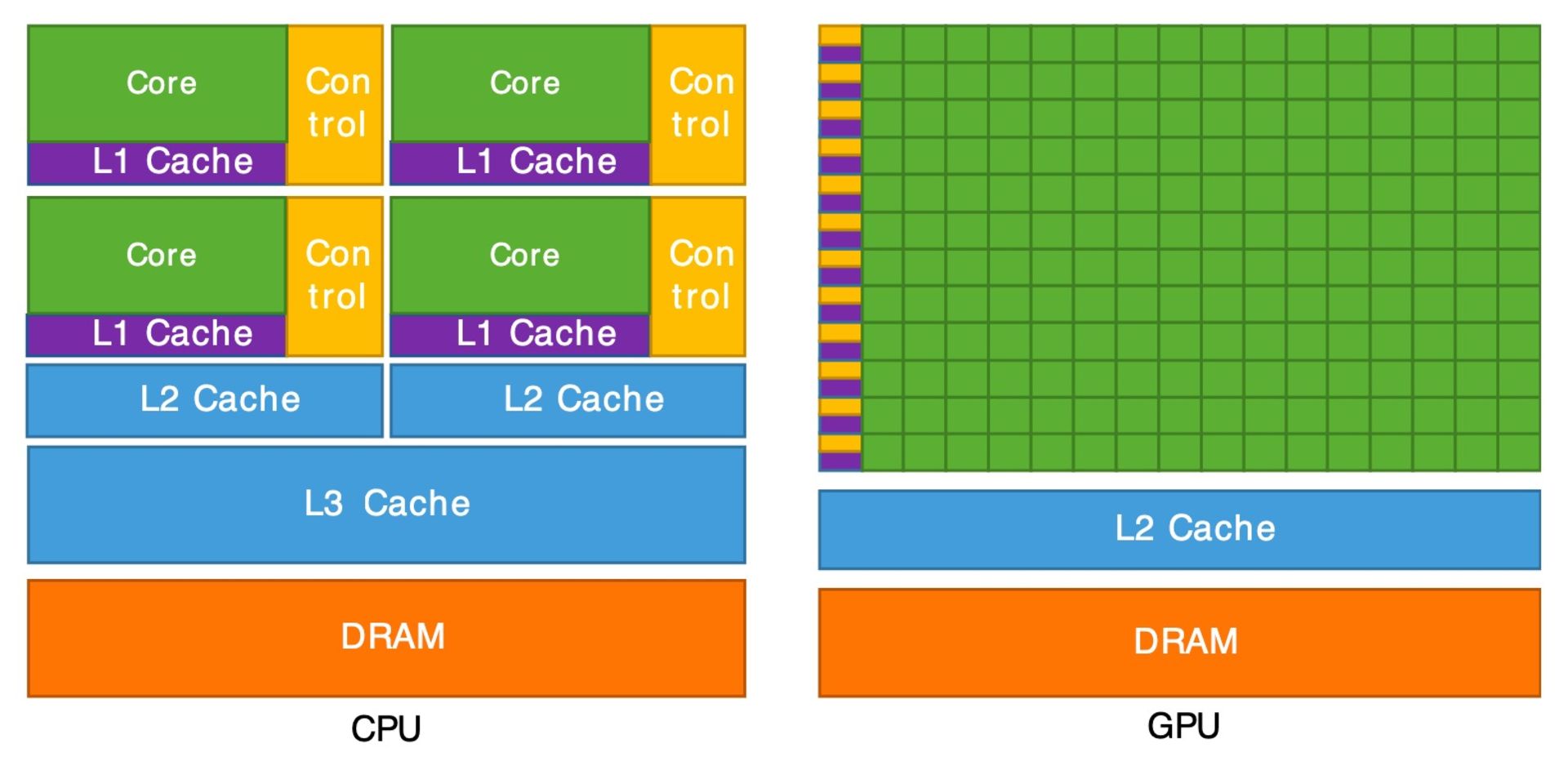
From the comparison of the overall architecture of the processors and graphics cards, we can find many similarities between these two units. Both use similar structures in the cache layers and both use a controller for memory and a main RAM. An overview of modern processor architecture suggests that low-latency memory access is the most important factor in processor design, with a focus on memory and cache layers (exact layout depends on vendor and processor model).
Each processor consists of several cache layers:
- Level one cache memory (L1) is the fastest, smallest, and closest memory to the processor and stores the most important data needed for processing.
- The next layer is the level two cache memory (L2) or the external cache memory, which is slower and larger than L1.
- The L3 cache memory in the processor is shared by all cores, and in terms of capacity, it has a larger volume and lower speed than the L1 and L2 cache memory; Like L3, L4 cache has a larger volume and lower speed than L1 and L2; The two are usually used interchangeably. If the data is not located in the cache layers, it is called from the main RAM (DDR).
Looking at the general overview of the GPU architecture (the exact layout depends on the manufacturer and model), we can see that the nature of this unit is focused on running the available cores instead of quickly accessing the cache memory or reducing latency. In fact, the GPU consists of several groups of cores that are located in the level one cache memory.
Compared to the processor, the graphics processor has fewer layers of cache memory and less capacity, this unit is equipped with more transistors dedicated to calculations and cares less about data recovery from memory; The graphics processor is developed with the approach of doing parallel calculations.
High-performance computing is one of the effective and reliable uses of parallel processing to run advanced applications; Precisely for this reason, GPUs are suitable for this kind of calculations.
In simple terms, let’s say you have two options for doing some kind of heavy computation:
- Using a small number of powerful cores that perform processes serially.
- Using a high number of not-so-powerful cores that can perform several processes simultaneously.
In the first scenario, if we lose one of the cores, we will face a serious problem; The performance of the other two cores will be affected and the processing power will be greatly reduced, on the other hand, if we lose a core in the second scenario, there will be no noticeable change in the processing process and the rest of the cores will continue to work.
The GPU performs several tasks at the same time and the CPU performs one task at a very high speed
The bandwidth of the GPU is much higher than the bandwidth of the processor, and therefore it performs parallel processing with high volume much better. The most important issue about graphics processors is that this processing unit is developed for parallel processing, and if the algorithm or calculations are secret and do not have parallelization capabilities, they are not executed at all and cause the system to be slow. CPU cores are more powerful than GPU cores and the bandwidth of this unit is much less than GPU bandwidth.
Familiarity with GPU architecture
At first glance, the CPU has larger but fewer computing units than the GPU. Of course, keep in mind that a core in the processor works faster and smarter than a core in the GPU.
Over time, the frequency of processor cores has gradually increased to improve performance, and on the contrary, the frequency of GPU cores has been reduced to optimize consumption and accommodate installation in phones or other devices.
The ability to perform processes irregularly can be seen as proof of the intelligence of the processor cores. As mentioned, the central processing unit can execute the instructions in a different order than the one defined for it, or predict the instructions needed in the near future and prepare the operands to optimize the system as much as possible and save time, before execution.
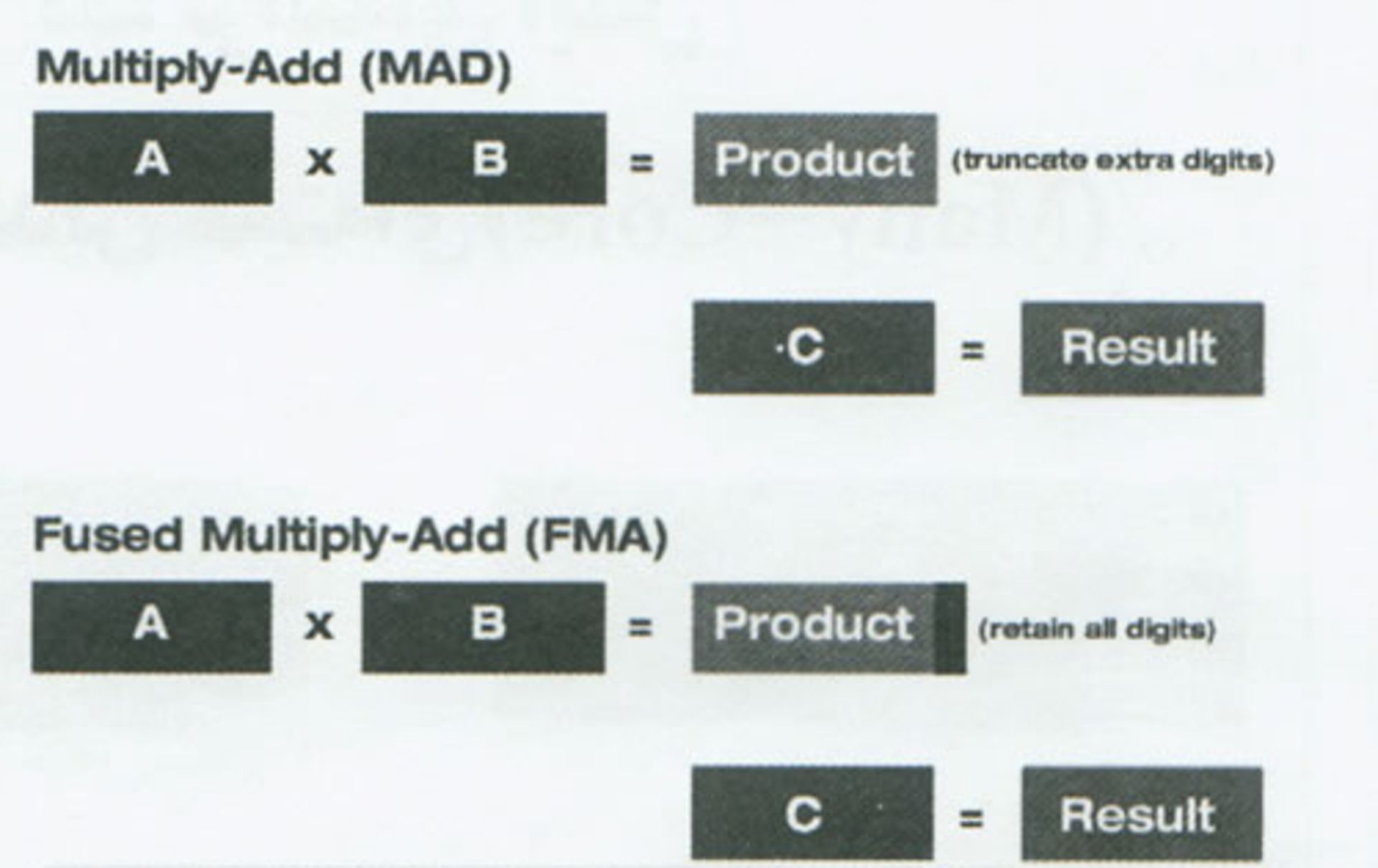
In contrast, the core of a graphics processor is not responsible for complexity and does not do much for processing outside of instructions and programs. In general, the main specialization of GPU cores was to perform floating-point operations such as multiplying two numbers and adding a third number (A x B + C = Result) by rounding the result to an integer, which is called multiply-add or MAD for short. It uses the same result with full accuracy (without truncation) in the multiplication stage, which is called Fused Multiplay-Add or FMA.
The latest GPU microarchitectures today are no longer limited to FMA and perform more complex operations such as ray tracing or tensor kernel processing. Tensor cores and ray tracing cores are also designed to provide hyper-realistic renderings.
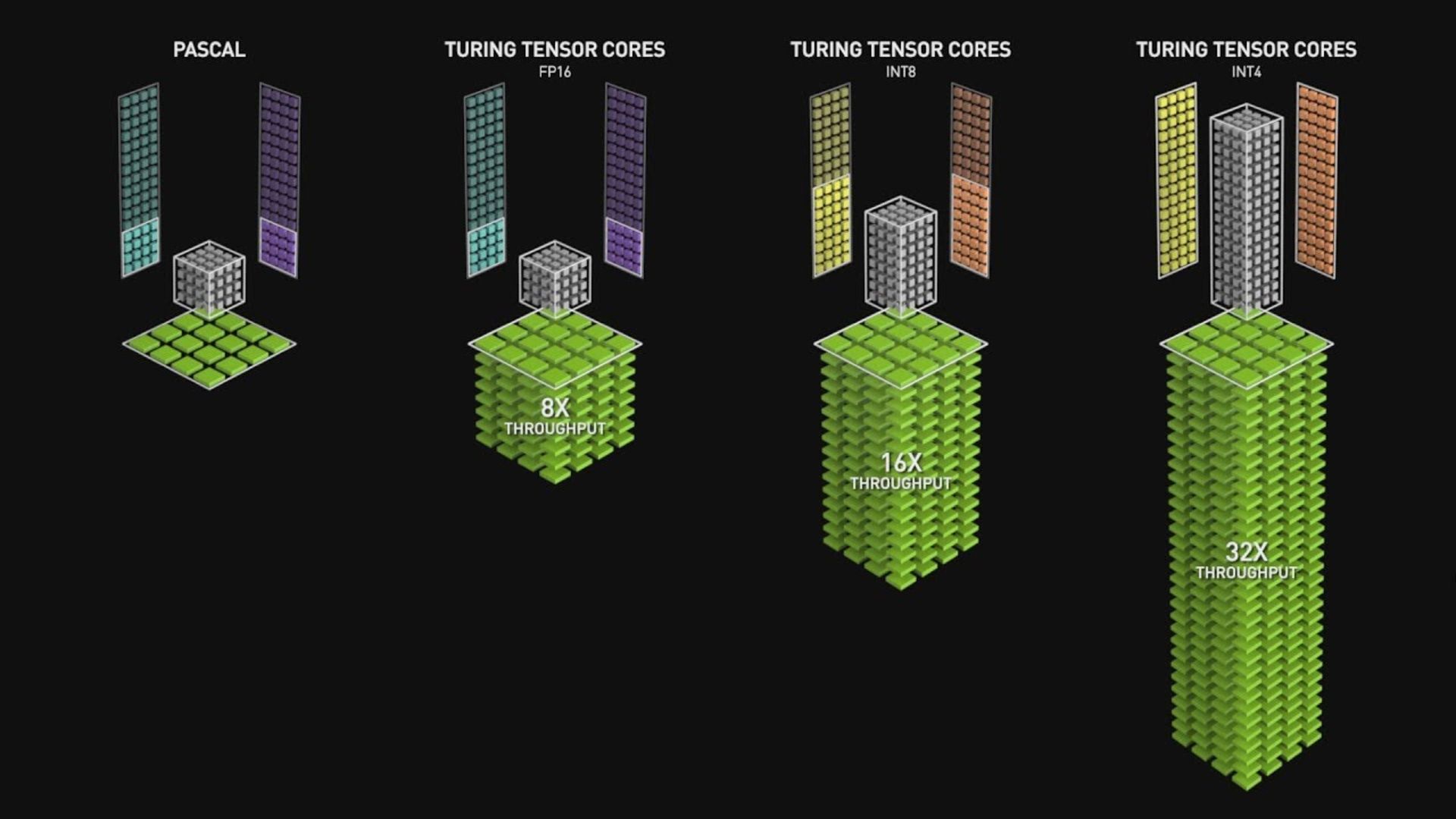
Tensor kernels
In 2020, Nvidia produced graphics processors equipped with additional cores that, in addition to shaders, were also used for artificial intelligence, deep learning, and neural network processing. These kernels are called Tensor. Tensor is a mathematical concept whose smallest imaginable unit has zero dimension (zero-by-zero structure) and contains only one value. By increasing the number of dimensions, other tensor structures are:
- One-dimensional tensor: vector (Vector with zero-in-one structure)
- Two-dimensional tensor: matrix (Matrix with one-in-one structure)
Tensor cores fall into the category of SIMD or “single instruction for multiple data” and their use in GPUs provides a much smarter chip than a calculator for graphics by providing all the computing and parallel processing needs. In 2017, Nvidia introduced graphics with a completely new architecture called Volta, which was designed and built targeting professional markets; This graphics card was equipped with cores for tensor calculations, but GeForce graphics processors did not use it.
At that time, the tensor cores were capable of multiplying decimal numbers up to 16-bit dimensions (FP16) and addition with 32-bit dimensions (FP32). Less than a year later, Nvidia introduced the Turing architecture; The only difference from the previous architecture was providing support for tensor cores for GeForce GPUs and data formats such as eight-bit integers.
In 2020, Ampere architecture was introduced in A100 graphics processors for data centers; In this architecture, the efficiency and power of cores have increased, the number of operations per cycle has quadrupled, and new data formats have been added to the supported set. Today, tensor cores are specialized and limited pieces of hardware that are used in a small number of consumer-specific graphics. Intel and AMD (the other two players in the world of computer graphics) do not have tensor cores in their GPUs, But maybe they will offer similar technology in the future.
- Tensor kernels are widely used in physics engineering and mathematics: they can perform complex calculations in electromagnetism, astronomy, and fluid mechanics.
- Tensor cores can increase the resolution of images: these cores extract images at a lower graphics level (or lower resolution) and increase the quality of images after rendering.
- Tensor cores increase frame rate: Tensor cores can increase frame rate in games after enabling ray tracing in games.
Ray tracing engine
In addition to cores and cache layers, GPUs may also include hardware to accelerate ray tracing, which simulates a light source shining on objects and creates different zoning in terms of light radiation. Fast ray tracing in video games can display more realistic and high-quality images.
Ray tracing is one of the biggest advancements in recent years in computer graphics and the gaming industry. At first, this feature was only used in the film industry, computer image production, and in animation and visual effects, but today PS5 and XBOX X series gaming consoles also support ray tracing.
In the real world, everything we see is the result of light hitting objects and reflecting it to our eyes; Ray tracing does the same thing in reverse and by identifying the light sources, the path of the light rays, the material, the type of shadow and the amount of reflection when it hits the objects. The ray tracing algorithm displays the reflection of light from objects of different genders in different and more realistic forms, draws the shadow of the objects that are in the path of the light beam depending on whether they are transparent or semi-transparent, and follows the laws of physics. For this reason, the images produced with this feature are very close to reality.

Off beam tracking engine (right side) versus on beam tracking engine (left side)
Nvidia first released ray tracing in 2018 on RTX series graphics under the Turing architecture, and then introduced a new driver that added ray tracing support to some GTX series graphics, which performed less well than the GTX series. They have RTX.
AMD also introduced ray tracing to the PS5 and Xbox XS series consoles by introducing the RDNA 2 architecture. Activating this feature in games reduces the frame rate due to the heavy processing load; For example, if a game runs at 60 fps on a system in normal mode, it may provide only 30 fps with ray tracing.
Frame rate, measured in frames per second (FPS), is a good measure of GPU performance, indicating the number of completed images that can be displayed per second; For comparison, the human eye can process about 25 frames per second, however fast action games need to process at least 60 frames per second to render a game stream smoothly.
What is GPGPU?
Many users abused the ability of parallel and fast processing of graphics processors in some way and transferred processes with the possibility of parallel calculations to this unit without considering the traditional task of the graphics processor. GPGPU or general purpose graphics processor was the solution that Nvidia introduced to solve this problem.
GPGPU (abbreviation of General Purpose Graphics Processing Unit) is the graphics processing unit that also performs non-specialized calculations (or CPU tasks) .
In fact, GPGPUs are used to perform tasks that were previously performed by high-powered CPUs, such as physics calculations, encryption/decryption, scientific computing, and the generation of digital currencies such as Bitcoin. Since GPUs are built for massive parallelism, they can reduce the computational burden on the most powerful processors. That is, the same cores used to shade multiple pixels simultaneously can similarly process multiple data streams simultaneously. Of course, these cores are not as complex as processor cores.
The GeForce 3 was Nvidia’s first GPU to feature programmable shaders. At the time, programmers aimed to make rasterized or bitmapped 3D graphics more realistic, and this Nvidia GPU provided capabilities such as 3D transformation, roughness mapping, and lighting calculations.
After the GeForce 3, the ATI 9700 GPU was introduced, equipped with DirectX 9, with more programming capabilities like the CPUs. With the introduction of Windows Vista, along with DirectX 10, integrated shader cores became standard. This newly discovered capability of GPUs enabled more CPU-based computing.
Since the release of DirectX 10, which featured integrated shaders for Windows Vista, more focus has been placed on GPGPUs, and higher-level languages have been developed to facilitate programming for computations on GPUs. AMD and Nvidia both had approaches to GPGPU development with programming interfaces (open source OpenCL and Nvidia’s CUDA).
What is CUDA?
Simply put, CUDA allows programs to use the GPU as a sub-processor. The processor transfers certain tasks to the graphics equipped with the CUDA core, which is optimized to process and calculate things like lighting, motion, and interaction as quickly as possible, and even performs processing from multiple paths simultaneously when necessary. The processed data is then sent back to the processor, which uses it for larger and more important calculations.
Advantages of CUDA kernels
Computer systems are based on software, so most of the processing must be programmed in program code, and since the main function of CUDA lies in calculation, data generation, and image manipulation, using CUDA cores helps programmers save time processing effects, rendering, and Reduce outputs to a high degree, especially in changes of scales, as well as simulations such as fluid dynamics and forecasting processes. CUDA also works great in light sources and ray tracing, and functions like rendering effects, encoding, video conversion, etc. are processed much faster with its help.
CUDA is designed to work with programming languages such as C, C++, and Fortran, making it easier for experts in parallel programming to use the GPU. In contrast, previous APIs such as Direct3D and OpenGL required advanced skills in graphics programming.
This design is more efficient than CPUs for parallel processing of large blocks of data, as in the following examples:
- Cryptographic hash functions
- machine learning
- Molecular dynamics simulation
- Physics engines
- Sorting algorithms
- Programming skills
Disadvantages of CUDA kernels
CUDA is Nvidia’s proprietary approach to introducing a GPU-like graphics processor (GPGPU), so you should only use Nvidia’s products to take advantage of it. For example, if you have a Mac Pro, you cannot use the capabilities of CUDA kernels, because this device uses AMD graphics for graphics processing; Additionally, fewer applications support CUDA than its alternative.
OpenCL; CUDA replacement
OpenCL is a relatively new, text-based system that is considered a replacement for CUDA. Anyone can use the functionality of this standard in their hardware or software without paying for the technology or a proprietary license. CUDA uses the graphics as a co-processor, while OpenCL transfers data entirely and uses the graphics more as a discrete processor. This difference in the way graphics are used may not be accurately measured, but another measurable difference between these two standards can be seen as the difficulty of coding for OpenCL compared to CUDA; As a user, you are not tied to any vendor and support is so extensive that most apps don’t even mention accepting it.

CUDA and OpenCL vs. OpenGL
As mentioned before, OpenGL can be seen as the beginning of the story of this competition; Of course, the purpose of developing this programming interface is not to use graphics as a general-purpose processor, and instead it is simply used to draw pixels or vertices on the screen. OpenGL is a system that allows graphics to render 2D and 3D images much faster than a CPU. Just as CUDA and OpenCL are alternatives to each other, OpenGL is an alternative to systems like DirectX on Windows.
Simply put, OpenGL renders images very quickly, and OpenCL and CUDA handle the necessary calculations when videos interact with effects and other media; OpenGL may place content in the editing interface and render it, but when it comes to color correction for this content, CUDA or OpenCL will do the math to change the pixels. Both OpenCL and CUDA can use the OpenGL system, and a graphics-equipped system with the latest OpenGL support will always be faster than a computer with a CPU and integrated graphics.
OpenCL or CUDA
The main difference between CUDA and OpenCL is the specificity of the CUDA framework, which was created by Nvidia and is open source compared to OpenCL. Assuming that the software and system hardware support both options, it is recommended to use CUDA if you have Nvidia graphics; This standard works faster than OpenCL in most cases. In addition, Nvidia graphics also support OpenCL, although the productivity of AMD graphics is higher than OpenCL. The choice between CUDA or OpenCL depends on the needs of the individual, the type of work, the type of system the workload, and its performance.
For example, Adobe explains on its website that, with very few exceptions, everything that CUDA does for Premiere Pro can also be done by OpenCL. However, most users who have compared these two standards believe that CUDA is faster than Adobe products.
The most prominent brands
In the graphics processor market, AMD and Nvidia are well-known names. The former used to be ATI and originally launched under the Radeon brand name for its GPUs in 1985; Then Nvidia became known as ATI’s competitor with the release of its first graphics processor in 1999. AMD bought ATI in 2006 and now competes with Nvidia and Intel on two different fronts. In fact, personal taste and brand loyalty are the most important factors that differentiate AMD and Nvidia.
Nvidia recently released GTX 10 series graphics, but AMD’s equivalents are generally more affordable choices. Other competitors such as Intel are also in the game and implementing their graphics solutions on the chip, but currently, AMD and Nvidia can be identified as the most prominent brands in this field. The processing speed of Nvidia graphics is lower than AMD graphics. Nvidia graphics with more cores and higher frequencies are suitable for gaming, but since they have a lower cache, they cannot reach AMD processors for performing some parallel processing such as mining and extracting digital currencies. In the following, we will briefly introduce the three leading brands in the world of graphics and graphic architecture, and in the near future, we will examine these competitors, their architectures, and products in detail in a separate article.
Intel
Intel is one of the largest manufacturers of computer equipment in the world, which operates in the field of hardware production, various types of microprocessors, semiconductors, integrated circuits, processors, and graphics processors. AMD and Nvidia are two prominent competitors of Intel and each has its own fans. Intel’s first attempt at a dedicated graphics card was the Intel740, which was released in 1998, but failed due to poorer performance than market expectations, forcing Intel to stop developing discrete graphics products. However, this graphics technology survived in the Intel Extreme Graphics product line. After this failed attempt, Intel tried its luck in the world of graphics once again in 2009 with the Larrabee architecture. This time, the previously developed technology was used in the Xeon Phi architecture.

In April 2018, news broke that Intel was assembling a team to develop discrete graphics processing units aimed at both the data center and gaming markets, bringing in Raja Kodori, former head of AMD’s Radeon Technologies Group. Intel announced early that it plans to introduce a discrete GPU in 2020. The first Xe discrete GPU, codenamed DG1, was released in October 2019 as a test drive and was expected to be used as a GPGPU for data center and self-driving applications. This product was initially made with 10nm lithography and then in 2021 with 7nm lithography and used 3D stacking packaging technology (Intel’s Foveros molding).
Intel Xe, or Xe for short, is the name of Intel’s graphics architecture, which has been used in Intel processors since the 12th generation. This company has also started developing discrete graphics and desktop graphics cards based on the Xe architecture and the Arc Alchemist brand. Xe is a family of architectures, each of which has significant differences from the others and consists of Xe-LP, Xe-HP, Xe-HPC, and Xe-HPG microarchitectures.
Unlike previous Intel GPUs that used execution units (EU) as the computing unit, Xe-HPG and Xe-HPC use Xe cores. Xe cores have vector and matrix computing logic units, and they are called vector and matrix engines, in addition to these units, they are also equipped with L1 cache memory and other hardware.
- Xe-LP (low power): Xe-LP is a low-power variant of the Xe architecture and is used as integrated graphics in 11th-generation Intel Core processors, Iris Xe MAX mobile discrete GPUs (codenamed DG1), and H3C XG310 server GPUs ( are used with the code name SG1). This series of graphics processors offers more processing frequency with the same voltage as the previous generation. In its largest configuration, Xe-LP has 50% more execution units (EU) than the 64 execution units of the 11th-generation graphics architecture in the Icelake series, and therefore its computing resources have been significantly increased. Along with the 50% increase in execution units, Intel has improved the architecture of Xe-LP graphics processors and instead of two calculation and logic units (ALU) with four paths in the previous generation, it uses eight paths for each calculation and logic unit. In addition, in the Xe LP architecture, a level 1 cache is also added, which reduces the delay in sending data, and supports end-to-end data compression, which increases bandwidth and performs tasks such as game streaming. It speeds up video chat recording, etc.
- Xe-HP (High Performance): Xe-HP is a high-performance, datacenter graphics optimized for FP64 performance and multi-tile scalability.
- Xe-HPC (High-Performance Computing): Xe-HPC is the high-performance computing variant of the Xe architecture. Each core in Xe-HPC includes 8 vector engines and 8 matrix engines, along with a large 512KB L1 cache.
- Xe-HPG (High-Performance Graphics): Xe-HPG is a high-performance graphics variant of the Xe architecture that uses the Xe-LP-based microarchitecture with improvements to Xe-HP and Xe-HPC. Xe-HPG has always been focused on graphics performance and supports hardware-accelerated ray tracing, DisplayPort 2.0, neural network-based supersampling (XeSS) similar to Nvidia’s DLSS, and DirectX 12 Ultimate. Each Xe-HPG core contains 16 vector engines and 16 matrix engines.
Nvidia
Nvidia was founded in 1993 and is one of the main manufacturers of graphics cards and graphics processors (GPU). Nvidia produces different types of graphics units, each offering unique capabilities. In the following, we briefly introduce the micro-architectures of Nvidia graphics units and the improvements of each compared to the previous generation:
- Kelvin: The Kelvin microarchitecture was released in 2001 and was used in the GPU of the original Xbox game console. GeForce 3 and GeForce 4 series graphics units were released with this microarchitecture.
- Rankine: Nvidia introduced the Rankine microarchitecture in 2003 as an improved version of the Kelvin microarchitecture. This microarchitecture was used in the GeForce 5 graphics series. The video memory capacity in this microarchitecture was 256 MB and it supported vertex and fragment shading programs. Vertex shaders change the geometry of the scene and create a 3D layout. Fragment shaders also specify the color of each pixel in the rendering process.
- Curie: Curie, a microarchitecture used in GeForce 6 and 7 series graphics, was released in 2004 as a successor to Rankine. The video memory capacity in Corey was 512 MB and it was the first generation of Nvidia graphics processors that supported PureVideo video decoding.
- Tesla: The Tesla graphics microarchitecture was introduced in 2006 and made several significant changes to Nvidia’s GPU lineup. In addition to being used in GeForce 8, 9, 100, 200, and 300 series graphics units, the Tesla architecture is also used in Quadro graphics products for things other than graphics processing. In 2020, after Elon Musk introduced the Tesla electric car, Nvidia stopped using the Tesla name to avoid further confusion.
- Fermi: Fermi was released in 2010 and offered features such as support for 512 CUDA cores, L1 cache /shared memory partitioning, 64KB capacity for RAM, and error correcting code (ECC) support. Some GeForce 8, GeForce 500, and GeForce 400 series graphics cards were produced based on this microarchitecture.

- Kepler: Kepler’s graphical microarchitecture was introduced after Fermi in 2012 and came with key improvements over the previous generation. This micro-architecture was equipped with new execution cores with simultaneous processing capability (SMX) and supported TXAA (anti-aliasing method). In the anti-aliasing technique in computer video, the information of the past frames and the current frame are combined to remove the unevenness in the current frame, and each pixel is sampled once in each frame, but in each frame, the sample is located at a different location in the pixel. Pixels sampled in past frames are combined with pixels sampled in the current frame to create a better-quality image. The Kepler microarchitecture consumes less power and the number of CUDA cores in it has increased to 1536. This micro-architecture is capable of automatic overclocking by enhancing the graphics processor and is equipped with the GPUDirect feature, which enables the communication of graphics units without the need to access the processor. Nvidia has used this micro-architecture in some GeForce 600, GeForce 700, and GeForce 800M series graphics units.
- Maxwell: Maxwell microarchitecture was released in 2014 and the first generation of GPUs based on this microarchitecture compared to Fermi, more efficient processors as a result of improvements related to logical partitioning control, reduction of dynamic power dissipation by eliminating frequency when the circuit is not in use. Scheduling of instructions and workload balancing, 64 KB of dedicated shared memory for each execution unit, improved performance with the help of native shared memory, and support for dynamic work parallelism. Some of the GeForce 700, GeForce 800M, GeForce 900, and Quadro Mxxx series graphics units were released with the Maxwell microarchitecture.
- Pascal: Pascal replaced the Maxwell microarchitecture in 2016. Graphics based on this microarchitecture ( GeForce 10 series ) compared to the previous generation of improvements such as NVLink communication support, for higher speed than the PCIe interface, High Bandwidth 2 (HBM2) memory equal to 720 GB, preemption processing capability ) or rollback (which by creating a temporary interruption in a running process, another process with a higher priority) and active balancing are used to optimize the use of GPU resources.
- Volta: Volta was a unique microarchitectural iteration released in 2017. Before Volta, most previous Nvidia GPU microarchitectures were developed for general use, but Volta GPUs were perfectly suited for professional applications; In addition, Tensor Cores were also used for the first time in this micro-architecture. As mentioned earlier, tensor cores are a new type of processing cores that perform specialized mathematical calculations and matrix operations and are specifically used in artificial intelligence and deep learning. Tesla V100, Tesla V100S, Titan V and Quadro GV100 series graphics units are developed based on the Volta microarchitecture.
- Turing: The Turing microarchitecture was introduced in 2018 and, in addition to supporting tensor cores, it also featured a number of consumer-focused GPUs. Nvidia uses this microarchitecture in its Quadro RTX and GeForce RTX series graphics processors. Turing supports RTX (Real-Time Ray Tracing) and is used for heavy calculations such as virtual reality (VR). Nvidia has used this microarchitecture for its GeForce 16, GeForce 20, Quadro RTX, and Tesla T4 graphics units.
- Ampere: Ampere is Nvidia’s newest microarchitecture, mostly used for high-performance computing (HPC) and artificial intelligence applications. The cores in this micro-architecture are tensor-type and support the third-generation NVLink interface, structural dispersion capability (turning unnecessary parameters to zero to enable the training of artificial intelligence models), second-generation ray tracing, MIG capability (abbreviation for Multi-Instance GPU) for active Separate partitioning and performance optimization of CUDA cores are equipped. Nvidia GeForce 30 series graphics units, workstations, and data centers are developed based on this microarchitecture.
In general, Turing may be considered Nvidia’s most popular microarchitecture, because Turing’s combined ray tracing and rendering capabilities create impressive 3D animations and realistic images that are very similar to reality. According to Nvidia, Real-Time Ray Tracing in graphics units based on Turing microarchitecture can calculate a billion rays per second to create graphics images.
AMD
AMD (abbreviation for Advanced Micro Devices) was founded in 1969 and now operates as a prominent competitor to Nvidia and Intel in the field of producing processors and graphics processors. After buying ATI in 2006, this company developed the products of this brand under its brand name. AMD graphics units are produced in several different series:
- Radeon series: common and common series that are the same ATI souvenirs.
- Mobility Radeon Series: Includes AMD’s low-power graphics, mostly used in laptops.
- Fire Pro series: powerful AMD graphics designed for workstations.
- Radeon Pro series: They are known as the new generation of Fire Pro graphics.
AMD graphics used to be numbered with four digits: Radeon HD 7750.

In these graphics, the bigger the model number, the stronger and newer the graphics. For example, HD 8770 graphics are stronger and more up-to-date than HD 8750; Of course, this does not apply to different generations. This means that graphics from the 7th generation cannot necessarily be compared with the graphics from the 8th generation without checking and only based on the generation number and consider it weaker. AMD changed the naming process of its products after the Radeon RX 5700 series graphics; RX 5700 XT and RX 5700 are the first graphics cards that were launched with AMD’s new naming scheme. AMD graphics units currently come in three general categories: the R5 series, the R7 series, and the R9 series.
- R5 and R6 series: low-end and relatively weak AMD graphics.
- R7 and R8 series: AMD’s mid-range graphics are suitable for editing in programs such as Photoshop and After Effects.
- R9 series: AMD’s most powerful graphics belong to this family and provide acceptable performance for gaming; As far as some R9 series graphics are designed for virtual reality or VR devices.
Currently, the only active extension for AMD graphics units is the XT extension, which indicates the high-end, better performance and higher frequency of that product.
The difference between graphics processor and graphics card
Since the graphics processor is a specialized unit for processing and designing computer graphics and has been optimized for this purpose, it performs this task much more efficiently than a central processor. This chip is responsible for most in-game graphics calculations, image rendering, color management, etc., and advanced graphic techniques such as ray tracing or shading are defined for it; On the other hand, the graphics card is a physical and hardware part of a computer systems that has many electronic parts on it.
The production technology of graphic cards has been accompanied by many changes from the past to today, and two or three decades ago these parts were known as display cards or video cards. At that time, graphics cards did not have the sophistication of today, and the only thing they did was display images and video on the screen. With the increase in graphics capabilities and the support of cards for various hardware accelerators to provide different graphics techniques, the name of graphics card was gradually used for these parts.
Graphics card components
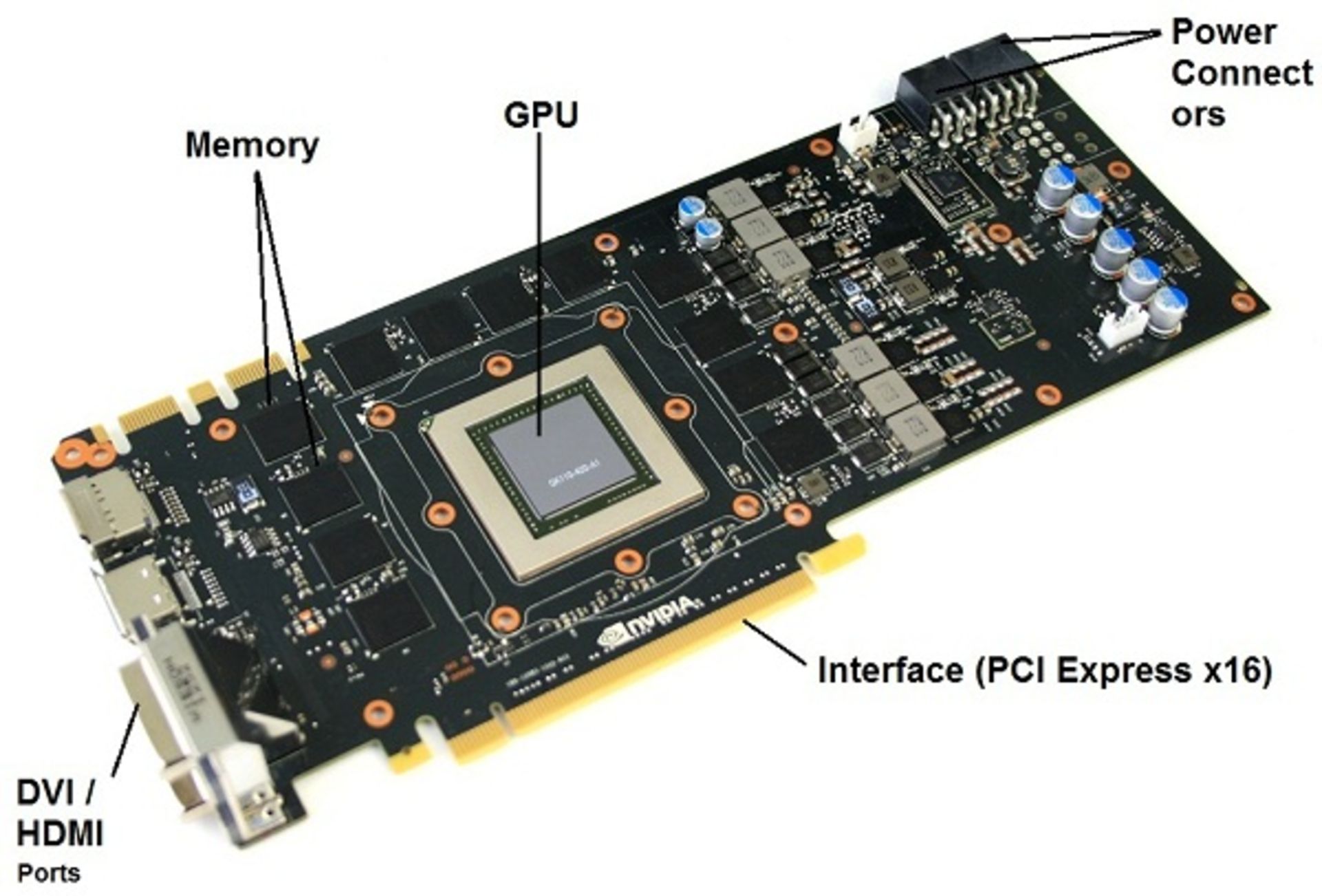
Today, these parts are more powerful than before and may provide the system required for different purposes such as gaming with different technologies. Therefore, all graphics cards do not have exactly the same components, but the key parts are the same. To use this piece, you will need to install the appropriate graphics driver for your graphics card on the system; This driver contains instructions on how to recognize and operate the graphics card and determines various specifications for running various games and programs. In addition to the graphics processor, the graphics card is equipped with other parts such as video memory, printed circuit board (PCB), connectors and cooling. You can get to know these parts in the next picture.
Video memory
Video memory is a place to store processed data, which is different from RAM or GDDR. This unit can be offered in different capacities depending on the use.
printed circuit board
A printed circuit board (PCB) is a board on which graphics card parts are placed and may consist of different layers. The material of these boards will be effective in the work quality of the graphic card.
Display connectors
After processing and performing calculations, the data needs cables and display connectors to be displayed on the screen. These cables use different types of connectors depending on the type of use of the product. For example, HDMI and DVI ports with more pins are used to display 4K resolution and very high frame rates, and VGA port is used to display images with lower resolutions; Today, most graphics cards have at least one HDMI port.
Bridge
For some high-end graphics cards, it is possible to use them together with other high-end graphics cards. Such a feature (Bridge) is a parallel processing algorithm for computer graphics that is used to increase processing power and is shown in Nvidia graphics cards with SLI (abbreviation of Scalable Link Interface) and in AMD graphics cards with the term Crossfire.
- SLI was first used by 3dfx in the Voodoo2 graphics card line; After buying 3dfx, Nvidia acquired this technology but did not use it. In 2004, Nvidia re-introduced the name SLI and intended to use it in modern computer systems based on the PCIe bus; But using it in today’s modern systems required compatible motherboards.
- Crossfire was also a technology introduced by ATI that allowed the simultaneous use of multiple graphics cards for the motherboard. Due to this technology, a controller chip was installed on the main board, which was responsible for controlling the intermediary channels and integrating their information for display on the screen; Officially, up to 4 graphics cards can be installed as Crossfire, in which case it is called Quad-Crossfire. This technology was first officially introduced in September 2005 to compete with SLI.
Graphic interface
The slot connecting the graphics card to the motherboard or support base was called APG in the past. After APG, another interface called PCI was introduced, and finally, what is known today as the graphics card and motherboard interface is PCIe or PCI Express, which plays the role of connecting, powering the board, and transferring information for the graphics card. In fact, PCI stands for Peripheral Component Interconnect and means peripheral component interface. In 2018, the PCI-SIG consortium published the general objectives of the sixth generation PCIe communication port; Two years later, this port was released in 2020, while its fourth generation has not yet become widespread, and graphics cards for normal use do not use the full capacity of PCIe 3.0.
The PCIe 6.0 port can transfer twice as much data as PCIe 5.0, i.e. 256 gigabytes per second of data through 16 paths, without the need to increase the bandwidth or more working frequencies and using current methods, and it is also compatible with its previous generations so that it can be used Available from older cards in new ports.
|
PCI Express bandwidth based on data transfer rate per direction (GB/second/direction) |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Bandwidth slot |
PCIe 1.0 (2003) |
PCIe 2.0 (2007) |
PCIe 3.0 (2010) |
PCIe 4.0 (2017) |
PCIe 5.0 (2019) |
PCIe 6.0 (2022) |
|
x1 |
0.25 GB/s |
0.5 GB/s |
1 gigabyte per second |
2 gigabytes per second |
4 gigabytes per second |
8 gigabytes per second |
|
x2 |
0.5 GB/s |
1 gigabyte per second |
2 gigabytes per second |
4 gigabytes per second |
8 gigabytes per second |
16 gigabytes per second |
|
x4 |
1 gigabyte per second |
2 gigabytes per second |
4 gigabytes per second |
8 gigabytes per second |
16 gigabytes per second |
32 gigabytes per second |
|
x8 |
2 gigabit per second |
4 gigabytes per second |
8 gigabytes per second |
16 gigabytes per second |
32 gigabytes per second |
64 gigabytes per second |
|
x16 |
4 gigabytes per second |
8 gigabytes per second |
16 gigabytes per second |
32 gigabytes per second |
64 gigabytes per second |
128 gigabytes per second |
Voltage regulator circuit
After the initial power supply by the PCIe interface, the current to the graphics card must be reviewed and adjusted. This task is the responsibility of the voltage regulator circuit (VRM), which provides the electric current required by various parts such as memory and graphics processors. The correct operation and application of regular, adequate, and timely voltages of this circuit can increase the durability of the graphics card and optimize energy consumption. Actually, the voltage regulator circuit decides how the power supply should be done. This circuit consists of four sections: input capacitor, MOSFET, choke, and output capacitor.
- Input capacitors: current is entered and stored in the circuit through input capacitors and sent to other parts of the circuit when necessary.
- MOSFETs: MOSFETs act like a bridge and pass the current stored in the input capacitors. There are two low-side and high-side MOSFETs in the voltage controller circuit; When the graphics need current, this current passes through the MOSFET High and when the graphics do not need the current, the current is stored in the MOSFET Low.
- Chokes: Chokes are electronic components that reduce current noise as much as possible. Graphics need smooth and stable flow to function properly, and chokes provide this by removing noise.
- Output capacitors: after filtering the current by the chokes and before sending the required current to the desired sections, the output capacitors remove the current from the circuit.
Cooling system
Every graphics card must be at an optimal temperature to perform at its best. The cooling system in the graphic card, in addition to reducing the working temperature of the product, increases the durability of the parts used in it. The system consists of two parts: a heatsink and a fan: the heatsink is usually made of copper or aluminum and is ideally passive. The main purpose of this section is to take heat from the graphics processor and distribute it to the surrounding environment; On the other hand, the fan is an active part of the graphics cooling system that blows air into the heatsink to keep it ready to remove heat. Some low-end graphics cards only have a heatsink, but almost all mid-range and high-end cards are equipped with a combination of a heatsink and a fan for proper and efficient cooling.
Types of graphics processor
Graphics processors in different types perform the task of performing calculations and graphics processing for systems; In the following, we will get to know the types of these graphic units, how they work, and the advantages and disadvantages of each:
iGPU
iGPU (abbreviation of Integrated Graphics Processing Unit) is an integrated graphics processing unit that is placed on the central processor chip or CPU. iGPU may be installed on the motherboard or placed next to the processor (in which case it is considered the same graphics processing unit in the integrated chip). These graphics units generally do not have much processing power and are not suitable for displaying advanced 3D game graphics and animations; Actually, they are designed for basic processing and it is not possible to upgrade them. The use of these graphics allows the system to be thinner and lighter, reducing power consumption and costs. AMD introduces its graphics processors as APUs.
Of course, today there are modern processors that can be surprisingly powerful with integrated graphics. Not all processors are equipped with an integrated GPU; For example, Intel desktop processors whose model number ends with F or the company’s X series processors do not have a graphics processing unit and therefore are sold at a lower price, and you will need a separate graphics card for graphics processing in systems equipped with this processor. had
Currently, AMD and Intel are trying to improve the performance of their integrated graphics processors, and Apple has also surprised many people with its silicon chips, especially in the M1 Max chip, which is a very powerful integrated graphics processor and can handle high-end graphics. to compete

dGPU
dGPU (abbreviation of Discrete Graphics Processing Unit) is a separate graphics processing unit that is used as a dedicated and separate chip in systems. A discrete GPU is usually much more powerful than an iGPU and makes it much easier to analyze large, sophisticated, 3D graphics data. In fact, to use gaming systems or advanced 3D rendering and design, having a powerful dGPU is essential. The discrete GPU can be easily replaced and upgraded; In addition to very high power, these units are also equipped with a dedicated cooling system and do not overheat when performing heavy graphics processing. It can be said that dGPUs are one of the reasons why gaming laptops are more expensive and heavier, with high power consumption and low battery life in these systems compared to normal laptops, for this reason, it is recommended only if you use your system for gaming to produce 3D graphics content. Or you use heavy tasks, buy a separate graphics processor.
Currently, the biggest names in the discrete GPU industry are AMD and Nvidia, although Intel has also recently launched its own laptop GPUs in the form of the Arc series, and plans to launch desktop graphics cards as well.
However, discrete GPUs require a dedicated cooling system to prevent overheating and maximize performance, which is why gaming laptops are much heavier than traditional laptops.
Cloud GPU
The cloud graphic processing unit provides the user with the possibility of using many graphic services on the Internet; That is, without providing a GPU, you can use the processing power of the graphics processor. Of course, it is understandable that cloud graphics do not offer that much special power, but it is suitable for those who do not have a large budget and do not need very advanced graphics processing. This group of people can pay different providers for the graphics cloud processing they receive based on their usage.
eGPU
An external graphics card or eGPU is a graphic that is placed outside the system, is equipped with a PCIe port and a power supply, and can be connected to the system externally through USB-C or Thunderbolt ports. Using these graphics allows the user to use powerful graphics in a compact and light system.
-
Mac computers equipped with the M1 chip do not support external graphics cards
In recent years, the use of external graphics has increased, and since the power of graphics processing and the quality of output images of laptops are generally lower than desktops, users have recently solved this problem by using external graphics. External or external graphics are mostly used for systems such as laptops, but some companies use these graphics units for older desktops with low processing power. Be careful that if it is possible to upgrade the laptop graphics, the use of external graphics will not be justified, but issues such as the large space required for external graphics, their high cost, etc., make users especially gamers use external graphics cards. Prefer to upgrade your desktop graphics system.
Mobile GPU
Mobile graphics determine our visual experience of phones and can even be decisive for some users (gamers) and show loyalty to a certain brand.
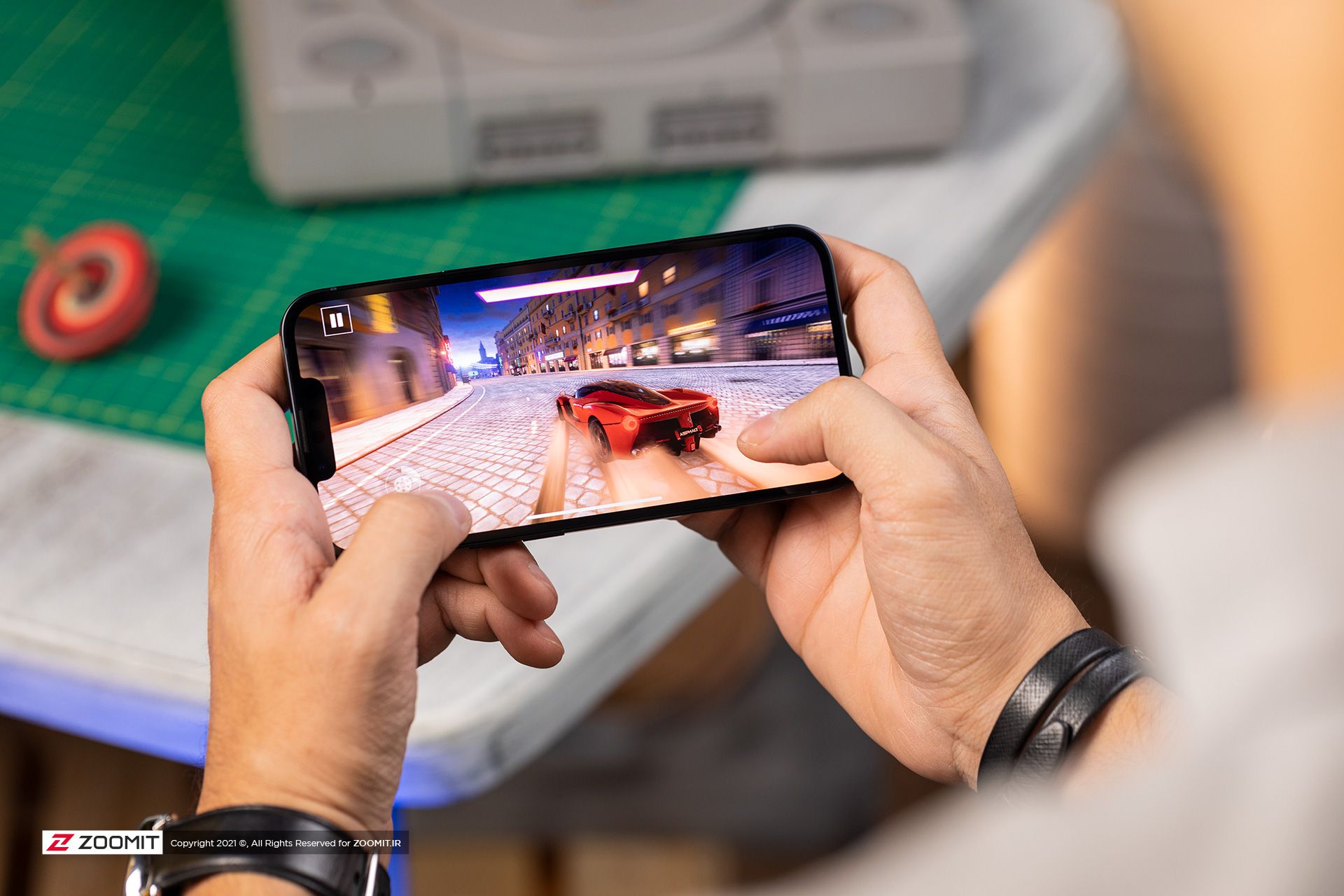

The mobile system on a chip (SOC) or in short the same chip that is in today’s phones, besides the central processing unit, has units for artificial intelligence processing, image signal for the camera, modem, and other important equipment, as well as a graphics processing unit. The mobile GPU was introduced to process heavy data such as 3D games and changed the world of phones, especially for gamers. As mentioned, the processing cores in the mobile graphics processor are less powerful than the processing cores in the central processors, but on the other hand, their simultaneous and fast performance makes it possible to display heavy content and complex graphics on phones.
Types of mobile GPUs
ARM is one of the main poles of the production of graphics processing units for phones and the owner of the famous Mali brand, Qualcomm has a large share of the phone graphics market with Adreno graphics processors, Imagination Technologies has been producing Power VR graphics processors for years. and Apple used this company’s graphics processors for a long time before developing its own graphics processor. It is interesting to know that unlike Apple, which has its own graphics processors, Samsung uses ARM or Qualcomm graphics processors for the processing and graphics calculations of its phones.
- logo; Mali GPU: Mali mobile GPUs are developed by ARM and are sold in different price ranges. For example, the graphics processor used in the Galaxy S21 Ultra is Mali-G78 MP14 and can perform graphics processing at high speed and power.
- Qualcomm; Adreno graphics processor: Along with the powerful Android processors it produces under the name of Snapdragon, Qualcomm also performs brilliantly in the production of mobile graphics processors. Like Mali GPUs, these units have a wide price range and target market. For example, the Adreno 660 GPU used in the Asus ROG Phone 5 gaming phone in 2021 was recognized as one of Qualcomm’s most powerful graphics.
- Imagination Technologies; Power VR graphics processor: Power VR graphics processors were once used in the most popular iPhones, but Apple abandoned the use of these graphics units by producing its own graphics for the A Bionic chip; Today, Power VR GPUs are mostly used in affordable MediaTek chips and in budget and mid-range phones from brands like Motorola, Nokia, and Oppo.
Other applications of graphics processors
GPUs were originally developed as an evolved unit of graphics accelerators to help lighten the workload of processors. Until the last two decades, they were often recognized as accelerators for rendering 3D graphics, especially in games. However, since these units have high parallel processing power and can process more data than the central processing unit (CPU), they were gradually used in fields other than gaming, such as machine learning, digital currency mining, etc. In the following, we will learn about other uses of graphics processors other than gaming:
Video editing
Modern graphics cards are equipped with video encoding software and can prepare and format video data before playback. Video encoding is a time-consuming and complex process that takes a lot of time to complete with the help of the central processing unit. With their very fast parallel processing capabilities, GPUs can handle video encoding relatively quickly without overloading system resources. Note that high-resolution video encoding may take some time even with powerful GPUs, but if the GPU supports higher-resolution video formats, it will perform much better than the CPU for video editing.
3D graphics rendering
Although 3D graphics are most commonly used in video games and gaming, they are increasingly being used in other forms of media such as movies, television shows, advertisements, and digital art displays. Creating high-resolution 3D graphics, even with advanced hardware, just like video editing, can be an intensive and time-consuming process.

Modern film studios often depend on advanced GPU technology to produce realistic and dynamic computer graphics, making the hardware a vital part of the filmmaking process. Digital artists also use computers equipped with advanced graphics processors to create abstract works that cannot be produced in the usual physical space and produce works of art different from what we have seen so far. With the right combination of hardware performance and artistic vision, GPUs can be a powerful creative resource for computing and media content processing.
Learning the machine
One of the lesser-known applications of modern GPUs is machine learning. Machine learning is a form of data analysis that automatically builds analytical models. Basically, machine learning uses data to learn, identify patterns, and make decisions independent of human input, and due to the very intensive nature of this system and the need for parallel processing, GPUs can be considered an essential part of this technology.

Machine learning is considered the foundation of technology and the use of artificial intelligence, and for that reason it is a complex computational process that requires a large amount of data to be entered for analysis . Software known as machine learning algorithms performs and models the analysis based on what is called training data or sample data. These obtained models are used to make predictions or decisions without the need for human intervention. This method has been widely implemented in various fields, from the medical world to email filtering systems to prevent receiving inappropriate content, and has made machine learning a vital aspect of modern data infrastructures.
Blockchain and digital currency mining
One of the more common uses of GPUs besides gaming is their use in mining or digital currency extraction. In the process of mining digital currencies or cryptocurrencies, system resources are placed at the disposal of the blockchain (or a continuous record of complex encryption algorithms for storing transaction data); Each entry in this record is called a block, which requires a certain amount of computing power to produce. Although blockchain technology has applications outside of digital currencies, it is generally used to mine digital currencies (especially Bitcoin); Of course, the mining process can be different depending on the desired digital currency.

Specifically, the Bitcoin mining process involves allocating hardware resources to create blocks in the Bitcoin blockchain. The more blocks are added to the blockchain, the more bitcoins are generated. Such a process consumes system resources and power and reduces system productivity when engaged in mining. The high throughput and relatively low energy requirements of GPUs make these units a suitable tool for performing the mining process, which has recently gained a lot of fans.
Frequently asked questions
-
What is the use of a graphics processor (GPU)?
-
-
What is the difference between CPU and GPU?
-
-
What is the difference between GPU and VGA?


You may like


Galaxy S24 FE review; Although insufficient steps in the path of evolution
Nowadays, it is rare to find anyone who is not somehow familiar with the Samsung Fan Edition series. Samsung’s FE series products are very popular thanks to their hardware offerings and build quality on par with flagship phones with a lower price tag. They are often referred to as flagship killers rather than fan-pleasers. On the other hand, the existence of strong competitors such as Xiaomi’s T series is a strong reason for the life of the FE family to continue.
-
Galaxy S24 FE review video
-
Galaxy S24 FE Design: Goodbye to the crowd
-
Galaxy S24 FE screen and speaker: accurate and attractive
-
S24 FE performance and charging: with the power of a full-fledged flagship
-
Galaxy S24 FE software: pseudo-flagship full of artificial intelligence
-
Galaxy S24 FE camera: more or less better and sometimes worse
-
Galaxy S24 FE camera comparison with S23 FE
-
Galaxy S24 FE; A product still involved with constant challenges
Artificial intelligence is considered to be the leading actor these days in the world of technology; Therefore, companies like Samsung have seized the opportunity to make the most of the capacity of the prevailing psychological space to be in the spotlight and use artificial intelligence as an important trump card against competitors.
Now it’s the turn of the FE series to inherit the artificial intelligence capabilities from their flagship brothers/sisters in addition to the hardware features; But not everything is artificial intelligence, and we should not forget that the FE series, with all its merits, is under the microscope; Because its previous generations have not left a very bright record in terms of chip performance stability and battery life. Has Samsung been able to think of a solution for this problem? We will find the answer to this question in the Galaxy S24 FE review.
Galaxy S24 FE was provided to Zomit by Safeservice for review.
Galaxy S24 FE Design: Goodbye to the crowd
The first big change that can be seen in the appearance of the S24 FE is not a change in the design language, but an increase in its size; Now the dimensions of the phone have increased from 6.5 to 6.7 inches, which may be good news for some and unpleasant for others; But since most of the phones have similar dimensions, maybe it would be better if Samsung did not touch the size of the phone to maintain the distinction and have a better chance to attract fans of compact phones.

With the increase in the dimensions of the phone, the screen-to-body ratio has reached 88%, which makes the wide margins of the previous generation less noticeable; I emphasize that they are less noticeable because the width of the borders around the screen in the Galaxy S24 FE does not change significantly compared to the previous generation, and you still have to get used to seeing them.
The Galaxy S24 FE’s screen protection has been improved after a major setback in the S23 FE with Gorilla Glass Victus+; But the back glass frame of the phone is still made of Gorilla Glass 5, and due to its shiny and transparent surface, it still has a high talent for absorbing fingerprints; However, it provides good friction with the hand and does not allow the phone to slide.

The curved and matte aluminum frame of the previous generation has been replaced by a flat frame, lest the Galaxy S24FA defy the design language of the Koreans this year; This change helps to maintain the stability of the phone in the hand; But it reduces the elegance of the phone and even with a 0.2mm thickness reduction, it looks rougher than the previous generation.
By increasing the size of the phone and using a larger battery, the weight of the S24 FE has increased by four grams and has reached 213 grams; Although the increase in the weight of the phone is not very noticeable; due to the increase in size, the device does not fit easily in the hand of the previous generation. The combination of these two things made me feel more like a mid-range phone than a flagship killer; Although, nowadays, Samsung phones from low-end to flagship have more or less the same appearance.




Galaxy S24 FE is produced in green, blue, yellow, silver, and gray (graphite) colors, relying on the IP68 standard, it can last for 30 minutes in 1.5 meters of water, on the bottom edge of the USB 3.2 Type-C port, slot Speaker and microphone holes and on the top edge hosts the SIM card port and secondary microphone holes and noise canceling. The power and volume up/down buttons are also placed on the right edge with the same arrangement as before.
Galaxy S24 FE screen and speaker: accurate and attractive
The Galaxy S24 FE uses the brand’s Dynamic AMOLED 2X OLED display, which renders content at FHD+ resolution, or 2340 x 1080 pixels, and a 120Hz refresh rate. Due to the 0.2-inch increase in screen size, the pixel density has been reduced to a very small amount that cannot be detected by the naked eye.

The Galaxy S24 FE panel is not LTPO and is low-power, and the refresh rate only moves between 60 and 120 Hz depending on the content; Therefore, the always-on display or AOD of the phone, unlike the S24 series, does not have the ability to display the background image and only displays the clock and notifications.
The S24 FE screen, like other Samsung phones, uses 8-bit color depth with the ability to display 16 million colors; Therefore, standards such as Dolby Vision are not supported, and you can only watch content with the HDR10+ standard; But the good news is that the brightness rate of the device when playing such content reaches more than 2240 nits based on the measurement of Zoomit; Of course, the maximum brightness under sunlight does not exceed 1695 nits, which is still 30% brighter than before.

The S24 FE display has two color profiles, Natural and Vivid, which are defined in the sRGB and DCI-P3 color spaces. From the S24 phones onwards, Samsung made changes to the Vivid profile that, according to its own words, shows colors more naturally; Therefore, by switching from the Natural profile to Vivid, by default, the colors do not recover the past freshness and wider coverage of the DCI-P3 color range, and we do not see any special change except the colors becoming colder.
|
Galaxy S24 FE display performance against the competition |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Product/Test |
Minimum brightness |
Maximum brightness |
contrast ratio |
sRGB |
DCI P3 |
||
|
manual Automatic |
local |
cover |
Average error |
cover |
Average error |
||
|
Galaxy S24 FE |
1.7 |
520 2240 (HDR) |
∞ |
99.5 percent (Natural) |
1.4 |
94.3 percentage (Vivid) |
3.2 |
|
Galaxy S23 FE |
1.9 |
607.5 1315 |
∞ |
98.7 percentage (Natural) |
1.5 |
100 percentage (Vivid) |
4 |
|
Galaxy S24 Plus |
0.8 |
587 2965 (HDR) |
∞ |
95.6 percent (Natural) |
3.2 |
83.3 percent (Vivid) |
4.6 |
|
Motorola Edge 50 Pro |
2/6 |
640 2300 (HDR) |
∞ |
100 percent (Natural) |
0.8 |
100 percent (Vibrant) |
1.2 |
|
Pixel 8 |
2 |
1228 2200 (HDR) |
∞ |
97.9 percent (Natural) |
0.8 |
84.3 percent (Adaptive) |
2.8 |
To experience more vivid colors, you can use the slider in the Advanced Settings section to increase the color intensity. By increasing Vividness as much as possible, you can restore that past visual experience; However, a small part of the DCI-P3 range falls under the S24 FE and does not cover it 100%.
The Natural profile displays completely neutral colors with high accuracy; Of course, the accuracy of the Vivid profile is also very good with DeltaE 3.2; But you will see the same tendency to be cold in the display of colors by choosing this profile.

There is an optical fingerprint sensor under the display, which is slightly lower than the S23 FE and its performance is as fast and accurate as before; The speed and accuracy of the device’s optical sensor cannot be compared with ultrasonic sensors; However, you can rest assured that there is no problem with the fingerprint recognition on the protective glass.
The Galaxy S24 FE uses the speakerphone as a second speaker to produce stereo sound. Speakers provide high and balanced sound volume. As with the Galaxy S23 FE, sound separation is good as long as you don’t plan on playing loud music; However, the bass may not have that usual thump in some songs.
S24 FE performance and charging: with the power of a full-fledged flagship
The presence of Exynos chips in the heart of Fan Editions has become a tradition and Samsung has chosen to follow the same procedure this year. Now that after a gap of one year, the basic and plus models of the S24 series have also been launched with the Exynos chip, Samsung is equipping it with the Exynos 2400e chip to differentiate between the flagship series and the fan edition. In addition, unlike last year, there is no news about the Snapdragon version and all S24 FE models are launched with the Samsung chip.
|
Technical specifications of the chip |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Specifications/Chip |
Exynos 2400 |
Exynos 2400e |
Exynos 2200 |
|
Central processor |
1 3.21 GHz Cortex-X4 core 2 2.9 GHz Cortex-A720 cores 3 2.6 GHz Cortex-A720 cores 4 cores of 1.95 GHz Cortex-A520 8 MB system cache |
1 3.11 GHz Cortex-X4 core 2 2.9 GHz Cortex-A720 cores 3 2.6 GHz Cortex-A720 cores 4 cores of 1.95 GHz Cortex-A520 8 MB system cache |
1 2.8 GHz Cortex-X2 core 3 2.52 GHz Cortex-A710 cores 4 cores of 1.82 GHz Cortex-A510 |
|
Graphics |
1095 MHz Xclipse 940 unit |
1095 MHz Xclipse 940 unit |
1306 MHz Xclipse 920 unit |
|
Memory controller |
4 16-bit channels RAM 4200 MHz LPDDR5X The bandwidth is 68.2 GB |
4 16-bit channels RAM 4200 MHz LPDDR5X The bandwidth is 68.2 GB |
4 16-bit channels RAM 4200 MHz LPDDR5 The bandwidth is 51.2 GB |
|
Record and play video |
8K30 / 4K120 10-bit H.265 |
8K30 / 4K120 10-bit H.265 |
8K30 / 4K120 10-bit H.265 |
|
Wireless connection |
Bluetooth 5.4 and Wi-Fi 7 |
Bluetooth 5.4 and Wi-Fi 7 |
Bluetooth 5.2 and Wi-Fi 6 |
|
modem |
Exynos 5300 modem Download 9640 MB Upload is 2550 megabits |
Exynos 5300 modem Download 9640 MB Upload is 2550 megabits |
Exynos 5300 modem Download 7350 megabits Upload is 3670 megabits |
|
manufacturing process |
Samsung 4 nanometers |
Samsung 4 nanometers |
Samsung 4 nanometers |
The Exynos chip at the heart of the Galaxy S24 FE is not much different from the Exynos 2400 at the heart of the flagships of the S24 series, and only the frequency of its powerful core is 100 MHz lower. Samsung says that the change in the frequency of the high-powered Exynos 2400e core helps to improve the chip’s energy consumption, higher stability, and better temperature control in various applications.

Looking at the benchmark results in the table below, we can see that the 100 MHz reduction in processor frequency in the usual benchmarks does not have a noticeable effect on the performance of the S24 FE compared to the S24, and with a small difference, it appears weaker in single-core and multi-core processing. Due to the same graphics processor, the performance of the S24 FE in this section is not significantly different from its flagship family.
|
Galaxy S24 FE performance against the competition |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Product/benchmark |
chip |
Speedometer 2.1 |
GeekBench 6 |
GFXBench |
|
|
Web browsing experience |
GPU computing power |
CPU computing power |
Game simulator |
||
|
Vulkan/Metal |
Single/Multi |
Aztec Ruins Onscreen/1440p |
|||
|
Vulkan/Metal |
|||||
|
Galaxy S24 FE |
Exynos 2400e |
300 |
15539 |
2077 6268 |
101 71 |
|
Galaxy S23 FE |
Exynos 2200 |
88 |
9874 |
1608 4014 |
55 38 |
|
Pixel 8a |
Tensor G3 |
135 |
6404 |
1763 4384 |
60 40 |
|
Xiaomi 13T Pro |
Density 9200 Plus |
121 |
7197 |
1292 3591 |
75 62 |
|
Notingphone 2 |
Snapdragon 8+ Gen 1 |
155 |
6746 |
1415 3959 |
60 51 |
|
Galaxy S24 |
Exynos 2400 |
242 |
16233 |
2141 6618 |
107 68 |
The generation gap between the S24 FE chip and the S23 FE is so great that it makes any comparison irrelevant. The Exynos 2400e not only beats its predecessor in all areas, including CPU and GPU processing power but also beats almost all the pseudo-flagships of other brands that we have reviewed at Zoomit.
Samsung Fan Edition 2024 appears 30% better in single-core processing and 60% better in multi-core processing and graphic computing power than the previous generation. The game simulator test also shows that thanks to an 80% improvement in results, you can count on the S24 FE with more confidence in running games.

In playing a heavy game like Genshin Impact, you can have a better evaluation of the performance of the Samsung chip in heavy and more realistic scenarios. In the situation where we set the game’s graphic settings to the highest setting, the game ran for a short time with an average of 55 frames per second; But after a few minutes, as the device warmed up to about 43 degrees Celsius, the performance dropped to 40 frames per second. Sudden frame drops were another problem we experienced in Genshin Impact.
Zomit has used GameBench software to obtain game frame rates.
GPU performance stability testing can give a better view of how the chip handles performance and temperature during heavy and long usage. The Galaxy S24 FE starts the test with a nearly 1,000-point gap over its S24 sibling but ends the test with an equal score. Such conditions show that the performance drop of the 2400e chip in heavy use is less than that of the Exynos 2400, which somehow indicates better performance management.
In terms of temperature control, the situation is not very favorable for the Samsung chip, and considering that we do not have a very good memory of the temperature condition of the Exynos chips, we look at this category with more sensitivity. During the stress test, the temperature of the phone’s body rose up to 46 degrees Celsius, which cannot be described by the words “progress” or “improvement”.

The Galaxy S24 FE battery has increased by 200 mAh compared to last year’s model, and considering that this year the screen size has also increased, the result obtained in the battery charging test looks promising. Galaxy S24 FE can charge for about 13 hours in daily use; Which means 4 more hours of charging than the previous generation.
|
Galaxy S24 FE battery life versus the competition |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Product/benchmark |
Display |
battery |
Play video |
Everyday use |
|
Dimensions, resolution, and refresh rate |
milliampere hour |
minute: hour |
minute: hour |
|
|
Galaxy S24 FE |
6.7 inches, 120 Hz 2412 x 1080 pixels |
4700 |
— |
13:04 |
|
Galaxy S23 FE |
6.4 inches, 120 Hz 2340 x 1080 pixel |
4500 |
— |
9:11 |
|
Pixel 8a |
6.1 inches, 120 Hz 2400 x 1080 pixels |
4492 |
20:00 |
12:00 |
|
Xiaomi 13T Pro |
6.67 inches, 120 Hz 2712 x 1220 pixels |
5000 |
16:39 |
10:49 |
|
Notingphone 2 |
6.7 inches, 120 Hz 2412 x 1080 pixels |
4700 |
25:50 |
14:58 |
|
Galaxy S24 |
6.2 inches, 120 Hz 2340 x 1080 pixels |
4000 |
27:55 |
12:51 |
This year, Galaxy S24 FE will enter the market with only 8 GB of RAM, which is not a good capacity for a pseudo-flagship Android device due to the artificial intelligence fever. In addition to models with storage space of 128 and 256 GB, its 512 GB version is also available to users. The 128GB model uses UFS 3.1 storage.
|
Galaxy S24 FE storage speed compared to competitors |
||
|---|---|---|
|
phone model |
Sequential reading rate |
Sequential write rate |
|
Galaxy S24 FE |
2426 MB UK |
1514 MB UK |
|
Galaxy S24 Ultra |
2473 megabytes |
1471 megabytes |
We had the 256GB model for review. According to the results of the benchmarks, it seems that the storage space in the 256 and 512 GB models is of the UFS 4.0 type, which provides high speed in reading and writing data.
Galaxy S24 FE software: pseudo-flagship full of artificial intelligence
In addition to the flagship chip, the Galaxy S24 FE inherits many software features from the Galaxy S24 family. Since we’ve been hearing Samsung’s AI a lot since the S24 series was announced, we expected to see at least some of Samsung’s native AI capabilities in this year’s Fan Edition. Fortunately, in the software department, the Koreans have been especially kind to their flagship this year.

Galaxy S24 FE offers a complete package of Samsung’s artificial intelligence features in its software. Functions such as Sketch To Image, live translation of calls or Live Translate, photo editing with artificial intelligence, artificial intelligence assistant functions such as Chat Assist and Note Assist, and of course, the attractive and extremely practical Circle To Search function are also present in S24 FE.
Thanks to the powerful chip, the Galaxy S24 FE can process some language models of artificial intelligence without the need for an Internet connection and also access the offline version of Google’s artificial intelligence, Gemina Nano. Since we have already talked about Samsung’s AI capabilities in detail in our Galaxy S24 Ultra review article, we suggest you check out this article.

The Galaxy S24 FE runs Android 14 out of the box, and even if we leave out the AI capabilities, we’ll find some interesting features at its heart. For example, the S24 FE now uses the Super HDR feature; In the sense that the brightness of the display is adjusted based on the bright and dark points of the photo independently of the brightness of the device itself, and like HDR videos, you can watch the photos more vividly and brighter than before. In addition to the promise of 7 years of updating the operating system, the S24 FE has another feature in common with this year’s Samsung flagships, which can encourage any user to buy it.
Galaxy S24 FE camera: more or less better and sometimes worse
For the S24 FE camera, the Koreans have not only adopted their usual procedure of using a triple combination of wide, ultra-wide, and telephoto, but they have not touched the sensors and lenses except for the telephoto camera. As before, the same 50-megapixel sensor used in the previous generation as well as the S22 to S24 phones, and the 12-megapixel sensor of the S23 FE ultrawide camera are present in this phone.

The telephoto camera uses an 8-megapixel sensor made by OmniVision instead of SK Hynix, which is not particularly different in terms of sensor dimensions and pixels, and offers three times magnification; Therefore, except for the role of the image signal processor in processing photos, no other factor can be considered to be involved in the difference in the output of the images.
|
camera |
Sensor |
Lens |
Color filter |
capabilities |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Wide camera (main) |
50 megapixels Dimensions 1/1.57 inches 1.0 µm pixels Dual Pixel phase detection autofocus |
23 mm Aperture f/1.8 Optical stabilizer |
Tetrapixel |
4K@30/60/120fps video recording 8K@30fps 1080p@30/60/120/240fps HDR10+ |
|
Ultrawide camera |
12 megapixels Dimensions 1/3 inch 1.12 µm pixels |
13 mm Aperture f/2.2 No anti-vibration |
RGB Bayer |
|
|
Telephoto camera |
8 megapixels Dimensions 1/4.4 inches 1.0 µm pixels Phase detection autofocus |
76 mm (3x magnification) Aperture f/2.4 Optical stabilizer |
RGB Bayer |
|
|
selfie camera |
10 megapixels Dimensions 1/3 inch 1.22 µm pixels |
25 mm Aperture f/2.4 Image-gyroscopic electronic stabilizer |
RGB Bayer |
filming 4K@30/60fps 1080p@30/60fps |
Samsung says that the S24 FE uses the ProVisual Engine to improve the quality of photos and remove noise and blurring caused by vibration, especially in the dark, and also prevents the loss of image quality in digital zooms. Also, thanks to the more powerful chip, it is now possible to record 8K videos at 30 fps and even 4K slow-motion video at 120 fps.
Galaxy S24 FE photo gallery in daylight








In general, the photos of S24 FE cameras are not much different from their previous generation, however, in some scenarios, this phone performs better, and in some other situations, the opposite of this happens.
Read more: Samsung Galaxy Z Flip 6 review
Galaxy S24 FE camera comparison with S23 FE
In this photo taken with the main camera, the Galaxy S23 FE is better in terms of dynamic range, and the S24 FE failed to establish a better balance between the shadows and highlights, and as a result, the details of the bright spots were burned; On the other hand, the yellowness of S24 FE photos compared to its previous generation is clearly visible.

Wide picture S23 FE

Wide picture S24 FE

S23 FE wide photo crop

S24 FE wide photo crop
In the examples below, the S24 FE ultrawide camera has better color and surface and has more contrast. It also appears better than the S23 FE in terms of detail and dynamic range. If you pay attention to the corners of the image, the distortion caused by the wide viewing angle of the camera is less.

S23 FE ultrawide photo

S24 FE ultrawide photo

Ultrawide photo crop S23 FE

S24 FE ultrawide photo cropping
The telephoto cameras of both phones are very close in performance; However, in some conditions, the Galaxy S24 can record more colorful, glossy, and contrasty photos; However, it still shows weakness in terms of dynamic range compared to the Galaxy S23 FE and is unable to extract details from bright spots.

S23 FE telephoto photo

S24 FE telephoto photo

S23 FE telephoto crop

S24 FE telephoto crop
To compare the details, I took pictures of both phones in 50-megapixel mode, and as you can see, the S24 FE was able to extract more details from the image; But this work comes at the cost of increasing the noise and over-sharpening of the images and makes it out of the natural state.

50 megapixel S23 FE photo

50 megapixel S24 FE photo

S23 FE 50-megapixel photo crop

S24 FE 50-megapixel photo crop
In the portrait images, we can also see that although the S24 FE photo may look more desirable, the Galaxy S23 FE has clearly depicted the shadows and highlights better and has not manipulated the light reflection in order to capture the skin tone closer to reality and, as a result, a more natural photo. .

Portrait photo S23 FE

Portrait photo S24 FE
In the dark, since the Galaxy S24 FE can capture more stable photos, instead of increasing the sensitivity, it slows down the shutter speed in order to capture less noisy photos. For this reason, details in shadows and darker areas may not be as discernible as on the S23 FE; But instead, less processing is applied to the photo, and therefore a more realistic photo can be seen.

Wide picture S23 FE

S23 FE wide photo crop

S23 FE telephoto photo

Wide picture S24 FE

S24 FE wide photo crop

S24 FE telephoto photo
In terms of details, the S24 FE excels in all cameras; If you pay attention to the ultrawide photo, the texture of the subject is destroyed due to software processing in Samsung’s veteran fan edition, while the details are clearly visible in the new generation.
Photo gallery at night








The selfie camera of the S24 FE is the same 10 megapixels as before and has not made any difference; However, surprisingly, the previous generation captures more vivid and high-contrast photos; Of course, in terms of details, there is no particular difference between them.


A product still involved with constant challenges
The one-year absence of the Exynos gave a second chance to the Korean fan edition to experience a significant upgrade in terms of hardware; So, upgrading from S23 FE to this phone can be seen as more logical than upgrading from S21 FE to S23 FE. Longer battery life and seven-year software support, along with artificial intelligence capabilities, are two other important factors that bring the previous generations of the FE series to their knees against this phone.
If we refer to the question at the beginning of the article, we can see that the problem of performance loss and heat that have always plagued the FE series has not been solved this year, and even the weakened version of the Exynos 2400 could not help it. It seems that this issue will continue to be the killer of Korean flagships until Samsung gives up Exynos.
Technology
What is the Metaverse and when are we going to live in it?
Published
4 days agoon
02/11/2024

What is the Metaverse and when are we going to live in it?
Do you remember the game Heavy Rain? The same unique game Quantic Dream, released in 2010 for PlayStation 3, depicts the mysterious story of the serial murder case known as Origami, in which the killer used rainwater to drown his victims. One of the four main characters in this game was an FBI agent named Norman Jayden who was sent to help the local police in the investigation of this case.
If you remember, Norman had a special pair of smoked glasses that did much more than just block the sun’s ultraviolet rays. The glasses, which were called ARI (an acronym for Added Reality Interface), helped Norman amazingly in searching the crime scene and analyzing the evidence.

When Norman put on these glasses, he could change the appearance of his work environment and instead of staring at dull and boring walls, he could imagine himself in the middle of the forest or even the planet Mars. The world that Norman saw behind the glass of his augmented reality glasses was Metaverse; A kind of alternative digital reality where people work, play, study, shop, and socialize and no longer need to connect to the Internet; Because they are always “online” in this world.
Call it whatever you want; Metaverse, Mirror World, cloud virtual reality, magicverse, or space internet. But one thing is certain: It is coming and it is going to make a huge change in human lifestyle.
-
Metaverse introduction video
-
What is the Metaverse?
-
The three main concepts of the Metaverse
-
Advantages of living in the Metaverse
-
The risks of Metaverse realization
-
Metaverse and the world of games
-
Metaverse and the world of movies and series
-
Metaverse and blockchain
-
What companies support Metaverse?
-
Meta (formerly Facebook)
-
Microsoft
-
Google
-
Nvidia
-
Epic Games
-
Animoka Brands
-
The future of Metaverse; How far are we from realizing the real Metaverse?
What is the Metaverse?

Matthew Ball, an investor and former head of strategy at Amazon Studios, has described the Metaverse with seven characteristics: The Metaverse is always active and “on”; It is experienced live and in real-time; It can host any size audience; It has a completely dynamic and unique economy; spread across digital and physical platforms and worlds; It is possible to transfer digital assets across these platforms; Its experiences and content are created by users and large companies.
In other words, it is a very wide network of always-on virtual environments where people can interact with each other and digital objects around them in the form of avatars or with the help of augmented reality glasses; It means a combination of immersive virtual reality, multiplayer online role-playing game and web surfing.
Metaverse is the successor of today’s Internet
Metaverse is a compound word consisting of meta meaning “beyond” and universe meaning “world” and it can be translated as “beyond the universe”. The term was first used in the science fiction book “Snow Crash” by Neal Stephenson in 1992.
This American author used the term Metaverse to describe a kind of virtual world where the protagonist socializes with others in his avatar, makes purchases, and even defeats his real-world enemies. Of course, the concept of a world similar to the Metaverse had become famous before this book, in 1984 with the cyberpunk novel Neuromancer written by William Gibson.
When we turn on the lights or open the refrigerator, we know that it is electricity that makes them work; But we usually don’t think about how it works. Likewise, artificial intelligence, sensors, and communication between the robot and the device will be the “electric current” that powers the Metaverse.
In the distant future, or maybe closer than we imagine, our physical world will become an infinite amount of data that can be processed by a computer, clicked on or walked through and searched like Google search. In this world, there will be new interfaces and ways to move and create content, and we will create new words and even architecture to host our digital version and the digital world around us.
This new convergence between the digital world and the physical world is based on 5G and 6G internet, quantum computing, and graphene processors, and our view of this world will be through the lenses of our virtual reality glasses. If you still find it difficult to imagine the Metaverse, the following conceptual video from Adobe company depicts a very exciting vision of the future of human life in this world:
Described by many as the successor to today’s Internet, the Metaverse is not a single destination that everyone will one day enter, but a complex network consisting of millions of destinations, hundreds of profiles, and dozens of browsers. According to Pim de Wit, founder and CEO of video game-sharing platform Medal:
The Internet is a vast collection of protocols, technologies, cables, and languages, as well as devices for accessing it and communication content and experiences. Metaverse will be the same way.
The three main concepts of the Metaverse

When we talk about the Metaverse, it is important to get familiar with its three main concepts: presence, interoperability, and standardization. ” Presence ” is the feeling of being in the virtual space in a real and concrete way and with other people. The results of several decades of research have shown that the quality of online interactions improves by creating a sense of real presence in this space. This sense of presence is also created through virtual reality technologies such as screens that are placed on the head.
The second important concept that differentiates the Metaverse from our current experience of the Internet is ” interactivity “. Interactivity means that we in the Metaverse can travel from one destination to another while carrying all of our digital assets, including avatars and collected virtual items. For example, you can use the shell of the gun that you bought in the game Counter-Strike, in the game Fortnite, or give it to your friends through Facebook. For example, you can drive the car you designed in Rocket League or even the Porsche website in Roblox.
The third concept is ” standardization “, which enables interoperability between platforms and services across the Metaverse. The standards considered for it allow its widespread use around the world. International organizations such as the Open Metaverse Interoperability Group define these standards.
Advantages of living in the Metaverse

Metaverse is a situation that is supposed to replace the current Internet and provide users with all its content but with much fewer access restrictions. Current online platforms allow users to move somewhat freely in the same area specific to each service, But they limit cross-platform interoperability.
For example, you are free to build anything you like in Minecraft; But you can’t transfer what you made in Minecraft to Fortnite. Meanwhile, Metaverse allows users to produce their desired content on any platform and distribute it freely throughout this digital world.
Unlike the current Internet, its users will experience the changes made by other users in real-time. If a user makes any changes in Metaverse, that change is permanent and immediately visible to everyone.
Persistence and interactivity allow users to maintain their identity and online experiences across the Metaverse, unlike the Internet. This means that in Metaverse, users no longer need to have a separate profile on Twitter, a character in Fortnite, and a Reddit account, but can be their true selves on all these platforms. This continuity of identity will be a fundamental factor in the formation of how to buy and consume content by Metaverse users.
In Metaverse, you can be present on all platforms with an avatar
Thanks to the Metaverse, we no longer need to be in the real world to work in the physical environment; Rather, our workplace will be in the same Metaverse. Virtual reality glasses and the Metaverse environment are made together, and in the near future, these glasses will have many applications in the workplace. For example, the glasses can be used to authenticate, and remember the names of colleagues, departments, and projects you’ve worked on before, and generally act as a remote window into offices, manufacturing facilities, and packaging plants around the world.
Virtual reality glasses can replace smartphones and laptops. Digital images, tactile feedback, biometric sensors, and audio playback and recording are all features of life in the Metaverse, and machine vision will also be an important part of this world.
AR glasses can also help people on their first day at work by showing the workflow in the most accurate detail possible. In a world where “remote” is fast becoming the norm, AR glasses can turn our home into a workplace, our workplace into a playground, and our lives into creative and colorful expressions of who we are.
Accessing the virtual world through these glasses also allows companies to reimagine their products or even their brand in innovative ways; Accelerate business processes and test their virtual version before manufacturing and distributing the product. Researchers and medical professionals can also use accurate virtual samples with the help of artificial intelligence to try new treatment methods without endangering the health of the patient or even animals.
The risks of Metaverse realization

Metaverse is not inherently dystopian. Perhaps the reason why many people think the nature of the Metaverse is subversive is because the word comes from Neal Stephenson’s 1992 dystopian sci-fi novel Snow Crash. Stories with a similar plot were written before Snowfall, including William Gibson’s Neuromancer (1984) and The Trouble with Bubbles (1953) by Philip K. Dick conveying to the reader the feeling that future technology is going to make the current situation worse.
However, the important thing is that without drama and unfortunate events, an attractive story cannot be formed, and that is why popular stories do not take place in an ideal and flawless world. However, since the 1970s, there have been stories in defense of the Metaverse that have focused on cooperation and creativity rather than dealing with issues such as profiteering and mind control.
The story of the Metaverse becomes scary when we refer to it as the “enterprise internet”. When the Internet was born, government labs and universities were the only institutions with access to the expertise, resources, and ambition to build this network, and few outside of this circle could imagine its commercial potential. But the story of Metaverse is completely different because its development is done by private businesses.
In 2016, long before the tech giants wanted to seriously consider the Metaverse, Epic Games CEO Sweeney told VentureBeat, “If a centralized corporation takes control of the Metaverse, it will become more powerful than any government and become a god on Earth. “
You may think this claim is exaggerated; But according to Citi and KPMG, Metaverse has the potential to make $13 trillion in profits every year by 2030. Financial services company Morgan Stanley also estimated this amount in the US and China at about 8 trillion dollars, and Goldman Sachs global projection company also estimated something between 2.5 and 12.5 trillion dollars. This is while McKinsey’s prediction of the worldwide revenue generation of Metaverse is 5 trillion dollars.
Jensen Huang, the founder and CEO of Nvidia, which is one of the ten largest public companies in the world, believes that the GDP of the Metaverse will eventually exceed the “physical world”. With these points in mind, the fear of the Metaverse is justified. The idea behind the Metaverse is that an increasing portion of our lives, work, recreation, time, wealth, happiness, and relationships will be spent in virtual worlds instead of solely through digital devices.
The Metaverse is supposed to connect our digital and physical economy as a parallel universe. As a result, the companies that control these parallel universes and their virtual atoms will become more powerful than those that run today’s digital economy.
Metaverse may exacerbate the problems of today’s digital age; including data security, misleading information, the power of platforms, and the mental health of users. Therefore, the philosophy, culture, and priorities of the companies that are going to take power in the Metaverse era will determine whether the future of the Internet is going to be better or worse than the current state.
On the other hand, life in the real world will never catch up with the virtual world. Being able to go out and enjoy nature and no multi-billion dollar company can stop that means a lot. The idea that in the Metaverse, our ability to live will be defined and limited by the giants of technology is truly terrifying.
Metaverse and the world of games
For many, video games are the forerunners of the Metaverse. Games such as Roblox, Fortnite, and Animal Crossing, in which gamers can create their own world, include some features of Metaverse. When Epic started developing Fortnite in 2017, they did not intend to create Metaverse. But what was introduced at the time as a castle defense game where gamers fought against zombies became an international phenomenon just a year later.
With millions of gamers flocking to the Battle Royale portion of Fortnite, which is something of a “Hunger Games” movie, the company quickly began adding social features to the game, such as voice chat and dance parties. According to Epic, the company’s revenue from Fortnite totaled more than $9 billion in 2018 and 2019, and that huge fortune came from the money gamers spent on purely virtual items like superhero costumes or banana suits for their characters. has achieved
For many, video games are the forerunners of the Metaverse
Now, Epic is not only introducing Fortnite as an interactive experience but as a Metaverse. Concerts of famous singers held on the platform of Fortnite attract millions of gamers. The Roblox game, where independent developers design popular children’s games, is perhaps the closest and broadest vision of the future Metaverse.
According to the company’s earnings report, in the first quarter of 2021, gamers spent nearly 10 billion hours playing on this platform, and more than 42 million users logged in daily. Gamers also spent $652 million on the platform’s virtual currency, Robux, which can be used to buy hats, weapons, balloons, and other digital items for their characters. Roblox founder and CEO David Bazowski says the company even holds business meetings on the platform.
Just as mail, telegram, phone, message and video are tools for teamwork, we believe that Roblox and Metaverse will join them as essential tools for business communication. Eventually, one day we might even be able to shop on Roblox.
Millions of games are created on Roblox every year, and a large part of the revenue from the sale of digital items and upgrades goes to the developers. There have been cases where teenage game makers have become millionaires in this way. However, it should be kept in mind that platforms like Fortnite, Minecraft, and Roblox are not Metaverse in themselves, but only destinations within the Metaverse. In the future where the Metaverse has arrived, there will be millions of such destinations, just like there are websites on the Internet today. Tim Sweeney, CEO of Epic, states:
Metaverse is not an app story with a list of different titles to download games and applications. In the Metaverse, you and your friends, along with your appearance and digital assets, can move from place to place and have completely different experiences, while still maintaining your connections across social networks.
He also said that it is possible that one day there will be a “tunnel” between platforms such as Roblox and Fortnite, through which gamers will be able to transfer characters and game items between the two games.
Metaverse and the world of movies and series

Perhaps there is a long time left until the realization of the Metaverse, and perhaps none of us will live to see such a day; But it is possible to experience aspects of what is supposed to be a part of the reality of human life in the future, right now in games like Fortnite or watching a conceptual image of the Metaverse in movies and series.
Among the films that have depicted an aspect of the Metaverse, Steven Spielberg’s Ready Player One is undoubtedly the most famous. In fact, many people suggest this movie to explain the Metaverse; Although in this movie we see that the entire control of this virtual world is in the hands of only one company, while in the real Metaverse, we will witness a completely decentralized world and no company or institution can rule in this world.
With this in mind, watching this movie is a good starting point for understanding the Metaverse and user experiences in virtual reality. Other films and series in which an aspect of the Metaverse is depicted include Minority Report (2002), Avatar (2009), The Matrix (1992), Iron Man (2008), Uploaded series (2020), Black Mirror series, Altered Carbon and animation. Ralph is the wrecker. The new series The Peripheral also deals with virtual reality headsets and simulated worlds.
Metaverse and blockchain

Conceptually, the Metaverse is a view of a decentralized world that is controlled and shaped by its users and citizens, not by governmental or international institutions. These citizens also need a platform and currency to buy and sell their digital products, which will be based on cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology.
Currently, companies like Decentraland and platforms like The Sandbox have created virtual worlds where gamers can use cryptocurrencies to create structures like amusement parks and even earn money from them.
Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) also play a central role in the Metaverse, giving people full ownership of their characters, collected in-game items, and even their virtual land. For example, an NFT of virtual land on Decentraland recently sold for nearly $1 million, one of the largest sales of this token model to date.
In Metaverse, the security of transactions and the identity of users is the responsibility of blockchain
There is no mention of governments and regulatory bodies in Metaverse, and it is the role of blockchain technology to ensure the security of transactions and the identity of users. In addition, NFT tokens allow Metaverse users to own their own custom items and move them from one platform to another, just like in the real world. For example, in Metaverse you can sell the plot of land you bought in Decentraland and use the money to buy weapons in Fortnite.
Meanwhile, cryptocurrencies will be considered as the only legal money used in the Metaverse and will draw the road map for the formation of the economic structure of the Metaverse. Of course, this Metaverse economy is already taking shape; Some companies have already auctioned their branded NFTs for hundreds of thousands of dollars.
Artur Madrid, CEO and founder of The Sandbox, points to the willingness of people to pay huge sums for digital assets in games, saying that gamers have already spent millions of dollars on these items; Items that do not exist externally and their value is defined only in the virtual world. He adds:
I think converting these assets into NFTs and creating an NFT-based economy will add a new layer to the current digital economy.
However, in the past few months and with the unprecedented fall in the value of cryptocurrencies, confidence in crypto has been somewhat lost; So many analysts doubt that cryptocurrencies have a place in the future of the Internet.
What companies support Metaverse?

Metaverse has been in the news ever since Facebook changed its name to Meta in 2021, and suddenly every company big and small wanted a stake in the future of the Internet. These companies, from Microsoft to Nvidia and even PepsiCo, have spent a huge amount of time and money to build products and platforms based on virtual and augmented reality; Because they believe that Internet users will spend a lot of time in the virtual world in the near future.
Along with companies such as Nike, Walmart, PepsiCo, and Adidas, big and well-known companies are making big investments in Metaverse projects, which you will learn about later.
Meta (formerly Facebook)
When Facebook cleverly changed its name to “Meta”, it became the most famous Metaverse company in the world, and the attention of the media and other technology companies was also drawn to the concept of Metaverse.
Just a little before changing the name to Meta, Facebook revealed its plans to invest 50 million dollars to build Metaverse; However, these plans have been going on for a long time. For example, Meta invested $2 billion in Oculus VR headset development unit in 2014, and four years later, the company’s CEO claimed that Metaverse would be owned by Meta for the next decade.
Mark Zuckerberg, the founder and CEO of the company, has made many statements about the company’s approach to the development of Metaverse and has predicted that in the short term, it will lose money on some projects.
However, Zuckerberg stated in June 2022 that Meta wants to have about “one billion people” active in the Metaverse. Also this year, Meta opened its first virtual reality headset store, and in September 2022, it launched the professional and powerful Meta Quest Pro virtual reality headset with a price of $1,499 and a fast Qualcomm Snapdragon XR+ processor.
-
Vortex, Microsoft’s Metaverse, will be based on mixed reality
With this product, Meta says, when a user smiles in the real world, their avatar will do the same. With the help of Meta VR headsets, users can interact with each other’s avatars in a network of virtual spaces called Horizon Worlds.
Microsoft
Microsoft differs from other Metaverse companies in that its plans to develop Metaverse are focused on creating work environments rather than games and entertainment. The people of Mountain View plan to link the digital world to the physical world by developing the Mesh platform in the Microsoft Teams program. The platform is based on mixed reality and facilitates team collaboration through mixed-reality glasses and virtual reality headsets.

By acquiring the virtual reality platform AltspaceVR in 2017 with the aim of using its intellectual property for Mesh, the Redmonds showed that their Metaverse plans have been in development for some time. On the other hand, the $68.7 billion acquisition of Activision Blizzard in January 2022 is also considered by some to develop the game infrastructure for Microsoft’s other Metaverse projects.
Google does not have a good track record in virtual reality projects. The name of this company is tied to the scandalous failure of Google Glass Glass in 2014; A project that became one of Google’s biggest projects due to many technical problems, privacy concerns, incorrect marketing, and lack of transparency about why it exists.
However, this failure does not mean that Google will not go for Metaverse projects or make other virtual reality glasses. Google announced this year that it has set up a private company worth 39.5 billion dollars to invest in Metaverse projects. Currently, the details of these projects are not available; But it will surely be as noisy as LaMDA artificial intelligence, which one of the Google employees claimed to have become self-aware.
Nvidia
Rio Labardian, vice president of Omniverse and simulation technology at Nvidia, said at the time that the company had decided from the beginning to be something beyond a chip company, pointing out that not long ago, many could not imagine Nvidia as a Metaverse company.
However, Nvidia recently unveiled its first infrastructure-as-a-service, NVIDIA Omniverse Cloud, which is set to offer developers and artists a set of cloud services to build and run Metaverse applications. Currently, companies such as Siemens, RIMAC, Volkswagen Group, PepsiCo, and Amazon are using Nvidia’s Omniverse technology.
Epic Games
Epic Games, one of the giants of the video game industry, is known by everyone for the Fortnite game; One of the most popular games that crossed one million players within 24 hours of its release. In April of this year, the company received $2 billion in capital from Sony and Kirkby, the company that owns LEGO, valuing the company at $31.5 billion.
Epic Games CEO Tim Sweeney said at the time that his company plans to compete with the biggest companies in the Metaverse: “This investment will help us accelerate the construction of the Metaverse and create spaces for gamers to have fun, create creative experiences through brands and communities for developers. “Content will help.”
Epic Games also has an infrastructure for Metaverse development; One is the extremely popular game engine Unreal Engine and the other is MetaHumans, a digital twin creation software that can be used to create avatars in Metaverse.
Animoka Brands
Animoca Brands is not as well known as the other companies on this list, But infinity is important in the discussion of the Metaverse. This company owns The Sandbox game, which is inspired by Minecraft and is based on blockchain. In the sandbox game, players can buy maps of virtual lands and get their ownership.
Animoka Brands has several blockchain game projects and supports several Metaverse companies, including Sky Mavis, the creators of Axie Infinity, and Yuga Labs’ online multiplayer game called Otherside. Animoka Brands managed to raise $358 million in January 2021, $75 million in July 2022, and $110 million in September this year for Metaverse projects and products.
The future of Metaverse; How far are we from realizing the real Metaverse?

It’s been exactly one year since the term “Metaverse” started floating around after the Verge spoke with Mark Zuckerberg about his company’s new plans. During this time, there has been a lot of discussion about what is often referred to as the “future of the Internet”, but to be honest, we still don’t know exactly what the Metaverse is and when and how it is going to shape the future of the Internet.
The Metaverse is not yet realized; Even if some Big Tech executives pretend that it is, or at least there is nothing left. On the other hand, changes do not happen all at once. We are in the mobile era today, But the first call that was made from the mobile network dates back to 1973; Similarly, the first wireless data network was in 1991; But it took 16 years to release the first iPhone.
According to some people, we are already living in a kind of Metaverse; Because a large part of our life has become completely digital. But it is probably a long time before we see in the real world, a Metaverse of the size of the movie “Ready Player #1”; Because there are still some obstacles on the way to the realization of the Metaverse. The biggest obstacle is hardware limitations.
Currently, the global Internet and computing capabilities around the world are not yet capable of supporting a sustainable digital world that can host millions of users simultaneously and instantaneously. Even if this level of network and computing power is available, the energy consumption of such an action will cause many problems for both power grids and the environment.
Read more: Metaverse is back
Metaverse may be realized in the distant future, But it is inevitable
In cases where the necessary technology exists to create the Metaverse, extensive cultural changes are necessary to encourage more people to use it.
According to a 2020 report by Thrive Analytics and ARTillery Intelligence, while the highest quality virtual reality and augmented reality technology is available to the American public, less than 20% of them have switched to using VR headsets.
Another big problem is the realization of interoperability, which is one of the three main pillars of the Metaverse. Currently, even the pioneers of it such as Fortnite do not allow gamers to transfer the content created on this platform to another platform. In order for interactivity to be created in the literal sense, it is necessary for the companies that own these platforms to give up some of their control over the content and user experience of their players.

Despite these problems, the Metaverse is most likely inevitable; Although future users may just refer to it as “the Internet”. The point here is that it is not supposed to push a button to transition from the internet age to the Metaverse; Rather, the it gradually emerges and embraces us. Just as no one noticed the transition from the first generation to the second generation Internet, the development of the Metaverse will occur naturally with the wider presence of people in the virtual world and linking their identity to the virtual life as much as possible.
On the other hand, technology giants are also trying to prepare their user community for life in the Metaverse earlier than their competitors. Among them, Facebook’s stance on Metaverse has created a lot of buzz. Mark Zuckerberg, the founder of Facebook, recently said that he plans to build the Metaverse with the help of this social network. He said that he expects people to see Facebook in the future not as a social network but as a Metaverse company.
You can visit the Nobitex exchange to buy Mana, the digital currency of Decentraland.
In his view, Metaverse is “a virtual environment where you can be with different people in digital spaces. It’s an embodied internet that you’re inside, not just looking in from the outside. We believe it is going to replace the mobile internet.
There will be no noticeable change between before and after Metaverse
Satya Nadella, the CEO of Microsoft, has also talked about his plans to create a “Metaverse company”. At this year’s Microsoft Inspire keynote, he described Metaverse as “a new layer of infrastructure stacks” where “the digital and physical worlds come together.”
Matthew Ball, former head of strategy at Amazon Studios, also describes Metaverse not as a virtual world, but as “the successor to the mobile Internet”; It means a framework for a highly connected and online life. From his point of view, there will be no sudden and obvious change between before and after the Metaverse. Instead, the Metaverse emerges incrementally by integrating different products, services, and capabilities.
Although games like Roblox and Fortnite are often mentioned as the pioneers of Metaverse; But the most important pioneer of the it is the Internet itself. If we think of the internet as a video tour of an apartment with a glimpse of every room, the Metaverse would be the apartment itself. It is true that we have not settled in this apartment yet, But we signed the lease a long time ago.
What do you think about Metaverse? Is the arrival of such a day inevitable and will the Metaverse help improve the quality of human life?
Frequently asked questions
-
What is the Metaverse?
-
-
How to enter Metaverse?
-
-
How to invest in Metaverse?
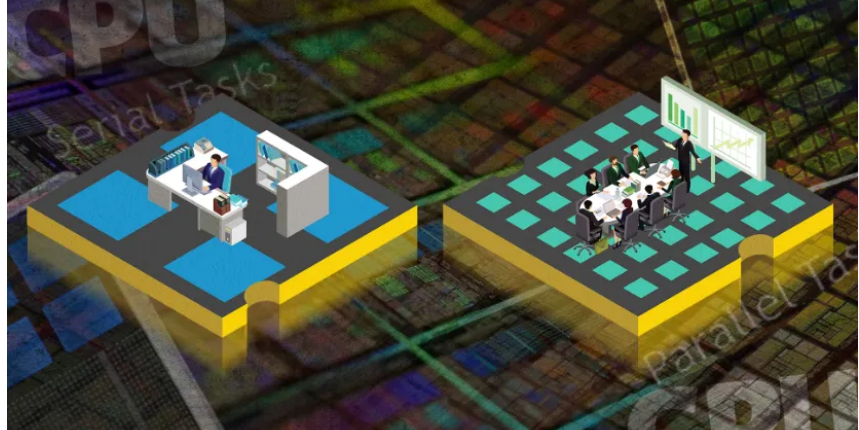


What is the difference between CPU and GPU?
CPU is a unit for performing the main processes in the computer, which we refer to in this article as the processor . GPU is also a unit for graphics processing with the ability to perform advanced mathematical calculations and machine learning. These units have a similar task, which is information processing .
In fact, the main difference between CPU and GPU is the type of information they process; For this reason, these two cannot be substituted for each other; But using the processor and GPU at the same time provides an ideal combination for the user and brings the best performance to Armaghan.
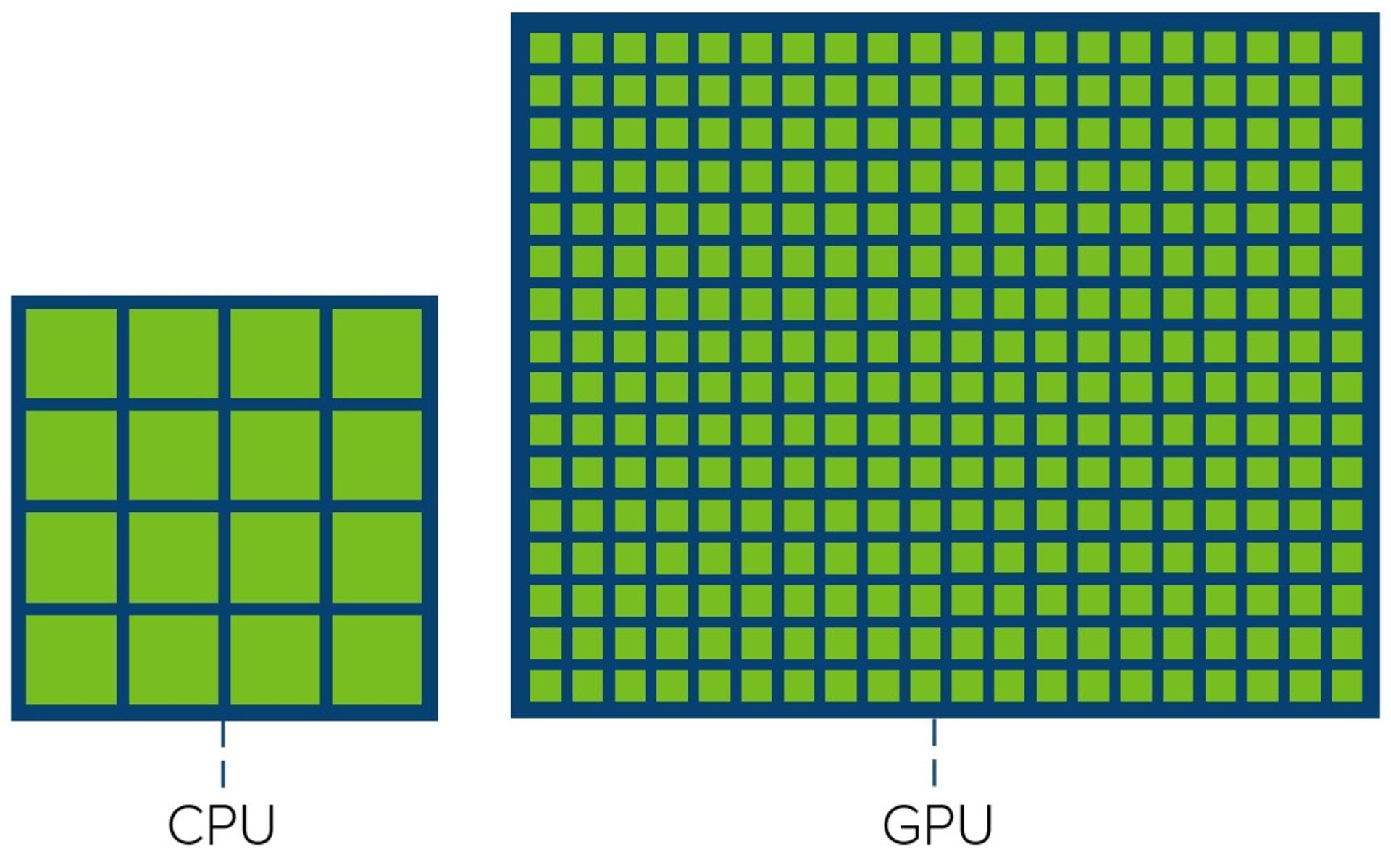
The graphic processor is located in smart devices such as phones, tablets, or televisions, and in computers it is usually used in the form of a graphics card to take on an important part of the task of processing games, videos, content, and even artificial intelligence, and the CPU also runs computer functional programs such as Manages operating system processes. This unit is called the computer brain. A GPU cannot perform processes as continuously as a CPU and is designed for a completely different performance. On the other hand, the CPU requires more memory for processing than the GPU.
What you read in this article:
-
What you read in this article:
-
What is a central processing unit (CPU) or processor?
-
What is a graphics processing unit (GPU) or graphics processor?
-
Similarities and differences between CPU and GPU
-
What are the advantages and disadvantages of a processor or CPU?
-
What are the advantages and disadvantages of a graphics processor or GPU?
-
Does the game require a GPU?
Computers can be used without a graphics processing unit; Of course, in this situation, you should not expect impressive and powerful graphic performance from this system; But computers without a CPU cannot survive and manage input and output data and run a program. What makes the graphics processor known as an important unit in the computer is the ability to perform parallel processing of this unit, which enables very fast data processing thanks to the number of more powerful cores.
What is a central processing unit (CPU) or processor?
The central processing unit or processor is the brain of any computer that directs the main processes and calculations in a computer system.
Computers work by processing binary data (zeros and ones) and we need the logical function of the processor to translate this binary data into a language that can be understood by software, graphics, animations and other processes. These logical functions include basic arithmetic and logical functions (AND, OR, and NOT) and input and output operations. For example, when you close or run a program, the processor sends the correct instructions to retrieve data from the hard disk and executes executable code from RAM.
When playing games, the CPU processes the graphics information to display on the display, and when compiling the code, the CPU handles all the calculations and math related to that code. In general, the processor or CPU is the brain of the computer that receives, processes, and calculates information and transfers it to an appropriate path. Each processor consists of the following standard components:
- Core(s): The main architecture of the processor is directly related to its cores, where all calculations and logical processing take place. Cores follow what is called an “instruction cycle”. In this cycle, the instructions are fetched from the memory and decoded through the logic functions of the kernel. At the beginning of development, all processors were single-core, and with the expansion of multi-core processors, the processing power of these units also increased.
- Cache memory: Cache memory is a very fast memory that is located inside the processor or on a board close to it and allows the processor to quickly access the required data. The larger the cache memory capacity of the processor, the more calculations this unit can process per second. For this reason, today, in the configuration of each CPU, different layers of cache memory are placed: L1 (the fastest), L2 and L3 (the slowest). The processor stores information that needs the fastest access in the first layer of cache memory or L1. Level one cache memory (L1) is the fastest and smallest memory and closest to the processor and stores the most important data needed for processing. Data with the next priority of access is stored in L2 and L3. Level two cache memory (L2) or external cache memory has a lower speed and larger volume compared to L1, and L3 cache memory is memory shared by all cores in the processor and has a larger volume and lower speed compared to L1 and L2. The processor moves the data with the lowest priority to the RAM or hard disk and calls them from the main RAM (DDR) when necessary.
- Memory Management Unit: The Memory Management Unit (MMU) controls the transfer of data between the processor and RAM during the instruction cycle process.
- Processor frequency and control unit: each processor performs calculations and processes with a specific frequency. This frequency shows the number of electrical pulses produced in a certain time period (one second) and determines the main method of data processing and transfer and the speed of the processor. The higher the processor frequency, the faster it processes.
An ideal combination of all these components provides conditions for the central processing unit to perform parallel calculations at high speed. With this process, computers run several programs at the same time, display the desktop, provide the possibility of web browsing, etc. In general, it can be said that processors are programmed in such a way that they can switch between operations very quickly in addition to doing one task with the least delay and the greatest speed. Actually, the way of processing in CPUs is serial.
What is a graphics processing unit (GPU) or graphics processor?
GPUs have the same functionality as CPUs and consist of similar components (core, memory, and other components). The most important advantage of GPU over CPU can be considered the ability to simultaneously manage multiple tasks and parallel data processing thanks to its large number of cores. In fact, the most prominent performance that GPUs provide is one of the complex processing tasks that the CPU can hardly handle.
The GPU is a complement to the processor that makes the workload of this unit lighter
An issue that arises in graphics processing is the parallel computation of complex mathematics that are called for graphics rendering. For example, a video game with complex graphics may render hundreds or thousands of polygons on the screen in a certain interval, each of which has a separate movement, color, light, etc. Since processors are not built to handle such workloads, graphics processing units (GPUs) come into play.
GPU cores tend to perform more poorly than CPU cores, and GPUs themselves tend to be less successful at interacting with hardware APIs. As mentioned, GPUs are particularly effective in processing large amounts of data at the same time. Instead of switching between multiple tasks, this processing unit simply receives instructions in batches and processes them in large quantities, and finally displays the desired graphics.
Similarities and differences between CPU and GPU
By comparing the general architecture of processors and GPUs, we can find many similarities between these two units. These units use similar structures in the cache layers and both use a controller for memory and a main RAM. The image below shows the number of cores in a processor and the number of cores in a GPU:
-638bb88e1d67bb742b22ca2e?w=1920&q=80)
An overview of the architecture of modern processors indicates that in this unit, focusing on memory and cache layers, access to memory with low latency is considered the most important factor in processor design. Needless to say, the exact layout depends on the vendor and processor model. Compared to CPUs, GPUs have fewer cache memory layers and less capacity. These units use more transistors for calculations and retrieving data from memory is not very important in them.
The graphics processor has been developed with the approach of performing parallel calculations, and High Performance Computing is one of the effective and reliable uses of parallel processing to run advanced applications. Suppose it has a small number of powerful cores with serial processing capability to perform some kind of heavy calculations.
In such a situation, if we lose one of the cores, the performance of the other two cores will be overshadowed and the overall processing power will be greatly reduced. If we have many and not so powerful cores that can perform several processes at the same time, if one of them is lost, there will be no noticeable change in the processing process and the rest of the cores will continue to work.
-638bb88fa7331cd9fb2ce706?w=1920&q=80)
In addition, the bandwidth of GPUs is much higher than the bandwidth of CPUs and they do parallel processing with a lot of volume much better. As we said, the most important thing about GPUs is that they perform parallel processing well, and if the algorithm or calculations are serial and do not have parallelization capabilities, they do not run at all and slow down the system. CPU cores are more powerful than GPU cores and the bandwidth of this unit is much less than GPU bandwidth.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of a processor or CPU?
Although GPUs are increasingly becoming a tool for high-performance processing today, there are still many important reasons why these units cannot be used as a replacement for CPUs. Some of these reasons are:
- Flexibility in performing different processes: processors can perform other processes and calculations in addition to graphics processing. Serial processing capability allows processors to manage multiple tasks in different contexts; Therefore, a powerful processor can provide more speed than a GPU in normal use.
- Speed in certain processes: CPUs sometimes perform better than GPUs in some situations. For example, the CPU is much faster than the GPU in handling several different types of system operations.
- Accuracy in performing calculations: Processors perform calculations of average mathematical equations more accurately and can more easily control the depth and complexity of calculations. This feature is very important when launching special programs.
- Memory access: Since the cache memory of processors has a large capacity, these units can perform a larger set of linear instructions and, as a result, more complex computing systems and operations.
- Low cost and availability: CPUs are more readily available, more widely produced, and more cost-effective for general and enterprise use.
In addition to the advantages that CPUs offer compared to GPUs, they also have disadvantages:
- Inability to perform parallel processing: CPUs cannot perform parallel processing as well as GPUs, so using these units to process thousands or millions of the same operations will not be efficient.
- Slow evolution process: according to Moore’s law, the development of more powerful processors becomes slower day by day, and their improvement process will be slower every year compared to last year; Of course, the expansion of multi-core processors has somewhat reduced this concern.
- Incompatibility with some systems: Not every system or software is compatible with every processor. For example, applications developed for Intel x86 processors will not run on ARM processors. Of course, this problem is not so troublesome; Because nowadays, most manufacturers use standard sets to develop their software.
Read more: MSI Prestige 16 AI review; A laptop that does not run out of charge
What are the advantages and disadvantages of a graphics processor or GPU?
Today, GPUs have found a growing niche among users and organizations looking to use high-performance computing to solve unique problems. The two main advantages of GPUs compared to CPUs are:
- High throughput: The GPU consists of a large number of cores that can perform the same operation in parallel and process large amounts of data at a very high speed compared to CPUs.
- Massively parallel computing: As we said, CPUs do complex calculations better than GPUs; However, GPUs excel at performing large-scale calculations where many similar operations are repeated.
In addition to the two mentioned advantages, the structure of the GPU allows developers and engineers to use the technology of this unit to run some high-performance applications:
- Bitcoin Mining: The Bitcoin mining process requires a lot of computing power to solve complex cryptographic hashes. The abundant processing power and the relatively low energy requirement of graphics processors have made these units a suitable tool for performing the extraction process, which has recently gained many fans.
- Machine learning: Modern GPUs are used in machine learning. Machine learning is a form of data analysis that automates the creation of analytical models. Basically, machine learning uses data to learn and identify patterns and make decisions independent of human input, and due to the very intensive nature of this system and the need for parallel processing, graphics processors can be considered an essential part of this technology.
Does the game require a GPU?
Having a graphics processor can make a significant change in the user experience of gamers. This unit is used in the presentation of graphic and video content and can have an impressive performance when playing games. In addition, the graphics processor performs the processes at a high speed and thus reduces the workload of the processor.
This means that the overall performance of the computer increases and games run better and smoother. Nowadays, game developers try to make the graphics of their products evoke a real experience for gamers; So it can be said that for better and more natural renderings, the presence of a graphics processor is necessary.


Galaxy S24 FE Review


Everything you need to know about GPU


What is the Metaverse and when are we going to live in it?


What is the difference between CPU and GPU?


Maybe the Earth is not doomed by the death of the sun


Everything about Cybercube and Robo Van; Elon Musk’s robotic taxis


Len Sassaman; The creator of Bitcoin

How did accidental release cause the 1977 Russian flu?


The Secret of the Hummingbird’s Amazing Adaptation


What is OBS Studio and how to use it?
Popular
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoWho has checked our Whatsapp profile viewed my Whatsapp August 2023
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoSecond WhatsApp , how to install and download dual WhatsApp August 2023
-



 AI2 years ago
AI2 years agoUber replaces human drivers with robots
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoHow to use ChatGPT on Android and iOS
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoThe best Android tablets 2023, buying guide
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoThe best photography cameras 2023, buying guide and price
-


 Humans2 years ago
Humans2 years agoCell Rover analyzes the inside of cells without destroying them
-


 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoHow to prevent automatic download of applications on Samsung phones









