Technology
Len Sassaman; The creator of Bitcoin
Published
1 week agoon


cryptographerNoun: A person who is an expert on creating codes and cyphers. Someone who studies cryptology.
himselfPronoun: he himself.
Noun: A person who is an expert on creating codes and cyphers. Someone who studies cryptology.
Len Sassaman; The creator of Bitcoin
Many of us may be new to the name Len Sassaman, but those who have been active in the field of cryptography and privacy for years know him as one of the leading figures in the foundational technologies of crypto.
Now, the HBO documentary on the subject of identifying Satoshi Nakamoto has once again drawn the world’s attention to this master of cyber security: this documentary, directed by Cullen Hubak and produced by Adam McKay, with the aim of investigating the mystery of the founder of Bitcoin, examines the issues such as whether Satoshi was alone or worked with his own partners and the impact of his work on the global financial environment.
One of the factors that links Len Sasamen to the face behind the mask of the creator of Bitcoin is the coincidence of his self-inflicted death with the disappearance of Satoshi. Join us as we review Len Sassaman’s life, philosophy, and some of his most important projects, and see if there is enough evidence to support the claim that he is the creator of Bitcoin.

Len Sassaman was born on April 9, 1980, in Pottstown, Pennsylvania, USA. During his childhood and adolescence, he spent most of his time with computers, calculations, and coding, and from the same time he started reading articles and books related to the protection of personal information. His early concern was the challenge of tracking people in the world around him.
Len spent his high school years at Hill School, and some say he developed depression around this time. People around him say: “Len was a very strange child; Because he had a very high intelligence.”
Unfortunately, the aggressive approach of doctors in treating depression had a strong negative impact on Len’s mind and caused the roots of mistrust to be institutionalized in him, especially to authoritative people.
Len Sassaman struggled with depression since he was a teenager
Len joined the community of cryptographers in the 1990s; That is when the Internet was just expanding and discussions about privacy and information control were very hot. At 18, he got a job at the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), the organization responsible for developing the foundations of the modern Internet, working on the TCP/IP protocols.
Sasaman and the cypherpunk movement
Len Sassaman moved to the San Francisco Bay Area in 1989, and after learning the fundamentals of the cypherpunk movement, he realized that his ideas were completely aligned with the group. Early on, he also met famous programmer Bram Cohen (who later developed BitTorrent) and decided to spend more time with him.
The philosophy of cypherpunks specifically focused on the interactions between humans and technology, the social and political effects of new technologies, and issues such as privacy, identity, and individual freedom. Len, like other activists of this group, believed that with the advancement of technology, the boundaries between real and virtual life will be blurred and this will lead to serious challenges in the field of individual and collective identity.
Cypherpunks prioritize principles such as identity individual freedom and privacy
Cypherpunks were also known as fierce critics of the existing political and economic systems, who tried to expose the negative effects of “institutionalism” on human life and find a way to resist the regulatory powers. The most outstanding new solution in this field was the creation of new identities in the virtual world.
Sasaman soon became one of the most prominent voices of this movement. He is a frequent speaker at crypto meetups and international conferences, sharing his ideas on privacy and digital freedom.
In a way, it can be said that what we know today as the basic principles of digital security and privacy on the Internet has its roots in the articles and speeches of Sasaman and other activists who, from the early years of the web’s growth, expressed their concern about the consequences of unfettered user data and sought to find They were an efficient solution to the potential challenges ahead.
PGP and cryptographic campaigns
During his time in San Francisco, Sassaman dedicated his life to the defense of personal freedoms and privacy through technical and political actions. At the age of 21, his name appeared in the media headlines for the first time due to the organization of protests against government surveillance and the imprisonment of a hacker named Dimitri Skylarov.

At the age of 22, he co-founded a startup to develop public key cryptography with Bruce Prince, a well-known open-source activist, but this startup was dissolved during the bursting of the dot-com bubble. Len then joined Network Associates to continue his work on PGP encryption, which later played a fundamental role in Bitcoin technology.
Along with Philip Zimmerman, Sassaman played a key role in the development of PGP
Along with Philip Zimmerman, the creator of PGP (Pretty Good Privacy), Sassaman played a key role in the development of this encryption tool. This software allowed people to encrypt their information and emails to protect them from the prying eyes of governments and hackers.
Their idea for cryptography based on private and public keys was developed and took on another color with the creation of digital signatures: users were able to seal their messages with a digital signature with their private key, and thus, recipients could be assured of the authenticity and integrity of messages during transmission. They were assured.
PGP was the strongest email encryption tool and allowed for digital signatures
In the 1990s, the cryptographic wars between privacy activists and governments intensified, and PGP was recognized as one of the main weapons in these confrontations. A strong believer in freedom of information and personal data protection, Sassaman helped Zimmerman improve and expand the software.
When introducing Bitcoin, Satoshi said that he hoped Bitcoin could be to financial transactions “what strong cryptography (i.e. PGP) was to file security.”
In the past, multi-user computer systems faced a similar challenge. Before strong encryption was invented, users had to work hard to protect their passwords. But then strong encryption became available to the public and there was no need to trust others. Now is the time to take the same approach to money.
– Satoshi Nakamoto
Other hackers remember Len Sassaman as smart and kind-hearted: some say he dropped everything to follow a squirrel during one of the cypherpunk sessions.
Some also remember the days when Sassaman would speed down the roads in his sports car, jokingly keeping one of the Monopoly cards with the title “Get Out of Jail Free” in case he was confronted by the police.
Len Sassaman; The creator of Bitcoin
Collaboration with Hal Finney
At Network Associates, Len met Hal Feeney, the second PGP developer after Zimmerman. By creating the RFC 4880 standard for OpenPGP interoperability, Hall attracted Sasaman’s attention and led him to exchange joint projects.
 Hal Finney, a colleague of Len Sassaman, had a close relationship with the creator of Bitcoin
Hal Finney, a colleague of Len Sassaman, had a close relationship with the creator of Bitcoin
Until years ago, many seasoned crypto experts considered Hal Finney to be the favorite to play Satoshi Nakamoto. Some also believe that he must have had a very close relationship with Satoshi. This makes Sasaman and Finny’s friendship more important:
Finney was the first person after Satoshi to contribute to Bitcoin coding and run a Bitcoin node. He was also the first person to receive Bitcoin from Satoshi himself and by inventing the Reusable Proof-of-Work System, he made the Bitcoin mining process more efficient and less expensive.
Hal Finney, Sasaman’s colleague, was the first person to receive Bitcoin from Satoshi himself
For this reason, if Finney is not Satoshi Nakamoto, he has definitely faked his extensive email interactions with the creator of Bitcoin and simultaneously contributed to the development of Bitcoin under two separate identities.
But Sassaman, who was trying hard to distance himself from the limelight during this time, often did his work in Finney’s shadow. The complicated relationship between the two leaves another question on the table: Was Finney a cover for Sassamen in addition to a friend and colleague?
Len and Hal had a very rare skill in common. Both of them were the developers of Remailer technology, which sends messages anonymously. The mechanism of this technology is very similar to Bitcoin, except that it was introduced before digital currency and distributes transactions instead of money.
Remailers were not only direct generators of Bitcoin technology, but also have deep roots in the intellectual history of decentralized transactions:
“The possibility of exchanging messages privately without revealing the real identity of people” was considered a long and influential step in decentralization. In this way, users could participate in transactions, show their credentials, and trade without surveillance systems being able to track their movements.
Sasaman considered the promotion of open-source projects as one of the necessities of a free digital society
In addition to his role as the operator of Advanced Remailers, or Mixmaster, Len also implemented similar technology for the Privacy Anonymizer, a tool for hiding users’ online identities.
On the other hand, Len always believed that open-source projects play an important role in creating a freer and safer society in the digital space. One of his important actions in this direction was the collaboration in the development of GnuPG, the open-source version of PGP, which was considered part of his extensive effort to grow and popularize the open-source culture.
Traveling to Belgium and working with crypto giants
After finishing high school, Len Sassaman had to work to support his family and did not get a chance to study at university. But thanks to his professional activities, he was invited to Belgium in 2004 to work as a senior researcher at the Computer Security and Industrial Cryptography (COSIC) team at KU Leuven University.
Led by Bart Pernell, one of the world’s most famous cryptographers, this team was an ideal platform for Len’s development.
 David Chaum, the godfather of digital currencies and Len Sassaman’s consultant professor
David Chaum, the godfather of digital currencies and Len Sassaman’s consultant professor
Sassaman’s doctoral advisor was none other than David Chaum, who is known today as the godfather of digital currencies. Although Chaum founded the entire cypherpunk movement, few people have had the opportunity to work with him directly; But Len made the most of this rare experience.
Len Sassaman met two of the world’s greatest cryptography professors at the University of Belgium
During this period, Len expanded his research in the field of security protocols and modern encryption methods to international levels, and at the same time, he taught as a professor of cyber security. Some of the people who studied in his classes later became famous figures in this field.
Sassaman regularly attended renowned conferences such as Defcon and enjoyed exchanging ideas with the best minds in the world of hacking and cryptography, But he clearly did not seek fame and scientific honors. According to those around him, Len often approached security issues with a critical and careful eye and expressed his views in a direct and forthright manner.
Len Sassaman February 11, 2006, at the 5th CodeCon conference with Meredith L. Patterson, a computer scientist and one of the speakers at the meeting. They got married some time later and by 2011 they had successfully completed several research projects together.
Meredith Patterson denies any claims that Sasamen is Satoshi Nakamoto.
Len Sassaman; The creator of Bitcoin
Sasaman Research: Was Satoshi Nakamoto an Academic Researcher?
Len worked at COSIC in Belgium until his death in 2011, during which time he wrote more than 45 valuable papers and was responsible for organizing more than 20 conferences.
His main focus of research is on developing privacy protocols that are practical and usable in the real world. One of the most important projects he did in these years in collaboration with Bram Cohen was called Pynchon Gate: a system that made it possible to retrieve the anonymous information of remailers through a distributed network without the involvement of a trusted third party.
This project was not unlike Bitcoin technology. Along the way, Len managed to find solutions to the Byzantium error, which was a major obstacle for previous peer-to-peer networks.
Sasaman’s research and projects provided solutions to solve the challenges of decentralized currencies
In the context of distributed computing, Byzantine fault tolerance refers to the ability of a network to remain active even when nodes are compromised or unreliable. In fact, the development of decentralized digital currency would not have been possible without the solutions of Len and the blockchain introduced by Chaum.
Between 2008 and 2010, parallel to the development of Bitcoin, Sassaman attended the International Financial Cryptography Association and held valuable meetings with Robert Hettinga, one of the first supporters and promoters of digital currencies.
But several clues suggest that Satoshi was also working at the university during Bitcoin’s development, as Gavin Anderson, founder of the Bitcoin Foundation, confirms this idea:
I think Satoshi Nakamoto is an academic figure, maybe a postdoctoral fellow or maybe a fellow professor who doesn’t want to be the center of attention.
On the other hand, Satoshi’s participation in the coding and comments section increased greatly during the summer and winter vacations, while his presence decreased in the late spring and fall of the year when academics were busier.
Some say that the “unique structure of Bitcoin” indicates that Satoshi has an academic background. For example, the New Yorker magazine wrote in 2011:
Whoever created Bitcoin has a deep understanding of cryptography. He has read academic papers, is highly intelligent and combines concepts in a completely new way.
When prominent security researcher Don Kaminsky first reviewed Satoshi’s code, he wanted to test it against nine different exploits, but was surprised to find that Satoshi had already predicted and fixed all of them.
A lot of evidence shows that Satoshi Nakamoto is an academic figure
Did Satoshi and Kaminsky have common experiences and expertise in information security science? The answer to this question is not clear to anyone, but the interesting point is that Sassaman and Kaminsky once coincidentally wrote a paper together that described methods of attacking public key infrastructures.
On the other hand, according to experts, the Bitcoin white paper was published in an academic format, with an abstract, conclusion, and MLA referencing style, while we do not see these details in other cypherpunk posts, nor in the white paper of Bitgold and similar currencies.
Satoshi Nakamoto was in Europe at the same time as Sasaman was living in Belgium
Research by the New Yorker shows that Satoshi Nakamoto’s writing style is closer to British English, although the technologies he developed are more American. Perhaps coincidentally, Len Sassaman, despite being American, used the same British English words.
Sasaman’s untimely death and suspicious synchronicities
 Len Sassaman and his wife Meredith Patterson
Len Sassaman and his wife Meredith Patterson
On July 3, 2011, the news of Len Sassaman’s suicide was confirmed by his wife, and it shocked the technology world, especially the cryptocurrency activists. Some rumors claimed that he died due to mental and emotional stress from a long battle with surveillance systems, but these theories were never definitively confirmed.
Satoshi Nakamoto disappeared exactly two months before Sasamen committed suicide
In the same year, Don Kaminsky announced at the Black Hat Briefings that a permanent and encrypted message to Sasaman’s memory was coded in the Bitcoin blockchain; A tribute that will forever remain in an immutable web of mana, just like Sasaman’s lasting impact on the world of technology.
But Sasamen’s death coincided with the disappearance of Satoshi Nakamoto: just 2 months before this incident, Nakamoto sent his last message:
I have moved on to other projects and probably won’t hear from me in the future.
After 169 code commits and 539 posts in the space of a year, Satoshi quietly disappeared. According to estimates, he had 1.1 million bitcoins at this time.
Sasaman spent most of his life in the shadows. Although Satoshi Nakamoto was never publicly named, the influence and traces of his ideas and technologies can be seen in many aspects of Bitcoin and blockchain technology. These coincidences, along with the striking similarities in the thoughts and approaches of these two figures, continue to cause much speculation about Satoshi Nakamoto’s true identity.
Was Len Sasaman the same as Satoshi Nakamoto? The answer to this question is still unclear. But certainly, Sasaman’s name will remain in the minds of technology enthusiasts as one of the hidden architects of the digital world and freedom of information.


You may like
-




Everything about Cybercube and Robo Van; Elon Musk’s robotic taxis
-




How do we know that our phone is infected with malware?
-




The biography of Ida Lovelace; The first programmer in history
-




What is OBS Studio and how to use it?
-




How to solve the problem of slow charging of the Android phone?
-



The new version of Copilot was unveiled; Microsoft artificial intelligence
Technology
Everything about Cybercube and Robo Van; Elon Musk’s robotic taxis
Published
3 days agoon
13/10/2024

Everything about Cybercube and Robo Van; Elon Musk’s robotic taxis
After years of passionate but unfulfilled promises, finally on October 11, 2024 (October 20, 1403) at the WE, Robots event, Elon Musk unveiled Tesla’s robotic taxis.
Appearing on stage an hour late, Musk showed off the Cybercube self-driving taxi: a silver two-seater that moves without a steering wheel or pedals.
The CEO of Tesla further announced the presence of 21 Cybercubes and a total of 50 self-driving cars at the Warner Bros. studio (California), where Tesla hosted the event with special guests only.

Tesla
“We’re going to have a very glorious future ahead of us,” Musk said, but gave no indication of where the new cars will be built. According to him, Tesla hopes to offer Cybercubes to consumers at a price of less than 30,000 dollars before 2027.
The company will reportedly begin testing “unsupervised FSD” with Model 3 and Model Y electric vehicles in Texas and California next year.
Currently, the company’s self-driving cars operate with supervised FSD, meaning they require human support to take control of the steering wheel or brakes at any time. Tesla needs to get several permits from the regulators of different US states (or other countries) to offer cars without steering wheel and pedals.
But Cybercube was not the only product that was unveiled at this ceremony. Alongside the line-up of Optimus robots likely to launch as consumer work assistants in the coming months, the unveiling of an autonomous robotic van that can carry up to 20 passengers or be used to carry goods also generated more excitement among the audience.

According to Musk, Robovans and Cybercubes use inductive charging and do not need a physical power connection for recharging. He also stated that “robovans” would solve the problem of high density and pointed to the transportation of sports teams, for example.
The CEO of Tesla has been drawing the dream vision of the company’s self-driving public transportation fleet for the shareholders for years and sees the company’s future in self-driving vehicles.
It is not bad to remind you that the WE, Robots event was the first product introduction event after the introduction of Cybertrack in 2019; The product, which entered the market in late 2023, has since been recalled 5 times in the United States due to various problems.
The event ended with Elon Musk’s “Let’s party” and a video of Optimus robots dancing, while Tesla’s CEO invited guests to take a test drive with the on-site self-driving cars inside the closed-off film studios.
However, experts and analysts of the self-driving car industry believe that the release of cybercabs will take longer than the announced schedule because ensuring the safety of these cars in scenarios such as bad weather, complex road intersections and unpredictable behavior of pedestrians will require many permits and tests.
Tesla shareholders still balk at Musk’s vague timetable for the production and delivery of new cars, as he has a poor track record of promising robotic taxis. But we cannot deny that this unveiling breathed new life into the world of self-driving technologies.
But where did the idea of robotic taxis, which Tesla CEO claims are 10 to 20 times safer than human-driven cars and reduce the cost of public transportation, start?

Tesla
In 2019, during a meeting on the development of Tesla’s self-driving cars, Elon Musk suddenly made a strange prediction: “By the end of next year, we will have more than a million robot taxis on the road.”
Tesla’s investors were not unfamiliar with the concept of fully autonomous driverless cars, and what surprised them was the timing and short window of time of the plans that Musk was announcing. His prediction did not come true until the end of 2020, but has been postponed many times; But in recent months, with the decrease in Tesla’s interest rate, Elon Musk has tried in various ways to divert Wall Street’s attention from the company’s main activity and draw it to a new point. At every opportunity, he explains that the company’s future lies not in the production of electric cars, but in the very exciting world of artificial intelligence and humanoid robots.
According to him, one of the most profitable businesses in the field of AI will be driverless taxis or robotaxis that work almost anywhere and in any condition. Musk believes that Tesla’s market value will reach several trillion dollars after the release of these cars, although with this, Tesla will enter a highly competitive market.
Tesla’s technology will face fierce competition from Alphabet’s Waymo, Amazon’s self-driving unit Zoox, and General Motors’ Cruise. Also, ride-sharing companies such as Uber and Lyft and Chinese companies such as Baidu and BYD are considered serious competitors of Tesla.
Can robotaxis really save Tesla from declining profitability? How close is the company really to the production of driverless and fully autonomous car technology, and what guarantee is there for the success of Elon Musk’s plans to form a vast network of robotic taxis?
The start of the internal project of Tesla’s self-driving taxis

Business Insider
Although Elon Musk has implicitly raised the idea of robotaxis since 2016; the design and development operations of these cars took on a more serious color from 2022. At this time, during Tesla’s first-quarter earnings call, Musk once again announced that the company is building robotic taxis that do not have any steering wheel, pedals, or any other controller for physical human driving.
He also said that these cars will be fully self-driving and will be available to the public by 2024, when Tesla completes its self-driving car project. Sometime later, at the opening ceremony of the Gigafactory in Austin, he mentioned that the robotaxis would have a futuristic design and probably look more like a Cybertruck than a Tesla Model S.
Tesla’s robotic taxis have no steering wheel, pedals, or any other controls for physical human driving
During the same meeting, a Tesla investor asked Musk if the robot taxis would be offered to utilities or sold directly to consumers. Musk did not answer this question but continued to emphasize that robot taxis minimize the cost of a car per kilometer of distance, and the cost of traveling with these cars will be lower than a bus or subway ticket.
Sometime before Musk’s statement, Tesla announced that it is producing fully autonomous and self-driving vehicles at a cost of $25,000, which can have a steering wheel or not. For this reason, no one knows yet whether Musk’s robotaxis project refers to these cars or not.
According to the announced timeline, Tesla had 32 months to complete the construction, legal permits, and software required for the robot taxis and align with acceptable standards for “level 5 autonomy.”
At the beginning of 2024, the subject of robotic taxis made the news again. Elon Musk, who seemed fed up with Tesla’s usual car business, emphasized that Tesla’s future does not depend on selling more electric cars, but mainly on artificial intelligence and robotics.
Unlike Uber, which is Tesla’s main competitor in this project, Musk does not want to rely on Model 3 sedans and SUVs like the Model Y for the development of robot taxis. According to Tesla’s statement, the company is generally working on the production of new dedicated vehicles, which will probably be called Cybercab.
The supply of robotaxis depended on the completion of Tesla’s autopilot technologies and the so-called full self-driving systems, and exact statistics of how much consumers will accept this innovative product and what new rules will be imposed in this field were not announced.
Car design

Teslaoracle
In terms of design, the interior of the car was expected to have differences from other Tesla electric cars to meet the demands of passengers; For example, two rows of seats facing each other, or doors that open in a sliding manner and facilitate boarding of passengers. Also, a car that is used as a taxi should have provisions for simple and quick cleaning of the interior and even disinfection.
The idea of robotaxis also received interesting design proposals from enthusiasts: some said it would be better for Tesla to optimize its public self-driving cars depending on different uses; For example, some of them have a place to rest for long distances, or others come with a monitor and several accessories that are suitable for working along the way.
Supporters said that these facilities improve people’s quality of life and even if a passenger devotes his travel time to something useful, he has saved the same amount of time.
Continuing speculation about the design of the Cybercube, a group of experts in the field of car research also said that in the coming years, Tesla could produce other vehicles that are suitable for special entertainment, such as watching movies, or other amenities for users who want to hang out with friends and fellow travelers along the way. To socialize yourself, have: just like sitting in a limousine.
The design of the Cybercube is similar to the Cybertruck van, but with doors that open from the top
But the initial design of the Cybercube, which was published on the Tesla website, was somewhat reminiscent of the Cybertruck, and there was no special feature even to make it easier for people with disabilities to ride.
Forbes also wrote in its latest report comparing self-driving cars of different companies that Tesla’s robot taxi will probably be a two-seater car with side-by-side seats and a retractable steering wheel because eventually, users will need a steering wheel to drive outside the areas that have the company’s support services. had

However the final design of the Tesla Cybercube was not similar to the self-driving cars of the startup Zoox or Zeekr.
With doors that open up like butterfly wings and a small interior, this car only hosts two passengers. As we might have guessed, the Cybercube looks a lot like the Cybertruck, but it’s sleeker and more eye-catching than the controversial Tesla pickup.
Hardware

Sugar-Design
So far, Tesla has not disclosed any information about the set of sensors that will be used in the robotaxis. The company talks about Autopilot technologies on its website, but what Elon Musk has so far described as a fully self-driving, driverless car will require more advanced sensors, software and equipment than Autopilot.
Tesla Autopilot cars are equipped with multiple layers of cameras and powerful “machine vision” processing, and instead of radar, they use special “Tesla Vision” technology that provides a comprehensive view of the surrounding environment.
In the next step, Tesla Autopilot processes the data from these cameras using neural networks and advanced algorithms, then detects and groups objects and obstacles and determines their distance and relative position.
Tesla’s Autopilot system is equipped with multiple layers of cameras and powerful “machine vision” processing and uses “Tesla Vision” instead of radar.
Car driving functions also include two important eras: 1. adaptive cruise control with traffic detection that changes the car’s speed depending on the surrounding traffic; 2. The Autosteer steering system makes the car move on a certain line with the help of cruise control and continues the right path, especially when it encounters a curve in the road.
These cars can park automatically, recognize stop signs and other road signs as well as traffic lights, and slow down if necessary. Blind spot monitoring, automatic switching between road lanes, and intelligent summoning of the car by mobile application are some other features of these cars.
Despite all security measures, all Tesla Autopilot cars still require driver supervision according to national laws and the company’s own announcement. For this reason, until this company provides new specifications and information about the sensors, cameras, and systems of the robot taxis, no expert can check their efficiency or risk.
Introducing the Robotaxis application

Tesla
In April 2024, Tesla released a brief report on the mobile application of robotaxis, and Elon Musk also said that the first of these cars would be unveiled in August (this date was later postponed).
In the initial images of the robotic taxis application, a button to call or summon a taxi and a little lower, the message of waiting time for the car’s arrival could be seen. The second image showed a 3D map and a small virtual vehicle following a path toward a waiting passenger. These images were very similar to the Uber app, except that it looked like a Tesla Model Y car was driving in it.
According to Tesla, passengers can adjust the temperature of the car as they wish when they are waiting for the taxi to arrive. Of course, other details such as the waiting time and the maximum passenger capacity of the car were also seen in the images of the application.
Passengers can adjust the temperature inside the car and their favorite music through the Tesla application
According to the published screenshots, in the next step when the vehicle reaches the origin and the passenger boards, the map view changes to the destination. Passengers can control the car’s music through the mobile application.
The app looks like a standard online ride-hailing app, but there’s no mention of the robotic nature of the car, which does all the driving automatically and autonomously. Elon Musk said in the same meeting:
You can think of Tesla’s robotaxis as a combination of Uber and Airbnb.
According to Musk, part of the fleet of robotic cars will belong to Tesla and the other part will belong to consumers. The owners of this group of robotic cars can give their cars to the taxi fleet whenever they want and earn money in this way.
Legal restrictions on removing the steering wheel and pedals

independent
Despite all his previous promises, Tesla’s CEO has been evasive in past interviews when asked if the robotaxis will have traditional controls like pedals and steering wheels. Tesla’s Robotaxi plans have been heavily questioned due to delays in early prototype development, making the answer to the above question more important than ever.
The reality is that by mid-2024, in theory, it could take months or even years to approve a vehicle without pedals and a steering wheel for public roads, while a more traditional-looking vehicle could come much sooner.
In a letter addressed to its shareholders, Tesla emphasized that it would need the permission of the federal government to deploy and operate robotaxis with a more radical and progressive design. The statement also stated:
Scheduling robotaxis requires technological advances and regulatory approvals, but considering their very high potential value, we intend to make the most of this opportunity and are working hard on the project.
Elon Musk also did not respond to a question about exactly what type of regulatory approval Tesla is seeking.
He was then asked by reporters if Tesla was seeking an exemption from the Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards (FMVSS) to develop and market a car without traditional controls. In response, Musk compared Tesla’s new product to Waymo’s local self-driving cars and said that products that are developed for local transportation are very vulnerable and weak. He added:
The car we produce is a universal product that works anywhere. Our robotaxis work well on any terrain.
Currently, car manufacturers must comply with federal motor vehicle safety standards that require human controls such as steering wheels, pedals, side mirrors, and the like. These standards specify how vehicles must be designed before they can be sold in the United States, and if a manufacturer’s new product does not meet these requirements, manufacturers can apply for an exemption; But the US government has set a limit of 2,500 cars per company per year.
The regulatory exemption cap would theoretically prevent the mass deployment of purpose-built self-driving vehicles from any AV company, including Tesla. To date, self-driving car advocates have tried hard to pass legislation to cap the number of driverless cars on public roads; But the bill is apparently stalled in Congress due to questions about the technology’s “level of reliability” and readiness.
Tesla will need an FMVSS exemption if it wants to remove the steering wheel and pedals from its self-driving cars
So far, only Nuro has managed to obtain an FMVSS exemption, allowing it to operate a limited number of driverless delivery robots in the states of Texas and California.
For example, General Motors’ Cruise unit applied for a waiver for Origin’s steering-less and pedal-less shuttle, but it was never approved, and the Origin program was put on hold indefinitely.


Startup Zoox (a subsidiary of Amazon) also announced that its self-driving shuttles are “self-certified”, prompting the US National Highway Traffic Safety Administration to launch new research to understand this newly invented concept. Issues such as strict legal processes and approval of the license caused other companies in this field to completely ignore the issue of removing the steering wheel and pedals. For example, Waymo’s self-driving cars, although operating on public roads without a safety driver, have traditional controls. Some time ago, the company also announced that it would finally introduce a new driverless car, but did not specify an exact date for it, nor did it mention FMVSS exemptions.
Thus, now that it has been determined that the final Cybercube car will be produced without traditional controls, Tesla must also pass similar regulatory hurdles.
The challenges of mass production of Tesla robotaxis

Sugar-Design
Apart from persuading the regulators and getting a city traffic permit, there have been many other challenges standing in the way of the success of the robotaxis project, some of which Tesla has passed and has not found an answer for others.
For example, Tesla claims that it has reached a reliable milestone in terms of technologies and hardware infrastructure, but incidents such as the crash of Uber’s self-driving car in 2018, which killed a pedestrian, or two severe crashes of cruise cars in 2023, have a negative public view. It followed people into driverless cars.
On the other hand, the current infrastructure of most American cities is designed for conventional cars and must be updated and developed again to support the multitude of robotic taxis . For example, installing smart traffic lights that can communicate with self-driving cars and provide them with real-time information is one of the basic needs of robot taxis. Also, the presence of clear road lines and legible traffic signs is very important for self-driving car sensors.
The mass production of robotaxis requires changing the road infrastructure
Contrary to Musk’s claim that “the roads are ready for permanent robot taxis,” self-driving cars from other companies are still plying urban and intercity roads in certain parts of the United States. Until July 2024, Tesla had about 2.2 million cars on American roads, which is far from Elon Musk’s target of a fleet of 7 million cars.
In the second stage, Tesla’s self-driving cars are equipped with advanced technologies such as a variety of cameras and sensors and data processing systems, which, apart from the cost of production, also increase the cost of maintaining equipment and keeping software up-to-date.
In the past year alone, some Tesla customers have been forced to pay an extra $12,000 to upgrade their cars’ self-driving capabilities, while there’s still no news of new features.
If we consider the average price of robotaxis between 150,000 and 175,000 dollars, it is not clear how long Elon Musk’s promise to potential buyers about the revenue-generating potential of these cars will take. Unfortunately, Musk’s prediction regarding the annual gross profit of 30,000 dollars for the owners who give their cars to other passengers does not have statistical and computational support.
Developing new insurance models for self-driving cars will be one of Tesla’s serious challenges
The development of suitable insurance models for self-driving cars will also be one of Tesla’s serious challenges, because insurance companies must be able to correctly assess the risks and possible costs of robotaxis; Therefore, Tesla must cooperate with insurance companies from different angles to reach a comprehensive plan that both customers and companies are satisfied with.
In addition to paying attention to technological and legal issues, Tesla must gain people’s trust in its new series of fully automatic and driverless cars, and for this purpose, it will be necessary to hold advertising campaigns and extensive training programs to familiarize consumers with the company’s technologies and reduce the concerns of end users. was
The status of the project in 2024 and the concern of shareholders

Tesla
In 2024, Elon Musk postponed the unveiling date of robotaxis to August 8 and then to October 10. In April, he told Tesla’s investors, who were frustrated by the uncertain progress of production of the cars.
All the cars that Tesla produces have all the necessary hardware and computing for fully autonomous driving. I’ll say it again: all Tesla cars currently in production have all the prerequisites for autonomous driving. All you have to do is improve the software.
He also said that it doesn’t matter if these cars are less safe than new cars, because Tesla is improving the average level of road safety. A few weeks later, he released another video in which he summarized meeting Tesla’s goals in three steps:
- Completing the technological features and capabilities of fully autonomous vehicles
- Improving car technology to the point where people can ride driverless cars without any worries
- Convincing the regulators that the previous option is true!
While other companies producing self-driving cars go from city to city to obtain the necessary permits and try to expand the range of activities of cars by proving the safety of their products, NBC recently revealed in its report that Tesla even the states of California and Nevada, which employ the most employees. has not received a license to test these cars.
Tesla has not yet received permission to test robotaxis in the US states
In July, Musk told investors that anyone who does not believe in the efficiency and value of robotaxis should not be a Tesla investor. Meanwhile, the California Department of Motor Vehicles recently filed a lawsuit against Tesla, accusing the company of falsely advertising Autopilot and fully automated systems.
In addition to specifying the monthly cost and upfront payments for fully autonomous cars, the case also addresses the issue that both types of systems require drivers to be behind the wheel and control the vehicle’s steering and braking.
The unveiling of the Cybercubes in October 2024 seemed to ease the mind of Tesla shareholders somewhat, but during the night of the company’s big event, some of them expressed their concern about Musk’s uncertain timings to the media.
What do experts and critics say?
Some critics say that it is not possible for Elon Musk’s robot taxi to be produced and released according to his schedule. Referring to Waymo vehicles that make 50,000 road trips every week, this group considers Tesla’s silence regarding the request for technical information of the vehicles unacceptable. From their point of view, Musk is just continuing to make vague promises about this car.
In response to critics, Elon Musk emphasizes one sentence: that Tesla is basically an artificial intelligence and robotics company, not a traditional automobile company. So why doesn’t he try to clarify the obstacles that stand in the way of Tesla’s actions to realize the old idea?
On the other hand, the technology academies remind that Tesla’s systems have not reached level 5 autonomy, that is, conditions that do not require any human control. The MIT Technology Review writes:
After years of research and testing of robotic taxis by various companies on the road, mass production of these cars still has heavy risks. To date, these vehicles only travel within precise, pre-defined geographic boundaries, and although some do not have a human operator in the front seat, they still require remote operators to take over in an emergency.
R. Amanarayan Vasudevan , associate professor of robotics and mechanical engineering at the University of Michigan, also says:
These systems still rely on remote human supervision for safe operation, which is why we call them automated rather than autonomous; But this version of self-driving is much more expensive than traditional taxis.
Tesla is burning direct investor money to produce robotaxis, and it is natural that more pressure will be placed on the company to get more reliable results. The balance between costs and potential revenues will come when more robotaxis hit the roads and can truly compete with ride-sharing services like Uber.
Despite numerous legal, infrastructural and social challenges, the unveiling ceremony of Cybercube and RoboVon puts not only the technology levels of self-driving cars but the entire transportation industry on the threshold of a huge transformation. The entry of Tesla’s robotic taxis into the market can even affect the traditional taxi service model, but how long will it take for the transition from this unveiling to the actual launch
Technology
How do we know that our phone is infected with malware?
Published
5 days agoon
11/10/2024

How do we know that our phone is infected with malware?
Today’s smartphones are not just a means to communicate with others, for many of us, they are a personal notebook, a family photo and movie album, a mobile bank, and a device for storing important daily information. These cases clearly remind us of the high importance of taking care of the phone and paying attention to the security of the information stored in this device.
Android and iOS operating systems become more secure with each update; But again, it is possible that due to reasons such as rooting the Android phone or jailbreaking the iPhone phone, we expose our phone to malware that in many cases enters the victim’s devices with the aim of stealing information and causing financial losses. .
Although hackers very cleverly infect victims’ phones with their desired malware, after the device is infected, there are changes in the normal operation of your phone, and by identifying them and contacting a repairman in time, you can remove the malware from your phone and prevent serious damage. Next, join us to get to know the 7 signs that indicate your phone is infected with malware and learn how to get rid of it.
-
7 signs of phone virus infection
-
Abnormal increase in internet usage
-
Strange ads appear on the phone
-
Quick battery drain
-
Disabling phone apps and random device startup
-
Overheating of the phone body
-
Show unknown and new apps on the phone
-
Unstable internet connection or constantly dropping calls
-
How to remove malware from the phone?
-
How to prevent the phone from being infected with malware?
7 signs of phone virus infection
If your phone has recently experienced one or more of the following problems, it is likely that a malware is active on your phone:
Abnormal increase in internet usage
Many malware are usually designed to run permanently in the background of the phone and send personal information or files from the victim’s device to the hacker or download malicious files and hide them in certain parts of the phone. do This process is one reason for the phone’s internet to run out early because it increases the device’s internet usage unexpectedly to the point where, with a little precision, you can notice the difference between your usage in the current time period and, for example, the last week or month.

Adobe Stock
To find out how much data is being used on your mobile phone (SIM card internet), go to one of the two paths below and see exactly how much internet each app consumes and if this amount is in line with what you expect from that app’s functionality. Does it match or not?
Information about the amount of internet usage on the Android phone
- Enter Settings.
- Tap the Connections option.




- Go to Data usage and Mobile data usage respectively.
Information about the amount of internet usage on the iPhone
- Enter Settings.
- Tap on Cellular and Cellular Data respectively.
If the Internet consumption by an application is much more than you expect or that application should not connect to the Internet, it is better to consider the application as malware and delete it from your phone.
Strange ads appear on the phone
Most cybercriminals design mobile malware with the goal of making money. Part of this revenue is generated by displaying strange random ads (for example, immoral sites) on victims’ phones. This type of advertisement, known as adware, directs victims to certain sites that are either designed to steal more information from the person, are phishing in nature, or encourage the victim to download malicious software and install it on their phone or even computer.
-
What is malware and how to prevent it?
-
What is phishing? How to identify scam sites?
In addition, displaying multiple ads on your phone slows down the phone; A process that puts a lot of pressure on the battery and other hardware of the device; Of course, this is in the most optimistic scenario. If you click on these ads and don’t use IP masking tools (such as a VPN), there is a risk that your IP will be exposed to the cybercriminals behind this malware. Then, in addition to infecting your phone, you have to worry about the dangerous things hackers are doing with your IP.
Quick battery drain
If you have made sure of the health of your phone’s battery using Android or iPhone battery health testing methods, or if you have recently replaced the phone’s battery, but still have to charge it several times during the day, you should consider the possibility that the phone is infected with malware. The 24-hour running of malware in the background of the phone increases battery consumption to a great extent, and in addition to draining the battery quickly, it can increase the temperature of the device body.
Disabling phone apps and random device startup
It is normal for the apps installed on the phone to crash occasionally and it may happen for various reasons, including the app not being up-to-date; But this process should not be repeated constantly. If, in a short period of time, a significant number of apps on your phone freeze, don’t work as expected, close suddenly, or stop working completely, and won’t go back to their previous state even with an update, the hypothesis that your phone is a is infected with malware; is strengthened

In addition, if the phone restarts automatically and the process of loading the phone’s user interface after startup takes longer than before, it could be a sign of malware in your phone that restarts the phone every time it stops working and restarts in the background. The phone should run.
Overheating of the phone body
It doesn’t matter if you are doing simple tasks with your phone or playing games and heavy software is running; If your phone is infected with malware, the body of the phone will become abnormally hot. This heat will not only prevent you from working with the phone, but by damaging the hardware of the device, it will slow down its performance when running your favorite programs.
Sudden and excessive heat in the body is a very serious alarm about the possibility of malware in the phone
Unfortunately, in most cases, there is no uniform process to heat up a phone infected with malware, and you may face this excessive heat once when running a light messenger like WhatsApp, and another time even when running a heavy program, the heat generated in The body should not attract so much attention to itself.
In any case, sudden heat generation in the body of the device that was not there before or was not present at this intensity is a serious alarm about the possibility of malware in your phone and you should show your phone to a professional repairer as soon as possible.
Show unknown and new apps on the phone
Besides executing commands to send your information to their designers, malware may also download and install new apps on your phone. These programs may seem harmless on the surface (for example, they look like an exercise training program), but ultimately, they are not installed on your device with good intentions and often do things like track your traffic and display numerous advertisements intended by malware designers or in Worse, they steal your personal and sensitive information (such as passwords to social media accounts).

Adobe Stock
Be aware that most of these unknown and new apps usually have unreasonable permissions that allow them to access sensitive parts of the phone such as contacts, gallery, storage (phone and memory card), camera and microphone.
Unstable internet connection or constantly dropping calls
Malware communication on a phone or the malware designers’ server interferes with your phone’s ability to maintain a stable connection to the Internet or prevent call drops. If other devices that use the same Wi-Fi connection as you do not face the problem of unstable Internet connection, or if in the area where you are present, the SIM card antenna of other phones has no problem, you should suspect the possibility of your phone being infected with malware.
How do you remove malware from the phone?
If you see one or more of these symptoms on your phone and you suspect that your phone is infected with malware, you can identify the malware infecting your device and remove it through the following methods:
1. Removing malware from the phone through Safe Mode
Since most malware runs continuously in the background of the phone and closing them forcibly is not possible in some cases; It is better to delete the programs you suspect from your phone through Safe Mode. Android’s Safe Mode feature allows you to run the phone only with default system apps.
To enter Safe Mode on most Android phones, press and hold the Power button until the phone turns on and enters Safe Mode settings. In this mode, all the apps you have installed on the phone will be disabled and you can safely remove anything unusual and suspicious you see or apps you feel are infected from the phone.
-
The best antivirus for Android phones
-
Do you have an iPhone and are worried about being hacked? Enable Lockdown Mode
If you are using an iPhone, turn off the phone first to enter Safe Mode, similar to Android phones. After that, press and hold the power button for a few seconds. After the device turns on, press and hold the Volume Down button until the Apple logo appears on the screen, then release it to enter Safe Mode. Keep in mind that, unlike Android phones, different models of iPhones are equipped with a feature called Lockdown Mode, by which, if the phone is targeted by malware or hackers, the functionality of the device will be limited until you remove this malware.
2. Install antivirus
Installing a powerful antivirus on your phone is the easiest way to identify and remove malware
Sometimes, even after entering Safe Mode, you may not be able to identify and remove malicious programs from your phone. In such a situation, you can take the help of a good antivirus.
Be careful not to use free antiviruses as much as possible, as many of these programs either don’t provide the functionality you need or are just malware hiding behind the title of antivirus.

3. Restore the phone to factory settings
Some malware, for reasons such as being new, may not be detectable even by the most up-to-date versions of antiviruses, and despite installing several strong antiviruses, you may still struggle with one or more of the symptoms we mentioned at the beginning of the article. In this case, you will have no choice but to restore the phone to factory settings.
If you have important information and have already saved a backup copy of the phone data, to restore the iPhone to its factory settings, go to Settings > General > Transfer or Reset iPhone tap Reset, and select Reset All Settings to reset all the phone data. delete
In Android devices, the path to the factory reset option may be different in different brands. For example, if your phone is a Samsung, you can restore your phone to factory settings as follows:
- Go to Settings and click on Reset from the General Management section.
- Select the Factory Data Reset option.
How to prevent the phone from being infected with malware?
Contrary to what some people think, most malware is designed with the intention of causing serious harm to victims, and they usually do so within the first hours and days of entering the victim’s machine. Since many of us, due to ignorance of the signs of the phone being infected with malware, find out about the presence of malicious software in our phone late, sometimes even removing the malware does not have a special effect on the phone’s performance; Because this malware has already caused the damage desired by cybercriminals.
Being vigilant and careful to prevent malware from entering the phone is the most important step to prevent the phone from being infected with malware.
This shows the importance of being vigilant and careful to prevent malware from entering the phone. Observing these things can help you achieve such a goal so that you can better protect the security of your phone:
1. Download your favorite apps from Google Play or App Store
Many users, eager to use modded versions of a paid program, download that program from unknown sites and easily expose their phones to the risk of being infected by malware. Hence, it is essential to download Android and iOS apps only from Google Play or App Store. Fortunately, sometimes some paid apps become free for a limited time and you can install them instead of the modded version. At Zomit, we regularly feature paid Android and iPhone apps that have become free today.
2. Pay attention to the opinions of other users about a program
Showing excessive and unusual ads, not providing the functionality claimed by the creators, constantly crashing the program or directing the user to links outside the program are among the alarm bells of suspected malware programs that are often written by users in the comments section of a program. They can be a good clue to dissuade you from downloading that program.
3. Pay attention to the permissions of each program
Suspicious access that doesn’t need to be requested for certain apps can be a red flag for you. For example, if you download a reader app, it shouldn’t ask you to access the camera, audience, or gallery.

Adobe Stock
4. Do not download files from unknown devices
If you keep your phone’s Bluetooth on continuously due to using wireless headphones or Bluetooth hands-free, or the device’s AirDrop is always on, you should not accept files from unknown devices; Because this file (even in the form of a photo) may spread some kind of malware in your phone.
This includes receiving emails from unknown sources. Although you cannot prevent receiving these types of emails; if you receive them, you should not open these emails on your phone or computer and it is better to delete them immediately and block the sender of the email.
Read more: How to increase the security of Android phones?
5. Do not click on anonymous links
Many mobile phones get infected with malware by clicking on unknown links received through SMS or social media messages. You should note that you should never click on any unknown link, even from a familiar person. Or if you are determined, take help from reliable websites to determine if the link is safe.
Paying attention to the signs that your phone is infected with malware, as well as following the recommendations that can prevent malicious programs from entering your phone, are very important steps that keep your phone safe and prevent cybercriminals from stealing your personal and sensitive information.
Has your phone ever been infected? What solution did you use to fix it? Did you succeed in removing the virus?
Technology
The biography of Ida Lovelace; The first programmer in history
Published
6 days agoon
10/10/2024

The biography of Ida Lovelace; The first programmer in history
Ida Lovelace lived in the Victorian era; A time when dreamers were ridiculed if they talked about cars, and technologies such as computers had no place even in the minds of the geniuses of the time; Decades before the invention of the typewriter and the telephone, in a society where women were denied the right to vote and their role was defined only in household affairs.
Many of Lovelace’s contemporaries did not take her achievements seriously because of her gender. But he was determined to break all the unseen and unspoken boundaries: in collaboration with Charles Babbage, a famous professor and inventor, he created a concept that would be put into practice a century later: programming.
This article was updated on the occasion of Ida Lovelace Day to honor the achievements of women in STEM on October 18, 1403.
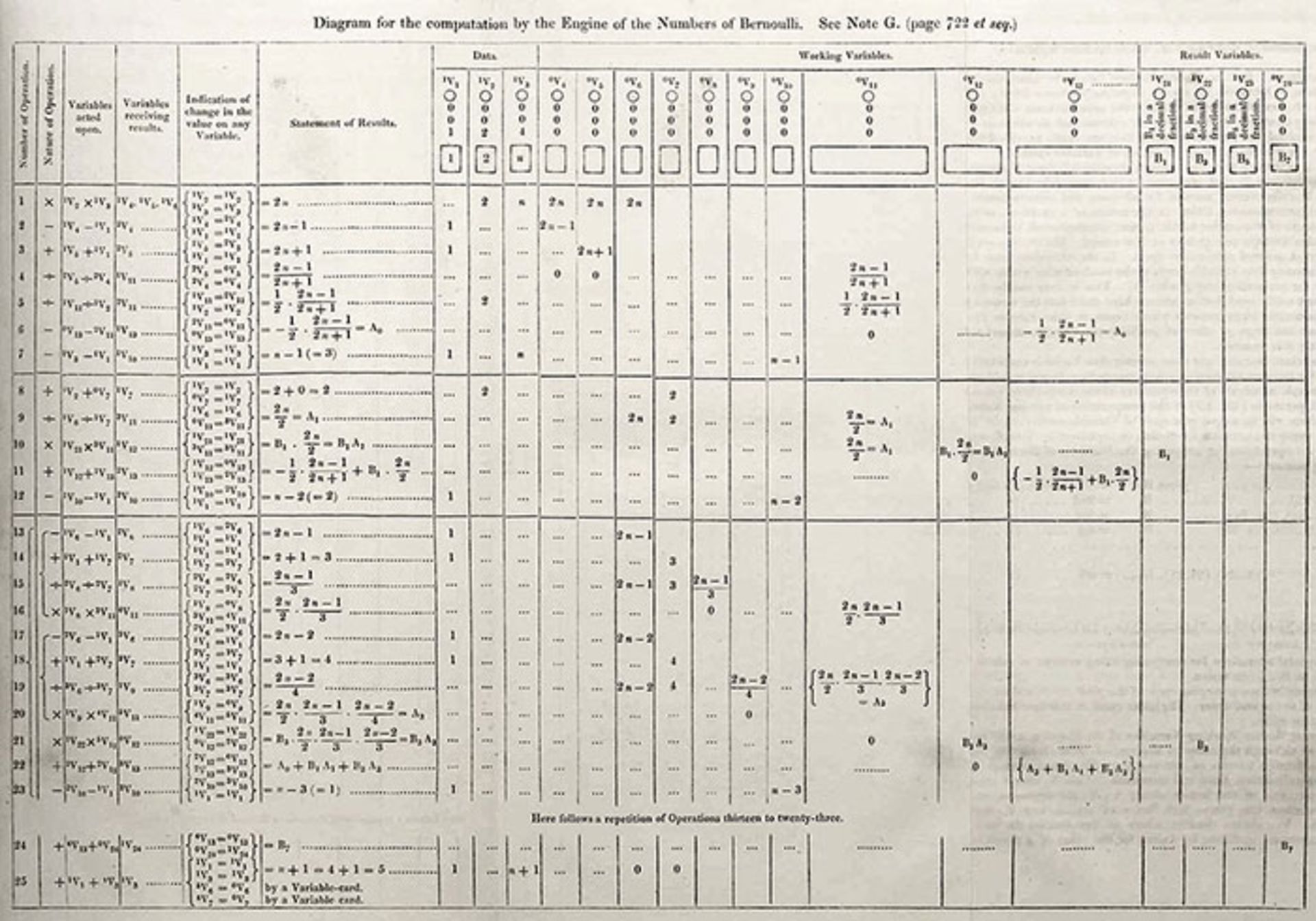
Ida not only wrote an algorithm to calculate Bernoulli numbers but also saw the potential of Babij’s Analytical Engine beyond simple mathematical calculations. He even predicted that one day this machine would be able to make music, produce graphic works, and have various applications in science. He wrote in his notes:
An analytical engine can process equations and analytic expressions just as we deal with letters and symbols in mathematics. In fact, it can be said that this machine writes computational poetry.
Lovelace’s life is a true story of the power of breaking stereotypes, overcoming social barriers, and most importantly, restless and eager minds. He had no idea that one day he would be called the world’s first programmer. However, throughout his short life, he was rebelling and striving for what troubled his mind.
In addition to being a mathematical genius, Ida always had a poetic spirit and considered her achievements to be a combination of science and poetry. Through his progressive and extensive activities, he managed to expand his social connections and share his thoughts and theories with prominent thinkers of that time, such as Andrew Cross, David Brewster, Charles Wheatstone, Michael Faraday, and even Charles Dickens.
Join us as we continue to review the life of this great pioneer who wishes to pave the way for the prominent presence of women in the fields of science and technology.

Born in the womb of contradictions
Ada Lovelace was born on December 10, 1815, in a family where there was no homogeneity. His father, Lord Byron, the famous romantic poet, was often known for his emotional and critical spirit, but his mother, Isabelle Milbanke Byron, was a practical mathematician who prioritized rational behavior and decisions above all else.
Lord Byron, who longed for a son, left his wife and child one month after Ida’s birth and left England completely three months later. Isabel, who was worried that her father’s revelry and fantasy spirit would overshadow Ida’s life, tried her best to keep her daughter away from the poetic world. For this reason, he encouraged him to learn complex scientific and mathematical concepts from his childhood.
Ida Lovelace’s mother encouraged him to learn complex scientific and mathematical concepts
This strict upbringing style, while it strengthened Ida’s abilities in mathematics and logic, did not prevent her from completely withdrawing from the attractions of the world of imagination. He was in love with mathematical problems and he was fascinated by fantasy and poetry. The complex combination of these two elements, i.e. creativity and logic, made him have a different approach to mathematics than other famous people of his time.
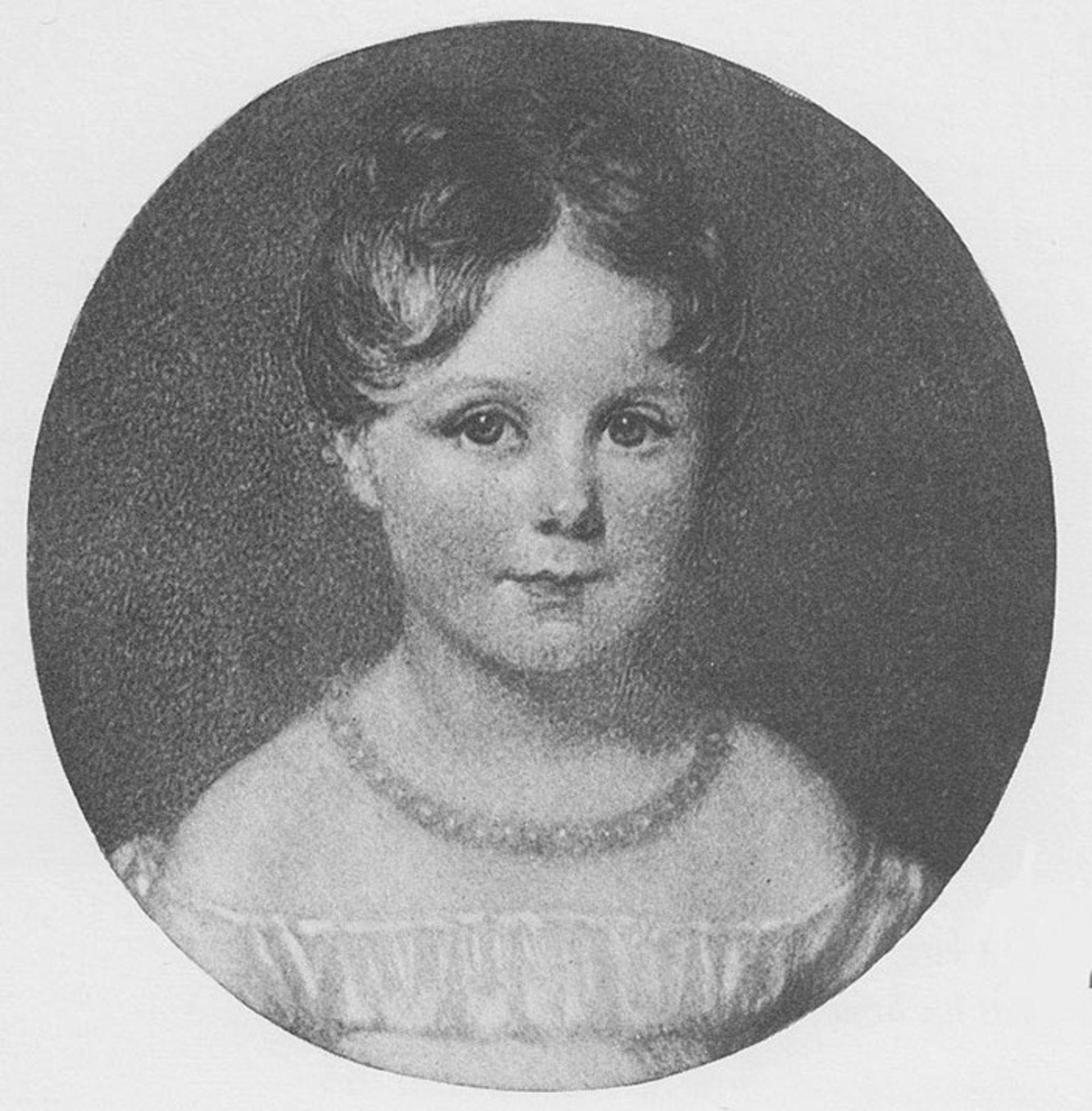 Ida Lovelace at 4 years old
Ida Lovelace at 4 years old
Education in childhood and adolescence
Isabel Byron hired several professional private tutors to teach her daughter history, literature, French, geography, music, chemistry, needlework, cursive, and mathematics.
Lovelace cultivated the love of mathematics and poetry at the same time
One of these prominent professors was Mary Somerville, who was considered one of the foremost mathematicians of her time and who personally believed strongly in the empowerment of women. Somerville had a profound effect on Ida’s mind and taught her how mathematics can be used as a tool to analyze and interpret the world around her.
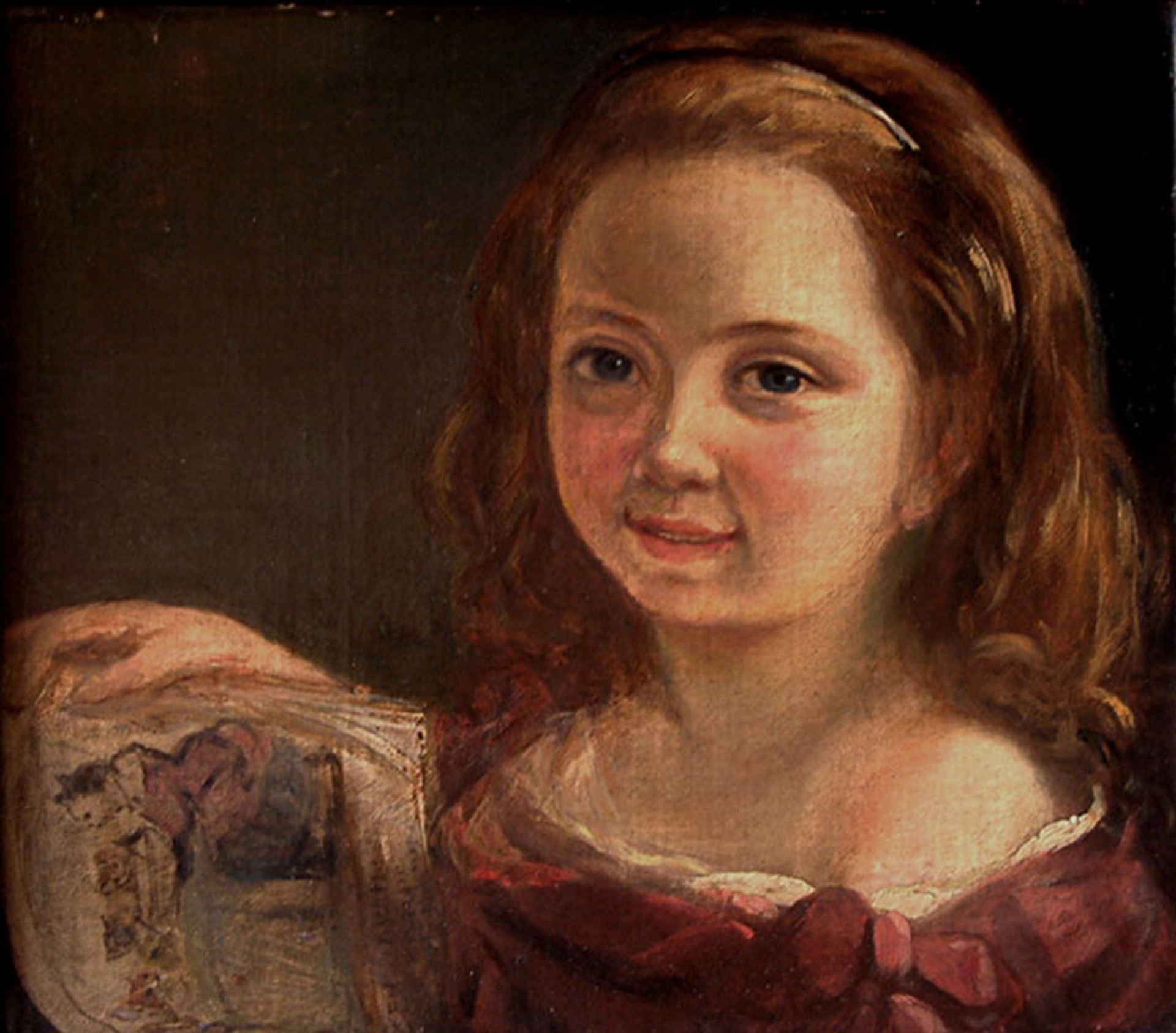 Ida Lovelace at 7 years old
Ida Lovelace at 7 years old
When Ida reached the age of eleven, she went on a tour of Europe with her mother to learn about the progress of science and technology in other countries.
On his return from the trip, Lovelace fell in love with the idea of flying machines and drew many sketches of steam-powered machines that imitated the movement of birds. He even wanted to publish his research in a book called Flyology, but Lady Byron felt threatened by the idea that her daughter would suffer her father’s fate by fantasizing.
At the age of 12, Lovelace had drawn many designs of flying cars
The mother’s new and serious decision was to move from the beautiful rural area of Lovelace to the elite society of London, where most of the men were not members of traditional or political groups and spent their wealth on things like botany, astronomy, and geology.
In the early 19th century, there were still no professional “scientists” (in fact, the word scientist was first coined in 1836 by William Wavell), and although the new settlement was considered the seat of society’s gentry, “noble” women still participated in the activities Thinking was a condemned thing.
At the age of 14, Ida contracted measles (or according to some accounts, encephalitis) and stayed in bed for three whole years. During this period, he did not stop studying and learning, as he wrote in one of his notes:
Mathematics is not only a tool for solving mundane problems, but it can also open a window to the unknown, where human imagination and creativity are challenged.
By reviewing the works of Isaac Newton and Euler, Ida reached a new understanding of the scientific concepts of physics, mechanics, and chemistry and improved her analytical abilities in a more advanced way.
Historical meeting: getting to know Charles Babbage and the computing engine
After recovering from her illness at the age of 17, Ida attended London court parties and met the King of England. At one of these parties, she met 41-year-old Charles Babbage, whose eldest son was the same age as Ida.
Babbage was Lucassi’s mathematics professor at Cambridge University and soon became fascinated by Lovelace’s talent and interest in mathematics. That’s why he invited him and his mother to meet again to see the computing engine he had just built: a 0.6-meter-tall hand-cranked machine with 2,000 pieces of brass, now housed in London’s Science Museum.
Meeting Charles Babbage and seeing his calculating machine changed Ida Lovelace’s life forever
Lady Byron called this device “thinking machine”; Because through it, the figures could be raised to the power of 2 and 3 and the root of the quadratic equations could be extracted. But none of those present knew that Babij’s invention would change Ida’s life forever.
 Ida Lovelace at the age of 17
Ida Lovelace at the age of 17
Charles Babbage had been thinking for years that maybe one day he would build a different car. A device that can process various types of polynomials with specified powers in different ways and automatically display the results after receiving the input values. According to him, this device would save people from common mistakes in “mathematical circles”.
Babbage received a Medal of Honor for his computing engine prototypes and received funding from the British government to build his machine. He worked on such ideas from 1822 to 1827 and then presented his manuscript table of logarithms to the university. This table was reprinted for a hundred years.
During this time, he lost his wife and traveled around Europe to escape depression. After returning to England, he wrote a book called “Reflections on the Decline of Science in England”, which was interpreted as a speech against the Royal Society and caused him trouble.
However, he remained focused on the idea of the calculating machine, and finally in 1833 he built a small example of this machine, which, of course, did not yet have a printer. This was the same device that Ida Lovelace saw in his house.
Ida, who continued to associate with Mary Somerville, shared her enthusiasm for Babij’s innovative device, and the two discussed it for a long time. Encouraged by Somerville, Lovelace turned to the study of Euclidean geometry. But at the same time, in a letter, he asked Babbage to send him the design drawings of this machine to get a better understanding of how it works.
Lovelace started teaching mathematics to women and girls at the age of 19
In 1834, Ida accompanied her mother on a humanitarian tour of factories in the north of England and got to know the details of the most advanced equipment they had. In this tour, they also visited the Jacquard Loom machine, which was invented in 1801 by Joseph Marie Jacquard to produce cloth. On the way back, he talked with the daughter of one of his mother’s friends and taught her some math.
This event lit up the first spark of the necessity of women’s empowerment in Ida’s mind, and that’s why she decided to continue teaching her new friends and other girls even remotely and through letters. In his letters, he also wrote notes to clarify the minds of his students, such as “When something can be proved directly, never go for indirect proof.”
Charles Babbage, on the other hand, seemed to have underestimated Ida at first and simply wanted to keep an enthusiastic and talented youngster at his side at scientific parties. But Lovelace analyzed his ideas more stubbornly and curiously than ever. It wasn’t long before Babij shared with him his academic thoughts, computational ideas, and even the problems he had with the government.
 Charles Babbage, the famous English mathematician and the father of computing
Charles Babbage, the famous English mathematician and the father of computing
In the spring of 1835, 19-year-old Ida married William King, a friend of Somerville’s son. King studied at Cambridge and had a government job.
Over the next few years, they had three children, but Ida was also studying advanced trigonometry while managing the family. William’s successful activities during this period led to his promotion to the rank of Earl, and their surname was changed to Lovelace from this date.
After the birth of her third child, Ida decided to return to the field of mathematics, and to avoid the common gossip of society, she asked Charles Babbage to find an experienced teacher for her. This new professor was Augustus de Morgan: the first professor of mathematics at London College, a famous logician, and the author of several academic books.
In his correspondence with Babbage, Lovelace expressed his interest in discrete mathematics and described, for example, how he found a formula for the game of solitaire. But De Morgan, according to the traditional routine of teaching mathematics, started his work with differential and integral calculus.
By this time, Babbage had written numerous papers and had failed several times in building the final computing engine, which he called the Difference Engine. He finally came up with a new idea: maybe it would be better to build an analytical engine that supports all kinds of mathematical operations instead of a machine that only calculates “differences”.
Modern definitions of Babij’s analytic machine are called Turing’s complete
The initial design of Babbage’s analytical machine was very extraordinary and professional. This design showed the great genius of the English scientist because it was later known as the first programmable computer in history. In modern definitions, this machine is called a complete Turing machine.
Babij Analytical Machine had parts such as mathematical logic, control flow using loops, instruction branching, and separate memory. The interesting point is that all these parts worked with steam power or by hand and with mechanical parts.
Lovelace’s article on Analytical Engine
Babbage’s research and ideas were not well received in England but caused a lot of noise in other European countries. He was even invited to Turin to give a lecture on the Analytical Engine and was honored by the Italian government.
Babbage had never published a paper on the differential engine or the analytical engine, but in October 1842, after this lecture, an engineer named Luigi Menabera wrote a paper based on his remarks. After reading the article, Ida decided to translate it into English and give it to British publications.
After reviewing the translation of the article, Babij suggested Ida write her own narrative from the analytical engine because she believed in Ida’s ability and knowledge. In February 1843, Lovelace decided to translate the same article in a more complete and orderly manner, adding his own extensive notes.
Ida’s notes on the “Manabra” article became more detailed and important than this article itself
Ida’s notes continued in alphabetical order from A to G, and section G contained her famous algorithm. These notes were three times the text of the original article. Finally, when her translation was published as Sketch of Charles Babbage’s Analytical Engine, the bulk of the paper was Ida’s writing, which included algebraic equations to explain how the Analytical Engine performed mathematical equations.
Babbage also sent Ida one of the most difficult equations (Bernoulli’s numbers) to add to his research. The important point is that Ida found some problems in Bebij’s equations that Bebij himself later named as serious mistakes. In constant correspondence with Babbage, Lovelace worked diligently on his writings for months.
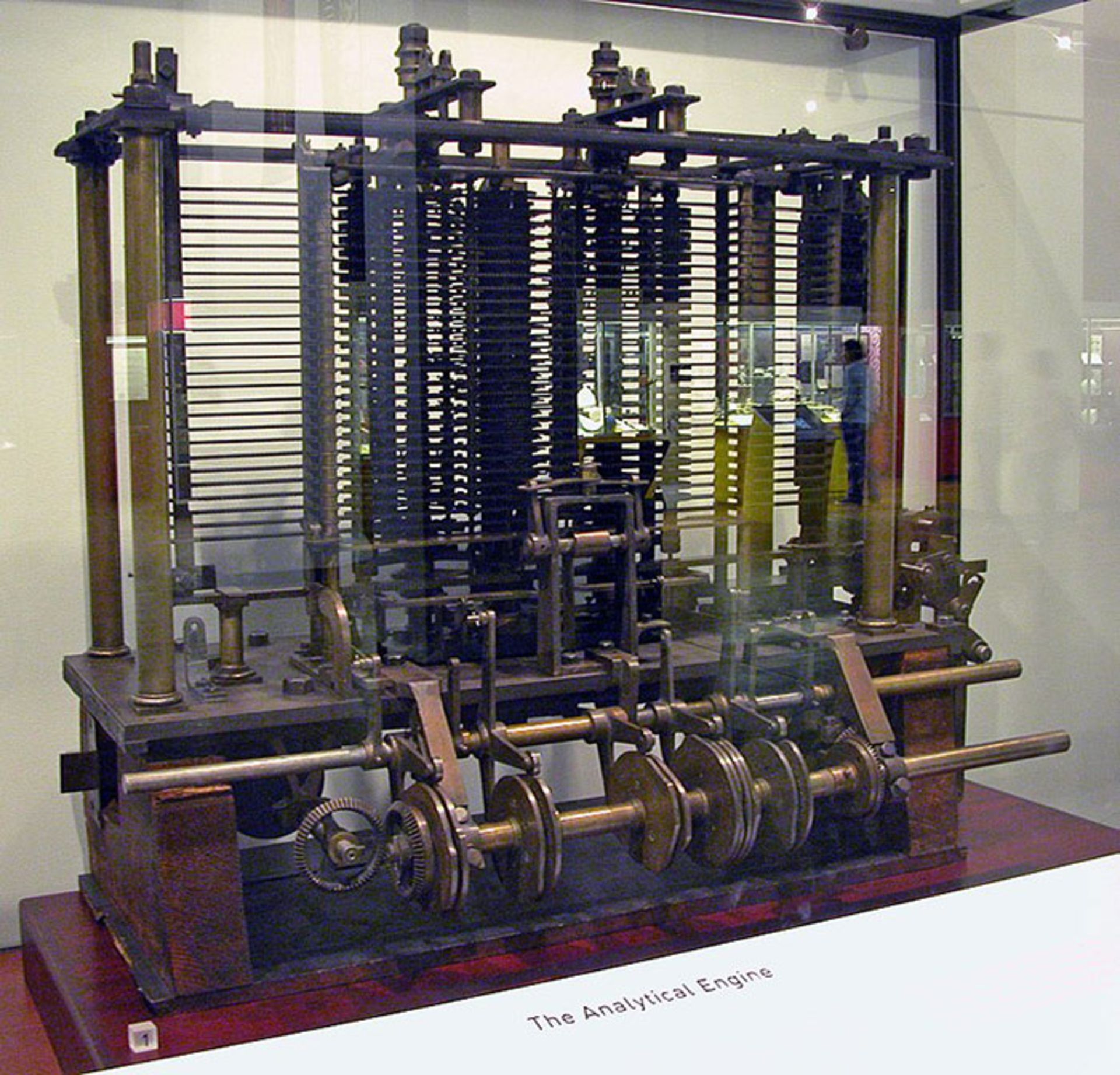 A completed example of the Analytical Engine in the London Science Museum
A completed example of the Analytical Engine in the London Science Museum
Lovelace’s algorithm and the first computer program
In this paper, Lovelace designed an algorithm for calculating Bernoulli numbers, which became his most important achievement, and years later he registered his name as the world’s first programmer.
Lovelace’s algorithm was based on a series of logical, step-by-step instructions: he explained in detail how data entered the analytical machine, processed it, and finally produced output, emphasizing that the machine could operate automatically through detailed instructions and beyond an engine. Simple calculations.
In other words, Lovelace showed in this algorithm that the analytical machine can obtain the next values based on certain inputs (for example, the initial value or previous values from the Bernoulli series). This process was such that the machine continuously continued the operation until reaching the final result.
Thus, it was Lovelace who proved that the Babbage machine could function as a “programmable machine”.
Lovelace said the analytic machine could also be used to process other types of data, such as music
In part of the paper, Lovelace noted that the Analytical Engine could be used to process other types of data, such as music. He clearly stated that such machines are able to make sounds or even music based on specific algorithms.
Ida, on the other hand, clearly understood the traditional view of programming: that we write programs to perform tasks that we know how to perform. He explained that an analytical machine cannot process thought or anything by itself.
He also noted that when we translate “analytical facts and formulas” into a form that a machine can process, we gain new perspectives on many topics in the field. These views make us examine the issues more deeply.
In short, Lovelace’s algorithm had three important features:
- Automation of calculations
- Repetition, which is known today as loop in programming.
- Conditions and decision-making are common today in “if-then” structures in programs.

In her studies, the English mathematician lady also explained the defects of Babbage’s analytical machine. This discovery of errors is known as the first debug process in history. Lovelace’s studies deepened in the following years, and he attempted to use mathematics to decode the neural processes underlying emotions.
In addition to the program, the first debugger in history was named Ida Lovelace
Ida introduced these studies as “computation on the nervous system”. To present his studies, he met with Andrew Cross to build an electrical model of his findings. Of course, this decision was never final.
Ida created a new era in computer science with his article. He added a new concept to machines and showed their capacity for more than simple mathematical calculations. His action was the first step towards understanding modern computers beyond calculators.
Lovelace’s algorithm had three important features: automating calculations, programming loops, and conditional structure
The first programmer in history believed that anything that can be converted into numbers, such as music, alphabets, or images, has the ability to be calculated and changed by computers. In other words, the analytical machine could change the way of working in all parts of the world and not only mathematics.
Ida’s way of thinking and opinions showed that she had developed her own thinking beyond her mother’s strict methods. He included an imaginative and visual approach in his studies. Despite the fact that the general studies of this scientist were based on mathematics, his mind moved beyond equations and algorithms to explore new possibilities. For this reason, Babij used the term “magician of numbers” to describe this lady.
However, Ida’s studies and Babij’s research were never implemented. Babbage was unable to finish building his car, but in 1991 a prototype of his car was built with minor modifications and was fully operational. The next thing happened years later with the appearance of Alan Turing.
Read more: Len Sassaman; The creator of Bitcoin
Turing became interested in Ida’s research but disagreed with the scientist about artificial intelligence. Ida believed that artificial intelligence would not be created and machines would only execute instructions. Turing had an opposite theory and finally proved it.
At one point in history, Lovelace and Babbage’s relationship was accompanied by a small controversy: Babbage intended to write an anonymous introduction at the beginning of Lovelace’s book criticizing the government for supporting his machine plan.
Of course, the publication rules did not allow such a thing, and Babbage also asked Lovelace to remove the introduction. Lovelace did not accept this request and this act became an excuse for their short-term argument. Of course, the relationship between the two improved in the following years to the point that even Lovelace asked Babbage to relieve her of cancer in her final years.
Her Death
After the publication of the article, Ida Lovelace was ill for a long time; But he continued to interact with Michael Faraday, who he called “a rising star in the world of science.” He had decided to launch a new journal and therefore he corresponded and exchanged ideas with various scientists.
Ida changed history not with her program but by realizing the potential of computers
Ida had brilliant ideas and writings in the field of physiology and the nervous system, But financial and health problems prevented his work from progressing. Her husband William, who worked for some time in publishing books and magazines, left her for unclear reasons.
The fact was that Ida was always under a storm of blame for hanging out with male colleagues and her father’s friends, and her efforts to teach women and girls were not welcomed by society.
During 1851-1852, Ida Lovelace’s condition worsened to the point where she asked Babbage’s friend Charles Dickens to visit her and read one of his books to her with an account of his death.
Lovelace chose Charles Babbage as her executor to be buried next to her father, Lord Byron (who also died early). Finally, on November 27, 1852, Lovelace died at the age of 36 while experiencing severe and prolonged pain.
 An example of the Ada programming language
An example of the Ada programming language
One of the great monuments that keep the memory of this leading mathematician alive is the Ada programming language, which was developed by the US Department of Defense and registered in the country’s military standard in 1980. Also, since 1998, the British Computer Association has been awarding the “Lovelace Medal” every year to a person who has significant achievements in the field of software engineering.
In recognition of the lifetime efforts of the first programmer in history, Ida Lovelace Day is celebrated on the second Tuesday of October with the aim of increasing the role of women in science, technology, and engineering.
Ida Lovelace’s achievements were beyond her time. Not only did he write the first machine-executable algorithm, he also foresaw the endless potential of computers. Concepts such as the loop in programming and the distinction between data and processing, which are considered self-evident principles of computer science today, have their roots in his innovative ideas.
Although Ida Lovelace’s work was never recognized during her lifetime and some of her ideas remained unknown for several centuries, over time her name became a model of perseverance and progress and one of the main symbols of the movement to promote the participation of women in STEM.
He wrote in his notes: “Our limitations exist only in our minds. There are no barriers that women cannot overcome. They just have to believe in themselves.


Europa Clipper, NASA’s flagship probe was launched

How did accidental release cause the 1977 Russian flu?


Everything about Cybercube and Robo Van; Elon Musk’s robotic taxis


How do we know that our phone is infected with malware?


The biography of Ida Lovelace; The first programmer in history


The Strawberry Project; The OpenAI artificial intelligence model


The biography of Andy Rubin, the creator of Android


Why doesn’t Jupiter have big and bright rings like Saturn?


Everything you need to know about the Windows Blue Screen of Death


Why do none of the moons of the solar system have rings?
Popular
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoWho has checked our Whatsapp profile viewed my Whatsapp August 2023
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoSecond WhatsApp , how to install and download dual WhatsApp August 2023
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoHow to use ChatGPT on Android and iOS
-



 AI2 years ago
AI2 years agoUber replaces human drivers with robots
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoThe best Android tablets 2023, buying guide
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoThe best photography cameras 2023, buying guide and price
-


 Humans2 years ago
Humans2 years agoCell Rover analyzes the inside of cells without destroying them
-


 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoHow to prevent automatic download of applications on Samsung phones
