Space
Publication of the latest map of the distribution of dark matter in the universe
Published
2 years agoon
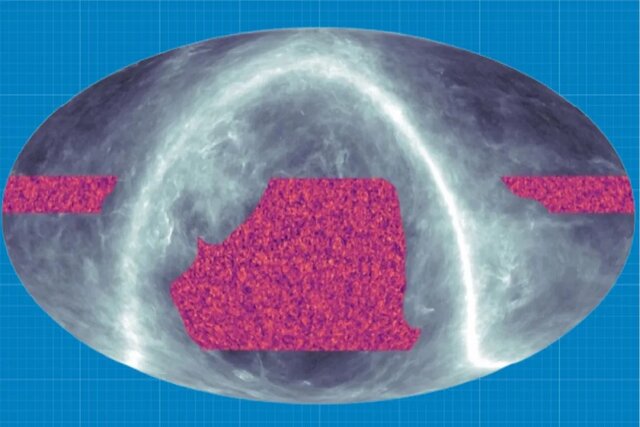

Publication of the latest map of the distribution of dark matter in the universe . A ground-breaking new map depicts how the mysterious dark matter is distributed, and cosmologists say they have created this detailed map of dark matter to understand the expansion of the universe. The new map uses light from the cosmic background radiation (CMB) as a background light to show all the matter between us and the Big Bang.
Publication of the latest map of the distribution of dark matter in the universe
In this article we’re going to read about the publication of the latest map of the distribution of dark matter in the universe. The cosmic world is full of mysteries that scientists have been trying to discover for centuries. Dark matter is one such puzzling mystery, and understanding it can help us learn more about the evolution and structure of the universe.
Now, using the Atacama Cosmological Telescope (ACT), researchers have created a detailed map of invisible dark matter. This groundbreaking new image depicts mysterious dark matter distributed across a quarter of the entire sky.
The creation of this map confirms Albert Einstein’s theory about how massive cosmic structures and light curves grow over the 14 billion-year span of the universe.
Blake Sherwin, professor of cosmology at the University of Cambridge and head of the ACT group, said in a statement: “We have mapped the invisible dark matter in the sky to the greatest distances, and we clearly see the characteristics of this invisible universe, which is hundreds of millions of light-years across and looks exactly like this.” which our theories predict.
More than 160 researchers reviewed ACT data under the auspices of the US National Science Foundation. However, capturing the properties of dark matter, which makes up 85 percent of the universe, has been difficult.
Because dark matter does not interact with light or other types of electromagnetic radiation, it is difficult to probe, and gravity is the only thing that can reveal information about dark matter.
Dark matter is a type of matter that has been hypothesized in astronomy and cosmology to explain phenomena that appear to be caused by the presence of a certain amount of mass that exceeds the mass observed in the universe.
Dark matter cannot be seen directly with a telescope. Dark matter is called “dark” because it apparently has no interaction with the electromagnetic field; This means that it does not emit electromagnetic radiation (such as light), does not reflect it, and does not absorb it; Therefore it is not visible. In other words, dark matter is a substance that does not react to light; Instead, the existence and properties of dark matter can be inferred indirectly through the effects of gravity on visible matter, radiation, and the large-scale structure of the universe.
According to data from the Planck mission team in 2013 and based on the Standard Model of Cosmology, the total mass energy in the known universe consists of 4.9% ordinary matter, 26.8% dark matter, and 68.3% dark energy. This means that dark matter constitutes 26.8% of the total matter in the universe, and dark energy and dark matter together constitute 95.1% of the total contents of the universe.
Astrophysicists proposed the dark matter hypothesis to explain the difference between the mass calculated for giant celestial bodies by either using their gravitational effects or using the luminous material inside them (stars, gas, dust).
This hypothesis was first proposed by Jan Evert in 1932 to explain the orbital velocities of stars in the Milky Way and by Fritz Zwicki in 1933 to explain evidence of “missing mass” in the orbital velocities of galaxies in galaxy clusters. After that, many other observations were made which indicated the existence of dark matter in the universe. Among these observations, we can mention the observation of the rotational speeds of galaxies by Vera Rubin in the 1960s-1970s, the gravitational convergence of background objects by galaxy clusters such as the Bullet cluster, and temperature anisotropy patterns in the cosmic background radiation.
Cosmologists agree that dark matter is composed mostly of some unknown subatomic particle. Searching for this particle using various means is one of the main efforts of elementary particle physics.
Although the existence of dark matter is generally accepted by the scientific community, alternative theories of gravity have also been proposed. For example, we can refer to modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) or tensor-vector-fence gravity (TeVeS), which try to explain these unusual observations without the need to introduce additional mass. For this purpose, the researchers observed the distortion of light left over from the Big Bang, when the universe was only 380,000 years old. This type of scattered light travels freely throughout the universe and is known as cosmic background radiation (CMB).

In cosmology, cosmic background radiation is electromagnetic radiation that covers the entire universe. This radiation has the spectrum of a black body with a temperature of 2.726 Kelvin. Therefore, the maximum of this radiation is in the microwave range with a frequency of 160 GHz and a wavelength of 1.9 mm. Cosmologists consider cosmic background radiation to be the best evidence for the Big Bang theory.
The gravitational pull of large, heavy structures, including dark matter, bends cosmic background radiation on its 14-billion-year journey toward us, much like a magnifying glass bends light as it passes through its lens, the researchers’ statement explained.
Read More: Astronomers have identified the most distant galaxy
In addition, this research adds to the ongoing debate about the “crisis in cosmology”, which focuses on the discrepancy in the measurement of the age of the universe and the need to know how much it is expanding. This crisis stems from different measurements of the cosmic background light rather than the CMB. These deviations show that the dark matter in the standard model of cosmology is not considered enough and this model is incorrect.
“This map remarkably provides measurements that show that both the bulge of the universe and its growth rate after 14 billion years of evolution are exactly what you expect from the model,” says Mathew Madhavacheril, an assistant professor in the Department of Physics and Astronomy at the University of Pennsylvania. You would expect standard cosmology based on Einstein’s theory of gravity.
This research will be presented at a scientific conference that is being held from April 10 to 14 at Kyoto University.


You may like
-




How far is the earth from the moon? Everything you need to know!
-




Maybe the Earth is not doomed by the death of the sun
-


Alien life may be hiding under the Martian ice cover
-



Why is it still difficult to land on the moon?
-




Europa Clipper, NASA’s flagship probe was launched
-




Dark matter and ordinary matter can interact without gravity!
Space
How far is the earth from the moon? Everything you need to know!
Published
1 day agoon
11/11/2024

When the moon reaches its minimum distance from the earth, perigee is known and it is about 363 thousand 300 km away from the earth.
How far is the earth from the moon? Everything you need to know!
The Moon is the only natural moon of the Earth, which was formed about 4.5 billion years ago. This moon rotates in an elliptical orbit around the earth and its light reflects the light of the sun. From the earth, the moon is the most distinct and the brightest body in the night sky, and due to the change in its distance and position relative to the earth and the sun, it can be seen in different ways.
These two heavenly bodies are very important in our understanding of the world not only because of their distance from each other but also because of their gravitational interactions and mutual effects on each other. But how far is the earth from the moon? The answer is not as simple as you think.


In this article, we will examine the average and exact distance of the moon from the earth and compare it with other objects, and you will find out why the answer to this question is not just a number.
The elliptical orbit of the moon
No orbit is perfectly circular. Some orbits are very close to circular, but all are at least slightly elliptical. Astronomers can measure how close an orbit is to a perfect circle by calculating the ” eccentricity ” of the orbit. This value is expressed with a number between 0 and 1. In fact, a circle can be considered a special kind of ellipse whose eccentricity is 0.
Among all the planets of the solar system, the orbit of Venus has the lowest eccentricity and the closest circular orbit with a value of 0.007. Mercury also has the most irregular or elliptical orbit with a value of 0.2.
The eccentricity of the moon’s orbit is 0.05. Besides, the Earth is not in the center of the moon’s orbit. Rather, it is located in one of the foci of the moon’s elliptical orbit; Therefore, it is closer to one edge of the circuit than the other. All these factors cause the distance between the moon and the earth to change constantly.


For this orbit, ” Apogee “, ” Meridian ” and ” Medium Distance ” are defined and astronomers tend to talk about these 3 parameters when talking about the distance between the Earth and the Moon. In the following, we will introduce each of these indicators.
The shortest distance between the moon and the earth: perigee
When the moon reaches its minimum distance from the earth, perigee is known and it is about 363 thousand 300 km away from the earth.
If the perigee coincides with the phase of the full moon, it is called ” supermoon “. Supermoons appear approximately 17 percent larger and 30 percent brighter than the dimmest moon of the year. Since the moon’s gravity exerts a pulling force on the earth’s oceans to create high tides, the closer the moon is to the earth around the perigee, it can also create higher than normal high tides.
The greatest distance between the moon and the earth: apogee
At the farthest point from the earth, the moon is about 405,696 km away from us, and astronomers say that the moon is at its peak.


The moon at its peak is called ” the moon of wisdom “. The crescent moon will not be visible, but if the new moon phase that creates the eclipse coincides with the zenith, the smaller disk of the moon will be very visible in the sky. While annular eclipses are spectacular on their own, when the Moon is at its peak, it does not completely block the Sun, but instead leaves a ring of the Sun’s disk visible to observers on Earth.
How many kilometers is the distance from the earth to the moon?
As you have seen, the distance between the moon and the earth at the apogee and perigee is 42 thousand 592 km, which is more than three times larger than the diameter of the earth!
In response to the question ” How far is the moon from the Earth?” To give a number, scientists have introduced an average distance. The average distance is the average distance between the Earth and the Moon, which was calculated to be 384,400 kilometers.
History of Moon Distance Measurement
Until the late 1950s, all measurements of the Moon’s distance were based on optical angular measurements. The first accurate measurement was made by Hipparchus in the second century BC. After him, many astronomers tried and obtained new methods and more accurate figures.


But the space age was a turning point in increasing the accuracy of this measurement and the results improved a lot. During the 1950s and 1960s, experiments were conducted using radar, lasers, and spacecraft, which were advanced using computer modeling and processing.
Methods of measuring the distance between the moon and the Earth
The methods of measuring the distance between the moon and the earth improved over time and their accuracy also increased. Some important or interesting methods for determining the lunar distance that has been used throughout history are listed below:
- Parallax : The oldest method for determining the moon’s distance is the simultaneous measurement of the moon’s angle and a reference point from several locations. Before precise mechanical chronometers, the synchronizing event for this was usually during a lunar eclipse or the moment the moon passed meridian (provided the observers were of the same longitude).
- Lunar eclipse: The first attempts to measure the distance to the moon were made by observing the geometry of the lunar eclipse and using trigonometry. The Greek astronomer and mathematician Aristarchus of Samos recorded the first reports using this technique in the 4th century BC, and after him, Hipparchus also used this method. ” Ptolemy ” also used this method later.


- Crossing of the meridians: For the first time, ” Andrew Crumlin “, a French astronomer, observed the meridian crossings of the moon in one night from 2 different places while traveling.
- Lunar occultation: By recording the moment when the moon covers a background star, the distance to the moon can be determined. Of course, if measurements are made from several known locations. Astronomers calculated the distance to the Moon by observing 4 occultations out of 9 locations in 1952.
- Radar : The distance to the moon can be obtained by the reflection of radio waves and its return time. This work was done for the first time in 1946 as part of the ” Diana Project “.
- Laser range finder: In 1962, a team from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and a team at the Soviet Crimea Astrophysical Observatory conducted an experiment that measured the round-trip time of laser pulses reflected directly from the surface of the moon. Today, this method is the most accurate method of measuring the distance between the moon and the earth. Apollo astronauts sent reflectors to the moon.
How many hours is the distance from the earth to the moon?
The time it takes to reach the moon or the time interval between the moon and the earth depends on the type of spacecraft, whether the mission is human or robotic, the speed, and the path you travel; For example, the Apollo 11 mission, which was the first manned mission to the moon, lasted about 8 days.
Of course, faster spacecraft can reduce this time to about 3 days, which is the average time to reach the moon. Currently, new research and technologies may further optimize the travel time to the moon.
The first spacecraft that tried to reach the moon was ” Luna 1 ” belonging to the Soviet Union in 1959. Luna 1 was a globular satellite launched without a propulsion system. Unfortunately, the spacecraft failed to complete its mission but reached the Moon’s approach within 34 hours (one day and 10 hours).
Luna 1 is currently hovering around the solar system, between the orbit of Earth and Mars, and it is interesting to know that although its technology was not very advanced, it is one of the fastest trips to the moon!
Now we want to review the longest and shortest distance between the moon and the earth and check this distance with different vehicles.
The longest and shortest time
Currently, the record for the shortest travel time to the moon is held by the ” New Horizons ” spacecraft with a time of 8 hours and 35 minutes. Of course, that’s because the spacecraft didn’t slow down or approach the moon’s orbit but instead flew on its way to Pluto.
The longest journey is also held by Smart 1, the European Space Agency’s ion engine-powered spacecraft launched in 2003. Instead of traveling in a straight line, Smart 1 circled the Earth to reach the Moon. The ion engine combined with the gravity assist maneuvers resulted in very high fuel consumption and took 13.5 months to complete the trip!


How many days did the Apollo missions reach the moon?
Human space travel usually takes longer than robotic travel. NASA sent nine manned Apollo missions to the moon, six of which landed successfully. Apollo 8 was the first mission to orbit the Moon and was one of the fastest trips of the Apollo program, lasting 2 days, 21 hours, and 8 minutes.
Each of the spacecraft spent about 3 days traveling in space, and the change in their arrival time is due to orbiting and stopping.
If we were to drive to the moon, how far would we be?
The time to reach the moon by car depends on the type of car and the position of the moon at its peak or perigee. But to answer this question, we will assume that the hypothetical vehicle is similar to today’s cars and that the moon is at an intermediate distance.


Considering that the average distance between the moon and the earth is approximately 384,000 and the average speed of cars is about 100 km/h, this trip will take at least 1,600 days (equivalent to 4.5 years). As it is clear from the figures, traveling to the moon requires special technology and conditions that cannot be compared to normal driving!
At the speed of light, how many hours is the distance between the moon and the earth?
The speed of light in a vacuum is about 299 thousand 792 kilometers per second. To calculate the time it takes for light to travel from the Earth to the Moon, we can divide by the average distance from the Earth to the Moon, the answer is 1.28 seconds; Therefore, it takes less than 2 seconds for light to reach the moon from Earth!


To give you an idea of this value, we also want to describe the distance of the sun from the moon or the earth. Since the moon revolves around the earth and the earth revolves around the sun, the distance between the moon and the earth from the sun is the same.
On average, the Earth and the Moon are about 150 million kilometers from the Sun. But this distance is so much compared to the Earth and the Moon that it takes 8 minutes for sunlight to reach us.
Read more: Why is it still difficult to land on the moon?
The effect of the distance of the moon on the earth
The distance of the moon from the Earth is very important in various scientific, natural, and cultural fields. This distance, which is very suitable, plays an important role in natural phenomena and our daily life, which we mention below:
- Tides: We know that the tides in our oceans are caused by the gravitational pull of the moon and the sun and the rotation of the earth. Tides have a great impact on marine ecosystems, marine life, and energy supply through sea power plants. At perigee, the moon’s gravitational pull will be slightly stronger than usual.
- Stability of the earth’s axis : The existence of the moon and its proper distance from the earth help to stabilize the earth’s rotation axis. This stability causes regular changes in seasons and weather.


- Cultural and historical influences : The moon is known as a symbol of beauty and mystery in different cultures. Lunar calendars and many festivals are directly related to the moon.
- Space exploration : The suitable distance of the moon from the earth has made it an attractive target for space exploration. Reaching the moon is considered the first step of man in space exploration and travel to other planets.
The moon is moving away from us!
The moon was once closer to the earth and with the passage of time this distance increased. Astronomers are now sure that the moon moves 3.8 cm away from Earth every year, the same rate as your fingernails grow!
The astronauts of the Apollo 11, 14 and 15 missions and the 2 Soviet Mars rovers, ” Lonokhod 1 ” and ” Lonokhod 2 “, left a total of 5 reflectors on the surface of the moon; Astronomers on Earth can therefore reflect laser beams from these mirrors and record the time of the laser return.


We know how fast the laser beam moves (speed of light), so we can easily calculate the distance the laser beam has traveled. This method is so accurate that scientists notice the increase in the distance between the Earth and the Moon.
In the distant future, total solar eclipses will disappear, leaving only today’s images; Because the moon will appear far away and smaller and will not be able to completely cover the sun’s disk.
It looks like we’re in a good period of the moon’s distance from the earth, a period where the moon is big and bright in the night sky, it’s still exciting to travel to, and total solar eclipses still happen!
Summary
The distance between the moon and the earth changes constantly due to its elliptical orbit, and the moon is at the farthest (apex) or closest (periphery) distance from us during its rotation around the earth. This distance has a difference of 42 thousand 592 kilometers between the peak and the perigee; For this reason, scientists have introduced an average distance. The average distance is the average distance between the Earth and the Moon, which was calculated to be 384,400 kilometers.
The time it takes to reach the moon or the distance between the moon and the earth also depends on the type of spacecraft, whether the mission is human or robotic, and the speed and path you travel. But it takes an average of 3 days for a spacecraft to reach the moon and the speed of light to reach the moon is less than 2 seconds.
The distance of the moon from the earth is very important and creates seasons and tides. But this distance is increasing and the moon is getting further away from us every day


Maybe the Earth is not doomed by the death of the sun
Will the sun one day destroy the earth? This may or may not happen. Astronomers have spotted a rocky planet the size of Earth orbiting a white dwarf, hinting at a future in which our planet outlives its star.
In 6 billion years, the sun will grow and become a red giant star. At this point, Mercury and perhaps Venus will be swallowed up, and for a long time, we thought that planet Earth would also be incinerated. But maybe the blue planet is not doomed, even though it may become an uninhabitable world in the next 6 billion years.
According to the New York Times, scientists have discovered a rocky planet orbiting a star that has passed its red giant phase. The planet now orbits a white dwarf, a smaller stellar body left over after a star burns out.
Importantly, the planet appears to have once been in the same position as the Earth now orbits our Sun. Before being swallowed up by its dying star, the rocky planet was pushed into a distant orbit, twice the distance between Earth and the Sun. In this way, the discovered world is considered the first rocky planet that has been seen rotating around a white dwarf.
A rocky Earth-like planet has survived the destruction of its star
“We don’t know if Earth can survive,” said astrophysicist Kaming Zhang of the University of California, San Diego, who led the study published in the journal Nature Astronomy. “If it survives, it will become such a system.”
The rocky planet is about 4,000 light-years away and in 2020, the South Korean Radio Astronomy Observatory discovered it using a process called gravitational microconvergence. The Korean team observed the star of the rocky planet while passing in front of a distant star, and that star magnified the amount of light reaching the telescope by a thousand times. This effect, known as convergence or gravitational lensing, makes it possible to identify very distant and faint objects.
That particular event was a one-off event, and the chances of further detailed observations are limited until powerful new telescopes can get a better look at the rocky planet in the future. But Dr. Zhang and his team were able to do more last year at the Keck Observatory in Hawaii and found out that the planet’s star is actually a white dwarf.
The researchers calculated that at least two objects are orbiting the white dwarf. One of them was a brown dwarf; That is, the failed star that had never ignited by nuclear fusion and was located at a great distance from the central star. But the other object is a planet with a mass of about 1.9 times that of Earth, which orbits closer to the star’s period and is therefore likely to be a rocky world.
By modeling the evolution of the star system, Zhang’s team calculated that the planet may have once been in a habitable orbit like Earth. The star was probably the same size as ours. “We expect the star to have been roughly the same mass as the Sun,” Dr. Zhang said.
 Gravitational convergence shows the white dwarf shown by the vertical white lines. The researchers captured images of the star years before the event (a), shortly after the background star peaked in 2020 (b), and after it disappeared in 2023 (c).
Gravitational convergence shows the white dwarf shown by the vertical white lines. The researchers captured images of the star years before the event (a), shortly after the background star peaked in 2020 (b), and after it disappeared in 2023 (c).
But as the star ran out of fuel, it lost some of its mass, causing the rocky planet’s orbit to lengthen. The rocky planet escaped from the expanding red giant phase of the star and survived to the white dwarf stage.
A handful of gas planets have been found orbiting white dwarfs, but they were either in more distant orbits or had migrated inward and closer after the red giant phase. “If Dr. Zhang’s diagnosis is correct, this would be the first rocky planet orbiting such a star,” said Susan Mulally, an astronomer at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Maryland. “It’s definitely the smallest and clearest rocky planet we’ve ever found around a white dwarf.”
A handful of gas planets have been discovered orbiting white dwarfs
Stephen Kane, an astronomer at the University of California Riverside, noted that he was excited when he first read the paper. He has previously investigated whether planets can survive when their stars pass through the red giant phase, so he is intrigued by the new discovery. However, the presence of the brown dwarf complicates everything. If the brown dwarf was once closer to the star but moved outward, it could change the dynamics of the entire system, he explained. That means, maybe there are other planets that have been thrown out and the planets that are currently observed are among the survivors.
NASA is scheduled to launch the Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope before 2027 and is expected to find more planets through gravitational microconvergence. Perhaps some of them are orbiting white dwarfs.


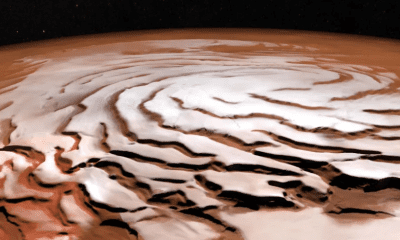
Alien life may be hiding under the Martian ice cover
A new study suggests that the conditions necessary for photosynthesis on Mars may exist beneath the dusty ice cover in the Red Planet’s mid-latitudes.
Photosynthesis is a process by which living organisms such as plants, algae, and cyanobacteria can produce chemical energy. This process requires water and light to progress and produces much of the oxygen in the Earth’s atmosphere. According to the new findings, Martian ice layers of sufficient thickness can filter out intense solar radiation while still allowing sunlight to penetrate beneath them for photosynthesis, creating so-called “radiatively habitable” zones.
Since the process of photosynthesis is suitable for light, the new results should be considered in sufficient light conditions. While the findings don’t prove that life exists on Mars, or even existed in the distant past, they can give scientists ideas to search for. Aditya Kholler, a postdoctoral researcher and research supervisor at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, says the Martian dusty ice in the mid-latitudes is exposed to sunlight and could be an accessible environment to search for life on Mars today.
 Images of the Red Planet from NASA’s Mars Exploration Orbiter (MRO).
Images of the Red Planet from NASA’s Mars Exploration Orbiter (MRO).
Earth vs. Mars
Both Earth and Mars are located in a range known as the Sun’s life belt; A region around a star where the temperature is favorable for the flow of surface liquid water. Although 71% of Earth’s surface is covered by liquid water oceans, Mars has a mostly dry landscape.
Discoveries of Mars rovers such as Curiosity and Perseverance have shown that conditions on Mars are different. Surface features such as dry lake beds and river forks discovered by these robots indicate the presence of surface liquid water billions of years ago. Additionally, Mars missions such as the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) have often discovered water ice in unexpected areas.
According to scientists, Mars lost its liquid water billions of years ago; Just as the planet’s magnetic field weakened (Earth’s magnetism is still very strong) and much of its atmosphere was lost. Thus, there were few barriers to surface water evaporation. The absence of a thick atmosphere also means that today’s Mars is under the bombardment of harmful ultraviolet radiation from the sun, which is fatal for living organisms and can destroy the complex molecules needed for life.
 NASA’s Discovery Orbiter image of craters in the Cyrene region of Mars.
NASA’s Discovery Orbiter image of craters in the Cyrene region of Mars.
Unlike Earth, Mars does not have an ozone protective shield; As a result, the level of surface ultraviolet radiation is 30% higher than that of the earth; Therefore, photosynthesis on Mars probably occurs in places that are inside the dusty ice; Because the dusty ice cover can block harmful UV rays on the surface of Mars, and liquid water is highly unstable due to the planet’s dry atmosphere.
Using computer simulations, the researchers found that Martian dusty ice may melt from the inside and that the overlying ice cover prevents shallow subsurface liquid water from evaporating in the dry Martian air. According to Kholer:
Thus, two key elements for photosynthesis could be present in mid-latitude Martian dust ices. Photosynthesis requires sufficient amounts of sunlight as well as liquid water. Two previous independent simulations of dense Martian snow show that if small amounts of dust (less than one percent) are present in the snow, subsurface melting could occur in the mid-latitudes of present-day Mars.
“With the discovery of dusty ice that was exposed a few years ago within snow masses in Martian glaciers, there is a mechanism for subsurface melting that could underlie the formation of shallow subsurface liquid water,” Kholer added. According to Kholer, the dusty ice on the ice cap can block UV radiation from the surface of Mars and also allow sunlight to penetrate below the surface for photosynthesis.
 An image from NASA’s Discovery Orbiter of a puddle in the Dao Wallis region of Mars.
An image from NASA’s Discovery Orbiter of a puddle in the Dao Wallis region of Mars.
The depth required for the formation of radiative habitable zones depends on the amount of dust in the ice. Very dusty ice can block a lot of sunlight, the researchers’ simulations show. However, ice with 0.01 to 0.1 percent dust allows for the formation of a radiative zone between 5 and 38 cm deep. Less contaminated ice allows for a deeper and wider radiation zone at a depth between 2.2 and 3.1 meters.
According to researchers, the polar regions that have the most ice on Mars are too cold for habitable radiation zones; Because they do not have the subsurface melting mechanism. Such a mechanism probably occurs in the middle latitudes of the Red Planet.
Scientists have taken scientific support for their theory from evidence on planet Earth. Kholer says:
I was surprised to learn that similar areas for life exist within dusty and sedimentary polar ice. These areas are called cryoconite cavities and are formed when dust and sediment on the ice melts into it because it is darker than the ice.
 Evidence from Earth: Cryoconite-formed cavities on the Matanuska Glacier, Alaska, 2012
Evidence from Earth: Cryoconite-formed cavities on the Matanuska Glacier, Alaska, 2012
Every summer, due to heating by sunlight, liquid water gathers around the dark dust inside the ice. This happens because the ice is semi-transparent, allowing sunlight to penetrate below its surface. According to Khüler, the researchers discovered that the tiny organisms that live in these shallow subsurface habitats on Earth usually go dormant in the winter, when there isn’t enough light to form liquid water in the dusty ice.
Of course, none of the above findings mean that photosynthetic life exists on Mars or probably ever existed; But it could inspire further research into the possibility of radiation habitats on the Red Planet. Kholer adds:
I am working with a group of scientists on improved simulations of where and when the ice melts on present-day Mars. Additionally, we are recreating these dusty ice scenarios in the lab to investigate them in more detail.
The results of the research were published on October 17 in the journal Communications Earth & Environment.


Fossils that scientists were wrong about


What is an earthquake and how does it happen?


How far is the earth from the moon? Everything you need to know!


7 Windows problems that may lead users to MacOS or Linux


Samsung Galaxy Ring Review

How did accidental release cause the 1977 Russian flu?


Europa Clipper, NASA’s flagship probe was launched


The Secret of the Hummingbird’s Amazing Adaptation


Why is it still difficult to land on the moon?


Biography of Geoffrey Hinton; The godfather of artificial intelligence
Popular
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoWho has checked our Whatsapp profile viewed my Whatsapp August 2023
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoSecond WhatsApp , how to install and download dual WhatsApp August 2023
-



 AI2 years ago
AI2 years agoUber replaces human drivers with robots
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoHow to use ChatGPT on Android and iOS
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoThe best Android tablets 2023, buying guide
-



 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoThe best photography cameras 2023, buying guide and price
-


 Humans2 years ago
Humans2 years agoCell Rover analyzes the inside of cells without destroying them
-


 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoHow to prevent automatic download of applications on Samsung phones
